Abstract
The location and sequence composition of a consensus element of the nucleotide binding site in both simian virus 40 (SV40) and polyomavirus (PyV) large tumor antigens (T antigens) can be predicted with the assistance of a computer-based pattern-matching system, ARIADNE. The latter was used to optimally align elements of T antigen primary sequence and predicted secondary structure with a "descriptor" for a mononucleotide binding fold. Additional consensus elements of the nucleotide binding site in these two proteins were derived from comparisons of T antigen primary and predicted secondary structures with x-ray structures of the nucleotide binding sites in four otherwise unrelated proteins. Each of these elements was predicted to be encompassed within a 110-residue segment that is highly conserved between the two T antigens residues 418-528 in SV40 T antigen and residues 565-675 in PyV). Results of biochemical and immunologic experiments on the nucleotide binding behavior of these proteins were found to be consistent with these predictions. Taken together, the latter have resulted in a topological model of the ATP binding site in these two oncogene products.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. M., Zucker F. H., Steitz T. A. Space-filling models of kinase clefts and conformation changes. Science. 1979 Apr 27;204(4391):375–380. doi: 10.1126/science.220706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat T. N., Blow D. M., Brick P., Nyborg J. Tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase forms a mononucleotide-binding fold. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 15;158(4):699–709. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90255-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley M. K., Griffin J. D., Livingston D. M. Relationship of oligomerization to enzymatic and DNA-binding properties of the SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90382-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
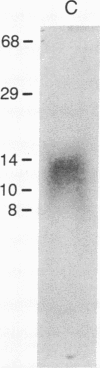
- Bradley M. K., Hudson J., Villanueva M. S., Livingston D. M. Specific in vitro adenylylation of the simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6574–6578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett R. M., Darling G. D., Kendall D. S., LeQuesne M. E., Mayhew S. G., Smith W. W., Ludwig M. L. The structure of the oxidized form of clostridial flavodoxin at 1.9-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4383–4392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R., Lane D. P., Tjian R. Use of monoclonal antibodies as probes of simian virus 40 T antigen ATPase activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11854–11858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R., Peden K., Pipas J. M., Nathans D., Tjian R. Biochemical activities of T-antigen proteins encoded by simian virus 40 A gene deletion mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):220–228. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clertant P., Cuzin F. Covalent affinity labeling by periodate-oxidized [alpha-32P]ATP of the large-T proteins of polyoma and SV40 viruses. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6300–6305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clertant P., Gaudray P., May E., Cuzin F. The nucleotide binding site detected by affinity labeling in the large T proteins of polyoma and SV40 viruses is distinct from their ATPase catalytic site. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15196–15203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clertant P., Seif I. A common function for polyoma virus large-T and papillomavirus E1 proteins? Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):276–279. doi: 10.1038/311276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Tornow J., Clark R., Tjian R. Properties of the simian virus 40 (SV40) large T antigens encoded by SV40 mutants with deletions in gene A. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):539–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.539-546.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Nathans D. Purification of simian virus 40 large T antigen by immunoaffinity chromatography. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):1001–1004. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.1001-1004.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans P. R., Hudson P. J. Structure and control of phosphofructokinase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):500–504. doi: 10.1038/279500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. C., Kuby S. A., Mildvan A. S. ATP-binding site of adenylate kinase: mechanistic implications of its homology with ras-encoded p21, F1-ATPase, and other nucleotide-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):907–911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. G., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. The protein identification resource (PIR). Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):11–15. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin B. E., Dilworth S. M. Polyomavirus: an overview of its unique properties. Adv Cancer Res. 1983;39:183–268. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)61036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney E. G., Harrison R. O., Fenno J. Monoclonal antibodies against simian virus 40 T antigens: evidence for distinct sublcasses of large T antigen and for similarities among nonviral T antigens. J Virol. 1980 Jun;34(3):752–763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.3.752-763.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hol W. G., van Duijnen P. T., Berendsen H. J. The alpha-helix dipole and the properties of proteins. Nature. 1978 Jun 8;273(5662):443–446. doi: 10.1038/273443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima H., Horii T., Ogawa T., Ogawa H. Functional domains of Escherichia coli recA protein deduced from the mutational sites in the gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(2):288–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00330682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. R. Characterization of the bovine papilloma virus plasmid maintenance sequences. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):391–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manos M. M., Gluzman Y. Genetic and biochemical analysis of transformation-competent, replication-defective simian virus 40 large T antigen mutants. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):120–127. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.120-127.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F., Clark B. F., la Cour T. F., Kjeldgaard M., Norskov-Lauritsen L., Nyborg J. A model for the tertiary structure of p21, the product of the ras oncogene. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):78–82. doi: 10.1126/science.3898366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mole S. E., Lane D. P. Use of simian virus 40 large T-beta-galactosidase fusion proteins in an immunochemical analysis of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):703–710. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.703-710.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai E. F., Sachsenheimer W., Schirmer R. H., Schulz G. E. Substrate positions and induced-fit in crystalline adenylate kinase. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul;114(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90281-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Moras D., Olsen K. W. Chemical and biological evolution of nucleotide-binding protein. Nature. 1974 Jul 19;250(463):194–199. doi: 10.1038/250194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwyzer M., Tai Y., Studer E., Michel M. R. Binding sites for monoclonal antibodies and for mRNPs on SV40 large T-antigen determined with a cleavage map. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Dec 1;137(1-2):303–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07829.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B., D'Alonzo J. S., Scolnick E. M. Identification of effector residues and a neutralizing epitope of Ha-ras-encoded p21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4725–4729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simanis V., Lane D. P. An immunoaffinity purification procedure for SV40 large T antigen. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):88–100. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szilagyi L., Balint M., Sreter F. A., Gergely J. Photoaffinity labelling with an ATP analog of the N-terminal peptide of myosin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 13;87(3):936–945. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga R. K., Terpstra P., Hol W. G. Prediction of the occurrence of the ADP-binding beta alpha beta-fold in proteins, using an amino acid sequence fingerprint. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 5;187(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabrecky J. R., Cole R. D. Localization of the ATP binding site on alpha-tubulin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Sep;225(2):475–481. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90056-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelwer C., Risler J. L., Brunie S. Crystal structure of Escherichia coli methionyl-tRNA synthetase at 2.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1982 Feb 15;155(1):63–81. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90492-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- la Cour T. F., Nyborg J., Thirup S., Clark B. F. Structural details of the binding of guanosine diphosphate to elongation factor Tu from E. coli as studied by X-ray crystallography. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2385–2388. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03943.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]