Abstract
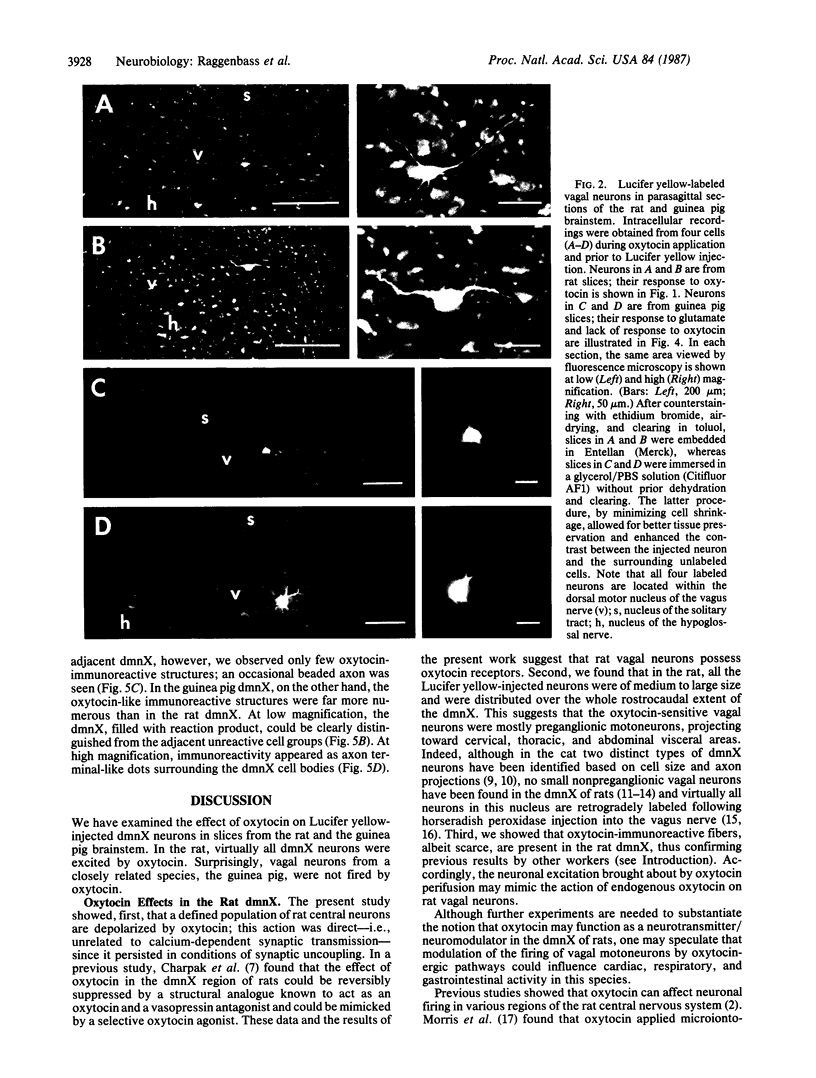
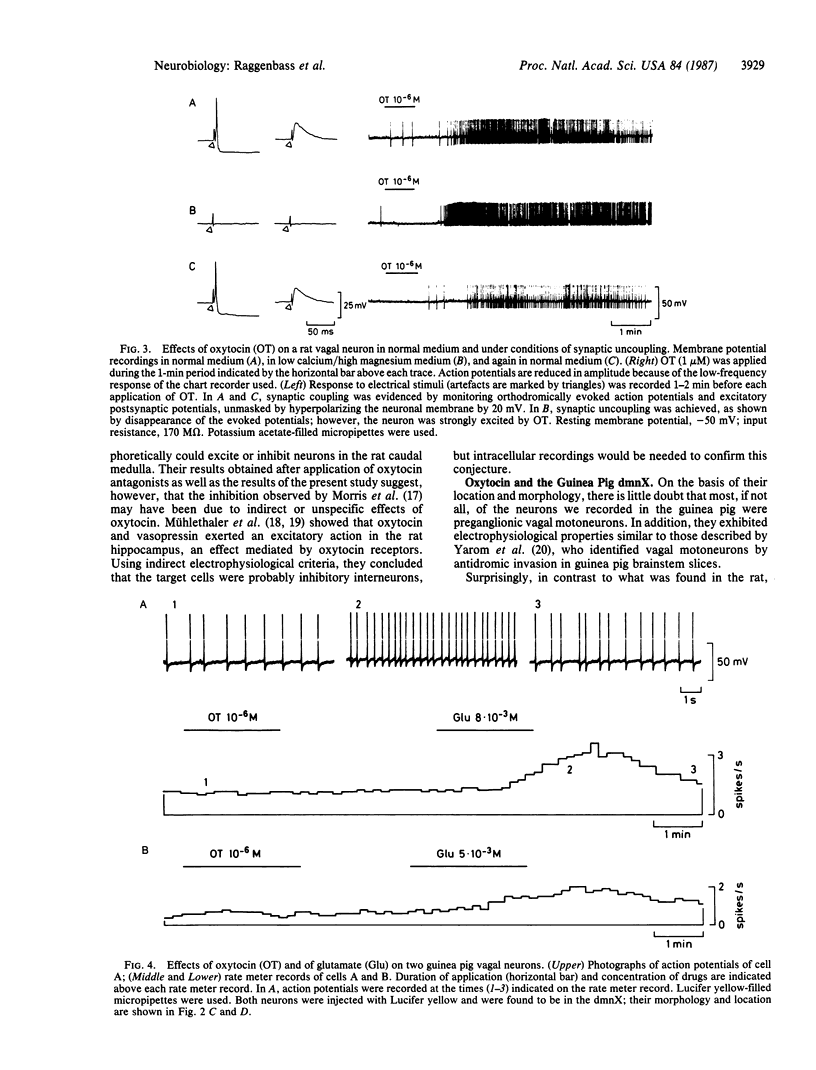
Intracellular recordings were obtained from vagal neurons and their response to oxytocin was investigated in slices from the rat and the guinea pig brainstem. After recording, Lucifer yellow was injected into the cells to verify their localization within the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve (dmnX). In the rat, virtually all neurons throughout the rostrocaudal extent of the dmnX increased their rate of firing in the presence of 10-1000 nM oxytocin and their membrane depolarized in a reversible concentration-dependent manner. This excitation was probably exerted directly on the impaled cells rather than being synaptically mediated, since it persisted in a low calcium/high magnesium medium or in the presence of tetrodotoxin. These data provide evidence for a direct membrane effect of oxytocin on a defined population of neurons in the rat brain. In the guinea pig, vagal neurons were fired by glutamate but were not excited by oxytocin, even though we detected many more oxytocin-immunoreactive structures in the guinea pig dmnX than in the rat dmnX. Therefore, homologous nuclei in the brains of two closely related mammals differ markedly in the density of oxytocinergic axons they contain. Unexpectedly, the magnitude of the electrophysiological effects of oxytocin on vagal neurons appeared inversely related to the amount of oxytocin-like immunoreactivity present in dmnX.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buijs R. M., Van Heerikhuize J. J. Vasopressin and oxytocin release in the brain--a synaptic event. Brain Res. 1982 Dec 2;252(1):71–76. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90979-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charpak S., Armstrong W. E., Mühlethaler M., Dreifuss J. J. Stimulatory action of oxytocin on neurones of the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve. Brain Res. 1984 May 21;300(1):83–89. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91342-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalia M., Fuxe K., Goldstein M. Rat medulla oblongata. II. Dopaminergic, noradrenergic (A1 and A2) and adrenergic neurons, nerve fibers, and presumptive terminal processes. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Mar 15;233(3):308–332. doi: 10.1002/cne.902330303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalia M., Fuxe K., Goldstein M. Rat medulla oblongata. III. Adrenergic (C1 and C2) neurons, nerve fibers and presumptive terminal processes. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Mar 15;233(3):333–349. doi: 10.1002/cne.902330304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalia M., Fuxe K., Hökfelt T., Harfstrand A., Lang R. E., Ganten D. Distribution of neurophysin II immunoreactive nerve fibers within the subnuclei of the nucleus of the tractus solitarius of the rat. Brain Res. 1984 Oct 29;321(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90682-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalia M., Fuxe K., Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Lang R., Ganten D., Cuello C., Terenius L. Distribution of neuropeptide immunoreactive nerve terminals within the subnuclei of the nucleus of the tractus solitarius of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Jan 20;222(3):409–444. doi: 10.1002/cne.902220308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalia M., Fuxe K. Rat medulla oblongata. I. Cytoarchitectonic considerations. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Mar 15;233(3):285–307. doi: 10.1002/cne.902330302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalia M., Sullivan J. M. Brainstem projections of sensory and motor components of the vagus nerve in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Nov 1;211(3):248–265. doi: 10.1002/cne.902110304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiraly M., Audigier S., Tribollet E., Barberis C., Dolivo M., Dreifuss J. J. Biochemical and electrophysiological evidence of functional vasopressin receptors in the rat superior cervical ganglion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5335–5339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie R. A., Gwyn D. G., Hopkins D. A. The central distribution of the cervical vagus nerve and gastric afferent and efferent projections in the rat. Brain Res Bull. 1982 Jan;8(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(82)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liposits Z., Sétáló G., Flerkó B. Application of the silver-gold intensified 3,3'-diaminobenzidine chromogen to the light and electron microscopic detection of the luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone system of the rat brain. Neuroscience. 1984 Oct;13(2):513–525. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90245-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantyh P. W., Hunt S. P. Changes in 3H-substance P receptor binding in the rat brain after kainic acid lesion of the corpus striatum. J Neurosci. 1986 Jun;6(6):1537–1544. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-06-01537.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J. H., Hopkins D. A. A light and electron microscopic study of the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Jan 1;195(1):157–175. doi: 10.1002/cne.901950109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J. H., Hopkins D. A. Ultrastructural identification of labeled neurons in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve following injections of horseradish peroxidase into the vagus nerve and brainstem. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Apr 10;206(3):243–252. doi: 10.1002/cne.902060304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean S., Rothman R. B., Herkenham M. Autoradiographic localization of mu- and delta-opiate receptors in the forebrain of the rat. Brain Res. 1986 Jul 16;378(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90285-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris R., Farmery S. M., Roberts C. J., Hill R. G. The effects of oxytocin and vasotocin analogues on the responses of rat brainstem neurones to oxytocin. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Jul 27;48(2):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlethaler M., Charpak S., Dreifuss J. J. Contrasting effects of neurohypophysial peptides on pyramidal and non-pyramidal neurones in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 1984 Aug 6;308(1):97–107. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90921-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlethaler M., Sawyer W. H., Manning M. M., Dreifuss J. J. Characterization of a uterine-type oxytocin receptor in the rat hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6713–6717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawchenko P. E., Swanson L. W. Immunohistochemical identification of neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus that project to the medulla or to the spinal cord in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Mar 1;205(3):260–272. doi: 10.1002/cne.902050306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarom Y., Sugimori M., Llinás R. Ionic currents and firing patterns of mammalian vagal motoneurons in vitro. Neuroscience. 1985 Dec;16(4):719–737. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90090-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]