Abstract
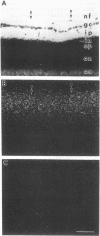
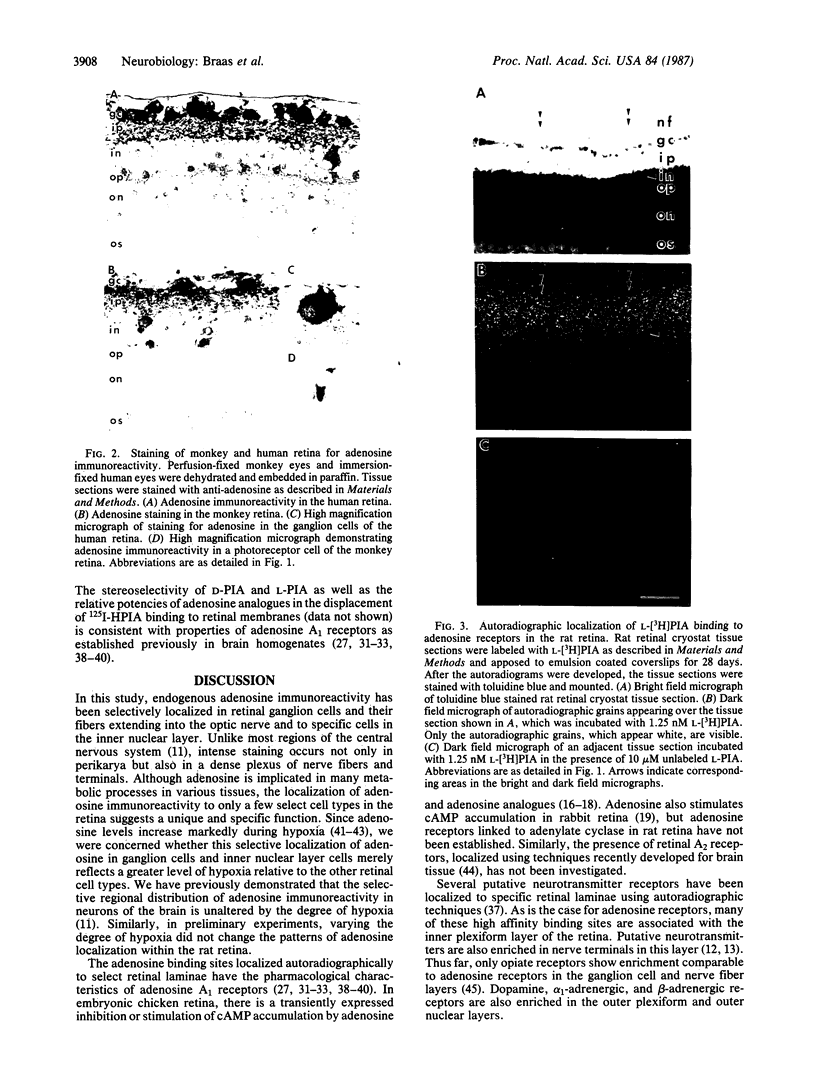
Using specific sensitive antisera against adenosine, we have immunocytochemically localized endogenous adenosine to specific layers of rat, guinea pig, monkey, and human retina. Highest adenosine immunoreactivity was observed in ganglion cells and their processes in the optic nerve fiber layer. Substantial staining was also found throughout the inner plexiform layer and in select cells in the inner nuclear layer. Adenosine A1 receptors, labeled with the agonists L-[3H]phenylisopropyladenosine and 125I-labeled hydroxy-phenylisopropyladenosine, were autoradiographically localized. The highest levels of binding sites occurred in the nerve fiber, ganglion cell, and inner plexiform layers of the retina in all the species examined. The distribution of adenosine A1 receptor sites closely parallels that of retinal neurons and fibers containing immunoreactive adenosine. These results suggest a role for endogenous adenosine as a coneurotransmitter in ganglion cells and their fibers in the optic nerve.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atweh S. F., Murrin L. C., Kuhar M. J. Presynaptic localization of opiate receptors in the vagal and accessory optic systems: an autoradiographic study. Neuropharmacology. 1978 Jan;17(1):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(78)90175-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes E. M., Jr, Thampy K. G. Subclasses of adenosine receptors in brain membranes from adult tissue and from primary cultures of chick embryo. J Neurochem. 1982 Sep;39(3):647–652. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb07941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisserbe J. C., Patel J., Marangos P. J. Autoradiographic localization of adenosine uptake sites in rat brain using [3H]nitrobenzylthioinosine. J Neurosci. 1985 Feb;5(2):544–550. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-02-00544.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blazynski C., Kinscherf D. A., Geary K. M., Ferrendelli J. A. Adenosine-mediated regulation of cyclic AMP levels in isolated incubated retinas. Brain Res. 1986 Feb 26;366(1-2):224–229. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91299-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boycott B. B., Wässle H. The morphological types of ganglion cells of the domestic cat's retina. J Physiol. 1974 Jul;240(2):397–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braas K. M., Newby A. C., Wilson V. S., Snyder S. H. Adenosine-containing neurons in the brain localized by immunocytochemistry. J Neurosci. 1986 Jul;6(7):1952–1961. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-07-01952.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Daly J. W., Snyder S. H. Adenosine receptors in brain membranes: binding of N6-cyclohexyl[3H]adenosine and 1,3-diethyl-8-[3H]phenylxanthine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5547–5551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canzek V., Wolfensberger M., Amsler U., Cuénod M. In vivo release of glutamate and aspartate following optic nerve stimulation. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):572–574. doi: 10.1038/293572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs G., Unabia G. Application of the avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) method to the light microscopic localization of pituitary hormones. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Jul;30(7):713–716. doi: 10.1177/30.7.6286753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. M., Londos C., Rodbell M. Adenosine receptor-mediated inhibition of rat cerebral cortical adenylate cyclase by a GTP-dependent process. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;18(3):598–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. W. Adenosine receptors. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1985;19:29–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fastbom J., Fredholm B. B. Inhibition of [3H] glutamate release from rat hippocampal slices by L-phenylisopropyladenosine. Acta Physiol Scand. 1985 Sep;125(1):121–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1985.tb07698.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Hedqvist P. Modulation of neurotransmission by purine nucleotides and nucleosides. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Jun 15;29(12):1635–1643. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger J. D. Localization of [3H]cyclohexyladenosine and [3H]nitrobenzylthioinosine binding sites in rat striatum and superior colliculus. Brain Res. 1986 Jan 22;363(2):404–407. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger J. D., Nagy J. I. Heterogeneous distribution of adenosine transport sites labelled by [3H]nitrobenzylthioinosine in rat brain: an autoradiographic and membrane binding study. Brain Res Bull. 1984 Nov;13(5):657–666. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(84)90198-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. R., Kuhar M. J., Hester L., Snyder S. H. Adenosine receptors: autoradiographic evidence for their location on axon terminals of excitatory neurons. Science. 1983 May 27;220(4600):967–969. doi: 10.1126/science.6302841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. R., Synder S. H. Autoradiographic localization of adenosine receptors in rat brain using [3H]cyclohexyladenosine. J Neurosci. 1982 Sep;2(9):1230–1241. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-09-01230.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harms H. H., Wardeh G., Mulder A. H. Effect of adenosine on depolarization-induced release of various radiolabelled neurotransmitters from slices of rat corpus striatum. Neuropharmacology. 1979 Jul;18(7):577–580. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(79)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller I. H., McIlwain H. Release of ( 14 C)adenine derivatives from isolated subsystems of the guinea pig brain: actions of electrical stimulation and of papaverine. Brain Res. 1973 Apr 13;53(1):105–116. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90770-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann K. P. Conduction velocity in pathways from retina to superior colliculus in the cat: a correlation with receptive-field properties. J Neurophysiol. 1973 May;36(3):409–424. doi: 10.1152/jn.1973.36.3.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleihues P., Kobayashi K., Hossmann K. A. Purine nucleotide metabolism in the cat brain after one hour of complete ischemia. J Neurochem. 1974 Aug;23(2):417–425. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb04374.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocsis J. D., Eng D. L., Bhisitkul R. B. Adenosine selectively blocks parallel-fiber-mediated synaptic potentials in rat cerebellar cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6531–6534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostopoulos G. K., Limacher J. J., Phillis J. W. Action of various adenine derivatives on cerebellar Purkinje cells. Brain Res. 1975 Apr 25;88(1):162–165. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90966-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostopoulos G. K., Phillis J. W. Purinergic depression of neurons in different areas of the rat brain. Exp Neurol. 1977 Jun;55(3 Pt 1):719–724. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(77)90296-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Reddington M. Autoradiographic evidence for multiple CNS binding sites for adenosine derivatives. Neuroscience. 1986 Oct;19(2):535–549. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90279-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. E., Patel J., Edley S. M., Marangos P. J. Autoradiographic visualization of rat brain adenosine receptors using N6-cyclohexyl [3H]adenosine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 17;73(1):109–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden J. Purification and characterization of (-)[125I]hydroxyphenylisopropyladenosine, an adenosine R-site agonist radioligand and theoretical analysis of mixed stereoisomer radioligand binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;26(3):414–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munshi R., Hansske F., Baer H. P. [125I]N6-(3-iodo-4-hydroxyphenyl)isopropyladenosine: the use of the diastereomers as ligands for adenosine receptors in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Apr 23;111(1):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90118-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy K. M., Snyder S. H. Heterogeneity of adenosine A1 receptor binding in brain tissue. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;22(2):250–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy J. I., Geiger J. D., Daddona P. E. Adenosine uptake sites in rat brain: identification using [3H]nitrobenzylthioinosine and co-localization with adenosine deaminase. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Mar 22;55(1):47–53. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy J. I., LaBella L. A., Buss M., Daddona P. E. Immunohistochemistry of adenosine deaminase: implications for adenosine neurotransmission. Science. 1984 Apr 13;224(4645):166–168. doi: 10.1126/science.6142530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newby A. C., Sala G. B. A new procedure for haptenizing adenosine leading to a more specific radioimmunoassay method. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 15;208(3):603–610. doi: 10.1042/bj2080603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Saito M. Inhibitory action adenosine, 5-HT (serotonin) and GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) on the postsynaptic potential (PSP) or slices from olfactory cortex and superior colliculus in correlation to the level of cyclic AMP. Brain Res. 1979 Jan 12;160(2):368–371. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90434-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paes de Carvalho R., de Mello F. G. Adenosine-elicited accumulation of adenosine 3', 5'-cyclic monophosphate in the chick embryo retina. J Neurochem. 1982 Feb;38(2):493–500. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb08655.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paes de Carvalho R., de Mello F. G. Expression of A1 adenosine receptors modulating dopamine-dependent cyclic AMP accumulation in the chick embryo retina. J Neurochem. 1985 Mar;44(3):845–851. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb12892.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez M. T., Ehinger B. E., Lindström K., Fredholm B. B. Release of endogenous and radioactive purines from the rabbit retina. Brain Res. 1986 Nov 19;398(1):106–112. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91255-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., Edstrom J. P., Kostopoulos G. K., Kirkpatrick J. R. Effects of adenosine and adenine nucleotides on synaptic transmission in the cerebral cortex. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;57(11):1289–1312. doi: 10.1139/y79-194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., Wu P. H. The role of adenosine and its nucleotides in central synaptic transmission. Prog Neurobiol. 1981;16(3-4):187–239. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(81)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer J. M., Anderson S. M. Nucleoside uptake by rat retina cells. Life Sci. 1981 Aug 31;29(9):939–946. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90396-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe U., Lenschow V., Ukena D., Ferry D. R., Glossmann H. [125I] N6-p-Hydroxyphenylisopropyladenosine, a new ligand for Ri adenosine receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Oct;321(1):84–87. doi: 10.1007/BF00586356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe U., Trost T. Characterization of adenosine receptors in rat brain by (-)[3H]N6-phenylisopropyladenosine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Sep;313(3):179–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00505731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J., Hoffmann K. P. Very slow-conducting ganglion cells in the cat's retina: a major, new functional type? Brain Res. 1972 Aug 25;43(2):610–616. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90416-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ukena D., Furler R., Lohse M. J., Engel G., Schwabe U. Labelling of Ri adenosine receptors in rat fat cell membranes with (-)-[125iodo]N6-hydroxyphenylisopropyladenosine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Jun;326(3):233–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00505324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unnerstall J. R., Niehoff D. L., Kuhar M. J., Palacios J. M. Quantitative receptor autoradiography using [3H]ultrofilm: application to multiple benzodiazepine receptors. J Neurosci Methods. 1982 Jul;6(1-2):59–73. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(82)90016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wamsley J. K., Palacios J. M., Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of opioid receptors in the mammalian retina. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Nov 18;27(1):19–24. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90199-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojcik W. J., Neff N. H. Adenosine measurement by a rapid HPLC-fluorometric method: induced changes of adenosine content in regions of rat brain. J Neurochem. 1982 Jul;39(1):280–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb04736.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Kuhar M. J. A new method for receptor autoradiography: [3H]opioid receptors in rat brain. Brain Res. 1979 Dec 28;179(2):255–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90442-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarbin M. A., Wamsley J. K., Palacios J. M., Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of high affinity GABA, benzodiazepine, dopaminergic, adrenergic and muscarinic cholinergic receptors in the rat, monkey and human retina. Brain Res. 1986 May 21;374(1):75–92. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90396-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Mello M. C., Ventura A. L., Paes de Carvalho R., Klein W. L., de Mello F. G. Regulation of dopamine- and adenosine-dependent adenylate cyclase systems of chicken embryo retina cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5708–5712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Calker D., Müller M., Hamprecht B. Adenosine regulates via two different types of receptors, the accumulation of cyclic AMP in cultured brain cells. J Neurochem. 1979 Nov;33(5):999–1005. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]