Abstract
In the title compound, C20H22O5, an S(6) ring motif is formed by an intramolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bond, which contributes to the stabilization of the molecule. In the xanthene system, the cyclohexane ring adopts a chair conformation, the cyclohexene ring adopts a half-boat conformation and the tetrahydropyran ring adopts a half-chair conformation. The mean plane of the four essentially planar atoms of the tetrahydropyran ring [r.m.s deviation = 0.092 (1) Å] forms a dihedral angle of 64.13 (6)° with the mean plane of the methoxyphenyl group. In the crystal, intermolecular O—H⋯O and weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link molecules into chains along the a axis, which are further stabilized by C—H⋯π interactions.
Related literature
For background to and the biological activity of xanthenes and their derivatives, see: Menchen et al. (2003 ▶); Saint-Ruf et al. (1972 ▶); Ion et al. (1998 ▶); Knight & Stephens (1989 ▶); Jonathan et al. (1988 ▶). For ring conformations, see: Cremer & Pople (1975 ▶). For hydrogen-bond motifs, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶). For standard bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶). For a related structure, see: Reddy et al. (2009 ▶). For the stability of the temperature controller used in the data collection, see: Cosier & Glazer (1986 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C20H22O5
M r = 342.38
Triclinic,
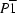
a = 7.1060 (1) Å
b = 7.8897 (1) Å
c = 15.1001 (2) Å
α = 91.285 (1)°
β = 101.251 (1)°
γ = 101.129 (1)°
V = 813.10 (2) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.10 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.44 × 0.23 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) ▶ T min = 0.957, T max = 0.990
21213 measured reflections
4715 independent reflections
4132 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.025
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.038
wR(F 2) = 0.110
S = 1.05
4715 reflections
231 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.46 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2009 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008) ▶; program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810050191/lh5179sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810050191/lh5179Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 is the centroid of the C14–C19 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O5—H1O5⋯O3i | 0.87 (2) | 1.93 (2) | 2.7877 (11) | 166.3 (18) |
| C6—H6A⋯O4 | 0.98 | 2.32 | 2.9266 (12) | 120 |
| C16—H16A⋯O5ii | 0.93 | 2.53 | 3.4172 (13) | 160 |
| C20—H20B⋯Cg1ii | 0.96 | 2.67 | 3.5206 (13) | 147 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 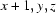 ; (ii)
; (ii) 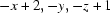 .
.
Acknowledgments
HKF and WSL thank Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM) for the Research University Grant (1001/PFIZIK/811160). WSL also thanks the Malaysian Government and USM for the award of a Research Fellowship. VV is grateful to the DST–India for funding through the Young Scientist Scheme (Fast Track Proposal).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Xanthene derivatives are very important heterocyclic compounds and due to their useful spectroscopic properties, they have been widely used as dyes, fluorescent materials for visualization of bio-molecules and in laser technologies (Menchen et al., 2003; Saint-Ruf et al., 1972; Ion et al., 1998). They have been reported for their agricultural bactericide activity, photodynamic therapy, antiflammatory effect and antiviral activity (Knight & Stephens, 1989; Jonathan et al., 1988). Due to their wide range of applications, these compounds have received a great deal of attention in connection with their synthesis. In the synthesis of these compounds, intermediates play a key role, because these compounds can be easily converted into acridines and other biological active compounds.
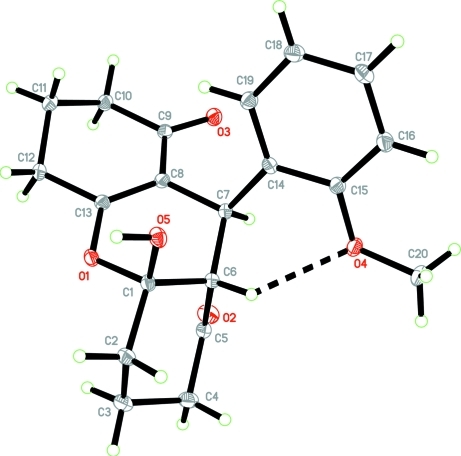
In the title compound, an intramolecular C6—H6A···O4 hydrogen bond (Table 1) contributes to the stabilization of the molecule (Fig. 1), forming an S(6) ring motif (Bernstein et al., 1995). The xanthene ring system consists of three rings which adopt different conformations. The cyclohexane ring (C1–C6) adopts a chair conformation with the puckering parameters Q = 0.5427 (11) Å, Θ = 4.67 (12)°, φ = 169.6 (15)° (Cremer & Pople, 1975). The cyclohexene ring (C8–C13) and the tetrahydropyran ring (O1/C1/C6/C7/C8/C13) adopt half-boat and half-chair conformations, with the puckering parameters, Q = 0.4831 (11) Å, Θ = 61.06 (13)°, φ = 176.13 (15)° and Q = 0.4497 (10) Å, Θ = 47.24 (13)°, φ = 87.44 (17)° (Cremer & Pople, 1975), respectively. The mean plane of the essentially planar atoms of the tetrahydropyran ring (C7/C8/C13/O1) [r.m.s deviation = 0.092 (1) Å] forms a dihedral angle of 64.13 (6)° with the methoxyphenyl group (C14–C20/O4). The bond lengths (Allen et al., 1987) and angles are within the normal range and are comparable to the related structure (Reddy et al., 2009).
In the crystal packing (Fig. 2), intermolecular O5—H1O5···O3i and C16—H16A···O5ii hydrogen bonds (see Table 1 for symmetry codes) link molecules into chains along the a axis which are further stabilized by C—H···Cg1ii interactions (Table 1), involving C14–C19 ring.
Experimental
A mixture of 2-methoxybenzaldehyde (0.365 ml, 0.0025 mol) and 1,3-cyclohexanedione (0.56 g, 0.005 mol) was refluxed in acetonitrile for 3 h. The progress of the reaction was monitored by TLC. After completion of the reaction, it was kept for 2 days for solid formation. The pure product was obtained by recrystallization of the crude product from ethanol. M.p.: 493–495 K, yield: 72%.
Refinement
Atom H1O5 was located from the difference Fourier map and was refined freely [O–H = 0.874 (18) Å]. The remaining H atoms were positioned geometrically [C–H = 0.93 or 0.98 Å] and were refined using a riding model, with Uiso(H) = 1.2 or 1.5 Ueq(C). A rotating group model was applied to the methyl group.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, showing 50% probability displacement ellipsoids and the atom-numbering scheme. The dashed line indicates the intramolecular hydrogen bond.
Fig. 2.
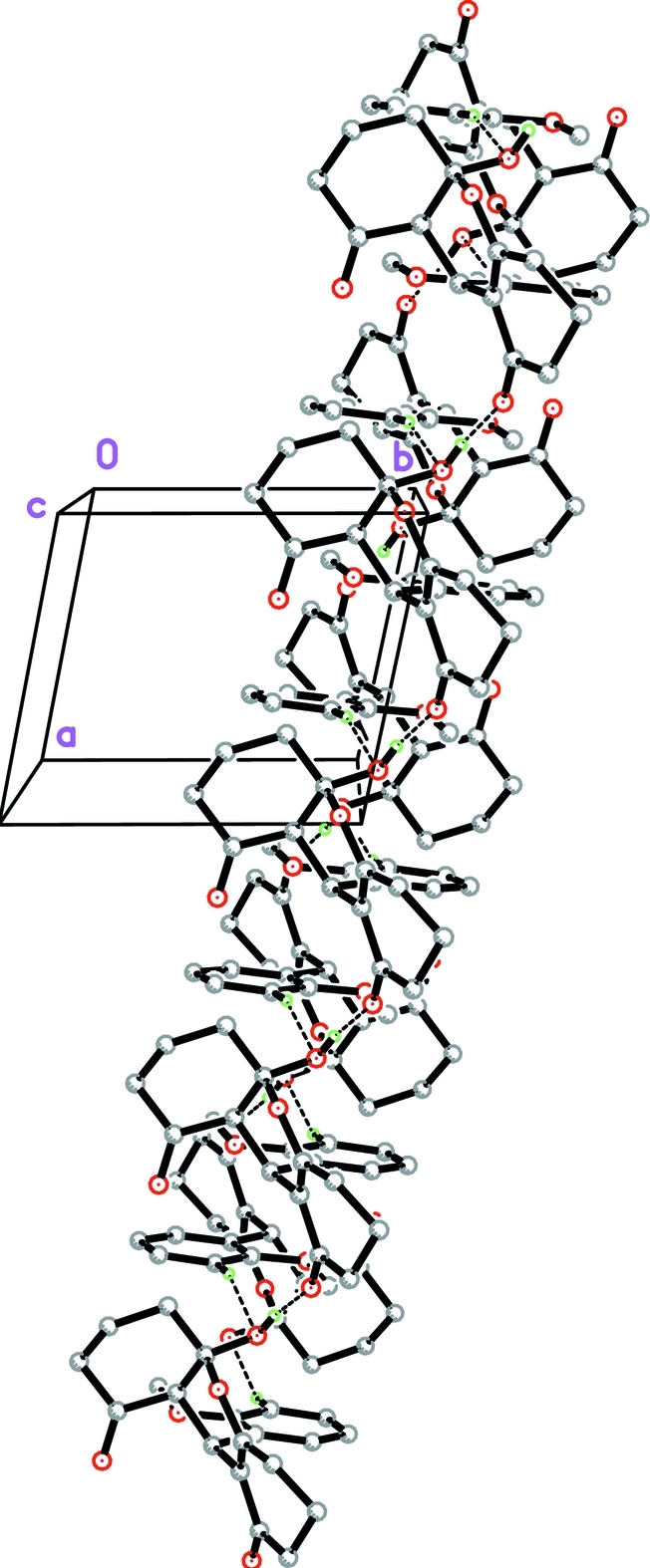
The crystal packing of the title compound, viewed along the c axis, showing a chain along the a axis. H atoms not involved in the intermolecular interactions (dashed lines) have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C20H22O5 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 342.38 | F(000) = 364 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.398 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 7.1060 (1) Å | Cell parameters from 9956 reflections |
| b = 7.8897 (1) Å | θ = 2.6–37.2° |
| c = 15.1001 (2) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| α = 91.285 (1)° | T = 100 K |
| β = 101.251 (1)° | Block, colourless |
| γ = 101.129 (1)° | 0.44 × 0.23 × 0.10 mm |
| V = 813.10 (2) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer | 4715 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 4132 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.025 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 30.0°, θmin = 2.6° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | h = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.957, Tmax = 0.990 | k = −11→11 |
| 21213 measured reflections | l = −21→21 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.038 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.110 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.057P)2 + 0.3385P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4715 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 231 parameters | Δρmax = 0.46 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. The crystal was placed in the cold stream of an Oxford Cryosystems Cobra open-flow nitrogen cryostat (Cosier & Glazer, 1986) operating at 100.0 (1) K. |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.99328 (11) | 0.05712 (9) | 0.14023 (5) | 0.01184 (15) | |
| O2 | 0.70333 (12) | 0.35590 (10) | 0.19525 (6) | 0.01849 (17) | |
| O3 | 0.34225 (11) | −0.15228 (10) | 0.17249 (5) | 0.01475 (16) | |
| O4 | 0.74431 (12) | 0.15152 (9) | 0.43898 (5) | 0.01407 (16) | |
| O5 | 1.11520 (11) | −0.03057 (9) | 0.28104 (5) | 0.01311 (15) | |
| C1 | 1.06767 (15) | 0.11229 (12) | 0.23546 (6) | 0.01072 (18) | |
| C2 | 1.24660 (15) | 0.25412 (13) | 0.23649 (7) | 0.01350 (19) | |
| H2A | 1.3340 | 0.2104 | 0.2039 | 0.016* | |
| H2B | 1.3158 | 0.2835 | 0.2986 | 0.016* | |
| C3 | 1.19583 (16) | 0.41749 (13) | 0.19413 (7) | 0.0163 (2) | |
| H3A | 1.1438 | 0.3927 | 0.1298 | 0.020* | |
| H3B | 1.3137 | 0.5066 | 0.2015 | 0.020* | |
| C4 | 1.04414 (17) | 0.48393 (13) | 0.23831 (8) | 0.0172 (2) | |
| H4A | 1.1005 | 0.5208 | 0.3012 | 0.021* | |
| H4B | 1.0064 | 0.5825 | 0.2075 | 0.021* | |
| C5 | 0.86650 (16) | 0.34065 (13) | 0.23232 (7) | 0.01310 (19) | |
| C6 | 0.90683 (15) | 0.17311 (12) | 0.27485 (6) | 0.01074 (18) | |
| H6A | 0.9570 | 0.2001 | 0.3398 | 0.013* | |
| C7 | 0.71877 (15) | 0.03250 (12) | 0.26338 (6) | 0.01037 (18) | |
| H7A | 0.6112 | 0.0933 | 0.2644 | 0.012* | |
| C8 | 0.67731 (15) | −0.05984 (12) | 0.17062 (6) | 0.01066 (18) | |
| C9 | 0.47820 (15) | −0.15295 (12) | 0.13264 (6) | 0.01103 (18) | |
| C10 | 0.43704 (15) | −0.24679 (13) | 0.04013 (7) | 0.01356 (19) | |
| H10A | 0.3871 | −0.1725 | −0.0052 | 0.016* | |
| H10B | 0.3363 | −0.3499 | 0.0383 | 0.016* | |
| C11 | 0.61838 (16) | −0.29864 (13) | 0.01678 (7) | 0.01432 (19) | |
| H11A | 0.6579 | −0.3863 | 0.0563 | 0.017* | |
| H11B | 0.5882 | −0.3473 | −0.0451 | 0.017* | |
| C12 | 0.78507 (16) | −0.14125 (13) | 0.02780 (7) | 0.01329 (19) | |
| H12A | 0.9051 | −0.1781 | 0.0224 | 0.016* | |
| H12B | 0.7561 | −0.0643 | −0.0200 | 0.016* | |
| C13 | 0.81329 (15) | −0.04614 (12) | 0.11791 (6) | 0.01064 (18) | |
| C14 | 0.71718 (14) | −0.09100 (12) | 0.33983 (6) | 0.01062 (18) | |
| C15 | 0.72872 (15) | −0.02412 (12) | 0.42848 (7) | 0.01140 (18) | |
| C16 | 0.72200 (16) | −0.13289 (13) | 0.49996 (7) | 0.01399 (19) | |
| H16A | 0.7337 | −0.0869 | 0.5585 | 0.017* | |
| C17 | 0.69757 (16) | −0.31127 (13) | 0.48290 (7) | 0.0150 (2) | |
| H17A | 0.6903 | −0.3844 | 0.5301 | 0.018* | |
| C18 | 0.68398 (16) | −0.38035 (13) | 0.39597 (7) | 0.0146 (2) | |
| H18A | 0.6674 | −0.4992 | 0.3847 | 0.018* | |
| C19 | 0.69553 (15) | −0.26938 (13) | 0.32551 (7) | 0.01285 (19) | |
| H19A | 0.6886 | −0.3158 | 0.2675 | 0.015* | |
| C20 | 0.79471 (17) | 0.22709 (13) | 0.52994 (7) | 0.0154 (2) | |
| H20A | 0.8251 | 0.3509 | 0.5289 | 0.023* | |
| H20B | 0.9066 | 0.1875 | 0.5625 | 0.023* | |
| H20C | 0.6861 | 0.1934 | 0.5593 | 0.023* | |
| H1O5 | 1.201 (3) | −0.067 (2) | 0.2552 (12) | 0.027 (4)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0112 (3) | 0.0143 (3) | 0.0096 (3) | −0.0001 (3) | 0.0038 (3) | −0.0002 (2) |
| O2 | 0.0168 (4) | 0.0169 (4) | 0.0226 (4) | 0.0053 (3) | 0.0039 (3) | 0.0048 (3) |
| O3 | 0.0130 (4) | 0.0158 (3) | 0.0160 (3) | 0.0021 (3) | 0.0054 (3) | −0.0011 (3) |
| O4 | 0.0207 (4) | 0.0119 (3) | 0.0100 (3) | 0.0039 (3) | 0.0036 (3) | −0.0005 (2) |
| O5 | 0.0144 (4) | 0.0141 (3) | 0.0132 (3) | 0.0058 (3) | 0.0053 (3) | 0.0034 (3) |
| C1 | 0.0112 (4) | 0.0117 (4) | 0.0091 (4) | 0.0014 (3) | 0.0027 (3) | 0.0007 (3) |
| C2 | 0.0111 (4) | 0.0148 (4) | 0.0141 (4) | −0.0001 (4) | 0.0041 (3) | 0.0004 (3) |
| C3 | 0.0160 (5) | 0.0134 (4) | 0.0194 (5) | −0.0004 (4) | 0.0065 (4) | 0.0020 (3) |
| C4 | 0.0175 (5) | 0.0116 (4) | 0.0229 (5) | 0.0006 (4) | 0.0076 (4) | 0.0002 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0158 (5) | 0.0115 (4) | 0.0129 (4) | 0.0022 (4) | 0.0058 (4) | 0.0000 (3) |
| C6 | 0.0114 (4) | 0.0110 (4) | 0.0098 (4) | 0.0015 (3) | 0.0030 (3) | 0.0000 (3) |
| C7 | 0.0110 (4) | 0.0109 (4) | 0.0093 (4) | 0.0018 (3) | 0.0026 (3) | 0.0003 (3) |
| C8 | 0.0119 (4) | 0.0099 (4) | 0.0099 (4) | 0.0019 (3) | 0.0021 (3) | 0.0003 (3) |
| C9 | 0.0125 (4) | 0.0097 (4) | 0.0112 (4) | 0.0026 (3) | 0.0029 (3) | 0.0014 (3) |
| C10 | 0.0132 (5) | 0.0143 (4) | 0.0122 (4) | 0.0009 (4) | 0.0025 (4) | −0.0024 (3) |
| C11 | 0.0161 (5) | 0.0126 (4) | 0.0140 (4) | 0.0012 (4) | 0.0044 (4) | −0.0025 (3) |
| C12 | 0.0156 (5) | 0.0137 (4) | 0.0108 (4) | 0.0014 (4) | 0.0052 (4) | −0.0016 (3) |
| C13 | 0.0119 (4) | 0.0098 (4) | 0.0099 (4) | 0.0016 (3) | 0.0021 (3) | 0.0010 (3) |
| C14 | 0.0098 (4) | 0.0121 (4) | 0.0100 (4) | 0.0017 (3) | 0.0027 (3) | 0.0014 (3) |
| C15 | 0.0106 (4) | 0.0121 (4) | 0.0118 (4) | 0.0021 (3) | 0.0032 (3) | 0.0004 (3) |
| C16 | 0.0155 (5) | 0.0157 (4) | 0.0109 (4) | 0.0028 (4) | 0.0035 (4) | 0.0014 (3) |
| C17 | 0.0162 (5) | 0.0153 (4) | 0.0139 (4) | 0.0025 (4) | 0.0039 (4) | 0.0046 (3) |
| C18 | 0.0159 (5) | 0.0119 (4) | 0.0155 (4) | 0.0020 (4) | 0.0026 (4) | 0.0017 (3) |
| C19 | 0.0130 (5) | 0.0130 (4) | 0.0122 (4) | 0.0022 (4) | 0.0022 (3) | −0.0003 (3) |
| C20 | 0.0189 (5) | 0.0158 (4) | 0.0112 (4) | 0.0043 (4) | 0.0020 (4) | −0.0025 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C13 | 1.3529 (12) | C8—C13 | 1.3574 (14) |
| O1—C1 | 1.4570 (11) | C8—C9 | 1.4607 (14) |
| O2—C5 | 1.2148 (13) | C9—C10 | 1.5151 (13) |
| O3—C9 | 1.2345 (12) | C10—C11 | 1.5253 (15) |
| O4—C15 | 1.3718 (12) | C10—H10A | 0.9700 |
| O4—C20 | 1.4350 (12) | C10—H10B | 0.9700 |
| O5—C1 | 1.3962 (11) | C11—C12 | 1.5227 (14) |
| O5—H1O5 | 0.874 (18) | C11—H11A | 0.9700 |
| C1—C2 | 1.5203 (14) | C11—H11B | 0.9700 |
| C1—C6 | 1.5345 (14) | C12—C13 | 1.4982 (13) |
| C2—C3 | 1.5255 (14) | C12—H12A | 0.9700 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9700 | C12—H12B | 0.9700 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9700 | C14—C19 | 1.3931 (13) |
| C3—C4 | 1.5378 (16) | C14—C15 | 1.4091 (13) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9700 | C15—C16 | 1.3964 (13) |
| C3—H3B | 0.9700 | C16—C17 | 1.3961 (14) |
| C4—C5 | 1.5098 (15) | C16—H16A | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9700 | C17—C18 | 1.3884 (14) |
| C4—H4B | 0.9700 | C17—H17A | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.5344 (13) | C18—C19 | 1.3976 (14) |
| C6—C7 | 1.5412 (14) | C18—H18A | 0.9300 |
| C6—H6A | 0.9800 | C19—H19A | 0.9300 |
| C7—C8 | 1.5133 (13) | C20—H20A | 0.9600 |
| C7—C14 | 1.5276 (13) | C20—H20B | 0.9600 |
| C7—H7A | 0.9800 | C20—H20C | 0.9600 |
| C13—O1—C1 | 117.22 (7) | C8—C9—C10 | 118.74 (9) |
| C15—O4—C20 | 116.87 (8) | C9—C10—C11 | 112.70 (8) |
| C1—O5—H1O5 | 106.7 (11) | C9—C10—H10A | 109.1 |
| O5—C1—O1 | 107.99 (7) | C11—C10—H10A | 109.1 |
| O5—C1—C2 | 112.32 (8) | C9—C10—H10B | 109.1 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 104.81 (7) | C11—C10—H10B | 109.1 |
| O5—C1—C6 | 108.38 (8) | H10A—C10—H10B | 107.8 |
| O1—C1—C6 | 109.47 (8) | C12—C11—C10 | 110.02 (8) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 113.68 (8) | C12—C11—H11A | 109.7 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 113.12 (9) | C10—C11—H11A | 109.7 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.0 | C12—C11—H11B | 109.7 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 109.0 | C10—C11—H11B | 109.7 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 109.0 | H11A—C11—H11B | 108.2 |
| C3—C2—H2B | 109.0 | C13—C12—C11 | 110.92 (8) |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 107.8 | C13—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 111.06 (9) | C11—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 109.4 | C13—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 109.4 | C11—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3B | 109.4 | H12A—C12—H12B | 108.0 |
| C4—C3—H3B | 109.4 | O1—C13—C8 | 123.96 (9) |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 108.0 | O1—C13—C12 | 111.00 (8) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 109.20 (8) | C8—C13—C12 | 125.03 (9) |
| C5—C4—H4A | 109.8 | C19—C14—C15 | 117.89 (9) |
| C3—C4—H4A | 109.8 | C19—C14—C7 | 122.94 (8) |
| C5—C4—H4B | 109.8 | C15—C14—C7 | 119.10 (8) |
| C3—C4—H4B | 109.8 | O4—C15—C16 | 123.04 (9) |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 108.3 | O4—C15—C14 | 115.90 (8) |
| O2—C5—C4 | 122.38 (9) | C16—C15—C14 | 121.05 (9) |
| O2—C5—C6 | 122.26 (9) | C17—C16—C15 | 119.48 (9) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 115.35 (9) | C17—C16—H16A | 120.3 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 109.28 (8) | C15—C16—H16A | 120.3 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 111.86 (8) | C18—C17—C16 | 120.50 (9) |
| C1—C6—C7 | 112.48 (8) | C18—C17—H17A | 119.8 |
| C5—C6—H6A | 107.7 | C16—C17—H17A | 119.8 |
| C1—C6—H6A | 107.7 | C17—C18—C19 | 119.31 (9) |
| C7—C6—H6A | 107.7 | C17—C18—H18A | 120.3 |
| C8—C7—C14 | 113.17 (8) | C19—C18—H18A | 120.3 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 109.55 (8) | C14—C19—C18 | 121.74 (9) |
| C14—C7—C6 | 114.28 (8) | C14—C19—H19A | 119.1 |
| C8—C7—H7A | 106.4 | C18—C19—H19A | 119.1 |
| C14—C7—H7A | 106.4 | O4—C20—H20A | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7A | 106.4 | O4—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C13—C8—C9 | 118.53 (9) | H20A—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C13—C8—C7 | 122.45 (9) | O4—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 118.73 (8) | H20A—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| O3—C9—C8 | 121.80 (9) | H20B—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| O3—C9—C10 | 119.41 (9) | ||
| C13—O1—C1—O5 | 71.99 (10) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −179.45 (8) |
| C13—O1—C1—C2 | −168.09 (8) | O3—C9—C10—C11 | −156.92 (9) |
| C13—O1—C1—C6 | −45.81 (10) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 25.45 (12) |
| O5—C1—C2—C3 | −175.06 (8) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −53.49 (11) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | 67.95 (10) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 50.03 (11) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −51.54 (11) | C1—O1—C13—C8 | 20.22 (13) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 54.04 (11) | C1—O1—C13—C12 | −160.09 (8) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −55.21 (12) | C9—C8—C13—O1 | 169.98 (8) |
| C3—C4—C5—O2 | −122.06 (11) | C7—C8—C13—O1 | −3.74 (15) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 56.91 (11) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | −9.66 (14) |
| O2—C5—C6—C1 | 125.76 (10) | C7—C8—C13—C12 | 176.62 (9) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −53.20 (11) | C11—C12—C13—O1 | 160.59 (8) |
| O2—C5—C6—C7 | 0.54 (13) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | −19.73 (13) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −178.43 (8) | C8—C7—C14—C19 | 4.92 (14) |
| O5—C1—C6—C5 | 174.47 (8) | C6—C7—C14—C19 | −121.40 (10) |
| O1—C1—C6—C5 | −67.98 (10) | C8—C7—C14—C15 | −171.98 (9) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 48.83 (11) | C6—C7—C14—C15 | 61.70 (12) |
| O5—C1—C6—C7 | −60.66 (10) | C20—O4—C15—C16 | 12.66 (14) |
| O1—C1—C6—C7 | 56.89 (10) | C20—O4—C15—C14 | −168.10 (9) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 173.70 (8) | C19—C14—C15—O4 | −178.20 (9) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 82.61 (9) | C7—C14—C15—O4 | −1.14 (14) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | −40.82 (10) | C19—C14—C15—C16 | 1.06 (15) |
| C5—C6—C7—C14 | −149.21 (8) | C7—C14—C15—C16 | 178.12 (9) |
| C1—C6—C7—C14 | 87.36 (10) | O4—C15—C16—C17 | 177.27 (10) |
| C14—C7—C8—C13 | −114.03 (10) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | −1.94 (16) |
| C6—C7—C8—C13 | 14.77 (12) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | 1.30 (16) |
| C14—C7—C8—C9 | 72.27 (11) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | 0.17 (16) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −158.94 (8) | C15—C14—C19—C18 | 0.46 (15) |
| C13—C8—C9—O3 | −170.97 (9) | C7—C14—C19—C18 | −176.48 (9) |
| C7—C8—C9—O3 | 2.98 (14) | C17—C18—C19—C14 | −1.07 (16) |
| C13—C8—C9—C10 | 6.60 (13) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| Cg1 is the centroid of the C14–C19 ring. |
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O5—H1O5···O3i | 0.87 (2) | 1.93 (2) | 2.7877 (11) | 166.3 (18) |
| C6—H6A···O4 | 0.98 | 2.32 | 2.9266 (12) | 120 |
| C16—H16A···O5ii | 0.93 | 2.53 | 3.4172 (13) | 160 |
| C20—H20B···Cg1ii | 0.96 | 2.67 | 3.5206 (13) | 147 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1, y, z; (ii) −x+2, −y, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LH5179).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cosier, J. & Glazer, A. M. (1986). J. Appl. Cryst. 19, 105–107.
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
- Ion, R. M., Frackowiak, D., Planner, A. & Wiktorowicz, K. (1998). Acta Biochim. Pol. 45, 833–845. [PubMed]
- Jonathan, R. D., Srinivas, K. R. & Glen, E. B. (1988). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 23, 111–117.
- Knight, C. G. & Stephens, T. (1989). Biochem. J. 258, 683–689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Menchen, S. M., Benson, S. C., Lam, J. Y. L., Zhen, W., Sun, D., Rosenblum, B. B., Khan, S. H. & Taing, M. (2003). US Patent 6 583 168.
- Reddy, B. P., Vijayakumar, V., Narasimhamurthy, T., Suresh, J. & Lakshman, P. L. N. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Saint-Ruf, G., De, A. & Hieu, H. T. (1972). Bull. Chim. Ther. 7, 83–86.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810050191/lh5179sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810050191/lh5179Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report