SUMMARY
Epithelial cells within the mammary gland undergo developmental programmes of proliferation and apoptosis during the pregnancy cycle. After weaning, secretory epithelial cells are removed by apoptosis. To determine whether members of the Bcl-2 gene family could be involved in regulating this process, we have examined whether changes in their expression occur during this developmental apoptotic program in vivo. Bax and Bcl-x were evenly expressed throughout development. However, expression of Bak and Bad was increased during late pregnancy and lactation, and the proteins were present during the time of maximal apoptotic involution. Thereafter, their levels declined. In contrast, Bcl-w was expressed in pregnancy and lactation but was downregulated at the onset of apoptosis. Bcl-2 was not detected in lactating or early involuting mammary gland. Thus, the pro-apoptotic proteins Bax, Bak and Bad, as well as the death-suppressors Bcl-x, Bcl-2 and Bcl-w, are synthesised in mouse mammary gland, and dynamic changes in the expression profiles of these proteins occurs during development.
To determine if changes in Bak and Bcl-w expression could regulate mammary apoptosis, their effect on cultured mouse mammary epithelial cells was examined in transient transfection assays. Enforced expression of Bak induced rapid mammary apoptosis, which could be suppressed by coexpression of Bcl-w. In extracts of mammary tissue in vivo, Bak heterodimerized with Bcl-x whereas Bax associated with Bcl-w, but Bak/Bcl-w heterodimers were not detected. Thus, Bak and Bcl-w may regulate cell death through independent pathways.
These results support a model in which mammary epithelial cells are primed for apoptosis during the transition from pregnancy to lactation by de novo expression of the death effectors Bak and Bad. It is suggested that these proteins are prevented from triggering apoptosis by anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins until involution, when the levels of Bcl-w decline.
Our study provides evidence that regulated changes in the expression of cell death genes may contribute to the developmental control of mammary apoptosis.
Keywords: Mammary gland, Breast, Apoptosis, Bak, Bcl-w
INTRODUCTION
Form and function in development depends on patterned regulation of proliferation and apoptosis. The control of apoptosis in developing systems is poorly defined, yet is vital to the understanding of many degenerative and proliferative diseases. One of the most dramatic examples of apoptosis in development occurs in the mammary gland during weaning. At this time lactational epithelial cells are removed by apoptosis and the tissue is remodelled in preparation for subsequent pregnancies (Strange et al., 1992). In the mouse, mammary gland undergoes developmental changes after lactation that result in tissue with a non-pregnant phenotype within 2 weeks of removing the suckling pups. The initial triggers for mammary apoptosis have not been defined, but candidates include altered availability of survival ligands such as IGF-1 and glucocorticoids, changes in interactions between mammary cells and their extracellular matrix possibly through increased matrix metalloproteinase activity, and the continued presence of apoptosis-inducing factors in milk that would normally be removed by suckling (Tonner et al., 1997; Feng et al., 1995; Lund et al., 1996; reviewed in Streuli et al., 1997).
The intracellular mechanism for regulating apoptosis has not been fully characterised. Several classes of cell-autonomous proteins have been identified as important mediators of the apoptosis response. These include membrane receptors, Bcl-2 family proteins, and the cysteine protease family of caspases (Farrow and Brown, 1996; Jacobson, 1997; Metcalfe and Streuli, 1997; Green and Kroemer, 1998). The Bcl-2 family is extensive and consists of pro-apoptotic proteins such as Bax and Bak and death-suppressors with homologous sequences such as Bcl-x and Bcl-w (Oltvai et al., 1993; Farrow et al., 1995; Gibson et al., 1996). These proteins are perceived as a switches which determine apoptotic cell fate, although their mode of action is not fully clear. They form homo- and heterodimers with each other and are able to insert into intracellular membranes of organelles (Wolter et al., 1997; Gross et al., 1998). In one model, Bcl-2 proteins regulate mitochondrial membrane homeostasis and the release of cytochrome c, which is a cofactor for caspase activation (Kluck et al., 1997; Vander Heiden et al., 1997; Zou et al., 1997). In another, pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members displace Apaf-1/Ced-4 from membrane-bound apoptotic inhibitors, thereby triggering the activation of downstream caspases (Conradt and Horvitz, 1998; Green and Kroemer, 1998; Adams and Cory, 1998). However, their full regulation is likely to be more complex since although some pro- and anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members form intermolecular interactions with each other in vivo, genetic evidence indicates that they can act in independent pathways to promote or repress apoptosis (Knudson and Korsmeyer, 1997).
Members of the Bcl-2 family are expressed to varying degrees in different cell types. Characterizing their profile in individual tissues is therefore essential for understanding the molecular control of apoptosis in specific developmental programmes. Common amongst methods to examine expression of Bcl-2 proteins are the use of cell lines for RNA and protein analysis and tissue samples for immunochemistry. However, major problems arise from interpreting such data since (1) cell lines are adapted to growing in culture and therefore have altered susceptibility to apoptosis, (2) cancer lines are often used which have genetically or epigenetically altered Bcl-2 protein expression profiles, and (3) suitable immunochemistry reagents are not always available, especially for studies on mouse tissue. A further approach is the use of knockout animals, which provides an indirect method for analyzing gene function within specific tissues, but is not appropriate in all situations. Mice with homozygous deletions in Bcl-x are embryonic lethal and those with Bcl-2 or Bax deletions do not show full gestational development, thus limiting their usefulness in studying mammary gland apoptosis (Motoyama et al., 1995; Veis et al., 1993; Knudson et al., 1995). In addition, the possibility of redundancy within the family argues that this approach may not reveal all the cell type-specific functions of each Bcl-2 protein.
To determine whether members of the Bcl-2 family might be involved in regulating apoptosis during mammary gland development, we have therefore examined the expression patterns of six members of this family in mammary tissue of normal mice in vivo. Our rationale is that by studying these proteins in vivo, without interference to their expression patterns by genetic modification or by removing cells from animals to culture, we would obtain a true picture of the Bcl-2 protein profiles in development. In addition, few studies have been undertaken to examine mechanisms of cell death in mammalian embryonic or postnatal development programmes. Moreover, a knowledge of individual players within the family that regulate apoptosis in mammary gland is a prerequisite for determining mechanisms of dysregulated survival in breast cancer.
Little is known of the Bcl-2 family in the breast although Bcl-2, Bcl-x and Bax are present (Hockenbery et al., 1991; Krajewski et al., 1994; Pullan et al., 1996; Zapata et al., 1998), and two reports have pointed at a functional role for Bax and Bcl-2 in mammary apoptosis (Heermeier et al., 1996; Jager et al., 1997). We now find that the pro-apoptotic proteins Bax, Bak and Bad, as well as the death-suppressors Bcl-x, Bcl-2 and Bcl-w, are synthesised in mouse mammary gland. Dynamic changes in the expression profiles of these proteins occur during development, suggesting that these changes may be involved in regulating post-lactational apoptosis. Our in vivo model concurs with culture experiments where we show that two recently identified members of this family, Bak and Bcl-w, have opposite roles in the apoptotic control of mammary epithelial cells. We conclude that the developmental programme of cell survival in vivo may be determined by extracellular cues that directly affect the levels and function of Bcl-2 family members.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Mice
Mammary tissue from ICR mice (Harlan Olac Ltd., Bicester, UK) was collected from: (1) 8 week old virgin animals, (2) mice pregnant for 3, 6, 9, 12 and 15 days after detecting a vaginal plug, (3) mice in full lactation for 9 days, and (4) mice where the pups had been removed for up to 12 days following a 9 day lactation period. RNA was prepared immediately and the rest of the tissue stored in liquid nitrogen for subsequent DNA and protein analysis. Three independent sets of tissues were used for these studies: (1) tissue from a single mouse at each developmental stage, (2) tissue pooled from three mice at each stage, and (3) tissue pooled from up to six mice at each stage. For every experiment, the results for each tissue set were virtually identical.
For the estrous cycle studies, 6-7 week old virgin ICR mice were staged at the same time each day for 2 weeks. This involved gently inserting the tip of a plastic pastette loaded with a small volume of PBS into the vagina, triturating several times to remove vaginal cells and examining the cellular composition after Methylene Blue staining. Once the animals had been demonstrated to be cycling regularly and a specific stage of the cycle had been unequivocally determined, one abdominal mammary gland was removed for whole-mount analysis and the other glands were snap-frozen and stored in liquid nitrogen. Two independent sets of tissues were used, each of which produced similar data.
Whole-mount preparation
Abdominal mammary glands were spread flat onto a microscope slide, briefly dried and fixed overnight in Telly's Fixative (70% ethanol, 5% formalin and 5% glacial acetic acid). The glands were defatted with three washes in 100% acetone (1 hour) before rehydrating through 100% and 95% ethanol. Cell nuclei were stained with 0.08% Haematoxylin (2 hours) before ‘blueing’ the stain with tap water. The glands were slightly destained to improve contrast using 50% ethanol acidified with 0.025 M HCl, dehydrated through 70%-100% ethanol (4 hours) and cleared with 50% methyl salicylate/50% ethanol, then 100% methyl salicylate. Photomicrographs were taken on Kodak Ektachrome 160T film using a Leica dissecting microscope.
Cell culture
Cell culture experiments were performed with first passage mammary epithelial cells from 14.5-18.5 day pregnant ICR mice, as described previously (Pullan et al., 1996). M1 murine myeloid leukaemia cells were cultured in DMEM medium (Life Technologies Ltd) supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal calf serum (Advanced Protein Products, Brierly Hill, UK). FSK-7 cells (Kittrell et al., 1992) were cultured in DMEM:F12 medium (Life Technologies) supplemented with 2% heat-inactivated fetal calf serum.
Analysis of DNA integrity
DNA was extracted from glands isolated at different stages of mammary development (Pullan et al., 1996). Tissues were ground to a powder in liquid nitrogen and were gently homogenized in 100 mM NaCl, 10 mM EDTA, 300 mM Tris, 200 mM sucrose, pH 8.0, SDS was added to 0.65% before incubation for 30 minutes at 60°C. Proteinase K (Boehringer-Mannheim) was added to 500 μg/ml and the sample incubated for 1 hour at 55°C. Potassium acetate was added to 500 μg/ml and the sample placed on ice for 30 minutes. Following centrifugation at 6000 rpm (4000 g) for 15 minutes (4°C), the supernatant was extracted three times with phenol:chloroform:isoamylalcohol (25:24:1), then chloroform:isoamylalcohol (24:1), and the DNA was precipitated with cold absolute ethanol. The DNA was dissolved in 50 μl TE buffer (10 mM Tris, 1 mM EDTA), pH 8.0 and treated with 5 μg DNAse-free RNAse (Sigma) for 30 minutes at 37°C. Following further phenol extraction and ethanol precipitation, equal amounts of DNA were separated on 2% agarose gels, stained with ethidium bromide and photographed.
Northern blotting
Total RNA was prepared as described previously (Streuli and Bissell, 1990). Electrophoresis of RNA was performed using the formaldehyde method (Sambrook et al., 1989) and RNA was transferred to Hybond-N membranes, which were probed with 32P-labelled or DIG-labelled (Boehringer Mannheim) cDNA fragments. The blots were probed and subsequently washed with 0.5× SSC, 0.2% SDS at 68°C, and exposed either to Kodak XAR film, or to Fujix Bas 2000 storage phosphorimaging plates for quantitative analysis. The probes used were gel-purified cDNA sequences, corresponding to bases 107-508 of the mouse Bax coding sequence, full-length mouse Bcl-x coding sequence, a 540 bp PstI fragment of mouse β-casein and an 18S cDNA probe.
PCR
First-strand cDNA synthesis was performed using the superscript preamplification system (Life Technologies). 1 μg of DNase I-treated total mammary gland RNA was mixed with oligo(dT)12-18 primer, incubated (10 minutes, 70°C) and placed on ice. A reaction mixture containing dNTPs, DTT, MgCl2 and PCR buffer was mixed with the RNA/primer mixture before being incubated for 5 minutes at 42°C. 200 units of Superscript II RT was added to the reaction for a further 50 minutes, and the reaction terminated for 15 minutes at 70°C. The reactions were Rnase H-treated before using them to amplify target cDNA sequences.
The forward and reverse primers used in the PCR amplification of the various cDNAs were all derived from mouse primary sequence except for Bad and Bcl-2, which were from the human sequence. Nucleotide numbers corresponding to the mouse cDNA sequence (starting at codon 1) are shown in Table 1, and nucleotides in parentheses represent the bases within the primers which are different to those in the mouse sequence.
Table 1.
Primer sequences used in the PCR amplification of various cDNAs
| cDNA | Accession number | Forward primer | Reverse primer | Product |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m Bax | L22472 | 1-ATGGACGGGTCCGGGGAGC-19 | 579-TCAGCCCATCTTCTTCCAGAT-559 | 579 bp |
| m Bak | Y13231 | 345-TTTAAGAGTGGCATCAGC-362 | 625-CATGATCTGAAGAAGAATCTGTG-602 | 280 bp |
| hu Bad | U66879 | 360-GAAGGGATGG(G)GGAGGAGC-378 | 577-CGATCCCACCAGGACTGGA-559 | 217 bp |
| hu Bcl-2 | M14745 | 1-ATGGCGCACGCTGGGAGAA-19 | 720-TCACTTGTGGCCCAGATAGGC-699 | 720 bp |
| m Bcl-x | X83574 | 1-ATGTCTCAGAGCAACCGGGAG-21 | 557-TTTCCGACTGAAGAGTGAGCC-537 | 557 bp |
| m Bcl-w | U59746 | 1-ATGGCGACCCCAGCCTCGGCCC-22 | 579-CTTGCTAGCAAAAAAGGCCCC-559 | 579 bp |
| rps29 | L31609 | 100-CTGATCCGCAAATACGGG-117 | 233-GCATGATCGGTTCCACTTG-215 | 134 bp |
Each combination of primers had specific cycling parameters: Bax: 94°C, 1 minute; 60°C, 30 seconds; 72°C, 2 minutes; Bak: 94°C, 1 minute; 53°C, 30 seconds; 72°C, 1 minute; Bad: 94°C, 1 minute; 58°C, 30 seconds; 72°C, 1 minute; Bcl-2: 94°C, 1 minute; 50°C, 30 seconds; 72°C, 2 minutes; Bcl-x: 94°C, 1 minute; 55°C, 30 seconds; 72°C, 2 minutes; Bcl-w 94°C, 1 minute; 55°C, 30 seconds; 72°C, 1 minute; rps29: 94°C, 1 minute; 55°C, 30 seconds; 72°C, 1 minute.
Details of the cycling parameters for each combination of primers are given in Table 1. All reactions were carried out for 40 cycles and then terminated with a 5 minute extension at 72°C followed by a soak at 4°C. PCR reactions were analyzed on 1.2% agarose gels followed by ethidium bromide staining.
Antibody preparation
Anti-Bax and anti-Bcl-2 antibodies were prepared by immunizing rabbits with a synthetic peptide of mouse Bax (residues 44-59) or mouse Bcl-2 (residues 41-54) coupled to KLH, and IgG from the resulting serum was affinity-purified on a Bax or Bcl-2 peptide column. The anti-Bax antibody was affinity-purified on a cyanogen bromide-peptide coupled column, whereas the anti-Bcl-2 antibody was purified on an affigel-15-peptide coupled column. In each case, the specificity of the anti-Bax and anti-Bcl-2 reactions were confirmed using excess peptide. The anti-Bcl-w and anti-Bcl-x antibodies were prepared by immunizing rabbits with a fusion protein of GST coupled to human Bcl-w (residues 1-172) or human Bcl-x (residues 1-233). IgG from the resulting serum was absorbed on a GST column, and subsequently affinity-purified on sepharose-conjugated Bcl-w or Bcl-x columns.
Western blotting
Total cell lysates were prepared from mammary tissue by homogenisation in NET lysis buffer (150 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA, 50 mM Tris, 1% NP40, 0.5 mM PMSF, 20 μM leupeptin, 2 mM aprotinin, pH 7.4). Samples of lysate were removed for protein estimation using the BCA assay (Pierce and Warriner, Chester, UK). Equal amounts of cell protein (20 μg) were separated by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. Gels were either stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue to confirm equal loading of cell proteins, or were transferred to Immobilon-P membrane (Millipore UK Ltd., Watford, UK). Membranes were blocked with 5% skimmed milk (Marvel) in PBS (overnight, 4°C) and incubated (2 hours, RT) with 1.4 μg/ml rabbit anti-Bax, 2 μg/ml mouse anti-Bak (Calbiochem, monoclonal antibody #AM03), 1:250 mouse anti-Bad (Transduction Laboratories, monoclonal antibody #B31420), 1:500 mouse anti-Bcl-x (Transduction Laboratories, monoclonal antibody #B22620), 2 μg/ml rabbit anti-Bcl-2 or anti-Bcl-w, or 1:1000 dilution of a monoclonal antibody to β-casein. Detection was achieved with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated sheep anti-rat IgG, sheep anti-mouse IgG or donkey anti-rabbit IgG (Amersham International, plc), followed by enhanced chemiluminescence detection (ECL, Amersham).
Immunoprecipitation and GST interaction studies
Tissue samples were extracted in NET lysis buffer (see above) and the protein content estimated as above. 100-1000 μg of cell protein in 500 μl NET lysis buffer including protease inhibitors (as above) was precleared of endogenous mouse IgG by incubation with 50 μl Protein A sepharose beads (1 hour, 4°C, Zymed) and centrifuged to pellet the beads (10 seconds). The purified antibodies raised against Bax, Bak, Bcl-x and IgG were immobilized onto CNBr-activated Sepharose 4B at 1 mg protein/ml packed beads. 20 μl bead-antibody complex was added to the precleared tissue lysate and gently vortexed (2 hours, 4°C). The beads were then washed three times in 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, before the bound protein was eluted from the beads with 50 mM diethylamine, pH 11.5. The eluted protein was mixed with sample buffer before loading. Samples were separated on 12.5% gels, transferred to Immobilon-P membranes and immunoblotted as above. For the GST-interaction studies, 100 μg of cell lysate was mixed with GST-Bcl-w activated beads (1 mg, 2 hours, 4°C). Immune complexes were washed in lysis buffer and finally resuspended in sample buffer. Precipitated proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions on 12.5% gels and western-blotted as above.
Transfection
Transient transfections were carried out with a mammalian inducible dual-vector system based on the steroid hormone ecdysone (Invitrogen, ecdysone-inducible expression kit). The expression vectors pINDBak, pINDantisenseBak, pINDBclw and pINDantisenseBclw were constructed by ligating an empty pIND vector to full-length human Bak or Bclw cDNA in either the sense and antisense orientations. Sequences were confirmed using the dye-terminator sequencing kit and an ABI sequencer (according to the manufacturer's recommendations; Perkin-Elmer Applied Biosystems; Warrington, UK). After cotransfection with pINDBak, pINDantisenseBak, pINDBclw or pINDantisenseBclw and pVgRXR (which expresses the heterodimeric ecdysone receptor), the transfected cells were stimulated by treatment with the synthetic ecdysone analogue, Muristerone A.
FSK-7 cells were seeded at a density of 7.5×104 cells/cm2 on coverslips coated with 0.2 μg/ml fibronectin. After reaching 60% confluence, the coverslips were transferred to 12-well dishes containing 1 ml of serum-free medium. Lipofectamine (Life Technologies) was used in the cotransfection of the plasmids pVgRXR and pINDBak (sense and antisense). Equal amounts of the two different plasmids, ranging from 0.6 μg to 5 μg, were cotransfected into FSK-7 cells using 10 μg Lipofectamine in a final volume of 600 μl serum and antibiotic-free medium (according to the manufacturers’ recommendations). For the Bak versus Bclw titration experiment the amount of sense pINDBak was maintained at 2 μg whilst the amount of pINDBclw (sense and antisense) ranged from 1.25-10 μg. In each case, transfection was carried out for 5 hours before replacing the transfection mixture with 2 ml serum-containing medium. The cells were allowed to recover for 16 hours before washing and incubating with medium containing 10 μM Muristerone A for a further 20 hours. Wells were washed in PBS and apoptosis of the detached cells was assessed after fixing cells in 2% paraformaldehyde in PBS, staining with 4 μg/ml Hoechst 33258, and examining nuclear morphology using fluorescence microscopy.
RESULTS
Apoptosis in ICR mice occurs at the lactationinvolution interface
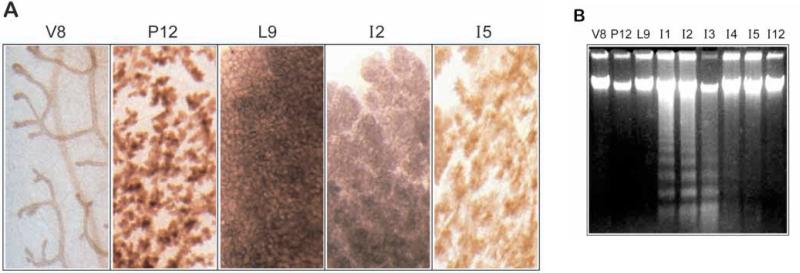
Profound remodelling events occur in the mammalian breast during the pregnancy cycle. The developmental programme of involution involves removal of lactational alveoli by apoptosis, combined with remodelling of the tissue to produce a naked branched ductal network characteristic of the non-pregnant animal (Fig. 1A). In all our studies, involution of mouse mammary gland was induced by pup removal after full lactation had been established over 9 days. In ICR mice this resulted in apoptosis within 1 day of weaning, remaining maximal until day 3 when the extent of apoptosis as assessed by DNA laddering began to decline (Fig. 1B). No fragmentation of the DNA could be detected in virgin, pregnant or lactating tissue, nor could it be seen in tissue that had largely remodelled at involution day 12, even after the use of Southern blotting to increase the sensitivity of detecting DNA ladders (data not shown). The kinetics of apoptosis in ICR mice are therefore different to those in other strains including Swiss and Balb/c, which have a slower onset of tissue remodelling (Strange et al., 1992; Lund et al., 1996).
Fig. 1.
Apoptosis in ICR mice occurs at the lactation-involution interface. (A)Whole mounts of mammary gland at different times of development stained with Haematoxylin show the ductal structures in 8 week virgin mice (V8) and the extent of proliferation after 12 days of pregnancy (P12) and 9 days of lactation (L9). Regression of the tissue is visible by day 2 of involution (I2) and extensive by day 5 (I5). (B) 5 μg genomic DNA extracted from the same developmental samples was subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis. Apoptotic DNA ladders appear within 1 day of involution and are maximal for the next 2 days. Apoptosis subsequently continues but is less extensive on day 4 and 5 and is largely absent by day 12.
Altered expression of Bax, Bak and Bad during involution correlates with apoptosis
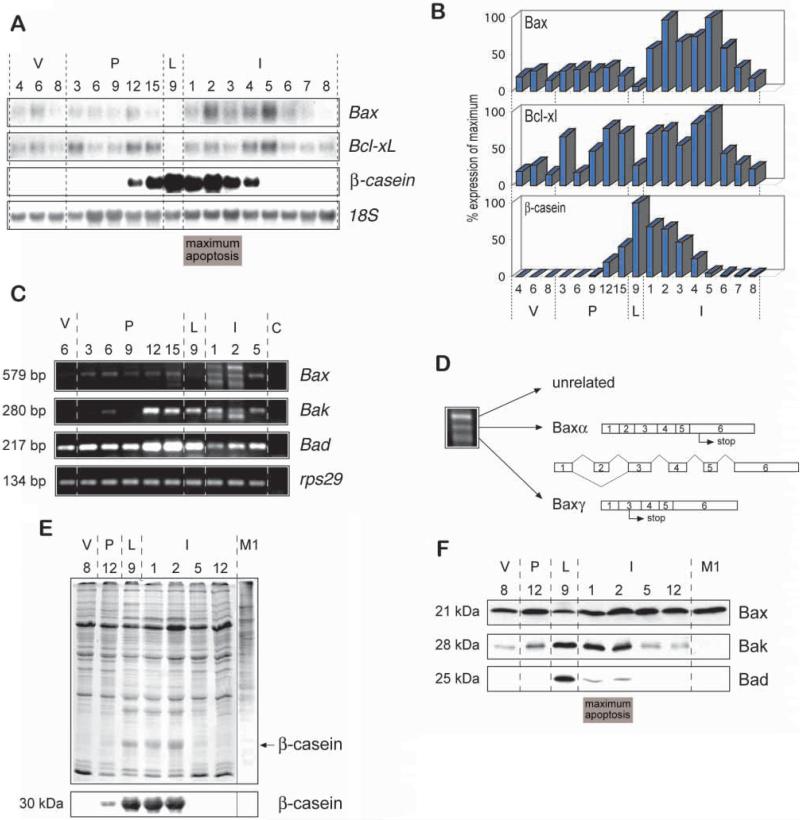
To determine whether changes in the expression of Bcl-2 related genes might be involved with the induction of mammary apoptosis, we examined their mRNA and protein levels at different stages of development. Initially we looked at the pro-apoptotic regulators, Bax, Bak and Bad. Northern blot analysis indicated that Bax mRNA levels were upregulated at the onset of involution, with the biggest increase in expression occurring at the lactation-to-involution interface (Fig. 2A,B). In contrast to the results obtained at the mRNA level, we did not observe an increase of Bax protein levels in western blots using anti-mouse Bax antibodies (Fig. 2E,F). However, when we examined the level of Bax mRNA by RT-PCR, we found that additional Bax mRNA species were present on days 1 and 2 of involution (Fig. 2C), possibly explaining the increased level of Bax mRNA detected by northern blotting. Three PCR products identified at this time point were cloned and sequenced (Fig. 2D). As expected the 579 bp product corresponded to mouse Baxα. The slower migrating band did not contain any sequence homologous to Bax, although interestingly, the lower molecular mass product was Baxγ (Oltvai et al., 1993), which has not previously been identified in vivo. The transcript of Baxγ results in a protein of approx. 5 kDa due to removal of exon 2 and a shift in reading frame, but it was not recognized by two different anti-amino-terminal Bax antibodies and may therefore not contribute to apoptosis itself (data not shown). However, the presence of this unusual spliced Bax mRNA indicates that mammary involution is not only associated with increased transcription of cell death-promoting genes but also with de novo splicing events, which could potentially generate novel apoptotic proteins.
Fig. 2.
High levels of pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins during involution correlate with apoptosis. (A,B) Total RNA was prepared from mammary gland for northern analysis. (A) 10 μg total RNA was blotted onto nylon membranes and hybridised with 32P-labelled mouse Bax and Bcl-x cDNA. Analysis of β-casein mRNA confirmed that the samples expressed the expected temporal pattern of milk protein genes and an 18S DNA probe was used to assess equal loading of the gels. (B) The blots were analyzed using storage phosphor imaging plates and a Fujix Bas 2000 bioimaging analyzer. The levels of specific mRNA were plotted after normalizing to the level of 18S rRNA. (C) RT-PCR of the cell death genes Bax, Bak and Bad confirmed the RNA profile of Bax as measured by northern blotting and indicated that expression of Bak and Bad were also regulated during development. A 29S ribonuclear protein (rps29) PCR analysis was included to ensure that equal concentrations of RNA were present in the PCR reactions. C, control with no cDNA in the PCR reaction. The faster migrating band in Bak PCR reactions was cloned and sequenced and found to be unrelated to Bak. (D) Multiple bands observed in the involuting day 2 sample of the PCR reaction for Bax were cloned and sequenced. The centrally migrating band corresponded to the major Bax transcript Baxa, while the faster migrating band corresponded to the transcript for Baxγ, which lacks exon 2. The slower migrating band contained a sequence which was unrelated to Bax. (E,F) Whole tissue lysates were prepared from the developmental samples and subjected to polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. (E) Coomassie staining showed that the protein samples were equally loaded. Western blotting indicated that β-casein was detected in late pregnancy, lactation and early involution, as expected. (F) Similar blots were incubated with antibodies directed against Bax, Bak and Bad. Confirmation of the Bax expression profile was validated using a second independently derived antibody directed against Bax (data not shown). An equal amount of protein from M1 murine myeloid leukaemia cells was included as a positive control for identification of the Bax protein. In each case, and in the subsequent figures, tissue was isolated from 4, 6, or 8 week virgin (v) mice, and at the indicated number of days of pregnancy (P), lactation (L) and involution (I).
A number of cell-death-inducing proteins homologous to Bax have recently been cloned but have not previously been examined in mouse mammary gland. RT-PCR revealed an increase in the expression of Bak mRNA in late pregnancy, which was retained until the end of the maximum peak of apoptosis in involution (Fig. 2C). The induction of Bak mRNA expression was reflected by enhanced levels of Bak protein in lactation and early involution (Fig. 2F). Similar results were obtained with Bad at the mRNA and protein levels (Fig. 2C,F). However, the levels of Bad protein were not completely comparable to the RNA levels, suggesting that Bad protein may be subject to more rapid turnover than its mRNA.
Our data show that the cell-death promoting genes, Bax, Bak and Bad are all expressed during mammary involution, thus they may act as potential inducers of apoptosis. Since the protein products of all three of these genes were present at high levels in lactation, it is possible that apoptosis is primed to occur towards the end of pregnancy or during lactation but is suppressed by the expression or activity of cell survival genes until involution.
Downregulation of Bcl-w in mammary epithelial cells during the transition from lactation to involution coincides with the induction of apoptosis
We next addressed whether expression of the cell death-suppressing genes, Bcl-x, Bcl-2 and Bcl-w was also regulated during mammary gland development. Bcl-x levels were not significantly altered. There were some fluctuations at the RNA level as measured by northern blotting (Fig. 2A,B) and RTPCR (Fig. 3A), and in levels of Bcl-x protein expression (Fig. 3B), however this death suppressor was always present. In contrast to another study (Heermeier et al., 1996), we found no evidence for the expression of Bcl-xS, an alternatively spliced death-promoting variant of Bcl-x, in mammary gland involution by either PCR or western blotting (data not shown).
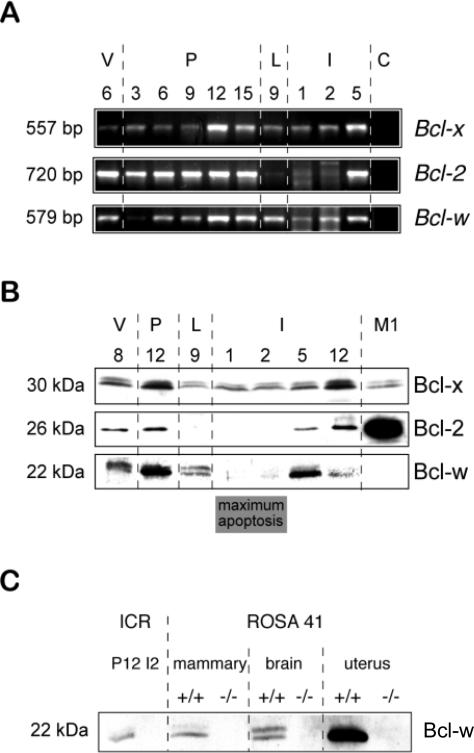
Fig. 3.
Downregulation of death-suppressing Bcl-2 proteins coincides with the induction of apoptosis. (A) RT-PCR analysis of Bcl-x, Bcl-2 and Bcl-w confirmed the RNA profile of Bcl-x as measured by northern blotting and showed that expression of Bcl-2 and Bcl-w were regulated during development. In several independent experiments, the Bcl-2 RT-PCR product was absent in lactation and expressed at low levels in involution, whereas the Bcl-w RT-PCR product was dramatically lower in the I1 and I2 samples than L9 but was not completely absent. (B) Whole tissue lysates were prepared from the developmental samples, separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, then analyzed by western immunoblotting. Blots were incubated with antibodies directed against Bcl-x, Bcl-2 and Bcl-w. Confirmation of the Bcl-w expression profile was validated using two additional and independently derived antibodies directed against Bcl-w (data not shown). Lysates from M1 cells were included as controls. (C) Whole tissue lysates were prepared from ICR mice in pregnancy (P12) and involution (I2) and directly compared with tissue lysates from brain, mammary gland and uterus of ROSA41 Bcl-w null mutant animals (–/–) and their wild-type littermates (+/+) (Ross et al., 1998). Western blotting confirmed the identity of the detected protein as Bcl-w.
Bcl-2 and Bcl-w, on the other hand, were modulated through development. Significantly, their expression was downregulated in involution during the period of maximal apoptosis (Fig. 3A,B). Bcl-2 was absent when tested by both RT-PCR and western blotting in lactation and the first 2 days of involution, although it returned at the later stages of involution during mammary gland remodelling. This agrees with previous data where we showed that Bcl-2 was expressed in the epithelial cells of mammary ducts but not in lactational alveoli (Pullan et al., 1996). Bcl-w is a novel cell survival gene, homologous to Bcl-2, which is found in a number of tissues (Gibson et al., 1996). It has been shown to have a role in controlling testis development (Ross et al., 1998; Print et al., 1998). We found that Bcl-w mRNA was present in the mammary gland and was expressed in late pregnancy and lactation, but levels decreased at the onset of involution (Fig. 3A), at which time its protein was low to undetectable (Fig. 3B). Since Bcl-w has not previously been examined in many tissues by western blotting, we confirmed our results using two independently derived antibodies to Bcl-w and obtained comparable data with each (data not shown). In addition, we validated the specificity of our antibody by showing that the band it recognized in western blots was absent in Bcl-w null mutant mice (Fig. 3C).
These studies show that the apoptosis-suppressors Bcl-2 and Bcl-w are downregulated during the involution process, and upregulated after the initial remodelling events have occured. Their absence at days 1 and 2 of involution may therefore contribute to the induction of mammary apoptosis.
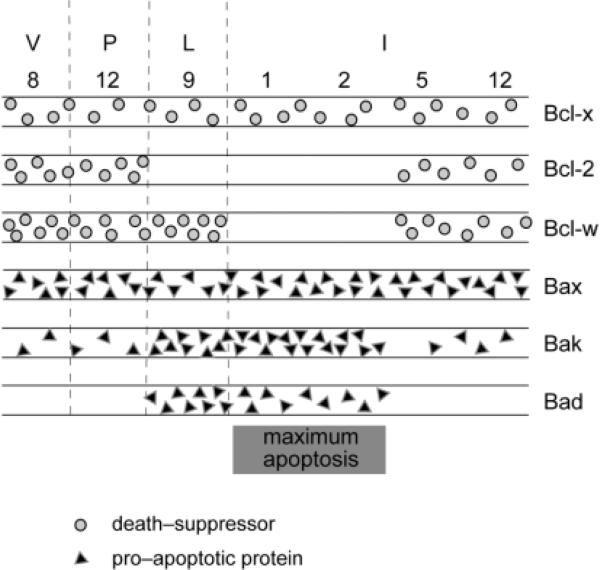
Together, our results indicate that the levels of both pro-and anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins are altered at different times during mammary gland development in vivo, and suggest that changes in the overall balance of cell death regulators may affect apoptotic outcome during this developmental processs (Fig. 4). It is noteworthy that all three anti-apoptotic proteins along with Bax and low levels of Bak are present in virgin and midpregnant tissue, whereas the situation is reversed during maximal apoptosis in involution with all three pro-apoptotic proteins and only Bcl-x being expressed.
Fig. 4.
Schematic representation of changes in the expression profiles of Bcl-2 family proteins during mammary development in the pregnancy cycle. Pro-apoptotic proteins are shown in triangles, while death-suppressors are in circles. More triangles/circles indicate a higher level of expression. Note that (1) Bcl-2 expression is absent in lactation and during the time of maximal apoptosis; (2) the death-promoting molecules Bak and Bad are upregulated at the pregnancy/lactation interface and are proposed to prime the gland for apoptosis, while the survival-promoting molecules Bcl-w and Bcl-x maintain mammary gland integrity during lactation; and (3) Bcl-w is downregulated in involution and may therefore allow apoptosis through the action of Bax, Bak and Bad.
The profile of Bcl-2 family proteins in purified mammary epithelial cells reflects their levels in lactating mammary gland
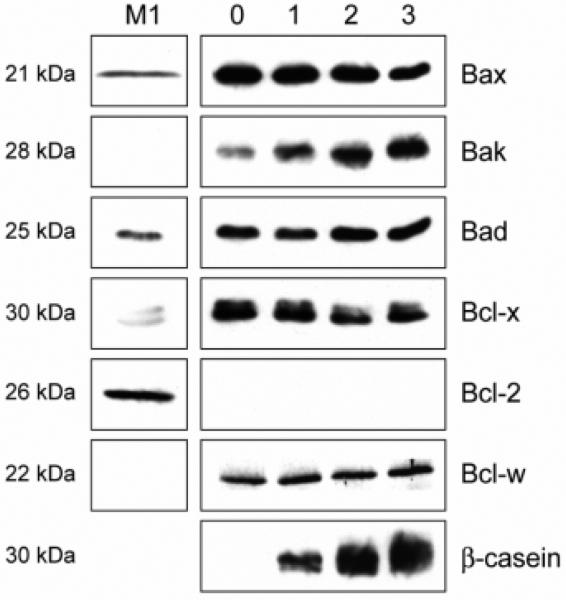
To determine whether the profile of Bcl-2 family proteins detected in vivo was representative of their expression in the epithelial cell compartment of mammary tissue, we examined their expression in primary cell culture. Luminal epithelial cells from late pregnant mammary gland were isolated, separated from the majority of myoepithelial and stromal cells (Pullan and Streuli, 1996), and cultured in an environment where the cells progress from a late pregnant to a lactating phenotype (Aggeler et al., 1991). In this model β-casein synthesis increased over several days, and in the most differentiated cells the expression profile of Bcl-2 family protein was similar to that in lactating mammary gland (Fig. 5; compare to L9 samples in Figs 2F, 3B and summary in Fig. 4).
Fig. 5.
Expression of the Bcl-2 family in an in vitro cell culture model mimics the late pregnant profile observed in vivo. Whole cell lysates were prepared from primary mammary epithelial cells cultured on a basement membrane matrix in the presence of serum for 2 days then washed and changed to serum-free medium containing differentiation hormones for 0, 1, 2 or 3 days (Pullan et al., 1996). Equivalent amounts of cell protein were separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, then analyzed by western immunoblotting. Blots were incubated with antibodies directed against Bax, Bak, Bad, Bcl-x, Bcl-2, Bcl-w and β-casein, and lysates from M1 cells are included as controls.
Altered expression of Bcl-2 family proteins in mammary apoptosis during the estrous cycle
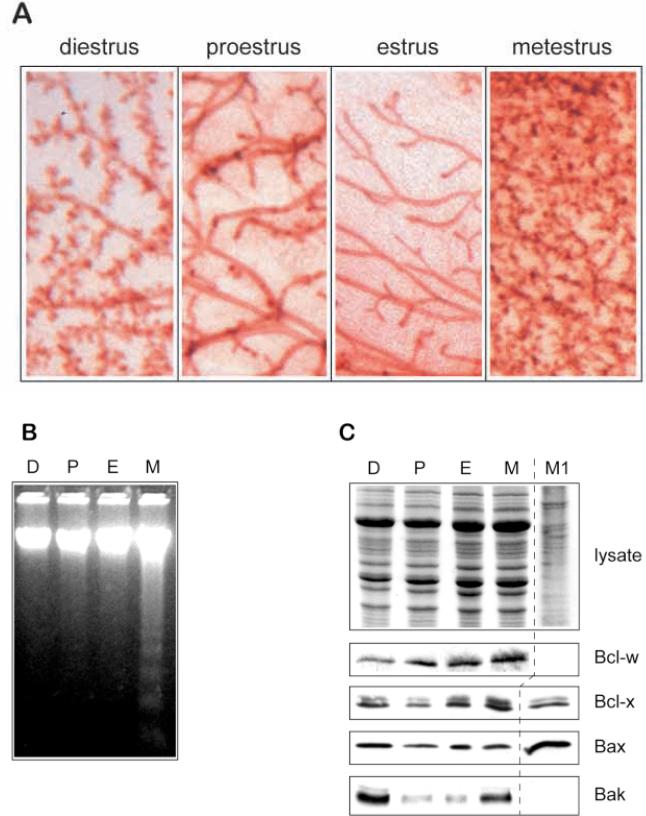
Further evidence in support of the hypothesis that changes in the expression of cell death regulators influence mammary epithelial apoptosis was provided by an additional developmental model. Female mice undergo an estrous cycle, characterized by four main stages: diestrus, proestrus, estrus and metestrus. ICR mice show dramatic structural changes within mammary gland during this cycle, which can be visualised in whole mounts (Fig. 6A). Following estrus, there is proliferation involving the appearance of many small newly branched ductal and prealveolar structures at metestrus, in preparation for a possible pregnancy. In the absence of conception, this is followed by remodelling of the tissue, returning the gland to a sparse network of ducts. Remodelling is accompanied by the characteristic DNA internucleosomal cleavage that occurs during apoptosis, most prominent at metestrus but continuing through diestrus (Fig. 6B). Similar apoptotic changes in estrous cycle have been noted in other strains of mice, but few show the same degree of morphological change as ICR mice (Andres et al., 1995). They have also been demonstrated in human breast during the menstrual cycle (Anderson et al., 1997).
Fig. 6.
Bak is implicated as a cell-death gene during mammary epithelial apoptosis in the estrous cycle. (A) Whole mounts of mammary gland of ICR mice at different times of the estrous cycle stained with Haematoxylin show the ductal structures in estrus, the extent of proliferation within 2 days at metestrus, and the progressive regression of the next few days through diestrus and proestrus. (B) 5 μg genomic DNA extracted from mammary gland from the same mice was subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis. Apoptotic DNA ladders appear during metestrus (M) and are absent in proestrus (P) and estrus (E). We did not detect ladders in the diestrus (D) sample by this method, possibly because of its lack of sensitivity, although apoptosis has previously been shown to occur at this stage of the cycle by in situ methods (Andres et al., 1995). (C) Whole-tissue lysates were prepared from mammary gland at different times of the estrous cycle and subjected to polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Coomassie staining indicates that the levels of protein were even in each sample (top panel). Similar gels were transferred to nylon and immunoblotted using antibodies directed against Bcl-w, Bcl-x, Bax and Bak. The levels of Bak in estrus correspond to those in the virgin tissue extracts shown in Fig. 2F, whereas its increased levels at metestrus correlate with the induction of apoptosis. Bad could not be detected in non-pregnant tissue at any stage of the estrous cycle.
We examined the levels of Bcl-2 family proteins and found that Bak was upregulated during the most prominent phase of apoptosis in metestrus and diestrus (Fig. 6C). The levels of Bax and Bcl-x did not change significantly, which was similar to our observations at involution. Bcl-w was expressed at each stage of the estrous cycle, whereas Bad protein was not detected at any stage of the cycle. In addition, levels of Bcl-2 were similar through the cycle (data not shown). Thus, changes in the level of the cell death-promoter Bak, correlate with the developmental onset of apoptosis during the estrous cycle in mammary gland.
Induced cell death caused by Bak in cultured mammary epithelial cells can be rescued by Bcl-w
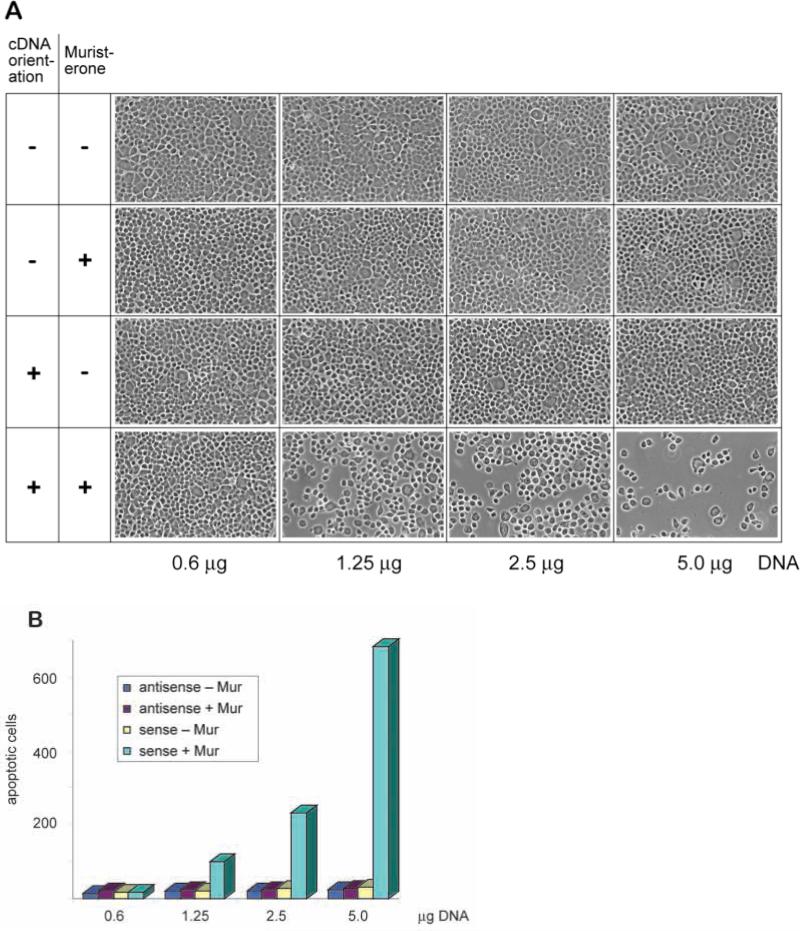
The results of the in vivo study suggest that increased Bak expression during mammary gland development might be causally related to apoptosis in vivo. To test for an apoptotic role of Bak, we examined its capacity to induce death in cultured mammary epithelial cells. The FSK-7 cell line was derived from mouse mammary gland (Kittrell et al., 1992). Sublines of FSK-7 isolated in our laboratory formed alveolar mammary structures when cultured on basement membrane substrata, thus showing an ability to undergo morphological differentiation (S. Runswick, D. Garrod and C. H. Streuli, unpublished data). On tissue culture dishes, the cells formed cobblestone monolayers and displayed very low rates of apoptosis. We demonstrated in transient transfection assays that Bak induced dramatic apoptosis of FSK-7 cells (Fig. 7). Transfections with Bak vectors that were driven by the ecdysone analogue, Muristerone A, resulted in apoptosis occurring over 20 hours, while antisense Bak constructs had no effect. We were not able to detect Bak protein in untransfected FSK-7 cells; however, low levels were expressed after Bak transfection but only in the presence of Muristerone A (data not shown). Transfections with increasing amounts of Bak vector DNA resulted in increasing numbers of apoptotic cells being released from the monolayer after induction with Muristerone A. Cells treated identically but without Muristerone A remained as an intact, confluent monolayer. The cells which detached in these assays were quantitated and only those detaching after transfection with the sense Bak construct showed apoptosis (Fig. 7B). Thus, Bak is competent to induce apoptosis in cultured mammary epithelia, supporting our hypothesis that it is a pro-apoptotic protein in mammary gland in vivo.
Fig. 7.
Enforced expression of Bak induces apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells. Transient cotransfections of pINDBak and VgRXR were carried out in the mammary epithelial cell line, FSK-7, using an ecdysone-inducible mammalian expression system. Cells were cotransfected for 5 hours in serum-free medium before being placed in serum-containing medium overnight. Bak induction was initiated after addition of 10 μM Muristerone A (Mur). Non-adherent cells were then scored for apoptosis by morphological phenotype after Hoechst 33528 staining. (A) Phase photomicrographs taken 41 hours after transfection indicate the effects of cotransfection of pINDBak, in either sense (+) or antisense (–) orientation, together with VgRXR, on FSK-7 cells in the presence or absence of Muristerone A. Equal amounts of the two plasmids, as indicated, were used for each transfection. (B) Graph indicating the number of apoptotic cells released from each 15 mm2 coverslip 41 hours after each transfection. Similar quantitative data were obtained in each of three separate experiments. These data confirm that in the presence of Muristerone A, increasing concentrations of the sense Bak construct lead to an increase in the number of apoptotic cells.
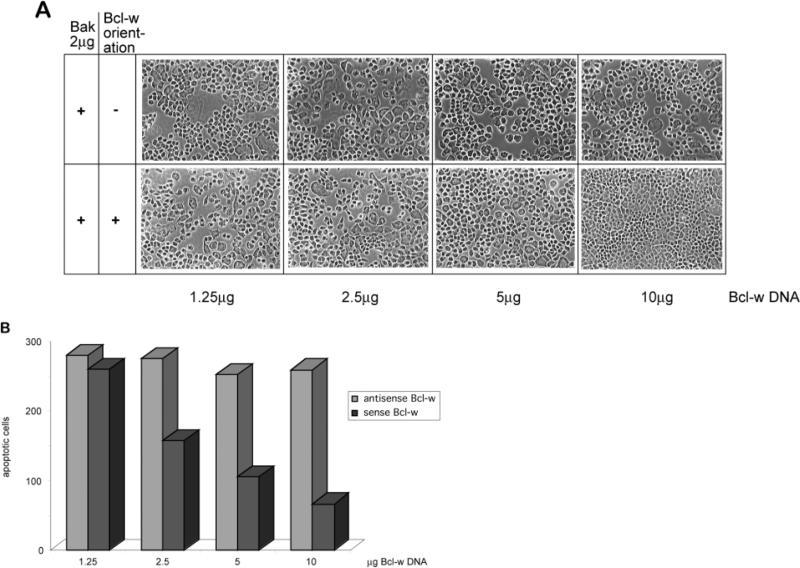
Elevated levels of Bak were expressed in lactating mammary gland in vivo and we hypothesized that expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-w might have contributed to the low level of cell death at this time. We therefore tested whether Bcl-w could suppress the death-promoting activity of Bak in cultured mammary cells. FSK-7 cells were transfected with levels of the sense Bak vector that triggered significant apoptosis. Bcl-w cotransfected with Bak had a striking and dose-dependent effect in reducing the extent of Bak-induced cell death (Fig. 8A,B). The inhibitory effect of Bcl-w only occurred when it was expressed in the sense orientation (Fig 8).
Fig. 8.
Bcl-w potentiates survival in FSK-7 cells undergoing Bak-induced apoptosis. Transient cotransfections of pINDBak, pINDBclw and VgRXR were carried out and analyzed as described in Fig. 7. Bak and Bcl-w induction was initiated after addition of 10 μM Muristerone A. (A) Phase photomicrographs were taken 41 hours after transfection, and (B) the number of apoptotic cells released from each 15 mm2 coverslip was calculated. Note that the transfections with more sense (+) Bcl-w vector DNA showed an increase in the cell density of the monolayer and a corresponding decrease in the number of released apoptotic cells. The antisense (–) Bcl-w construct was not able to suppress the cell death caused by Bak. In each case, cells treated identically but without Muristerone A remained in an intact, confluent monolayer (data not shown). The results are representative of three separate experiments.
Thus, Bcl-w is able to rescue mammary cells from Bak-induced apoptosis. This raises the possibility that its downregulation at the onset of involution might cause the induction of apoptosis in vivo.
Bcl-2 family partners for Bak and Bcl-w in the mammary gland
One of the ways in which Bcl-2 family proteins may regulate apoptosis is through homo- and hetero-dimerization (Oltvai et al., 1993). We therefore examined whether Bak and Bcl-w were able to form physical interactions, thereby possibly explaining their opposite roles in mammary apoptosis.
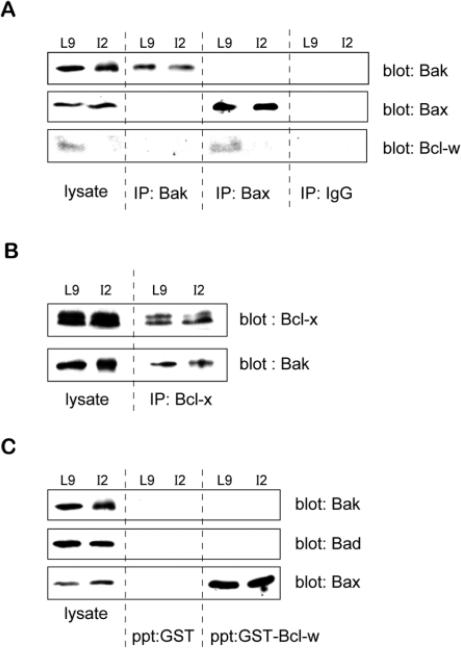
Initially we determined binding partners for Bak in mammary tissue extracts. Anti-Bak antibody was coupled to sepharose and used to immunoprecipitate Bak from extracts of lactating and involuting mammary gland. Subsequent immunoblotting revealed the presence of Bak not Bcl-w (Fig. 9A). However Bak did interact with Bcl-x, since sepharose-conjugated anti-Bcl-x immunoprecipitated Bak from mammary extracts (Fig. 9B). Since Bcl-2 is absent from lactating and involuting mammary gland (Fig. 3), these results suggest that Bak forms binding partners with Bcl-x but not Bcl-w at this time of development.
Fig. 9.
Binding partners for Bak and Bcl-w in the mouse mammary gland. (A-C) Equal amounts of tissue extracts from lactating (L9) or apoptotic involuting (I2) mouse mammary gland were precipitated with the indicated reagent and the identity of proteins in the precipitates identified by immunoblotting. In each case samples of lysate were also included on the same gels as positive controls (lysate). (A) Immunoprecipitations were performed with sepharoseconjugated anti-Bak and anti-Bax antibodies or control IgG, and the proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to nylon. The blots were probed with antibodies to Bak, Bax and Bcl-w. Note that Bcl-w was not present in Bak immunoprecipitates, but did interact with Bax. No Bcl-w was seen either in whole cell lysates or the Bax immunoprecipitates of the I2 sample. (B) Immunoprecipitations with sepharose-conjugated anti-Bcl-x antibodies were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to nylon, and probed with antibodies to Bcl-x or Bak. (C) Tissue extracts were mixed with either GST- or GST-Bcl-w conjugated sepharose beads for 2 hours before centrifugation and separation by SDS-PAGE The gels were transferred to nylon and subjected to immunoblotting using antibodies directed against Bak, Bad and Bax. These data confirm that Bcl-w interacts with Bax but not Bak or Bad in mammary epithelial cells. Note that the I2 lysate contains Bax, which is capable of binding GST-Bcl-w, but the absence of Bcl-w at this developmental stage precludes such an interaction taking place in vivo.
We also examined Bcl-w binding partners in mamary tissue extracts. Sepharose-conjugated anti-Bax antibody immuno-precipitated Bcl-w from extracts of lactating mammary gland, but not from involuting tissue from which Bcl-w was absent (Fig. 9A). Immunoprecipitation of Bak suggested that there was no interaction of Bak with Bcl-w (Fig 9A). Finally, a GSTBcl-w fusion protein was incubated with mammary gland lysates, and immunoblots revealed a specific interaction of Bclw with Bax, but not with Bak or Bad (Fig. 9C).
Together, these protein-protein interaction studies show that Bak and Bcl-w are not binding partners in the mammary gland in vivo. Given our results from the transfection study, Bak and Bcl-w may therefore function independently to regulate apoptosis. This concurs with a new view of apoptosis where some pro-and anti-apoptotic members of the family, such as Bax and Bcl-2, have been shown to regulate cell death independently and do not require interations between them (Knudson and Korsmeyer, 1997). However, we do find that in mammary gland Bak/Bcl-x and Bax/Bcl-w heterodimers exist, supporting a view that apoptosis is controlled through a balance between these two arms of the Bcl-2 protein family.
DISCUSSION
This study ties together observations on the regulated expression of Bcl-2 proteins in mammary gland development in vivo with their ability to induce or suppress apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells in culture. We demonstrate that Bak, which is expressed at high levels during lactation and involution in vivo, can induce apoptosis in culture. In contrast, Bcl-w, which is expressed during lactation in vivo but is not present during involution, suppresses the death-promoting activity of Bak in culture. Our transfection data obtained from the culture model provide the first evidence that Bcl-w can functionally antagonize Bak activity.
Our work also demonstrates that apoptosis during development of the mouse mammary gland in the pregnancy cycle is associated with changes in the expression levels of Bcl-2 family proteins. Thus, expression of Bcl-2 proteins is developmentally regulated in some tissues, indicating a novel mechanism for the control of apoptosis in development. Moreover, the control of apoptosis in vivo appears to be significantly more complex than has been apparent in culture studies using other cell systems, and involves multiple players. We favour a model whereby many pro- and anti-apoptotic regulators hold the survival of a cell in balance, and that their levels and function are regulated by extracellular signals.
Control of apoptosis by Bcl-2 family proteins in mammary gland
This leads to the question of what external factors regulate the expression of Bcl-2 family genes in mammary gland, and whether they directly impinge on the transcriptional and post-translational control mechanisms. Although the systemic hormonal changes regulating progression through estrous and pregnancy cycles are not the same, altered levels of circulating steroid hormones or prolactin, and reduced availability of locally acting survival factors such as IGF-1 or extracellular matrix, are all candidates for final cues to trigger apoptosis at the appropriate time (Tonner et al., 1997; Pullan et al., 1996; Lund et al., 1996). Of these, only steroids have so far been shown to affect expression of Bcl-2 proteins in mammary cells (Teixeira et al., 1995; Wang and Phang, 1995; Leung et al., 1998). Steroid flux is more predominant in controlling the estrous cycle than involution, and a report that estradiol suppresses Bak expression in MCF-7 cells may explain our own observation that the control of apoptosis in the estrous cycle is different to that in involution (Leung et al., 1998).
The downstream control of apoptosis through Bcl-2 proteins is still a subject of intense experimentation and speculation. Whilst changes in the expression of Bcl-2 proteins may provide a primary mechanism of specifying mammary apoptosis in vivo, it is probable that alterations in post-translational modifications, subcellular localization, or protein-protein interactions fine-tune the timing of apoptosis. Phosphorylation controls the function of Bad (Datta et al., 1997), but has not so far been demonstrated for Bax, Bak, Bcl-x or Bcl-w. In addition the role of phosphorylation in suppressing apoptosis by Bcl-2 is controversial since mutation studies suggest a possible requirement for phosphorylation (Ito et al., 1997), but cell cycle studies show that its phosphorylation is not involved with apoptosis and correlates instead with mitosis (Ling et al., 1998). Altered subcellular localization of Bcl-2 proteins, particularly Bax, has also been proposed to have significance for apoptosis (Wolter et al., 1997). We have begun a similar analysis in mammary gland in vivo, and preliminary experiments indicate that Bak may move from cytosol to a membrane fraction in involution (A. Metcalfe and C. H. Streuli, unpublished data).
Separate Bcl-2 family pathways may regulate survival in mammary gland
Notwithstanding these possible changes, it is still unclear to what extent Bcl-2 proteins regulate apoptotic progression through heterodimerization between opposing members of the family (Yin et al., 1994). Whilst some members of the family can interact in vivo and in vitro, there is now substantial evidence that death promoters and suppressors can control apoptosis independently of each other. For example, genetic evidence from doubly-deficient Bax/Bcl-2 mice indicates that these proteins function independently in the control of apoptosis (Knudson and Korsmeyer, 1997). In addition, mutations in Bcl-x that block its ability to bind Bax or Bak still protect against viral-induced apoptosis (Cheng et al., 1996), and a mutant form of Bcl-2 which does not bind Bax protects T cells from apoptosis in a transgenic mouse model (St Clair et al., 1997). Moreover, the anti-apoptotic function of Bcl-2 and Bcl-x can be opposed by Bak in the absence of any heterodimerization (Simonian et al., 1997).
One possible explanation for these findings is that the regulation of cell death involves many members of the Bcl-2 family. This in turn suggests that the precise expression profile needs to be defined for each cell type and taken into account when trying to interpret apoptotic mechanism. Examination of expression of a wide range of Bcl-2 proteins during the development of mammary gland suggests that many members of the family may be involved in regulating survival and apoptosis. The results of our culture study with mammary epithelial cells suggest that Bcl-w can protect against the apoptotic properties of Bak. However, our inability to demonstrate a physical interaction between Bcl-w and Bak in either tissue extracts or in vitro studies with GST fusion proteins indicates that any functional role they may have in vivo is through independent pathways. Indeed, the existence of Bak/Bcl-x and Bax/Bcl-w heterodimers in mammary tissue suggests the presence of two separate pathways working in concert to control survival in the normal gland. One possible advantage of such a system may be to ensure that aberrant apoptosis does not occur in the event of one gene being mutated or lost.
A hypothesis for the intracellular control of apoptosis in normal mammary gland
The results obtained from expression studies in vivo and functional experiments in culture lead to a hypothesis for the intracellular control of apoptosis in normal mammary gland. We suggest that involution is primed in lactation through the expression of Bak. However, sufficient Bcl-x and Bcl-w are present at this time to suppress its killing effects. When involution is stimulated following pup removal, the reduced levels of Bcl-w may alter the balance of pro-and anti-apoptotic regulators in favour of Bak- and Bax-mediated killing. The absence of Bcl-2 may also contribute to the potential of mammary cells to undergo apoptosis after lactation. Furthermore, the presence of Bad may also have a proapoptotic role, but confirmation of this possibility awaits further experimentation. A role for Bax in regulating susceptibility to apoptosis in human breast has been suggested following observations that its level is lower in many breast carcinomas (Krajewski et al., 1995; Bargou et al., 1995). Based on our study, it may now be more pertinent to compare the relative Bax/Bcl-w and Bak/Bcl-x ratios in normal and tumour tissue from patients with breast cancer as possible prognostic indicators of survival to this disease.
Conclusion
In summary, we have examined Bcl-2 family proteins in an in vivo model for apoptosis and demonstrate that they are regulated during mammary gland development. Their expression patterns correlate with the ability of specific members of this family, Bak and Bcl-w, to trigger or suppress apoptosis in cultured mammary cells. Our data from protein interaction studies of extracts from mammary tissue in vivo support the concept that some pro- and anti-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family control apoptosis independently.
Acknowledgments
CHS is a Wellcome Senior Fellow in Basic Biomedical Science. The authors are grateful to Professor Suzanne Cory (Molecular Genetics of Cancer Division, Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research, Royal Melbourne Hospital 3050, Australia) and Dr Caroline Dive for critical review of the manuscript. This work was funded by the Wellcome Trust and by a Medical Research Council ROPA award #G9413455 and by USPHS grant #HD-36437 to G. M.
REFERENCES
- Adams JM, Cory S. The Bcl-2 protein family: Arbiters of cell survival. Science. 1998;281:1322–1326. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5381.1322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aggeler J, Ward J, Blackie LM, Barcellos-Hoff MH, Streuli CH, Bissell MJ. Cytodifferentiation of mouse mammary epithelial-cells cultured on a reconstituted basement-membrane reveals striking similarities to development in vivo. J. Cell Sci. 1991;99:407–417. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.2.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson E, Clarke RB, Howell A. Changes in the normal human breast throughout the menstrual cycle: Relevance to breast carcinogenesis. Endocrine-Related Cancer. 1997;4:23–33. [Google Scholar]
- Andres AC, Zuercher G, Djonov V, Flueck M, Ziemiecki A. Protein-tyrosine kinase expression during the estrous-cycle and carcinogenesis of the mammary-gland. Int. J. Cancer. 1995;63:288–296. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910630224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargou RC, Daniel PT, Mapara MY, Bommert K, Wagener C, Kallinich B, Royer HD, Dorken B. Expression of the Bcl-2 gene family in normal and malignant breast- tissue – low Bax-alpha expression in tumor-cells correlates with resistance towards apoptosis. Int. J. Cancer. 1995;60:854–859. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910600622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng EHY, Levine B, Boise LH, Thompson CB, Hardwick JM. Bax-independent inhibition of apoptosis by Bcl-X(L). Nature. 1996;379:554–556. doi: 10.1038/379554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conradt B, Horvitz HR. The C-elegans protein EGL-1 is required for programmed cell death and interacts with the Bcl-2-like protein CED-9. Cell. 1998;93:519–529. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81182-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y, Greenberg ME. Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell. 1997;91:231–241. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80405-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrow SN, Brown R. New members of the Bcl-2 family and their protein partners. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1996;6:45–49. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(96)90009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrow SN, White JHM, Martinou I, Raven T, Pun KT, Grinham CJ, Martinou JC, Brown R. Cloning of a Bcl-2 homolog by interaction with adenovirus E1b 19k. Nature. 1995;374:731–733. doi: 10.1038/374731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng ZW, Marti A, Jehn B, Altermatt HJ, Chicaiza G, Jaggi R. Glucocorticoid and progesterone inhibit involution and programmed cell-death in the mouse mammary-gland. J. Cell Biol. 1995;131:1095–1103. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.4.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson L, Holmgreen SP, Huang DCS, Bernand O, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Sutherland GR, Baker E, Adams JM, Cory S. Bcl-W, a novel member of the Bcl-2 family, promotes cell-survival. Oncogene. 1996;13:665–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D, Kroemer G. The central executioners of apoptosis: caspases or mitochondria? Trends Cell Biol. 1998;8:267–271. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(98)01273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross A, Jockel J, Wei MC, Korsmeyer SJ. Enforced dimerization of Bax results in its translocation, mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. EMBO J. 1998;17:3878–3885. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.14.3878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heermeier K, Benedict M, Li ML, Furth P, Nunez G, Henninghausen L. Bax and Bcl-X(S) are induced at the onset of apoptosis in involuting mammary epithelial-cells. Mech. Dev. 1996;56:197–207. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(96)88032-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockenbery DM, Zutter M, Hickey W, Nahm M, Korsmeyer SJ. Bcl2 protein is topographically restricted in tissues characterized by apoptotic cell-death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1991;88:6961–6965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T, Deng X, Carr B, May WS. Bcl-2 phosphorylation required for anti-apoptosis function. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:11671–11673. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.18.11671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson MD. Apoptosis: Bcl-2-related proteins get connected. Curr. Biol. 1997;7:R277–R281. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(06)00136-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jager R, Herzer U, Schenkel J, Weiher H. Overexpression of Bcl-2 inhibits alveolar cell apoptosis during involution and accelerates cmyc-induced tumorigenesis of the mammary gland in transgenic mice. Oncogene. 1997;15:1787–1795. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kittrell FS, Oborn CJ, Medina D. Development of Mammary preneoplasias in vivo from mouse mammary epithelial cell lines in vitro. Cancer Res. 1992;52:1924–1932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluck RM, Bossy Wetzel E, Green DR, Newmeyer DD. The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: a primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science. 1997;275:1132–1136. doi: 10.1126/science.275.5303.1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson CM, Korsmeyer SJ. Bcl-2 and Bax function independently to regulate cell death. Nat. Genet. 1997;16:358–363. doi: 10.1038/ng0897-358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson CM, Tung KSK, Tourtellotte WG, Brown GAJ, Korsmeyer SJ. Bax-deficient mice with lymphoid hyperplasia and male germ-cell death. Science. 1995;270:96–99. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5233.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krajewski S, Blomqvist C, Franssila K, Krajewska M, Wasenius VM, Niskanen E, Nordling S, Reed JC. Reduced expression of proapoptotic gene Bax is associated with poor response rates to combination chemotherapy and shorter survival in women with metastatic breast adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1995;55:4471–4478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krajewski S, Krajewska M, Shabaik A, Miyashita T, Wang HG, Reed JC. Immunohistochemical determination of in-vivo distribution of Bax, a dominant inhibitor of Bcl-2. Am. J. Path. 1994;145:1323–1336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung LK, Do L, Wang TT. Regulation of death promoter Bak expression by cell density and 17 beta-estradiol in MCF-7 cells. Cancer Lett. 1998;124:47–52. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(97)00430-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling Y-H, Tornos C, Perez-Soler R. Phosphorylation of Bcl-2 is a marker for M phase events and not a determinant of apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:18984–18991. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.30.18984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund LR, Romer J, Thomasset N, Solberg H, Pyke C, Bissell MJ, Dano K, Werb Z. 2 distinct phases of apoptosis in mammary-gland involution – proteinase-independent and proteinase-dependent pathways. Development. 1996;122:181–193. doi: 10.1242/dev.122.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe A, Streuli C. Epithelial apoptosis. BioEssays. 1997;19:711–720. doi: 10.1002/bies.950190812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motoyama N, Wang F, Roth KA, Sawa H, Nakayama K, Negishi I, Senju S, Zhang Q, Fujii S, Loh DY. Massive cell death of immature hematopoietic cells and neurons in Bcl-x-deficient mice. Science. 1995;267:1506–1510. doi: 10.1126/science.7878471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ. Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in-vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell-death. Cell. 1993;74:609–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90509-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Print CG, Loveland KL, Gibson L, Meehan T, Stylianou A, Wreford N, de Kretser D, Metcalfe D, Köntgen F, Adams JM, Cory S. Apoptosis regulator Bcl-w is essential for spermatogenesis but appears otherwise redundant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1998;95:12424–12431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.21.12424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullan S, Streuli CH. The mammary gland epithelial cell. In: Harris A, editor. Epithelial Cell Culture. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 1996. pp. 97–121. [Google Scholar]
- Pullan S, Wilson J, Metcalfe A, Edwards GM, Goberdhan N, Tilly J, Hickman JA, Dive C, Streuli CH. Requirement of basement membrane for the suppression of programmed cell death in mammary epithelium. J. Cell Sci. 1996;109:631–642. doi: 10.1242/jcs.109.3.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross AJ, Waymire KG, Moss JE, Parlow AF, Skinner MK, Russell LD, MacGregor GR. Testicular degeneration in Bclw-deficient mice. Nat. Genet. 1998;18:251–256. doi: 10.1038/ng0398-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Cold Spring Harbor, MA: 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Simonian PL, Grillot DA, Nunez G. Bak can accelerate chemotherapy-induced cell death independently of its heterodimerization with Bcl-XL and Bcl-2. Oncogene. 1997;15:1871–1875. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair EG, Anderson SJ, Oltvai ZN. Bcl-2 counters apoptosis by Bax heterodimerization-dependent and -independent mechanisms in the T-cell lineage. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:29347–29355. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.46.29347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strange R, Li F, Saurer S, Burkhardt A, Friis RR. Apoptotic cell-death and tissue remodeling during mouse mammary-gland involution. Development. 1992;115:49–58. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli CH, Bissell MJ. Expression of extracellular matrix components is regulated by substratum. J. Cell Biol. 1990;110:1405–1415. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli CH, Dive C, Hickman JA, Farrelly N, Metcalfe A. Control of apoptosis in breast epithelium. Endocrine-Related Cancer. 1997;4:45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira C, Reed JC, Pratt MA. Estrogen promotes chemotherapeutic drug resistance by a mechanism involving Bcl-2 protooncogene expression in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1995;55:3902–3907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonner E, Barber MC, Travers MT, Logan A, Flint DJ. Hormonal control of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 production in the involuting mammary gland of the rat. Endocrinology. 1997;138:5101–5107. doi: 10.1210/endo.138.12.5619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander Heiden MG, Chandel NS, Williamson EK, Schumacker PT, Thompson CB. Bcl-xL regulates the membrane potential and volume homeostasis of mitochondria. Cell. 1997;91:627–637. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80450-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veis DJ, Sorenson CM, Shutter JR, Korsmeyer SJ. Bcl-2-deficient mice demonstrate fulminant lymphoid apoptosis, polycystic kidneys, and hypopigmented hair. Cell. 1993;75:229–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80065-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang TT, Phang JM. Effects of estrogen on apoptotic pathways in human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Cancer Res. 1995;55:2487–2489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolter KG, Hsu YT, Smith CL, Nechushtan A, Xi XG, Youle RJ. Movement of Bax from the cytosol to mitochondria during apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 1997;139:1281–1292. doi: 10.1083/jcb.139.5.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin XM, Oltvai ZN, Korsmeyer SJ. BH1 and BH2 domains of Bcl-2 are required for inhibition of apoptosis and heterodimerization with Bax. Nature. 1994;369:321–323. doi: 10.1038/369321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapata JM, Krajewska M, Krajewski S, Huang RP, Takayama S, Wang HG, Adamson E, Reed JC. Expression of multiple apoptosis-regulatory genes in human breast cancer cell lines and primary tumors. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1998;47:129–140. doi: 10.1023/a:1005940832123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zou H, Henzel WJ, Liu X, Lutschg A, Wang X. Apaf-1, a human protein homologous to C. elegans CED-4, participates in cytochrome c-dependent activation of caspase-3. Cell. 1997;90:405–413. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80501-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]