Abstract
Although postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a common chronic pain syndrome, the pathophysiology of this disorder is not well known and management is often very difficult. N-Methyl-D-Aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists are known to be effective in PHN, and magnesium, a physiological blocker of NMDA receptors, is widely used to treat various chronic pain disorders. Here, we present a case of the PHN refractory to conventional treatment, which was treated successfully with transforaminal epidural injection of magnesium sulphate at the affected dermatome.
Keywords: epidural injections, magnesium sulphate, N-Methyl-D-Aspartate receptor, postherpetic neuralgia
Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a chronic neuropathic pain syndrome that occurs after reactivation of varicella zoster virus infection with damage to sensory ganglia in nerve roots [1]. Numerous treatment strategies for PHN, including topical lidocaine patches, antidepressants, anticonvulsants, corticosteroids, opioids and nerve blocks, have shown some degree of efficacy [2], but the effects are often limited and many patients are refractory to these treatments. Previous report has suggested that N-Methyl-D-Aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists, such as ketamine can decrease pain associated with PHN. However, adverse effects such as psychomimetic effects limit its therapeutic use, even at low doses [3].
Magnesium, which is also a NMDA receptor antagonist, has been used in the treatment of neuropathic pain usually via the intravenous route and is free of psychomimetic side effects. However, the anti-nociceptive effect of intravenous magnesium remains controversial [4], and increases in serum magnesium concentration during and after administration may cause serious, sometimes fatal complications such as respiratory paralysis, hypothermia and coma. The epidural route of administration, especially the transforaminal epidural route, has advantages in target-specific delivery of drugs and reduction in the dose of medications used. Therefore, epidural administration is superior to systemic injection if the efficacy can be guaranteed.
Here, we present a patient with PHN refractory to conventional therapy treated successfully by transforaminal epidural magnesium injection (TFEMI).
CASE REPORT
A 60-year-old woman (height, 162 cm; weight, 61 kg) visited pain clinic with tactile allodynia and electric shock-like pain in the left dorsal scapular area around the T3 dermatome, which had been diagnosed as PHN about 1 month previously and attack of the herpes zoster was 1 year ago. The 100-mm visual analogue scale (VAS) of allodynia and electric shock-like pain was rated between 70 and 80 mm on a scale from 0 (no pain) to 100 (worst pain imaginable). The interlaminar epidural block was performed at the T3-4 space by the paramedian approach with 5 ml of 0.2% ropivacaine and 20 mg of triamcinolone acetate. Pregabalin and morphine at doses of 150 mg and 10 mg, respectively, twice a day, amitriptyline at a dose of 10 mg before sleep and topical lidocaine patches were prescribed. Dosages of all drugs were adjusted depending on the side effects during the follow-up period. Epidural blocks were repeated twice with a 1-week interval and the continuous intravenous infusion of ketamine (60 mg) was performed over a period of 1 hour twice a week under careful monitoring. The dose of ketamine was increased gradually up to 120 mg. After 1 month elapsed, electric shock-like pain was reduced to a VAS score of 30/100, but allodynia was not diminished (VAS score of 70/100).
After 4 months elapsed, we decided to administer magnesium sulfate via the intravenous route. And it was done with continuous intravenous infusion of 1,000 mg of magnesium sulfate in 50 ml of normal saline for 1 hour. Before and after infusion, the serum magnesium levels were checked. After magnesium therapy, she felt very good about her pain and the VAS of allodynia was reduced to 40-50. At 1-week follow-up, she was very satisfied with the treatment and reported the reduction of allodynia on the dorsal scapular area of up to 50% (VAS 25-30/100). However, the serum magnesium level had increased above normal range (2.3 mEq/L to 2.9 mEq/L) after infusion. Although it was below the serum level reveals of the adverse effect, we decided to stop intravenous infusion of magnesium sulfate. For more accurate and safe delivery of magnesium to the target site, we applied magnesium using the transforaminal epidural injection technique.
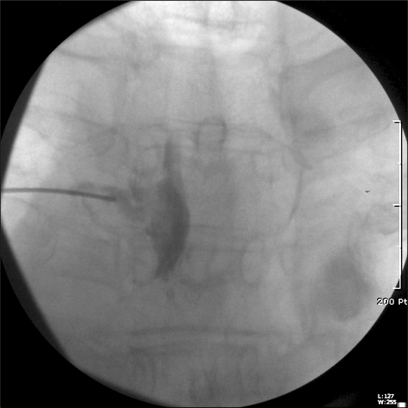
With the patient's informed consent, left T3 TFEMI was performed under fluoroscopy guidance. The patient was placed in the prone position and draped in the sterile manner. A 22-gauge, 3.5-inch spinal needle was advanced into the left. T3 nerve root foramen under fluoroscopic guidance. The final needle placement was confirmed on posterior-anterior and lateral fluoroscopic images. Identification of the T3 nerve root sheath and epidural space was performed using contrast media (Fig. 1). Then, 100 mg of magnesium sulphate and 1 ml of 0.2% ropivacaine (total volume, 2 ml) was carefully injected. TFEMI was repeated twice with a 1-week interval (total of three times) and the degree of pain decreased gradually during the follow-up period.
Fig. 1.
Posterior-anterior fluoroscopic image shows spreading of contrast media in left T3 nerve root and epidural space.
One week after the last procedure, the VAS score of allodynia decreased to 15/100 and all medications except pregabalin were discontinued. The VAS was 10/100 throughout 1-month follow-up, and pregabalin had also been tapered. The patient remained free of symptoms at 6-month follow-up.
DISCUSSION
To our knowledge, no previous report has described about the magnesium administration by the transforaminal epidural route in patients with neuropathic pain. Here, in our report of PHN patient, this treatment resulted in effective pain relief.
Previous studies have demonstrated the anti-allodynic effects of NMDA receptor antagonists in neuropathic pain disorders [3,5]. Among the currently available NMDA receptor antagonists, ketamine is the most widely used one for the treatment of neuropathic pain. However, ketamine is not always effective and psychomimetic side effects are frequent.
Magnesium can antagonize NMDA receptor channels by blocking calcium influx in a voltage-gated manner. Intravenous administration of magnesium is efficacious in the management of various conditions associated with neuropathic pain, including PHN [6,7]. Demirkaya and colleagues revealed 1 g i.v. Mg sulfate is effective in the treatment of migraine attacks [8] and Collins and colleagues reported that 70 mg/kg magnesium sulphate infusions in 4 hours for 5 days reduced pain in patients with complex regional pain syndrome [9]. Whether intravenous administration of magnesium can achieve a sufficient concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid to block NMDA receptors is unclear [4,10] and studies have reported on the limited efficacy of magnesium when administered via the intravenous route [11,12]. Furthermore, even if the dose of intravenously administered magnesium is not sufficient to present toxicity, patients are still at risk of magnesium overdose.
Neuraxial administration of magnesium is an "off-label" use, and the safety of this technique in human subjects is still undetermined. However, animal studies [13,14] showed that intrathecally administered magnesium was free of neurotoxicity, and recent studies have demonstrated the safety of magnesium administration via the epidural [15,16] or intrathecal [14,17] route in humans. Our patient showed no neurological deficit during the follow-up period.
In fact, the exact site of action of epidurally administered magnesium (i.e., spinal or supraspinal) remains unclear. However, comparison with previous reports regarding intravenous magnesium administration suggested that the low dose epidural magnesium used in our patient was unlikely to result in systemic effects.
In conclusion, TFEMI showed a favourable result in the treatment of intractable allodynia associated with PHN. This study was performed in only a single case, and further investigations are required to determine the efficacy of TFEMI in the management of allodynia in patients with PHN.
References
- 1.Loeser JD. Herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia. Pain. 1986;25:149–164. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(86)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kost RG, Straus SE. Postherpetic neuralgia--pathogenesis, treatment, and prevention. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:32–42. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199607043350107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Eide PK, Jørum E, Stubhaug A, Bremnes J, Breivik H. Relief of post-herpetic neuralgia with the N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor antagonist ketamine: a double-blind, cross-over comparison with morphine and placebo. Pain. 1994;58:347–354. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(94)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Arcioni R, Palmisani S, Tigano S, Santorsola C, Sauli V, Romanò S, et al. Combined intrathecal and epidural magnesium sulfate supplementation of spinal anesthesia to reduce post-operative analgesic requirements: a prospective, randomized, double- blind, controlled trial in patients undergoing major orthopedic surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2007;51:482–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2007.01263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Eide PK, Stubhaug A, Stenehjem AE. Central dysesthesia pain after traumatic spinal cord injury is dependent on N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activation. Neurosurgery. 1995;37:1080–1087. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199512000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Crosby V, Wilcock A, Corcoran R. The safety and efficacy of a single dose (500 mg or 1 g) of intravenous magnesium sulfate in neuropathic pain poorly responsive to strong opioid analgesics in patients with cancer. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2000;19:35–39. doi: 10.1016/s0885-3924(99)00135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Brill S, Sedgwick PM, Hamann W, Di Vadi PP. Efficacy of intravenous magnesium in neuropathic pain. Br J Anaesth. 2002;89:711–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Demirkaya S, Vural O, Dora B, Topçuoğlu MA. Efficacy of intravenous magnesium sulfate in the treatment of acute migraine attacks. Headache. 2001;41:171–177. doi: 10.1046/j.1526-4610.2001.111006171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Collins S, Zuurmond WW, de Lange JJ, van Hilten BJ, Perez RS. Intravenous magnesium for complex regional pain syndrome type 1 (CRPS 1) patients: a pilot study. Pain Med. 2009;10:930–940. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4637.2009.00639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Oppelt WW, MacIntyre I, Rall DP. Magnesium exchange between blood and cerebrospinal fluid. Am J Physiol. 1963;205:959–962. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.5.959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Felsby S, Nielsen J, Arendt-Nielsen L, Jensen TS. NMDA receptor blockade in chronic neuropathic pain: a comparison of ketamine and magnesium chloride. Pain. 1996;64:283–291. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(95)00113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ko SH, Lim HR, Kim DC, Han YJ, Choe H, Song HS. Magnesium sulfate does not reduce postoperative analgesic requirements. Anesthesiology. 2001;95:640–646. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200109000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Saeki H, Matsumoto M, Kaneko S, Tsuruta S, Cui YJ, Ohtake K, et al. Is intrathecal magnesium sulfate safe and protective against ischemic spinal cord injury in rabbits? Anesth Analg. 2004;99:1805–1812. doi: 10.1213/01.ANE.0000138039.04548.3D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chanimov M, Cohen ML, Grinspun Y, Herbert M, Reif R, Kaufman I, et al. Neurotoxicity after spinal anaesthesia induced by serial intrathecal injections of magnesium sulphate. An experimental study in a rat model. Anaesthesia. 1997;52:223–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1997.034-az0057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bilir A, Gulec S, Erkan A, Ozcelik A. Epidural magnesium reduces postoperative analgesic requirement. Br J Anaesth. 2007;98:519–523. doi: 10.1093/bja/aem029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Farouk S. Pre-incisional epidural magnesium provides pre-emptive and preventive analgesia in patients undergoing abdominal hysterectomy. Br J Anaesth. 2008;101:694–699. doi: 10.1093/bja/aen274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Buvanendran A, McCarthy RJ, Kroin JS, Leong W, Perry P, Tuman KJ. Intrathecal magnesium prolongs fentanyl analgesia: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Anesth Analg. 2002;95:661–666. doi: 10.1097/00000539-200209000-00031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]