Abstract
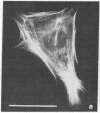
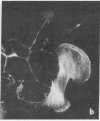
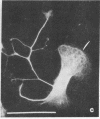
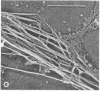
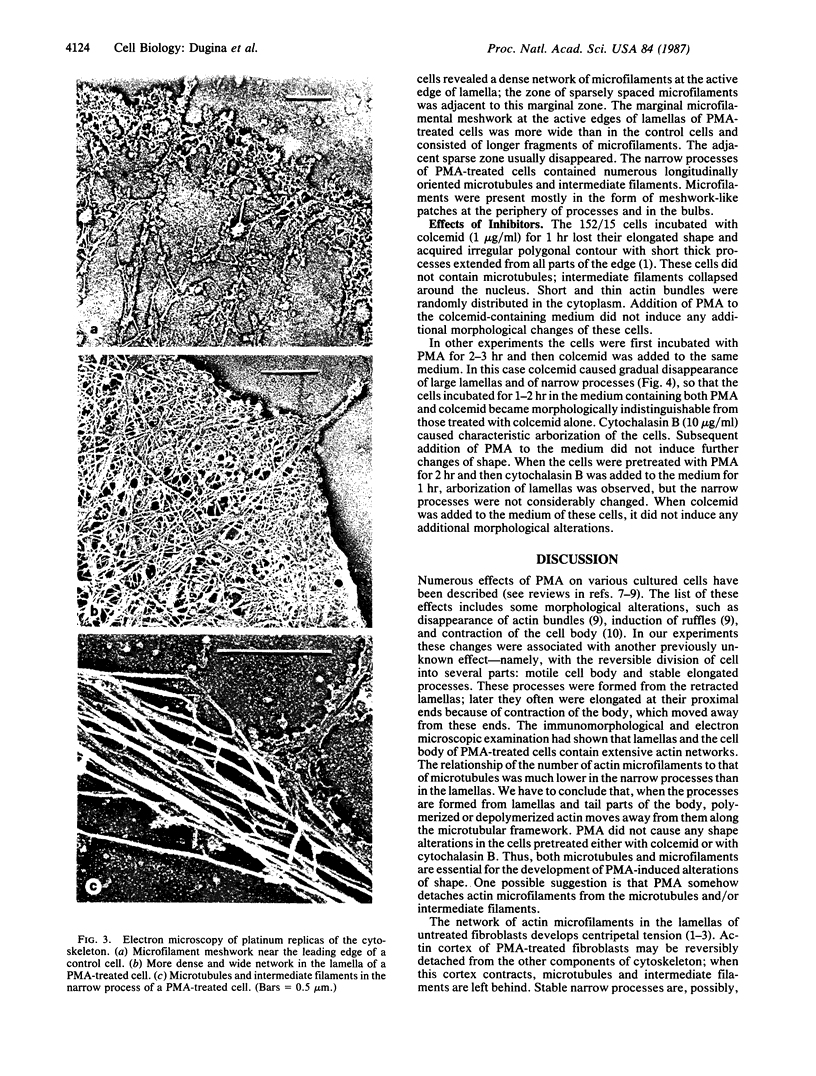
The phorbol ester phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) induced reversible alteration of the shape of fibroblastic cells of certain transformed lines--namely, partition of the cells into two types of domains: motile body actively extending large lamellas and stable narrow cytoplasmic processes. Dynamic observations have shown that stable processes are formed from partially retracted lamellas and from contracted tail parts of cell bodies. Immunofluorescence microscopy and electron microscopy of platinum replicas of cytoskeleton have shown that PMA-induced narrow processes are rich in microtubules and intermediate filaments but relatively poor in actin microfilaments; in contrast, lamellas and cell bodies contained numerous microfilaments. Colcemid-induced depolymerization of microtubules led to contraction of PMA-induced processes; cytochalasin B prevented this contraction. It is suggested that PMA-induced separation of cell into motile and stable parts is due to directional movement of actin structures along the microtubular framework. Similar movements may play an important role in various normal morphogenetic processes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bershadskii A. D., Brodskaia R. M., Mansurov P. G., Stavrovskaia A. A., Stromskaia T. P. Sviaz' mezhdu prikrepleniem kletok k substratu i ikh proliferativnymi kharakteristikami. Eksp Onkol. 1984;6(1):27–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driedger P. E., Blumberg P. M. The effect of phorbol diesters on chicken embryo fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 1977 Sep;37(9):3257–3265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliwa M., Nakamura T., Porter K. R., Euteneuer U. A tumor promoter induces rapid and coordinated reorganization of actin and vinculin in cultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):1045–1059. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon F., Magendantz M. Cytochalasin separates microtubule disassembly from loss of asymmetric morphology. J Cell Biol. 1981 Apr;89(1):157–161. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svitkina T. M., Shevelev A. A., Bershadsky A. D., Gelfand V. I. Cytoskeleton of mouse embryo fibroblasts. Electron microscopy of platinum replicas. Eur J Cell Biol. 1984 May;34(1):64–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Tsuda T., Hoshijima M. Role of protein kinase C in transmembrane signaling. J Cell Biochem. 1985;29(2):143–155. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240290209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vara F., Schneider J. A., Rozengurt E. Ionic responses rapidly elicited by activation of protein kinase C in quiescent Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2384–2388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasiliev J. M. Spreading of non-transformed and transformed cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985;780(1):21–65. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(84)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]