Abstract
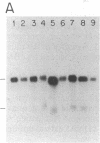
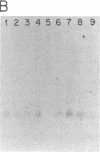
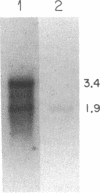
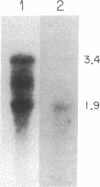
Two distinct beta subunits of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins have been identified by cDNA cloning and are referred to as beta 1 and beta 2 subunits. The bovine transducin beta subunit (beta 1) has been cloned previously. We have now isolated and analyzed cDNA clones that encode the beta 2 subunit from bovine adrenal, bovine brain, and a human myeloid leukemia cell line, HL-60. The 340-residue Mr 37,329 beta 2 protein is 90% identical with beta 1 in predicted amino acid sequence, and it is also organized as a series of repetitive homologous segments. The major mRNA that encodes the bovine beta 2 subunit is 1.7 kilobases in length. It is expressed at lower levels than beta 1 subunit mRNA in all tissues examined. The beta 1 and beta 2 messages are expressed in cloned human cell lines. Hybridization of cDNA probes to bovine DNA showed that beta 1 and beta 2 are encoded by separate genes. The amino acid sequences for the bovine and human beta 2 subunit are identical, as are the amino acid sequences for the bovine and human beta 1 subunit. This evolutionary conservation suggests that the two beta subunits have different roles in the signal transduction process.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Audigier Y., Pantaloni C., Bigay J., Deterre P., Bockaert J., Homburger V. Tissue expression and phylogenetic appearance of the beta and gamma subunits of GTP binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 9;189(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80830-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R. GTP-binding proteins. One molecular machine can transduce diverse signals. 1986 Jun 26-Jul 2Nature. 321(6073):814–816. doi: 10.1038/321814a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codina J., Stengel D., Woo S. L., Birnbaumer L. Beta-subunits of the human liver Gs/Gi signal-transducing proteins and those of bovine retinal rod cell transducin are identical. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 27;207(2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81486-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Fawzi A., Fraser E. D., Brown M. L., Northup J. K. Purification of a beta 35 form of the beta gamma complex common to G-proteins from human placental membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):176–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong H. K., Hurley J. B., Hopkins R. S., Miake-Lye R., Johnson M. S., Doolittle R. F., Simon M. I. Repetitive segmental structure of the transducin beta subunit: homology with the CDC4 gene and identification of related mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2162–2166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K. Characterization of transducin from bovine retinal rod outer segments. I. Separation and reconstitution of the subunits. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10495–10502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Codina J., Simons C., Birnbaumer L., Spiegel A. Antisera against a guanine nucleotide binding protein from retina cross-react with the beta subunit of the adenylyl cyclase-associated guanine nucleotide binding proteins, Ns and Ni. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):727–731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt J. D., Codina J., Rosenthal W., Birnbaumer L., Neer E. J., Yamazaki A., Bitensky M. W. Characterization by two-dimensional peptide mapping of the gamma subunits of Ns and Ni, the regulatory proteins of adenylyl cyclase, and of transducin, the guanine nucleotide-binding protein of rod outer segments of the eye. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14867–14872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff R. M., Axton J. M., Neer E. J. Physical and immunological characterization of a guanine nucleotide-binding protein purified from bovine cerebral cortex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10864–10871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Bokoch G. M., Northup J. K., Ui M., Gilman A. G. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Properties and function of the purified protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3568–3577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Northup J. K., Bokoch G. M., Ui M., Gilman A. G. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Subunit dissociation and guanine nucleotide-dependent hormonal inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3578–3585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Oinuma M., Ui M. Mechanisms for inhibition of the catalytic activity of adenylate cyclase by the guanine nucleotide-binding proteins serving as the substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5215–5221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeffler H. P., Ranyard J., Yelton L., Billing R., Bohman R. Gamma-interferon induces expression of the HLA-D antigens on normal and leukemic human myeloid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4080–4084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logothetis D. E., Kurachi Y., Galper J., Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. The beta gamma subunits of GTP-binding proteins activate the muscarinic K+ channel in heart. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):321–326. doi: 10.1038/325321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. R., Gilman A. G. The regulatory components of adenylate cyclase and transducin. A family of structurally homologous guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7059–7063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Lok J. M., Wolf L. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory unit of brain adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14222–14229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. The guanine nucleotide activating site of the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Identification by ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11416–11423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. The subunits of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Resolution, activity, and properties of the 35,000-dalton (beta) subunit. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11361–11368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roof D. J., Applebury M. L., Sternweis P. C. Relationships within the family of GTP-binding proteins isolated from bovine central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16242–16249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Northup J. K., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. The regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11517–11526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Bourne H. R. G proteins: a family of signal transducers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto K., Nukada T., Tanabe T., Takahashi H., Noda M., Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Hirose T., Inayama S. Primary structure of the beta-subunit of bovine transducin deduced from the cDNA sequence. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 28;191(2):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Hirose T., Miyake T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. The use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes. II. Hybridization of oligonucleotides of mixed sequence to rabbit beta-globin DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):879–894. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]