Abstract
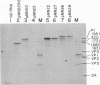
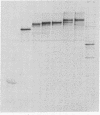
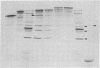
Plasmids have been constructed to generate substrates for the study of proteinases 2A and 3C of poliovirus. They contain the P1 (capsomer precursor) region of the poliovirus genome or P1 and part of P2 (a nonstructural precursor), which can be transcribed and translated in vitro. A transcript containing the entire 5' nontranslated region and the P1 region of the viral RNA gave poor translation in a reticulocyte translation system. Truncation of the 5' nontranslated region to its 3'-most segment gave acceptably good yields of radiolabeled P1. P1 was specifically processed to yield capsomer proteins by enzymes supplied in a postmitochondrial supernatant from poliovirus-infected cells. Thus, proteinase 3C can be supplied exogenously (in trans) and effect processing. This system may be used to provide P1 for the assay of proteinase 3C. Precursors that lacked either the 1A or 1D regions were poor substrates for proteinase 3C--observations that demonstrated a stringent structural requirement in processing by 3C. The translation product of a transcript encoding P1 and part of P2 was rapidly cleaved at the P1-P2 site in the absence of infected-cell extract. A transcript that contained a mutated 2A region gave a stable P1-P2 precursor that could be processed specifically by exogenous proteinase from infected-cell fractions. Processing of P1 appeared to require cleavage of the P1-P2 bond. These results support our previous data that 2A is the second polioviral proteinase and also provides a means of assaying proteinase 2A in vitro.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold E., Luo M., Vriend G., Rossmann M. G., Palmenberg A. C., Parks G. D., Nicklin M. J., Wimmer E. Implications of the picornavirus capsid structure for polyprotein processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sarnow P., Baltimore D. Genetic complementation among poliovirus mutants derived from an infectious cDNA clone. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1040–1049. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1040-1049.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. A., Ehrenfeld E. Translation of poliovirus RNA in vitro: changes in cleavage pattern and initiation sites by ribosomal salt wash. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):396–405. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90350-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celma M. L., Ehrenfeld E. Translation of poliovirus RNA in vitro: detection of two different initiation sites. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 15;98(4):761–780. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davanloo P., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Cloning and expression of the gene for bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2035–2039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Dorner L. F., Larsen G. R., Wimmer E., Anderson C. W. Identification of the initiation site of poliovirus polyprotein synthesis. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):1017–1028. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.1017-1028.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Milburn S. C., Edery I., Sonenberg N., Hershey J. W. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis following poliovirus infection correlates with the proteolysis of a 220,000-dalton polypeptide associated with eucaryotic initiation factor 3 and a cap binding protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14806–14810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of poliovirus polypeptides: antibodies to polypeptide P3-7c inhibit cleavage at glutamine-glycine pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3973–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Semler B. L., Ariga H., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Expression of a cloned gene segment of poliovirus in E. coli: evidence for autocatalytic production of the viral proteinase. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1063–1073. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90441-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle J. M., Chow M., Filman D. J. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus at 2.9 A resolution. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1358–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.2994218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Hunt T. Preparation and use of nuclease-treated rabbit reticulocyte lysates for the translation of eukaryotic messenger RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:50–74. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Kitamura N., Golini F., Wimmer E. The 5'-terminal structures of poliovirion RNA and poliovirus mRNA differ only in the genome-linked protein VPg. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5345–5349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallansch M. A., Kew O. M., Semler B. L., Omilianowski D. R., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E., Rueckert R. R. Protein processing map of poliovirus. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):873–880. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.873-880.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks G. D., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C. Encephalomyocarditis virus 3C protease: efficient cell-free expression from clones which link viral 5' noncoding sequences to the P3 region. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):376–384. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.376-384.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in vitro yields an active proteolytic processing enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):457–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Nicklin M. J., Murray M. G., Anderson C. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W., Wimmer E. A second virus-encoded proteinase involved in proteolytic processing of poliovirus polyprotein. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):761–770. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90790-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ypma-Wong M. F., Semler B. L. In vitro molecular genetics as a tool for determining the differential cleavage specificities of the poliovirus 3C proteinase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2069–2088. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Werf S., Bradley J., Wimmer E., Studier F. W., Dunn J. J. Synthesis of infectious poliovirus RNA by purified T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]