Abstract
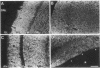
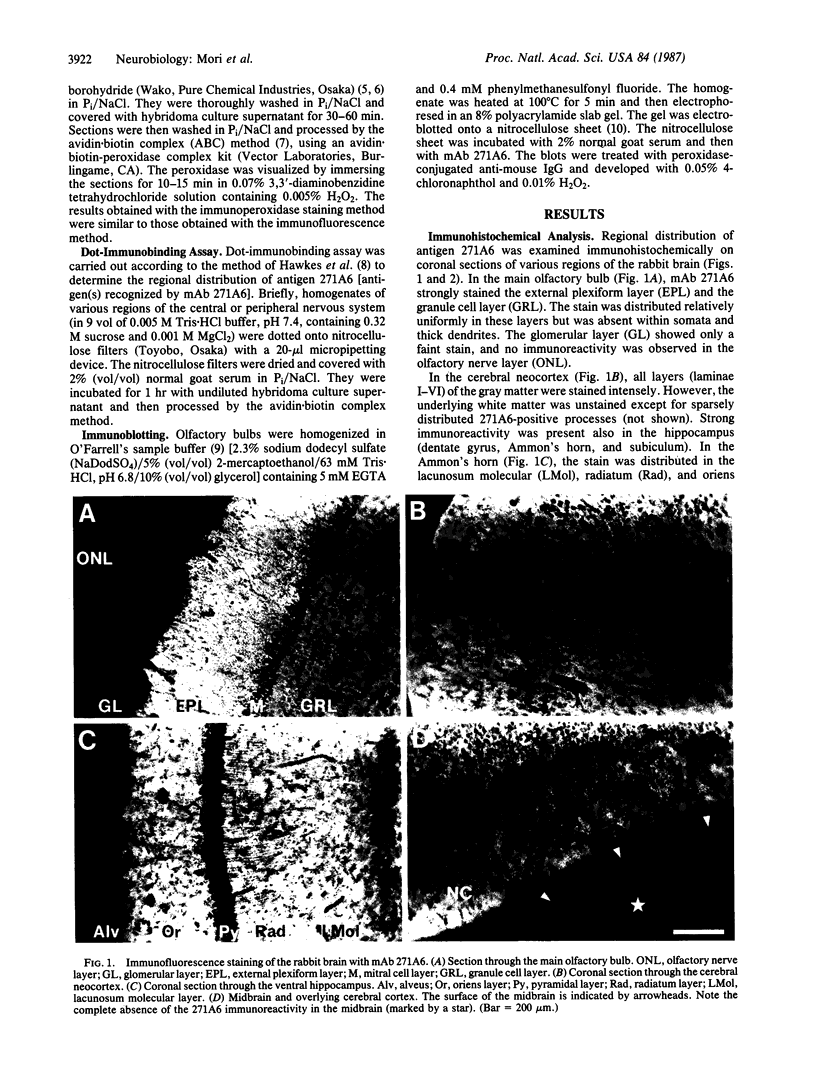
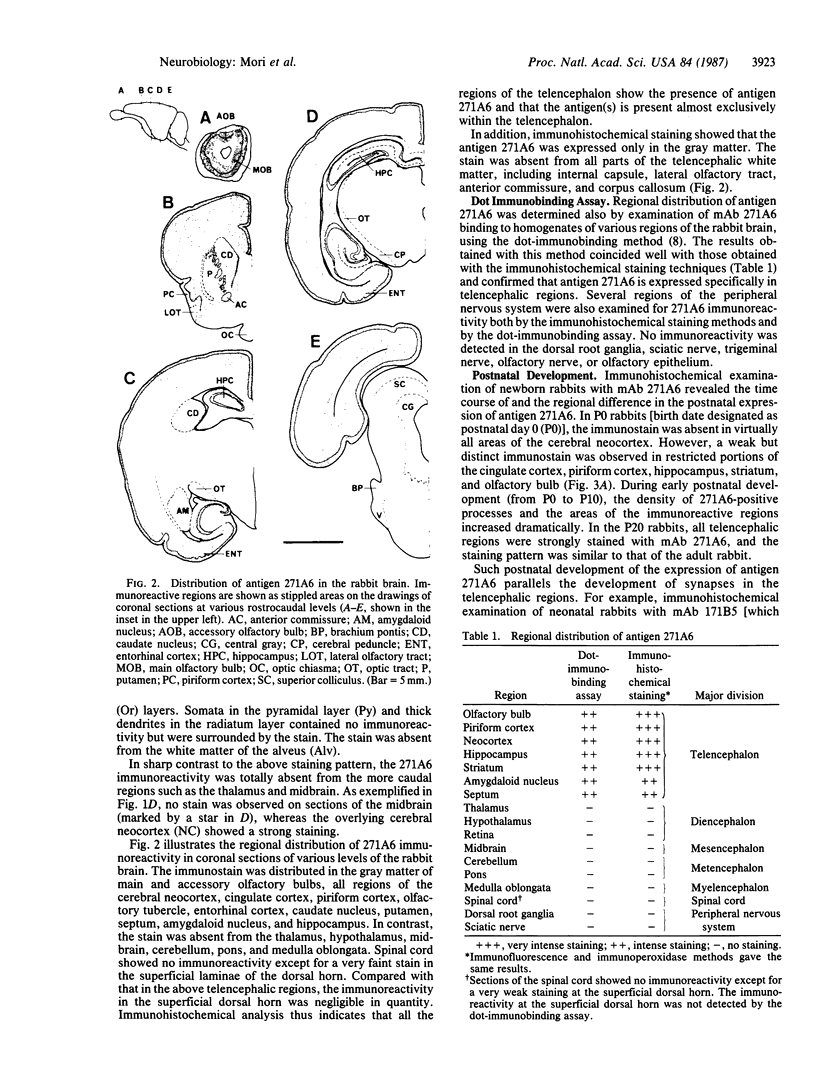
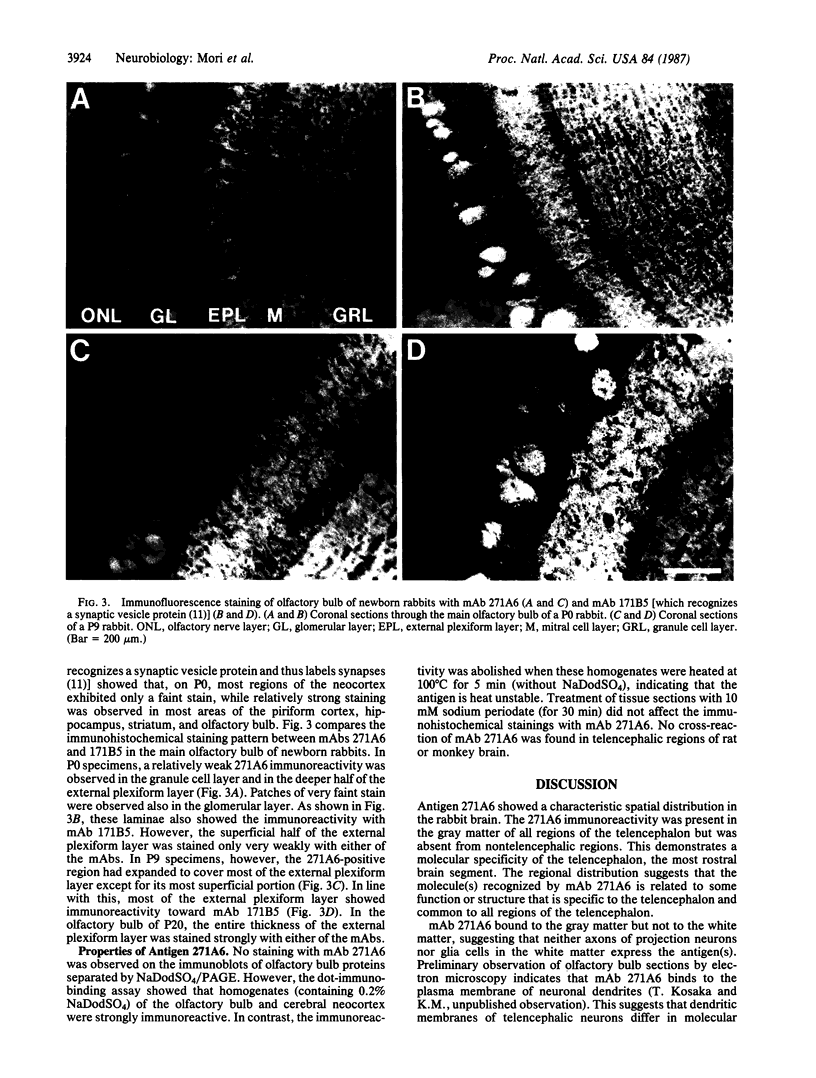
Immunohistochemical screening of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) raised against fractions rich in the dendrodendritic synaptosomes of the rabbit olfactory bulb revealed that one of the mAbs (mAb 271A6) recognized a telencephalon-specific antigen or antigens. Thus, the stain with mAb 271A6 was observed throughout the gray matter of all regions of the neocortex, piriform cortex, hippocampus, striatum, septum, and the amygdaloid nucleus, in addition to the main and accessory olfactory bulbs. The mAb 271A6, however, labeled neither nontelencephalic regions of the central nervous system nor the peripheral nervous system so far examined. Dot-immunobinding assays of homogenates of various brain regions also showed the telencephalon-specific distribution of the antigen designated as 271A6. Antigen 271A6 is developmentally regulated. At birth, the antigen was expressed in a small quantity only in phylogenetically older telencephalic regions such as the olfactory bulb, piriform cortex, striatum, cingulate cortex, and hippocampus. It was hardly detectable in most areas of the neocortex. The densities and areas of 271A6-positive structures increased during the early postnatal period. These results demonstrate a molecular specificity of the most rostral brain segment, the telencephalon. mAb 271A6 may be a good tool for obtaining a better understanding of the molecular basis of the segmental organization or the segment-specific functions of the brain.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Awgulewitsch A., Utset M. F., Hart C. P., McGinnis W., Ruddle F. H. Spatial restriction in expression of a mouse homoeo box locus within the central nervous system. 1986 Mar 27-Apr 2Nature. 320(6060):328–335. doi: 10.1038/320328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco A. E., McGinnis W., Gehring W. J., De Robertis E. M. Cloning of an X. laevis gene expressed during early embryogenesis coding for a peptide region homologous to Drosophila homeotic genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):409–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90371-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colberg-Poley A. M., Voss S. D., Chowdhury K., Gruss P. Structural analysis of murine genes containing homoeo box sequences and their expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. 1985 Apr 25-May 1Nature. 314(6013):713–718. doi: 10.1038/314713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cragg B. G. The development of synapses in the visual system of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Mar 15;160(2):147–166. doi: 10.1002/cne.901600202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaunt S. J., Miller J. R., Powell D. J., Duboule D. Homoeobox gene expression in mouse embryos varies with position by the primitive streak stage. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):662–664. doi: 10.1038/324662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J. The homeo box: a key to the understanding of development? Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90300-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds J. W., Hinds P. L. Synapse formation in the mouse olfactory bulb. I. Quantitative studies. J Comp Neurol. 1976 Sep 1;169(1):15–40. doi: 10.1002/cne.901690103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds J. W., Hinds P. L. Synapse formation in the mouse olfactory bulb. II. Morphogenesis. J Comp Neurol. 1976 Sep 1;169(1):41–61. doi: 10.1002/cne.901690104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornguth S., Juhl U., Knobeloch L., Sunderland E., Johnson T., Scott G. Isolation of dendrodendritic synapses from swine olfactory bulbs. Brain Res. 1976 Apr 9;105(3):423–435. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90591-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka T., Nagatsu I., Wu J. Y., Hama K. Use of high concentrations of glutaraldehyde for immunocytochemistry of transmitter-synthesizing enzymes in the central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1986 Aug;18(4):975–990. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90112-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Rubin G. M., Tjian R. Human DNA sequences homologous to a protein coding region conserved between homeotic genes of Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):667–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90261-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavilio F., Simeone A., Giampaolo A., Faiella A., Zappavigna V., Acampora D., Poiana G., Russo G., Peschle C., Boncinelli E. Differential and stage-related expression in embryonic tissues of a new human homoeobox gene. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):664–668. doi: 10.1038/324664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Hart C. P., Gehring W. J., Ruddle F. H. Molecular cloning and chromosome mapping of a mouse DNA sequence homologous to homeotic genes of Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90262-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obata K., Nishiye H., Fujita S. C., Shirao T., Inoue H., Uchizono K. Identification of a synaptic vesicle-specific 38,000-dalton protein by monoclonal antibodies. Brain Res. 1986 Jun 4;375(1):37–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90956-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Rathke P. C., Osborn M. Cytoplasmic microtubular images in glutaraldehyde-fixed tissue culture cells by electron microscopy and by immunofluorescence microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1820–1824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]