Abstract
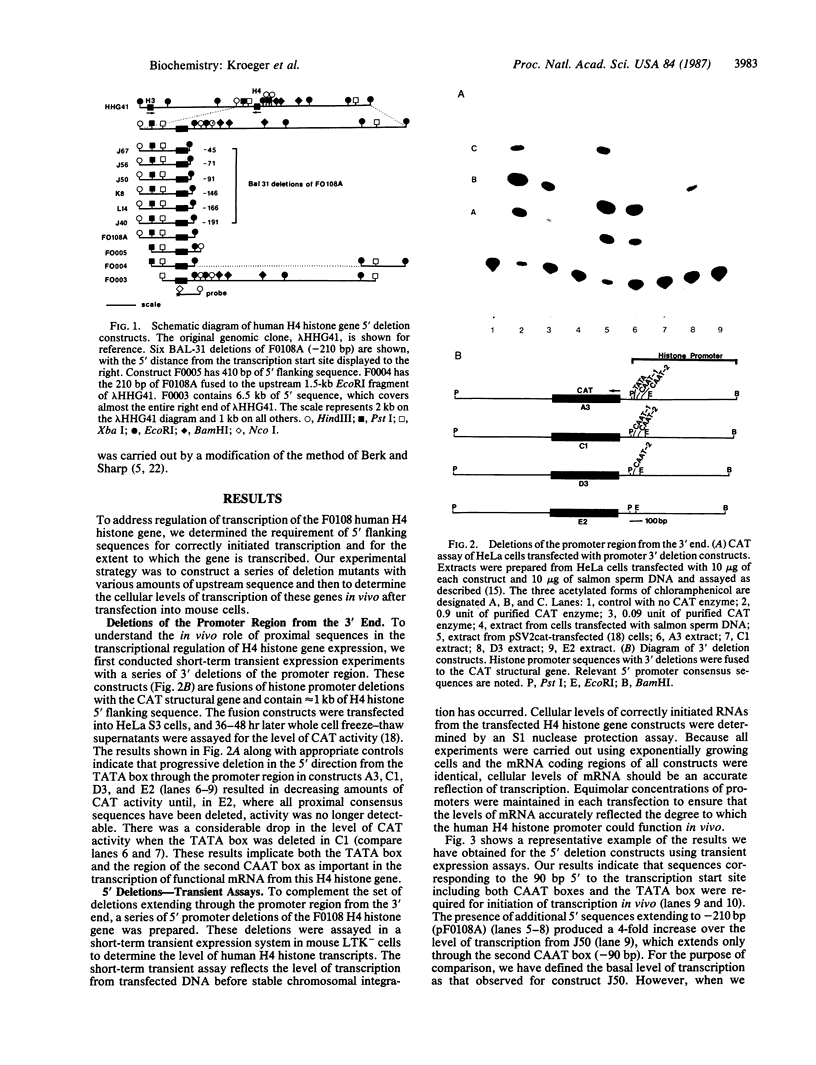
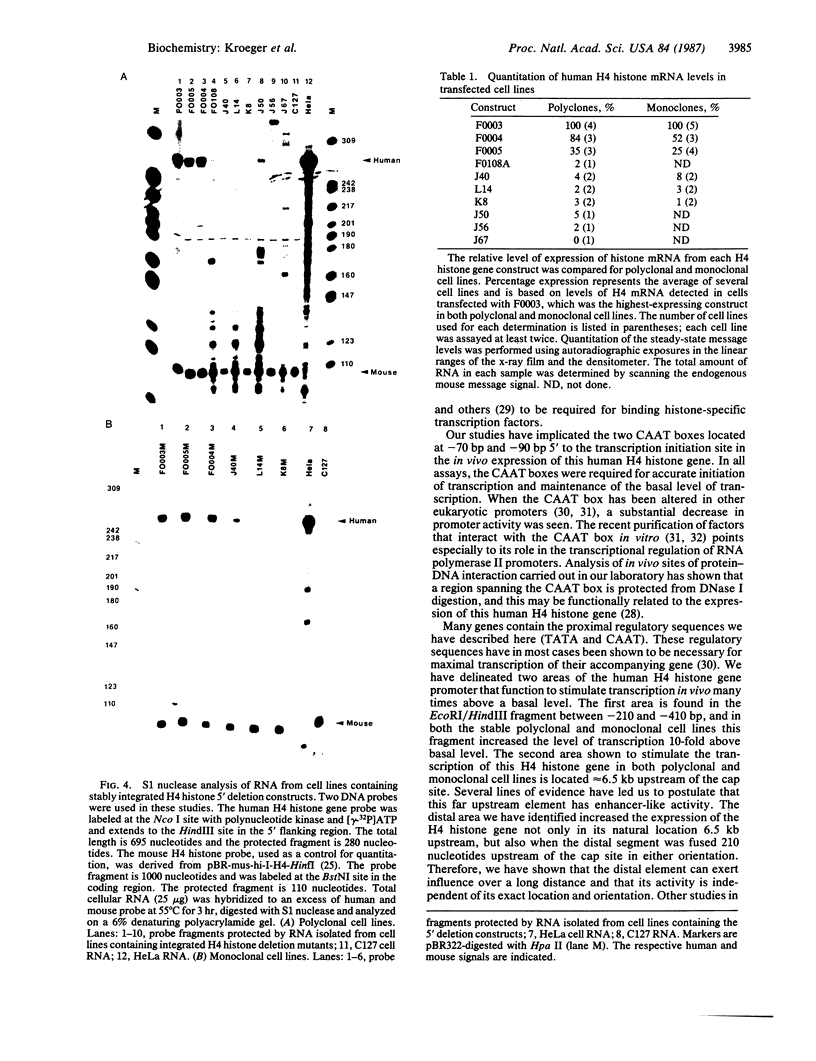
We have examined the sequences required in vivo to promote transcription of a cell cycle-regulated human H4 histone gene. Deletion mutants of the 5' flanking region were assayed in mouse cells or fused with the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) gene for assay in HeLa cells. The functional limits of the regulatory sequences were shown to extend at least 6.5 kilobases (kb) upstream. Sequences sufficient for correctly initiated transcription were found in the 70 base pairs (bp) immediately 5' to the cap site. A proximal element located 200-400 bp upstream increased the level of transcription several times above the basal level, although not to maximal levels. Maximal levels of expression were achieved with 6.5 kb of 5' flanking sequence adjacent to the proximal promoter sequences or when a distal enhancer element with both position- and orientation-independent function was moved proximal to the promoter. Our results indicate that a series of 5' cis-acting sequences are functionally related to the fidelity and level of expression of this human H4 histone gene.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumbach L. L., Marashi F., Plumb M., Stein G., Stein J. Inhibition of DNA replication coordinately reduces cellular levels of core and H1 histone mRNAs: requirement for protein synthesis. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 10;23(8):1618–1625. doi: 10.1021/bi00303a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird R. C., Jacobs F. A., Stein G., Stein J., Sells B. H. A unique subspecies of histone H4 mRNA from rat myoblasts contains poly(A). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6760–6764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capasso O., Heintz N. Regulated expression of mammalian histone H4 genes in vivo requires a trans-acting transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5622–5626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright I. L., Abmayr S. M., Fleischmann G., Lowenhaupt K., Elgin S. C., Keene M. A., Howard G. C. Chromatin structure and gene activity: the role of nonhistone chromosomal proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982;13(1):1–86. doi: 10.3109/10409238209108709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Hanly S. M., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. Distinct transcription factors bind specifically to two regions of the human histone H4 promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7241–7245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Homologous recognition of a promoter domain common to the MSV LTR and the HSV tk gene. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L., Schlaffer I., Wright K., Moreno M. L., Berand D., Hager G., Stein J., Stein G. Cell cycle-dependent expression of a stable episomal human histone gene in a mouse cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2315–2319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanly S. M., Bleecker G. C., Heintz N. Identification of promoter elements necessary for transcriptional regulation of a human histone H4 gene in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):380–389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G. Regulation of human histone gene expression: kinetics of accumulation and changes in the rate of synthesis and in the half-lives of individual histone mRNAs during the HeLa cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):539–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Zernik M., Roeder R. G. The structure of the human histone genes: clustered but not tandemly repeated. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):661–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg I. Histones. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:159–191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Structure of chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:931–954. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtler A. C., Sierra F., Clark S., Wells J. R., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Multiple H4 histone mRNAs of HeLa cells are encoded in different genes. Nature. 1982 Jul 8;298(5870):195–198. doi: 10.1038/298195a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Felsenfeld G. Nucleosome structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:1115–1156. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.005343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris T., Marashi F., Weber L., Hickey E., Greenspan D., Bonner J., Stein J., Stein G. Involvement of the 5'-leader sequence in coupling the stability of a human H3 histone mRNA with DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):981–985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tilly K., Maniatis T. Fine structure genetic analysis of a beta-globin promoter. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):613–618. doi: 10.1126/science.3457470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M., Marashi F., Green L., Zimmerman A., Zimmerman S., Stein J., Stein G. Cell cycle regulation of human histone H1 mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):434–438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M., Stein J., Stein G. Influence of DNA synthesis inhibition on the coordinate expression of core human histone genes during S phase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7927–7945. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R., Gorman C. M., Howard B. Minichromosome assembly of non-integrated plasmid DNA transfected into mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 24;13(10):3599–3615. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.10.3599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Birnstiel M. L. Structure and expression in L-cells of a cloned H4 histone gene of the mouse. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 5;151(4):607–625. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90426-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra F., Lichtler A., Marashi F., Rickles R., Van Dyke T., Clark S., Wells J., Stein G., Stein J. Organization of human histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1795–1799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra F., Stein G., Stein J. Structure and in vitro transcription of a human H4 histone gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):7069–7086. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.7069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sittman D. B., Graves R. A., Marzluff W. F. Histone mRNA concentrations are regulated at the level of transcription and mRNA degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1849–1853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullis R. H., Rubin H. Calcium protects DNase I from proteinase K: a new method for the removal of contaminating RNase from DNase I. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):260–264. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90519-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen A. J., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. A nuclear protein with affinity for the 5' flanking region of a cell cycle dependent human H4 histone gene in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1679–1698. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]