Abstract
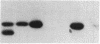
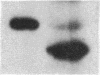
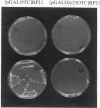
Expression of the subunit precursor of the human mitochondrial matrix enzyme ornithine transcarbamoylase (OTCase; EC 2.1.3.3) was programmed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae from a 2-micron plasmid by using an inducible galactose operon promoter. In the presence of the inducing sugar (galactose), two polypeptides were specifically precipitable with anti-OTCase antiserum: the human OTCase precursor (40 kDa); and the mature OTCase subunit (36 kDa). When yeast cells containing these species were lysed and fractionated, the OTCase precursor was found to be associated with mitochondrial membranes, while the mature subunit was found partly with mitochondrial membranes and partly in the soluble mitochondrial matrix-containing fraction. When OTCase enzymatic activity was assayed in fractions similarly derived from an S. cerevisiae strain devoid of yeast OTCase activity (an arg3 mutant) but expressing human OTCase, activity was detected specifically in the mitochondrial matrix fraction. A mutant human OTCase precursor containing an artificial mutation in the NH2-terminal leader peptide (arginine-23 to glycine) was similarly examined. As was previously observed with mammalian mitochondria, this precursor failed both to reach the matrix compartment and to be proteolytically processed; it also failed to exhibit OTCase enzymatic activity. Presence of OTCase enzymatic activity in an arg3 strain expressing wild-type precursor was utilized to obtain selective growth in a medium devoid of arginine but supplemented with the OTCase substrate ornithine. We conclude that, during evolution, the pathway of mitochondrial import utilized by the human OTCase precursor is conserved between yeast and humans, and that, by using selective growth conditions, it may be possible to examine genetically this pathway in S. cerevisiae.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conboy J. G., Fenton W. A., Rosenberg L. E. Processing of pre-ornithine transcarbamylase requires a zinc-dependent protease localized to the mitochondrial matrix. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Mar 15;105(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabeel M., Huygen R., Cunin R., Glansdorff N. The promoter region of the arg3 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: nucleotide sequence and regulation in an arg3-lacZ gene fusion. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):205–212. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01406.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daum G., Böhni P. C., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria. Cytochrome b2 and cytochrome c peroxidase are located in the intermembrane space of yeast mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):13028–13033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas M. G., McCammon M. T., Vassarotti A. Targeting proteins into mitochondria. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Jun;50(2):166–178. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.2.166-178.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton W. A., Hack A. M., Helfgott D., Rosenberg L. E. Biogenesis of the mitochondrial enzyme methylmalonyl-CoA mutase. Synthesis and processing of a precursor in a cell-free system and in cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6616–6621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff C. G., Moir D. T., Kohno T., Gravius T. C., Smith R. A., Yamasaki E., Taunton-Rigby A. Expression of calf prochymosin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1984 Jan;27(1):35–46. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90236-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb D. S., Gariépy J., Schoolnik G., Kornberg R. D. Synthetic peptides as nuclear localization signals. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):641–644. doi: 10.1038/322641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennig B., Koehler H., Neupert W. Receptor sites involved in posttranslational transport of apocytochrome c into mitochondria: specificity, affinity, and number of sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4963–4967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwich A. L., Fenton W. A., Firgaira F. A., Fox J. E., Kolansky D., Mellman I. S., Rosenberg L. E. Expression of amplified DNA sequences for ornithine transcarbamylase in HeLa cells: arginine residues may be required for mitochondrial import of enzyme precursor. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1515–1521. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwich A. L., Fenton W. A., Williams K. R., Kalousek F., Kraus J. P., Doolittle R. F., Konigsberg W., Rosenberg L. E. Structure and expression of a complementary DNA for the nuclear coded precursor of human mitochondrial ornithine transcarbamylase. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1068–1074. doi: 10.1126/science.6372096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwich A. L., Kalousek F., Fenton W. A., Pollock R. A., Rosenberg L. E. Targeting of pre-ornithine transcarbamylase to mitochondria: definition of critical regions and residues in the leader peptide. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):451–459. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90466-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C., Pesold-Hurt B., Suda K., Oppliger W., Schatz G. The first twelve amino acids (less than half of the pre-sequence) of an imported mitochondrial protein can direct mouse cytosolic dihydrofolate reductase into the yeast mitochondrial matrix. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2061–2068. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03892.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalousek F., François B., Rosenberg L. E. Isolation and characterization of ornithine transcarbamylase from normal human liver. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3939–3944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalousek F., Orsulak M. D., Rosenberg L. E. Newly processed ornithine transcarbamylase subunits are assembled to trimers in rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5392–5395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keng T., Alani E., Guarente L. The nine amino-terminal residues of delta-aminolevulinate synthase direct beta-galactosidase into the mitochondrial matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):355–364. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Kanda P., Kennedy R. C. Induction of nuclear transport with a synthetic peptide homologous to the SV40 T antigen transport signal. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):575–582. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90883-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpulla R. C., Nye S. H. Functional expression of rat cytochrome c in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6352–6356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt B., Hennig B., Köhler H., Neupert W. Transport of the precursor to neurospora ATPase subunit 9 into yeast mitochondria. Implications on the diversity of the transport mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4687–4689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Duncan M. J., Moir D. T. Heterologous protein secretion from yeast. Science. 1985 Sep 20;229(4719):1219–1224. doi: 10.1126/science.3939723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takiguchi M., Miura S., Mori M., Tatibana M. Transport of proteins into mitochondria: a high conservation of precursor uptake and processing system. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1983;75(2):227–231. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(83)90318-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urrestarazu L. A., Vissers S., Wiame J. M. Change in location of ornithine carbamoyltransferase and carbamoylphosphate synthetase among yeasts in relation to the arginase/ornithine carbamoyltransferase regulatory complex and the energy status of the cells. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 3;79(2):473–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11830.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Gilmore R., Blobel G. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90520-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe M. P., Ohta S., Schatz G. A yeast mutant temperature-sensitive for mitochondrial assembly is deficient in a mitochondrial protease activity that cleaves imported precursor polypeptides. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2069–2074. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03893.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]