Abstract
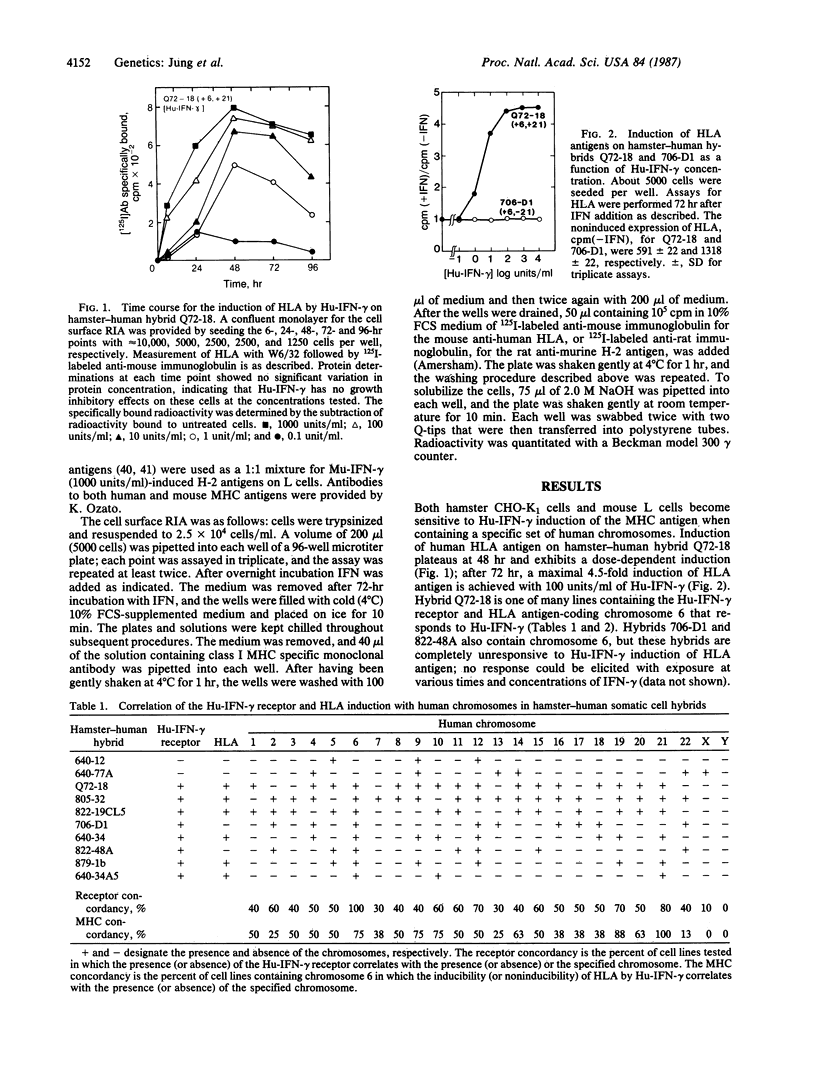
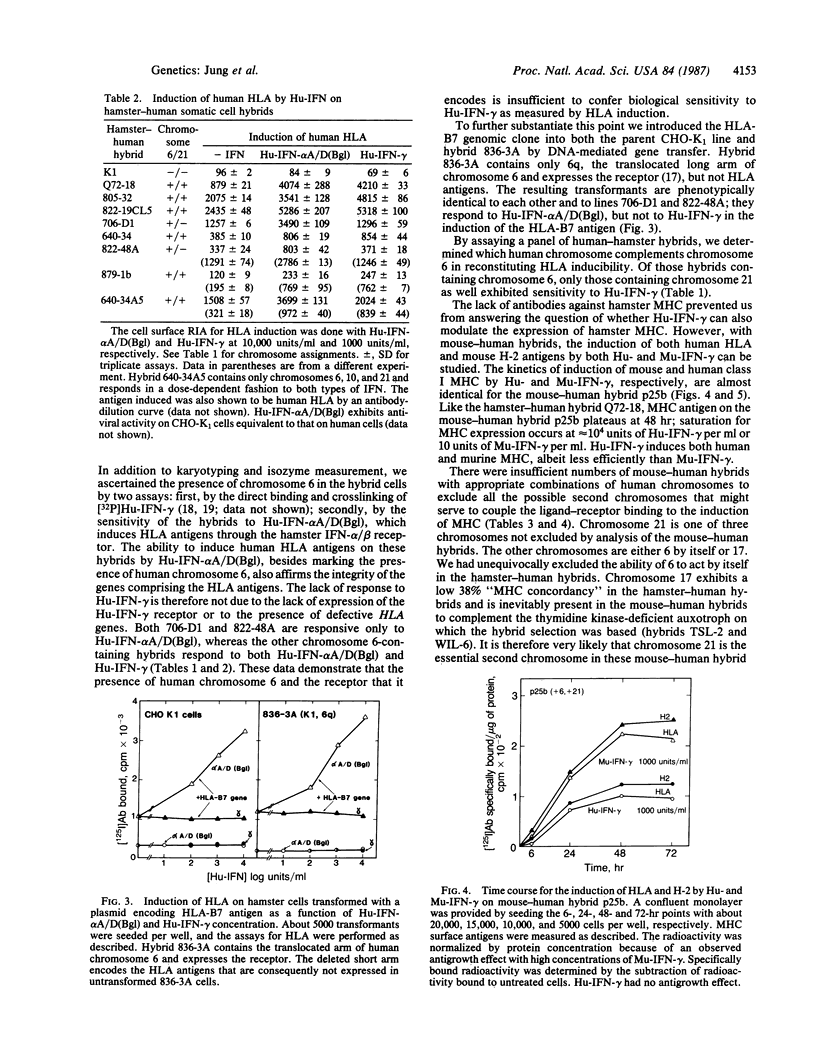
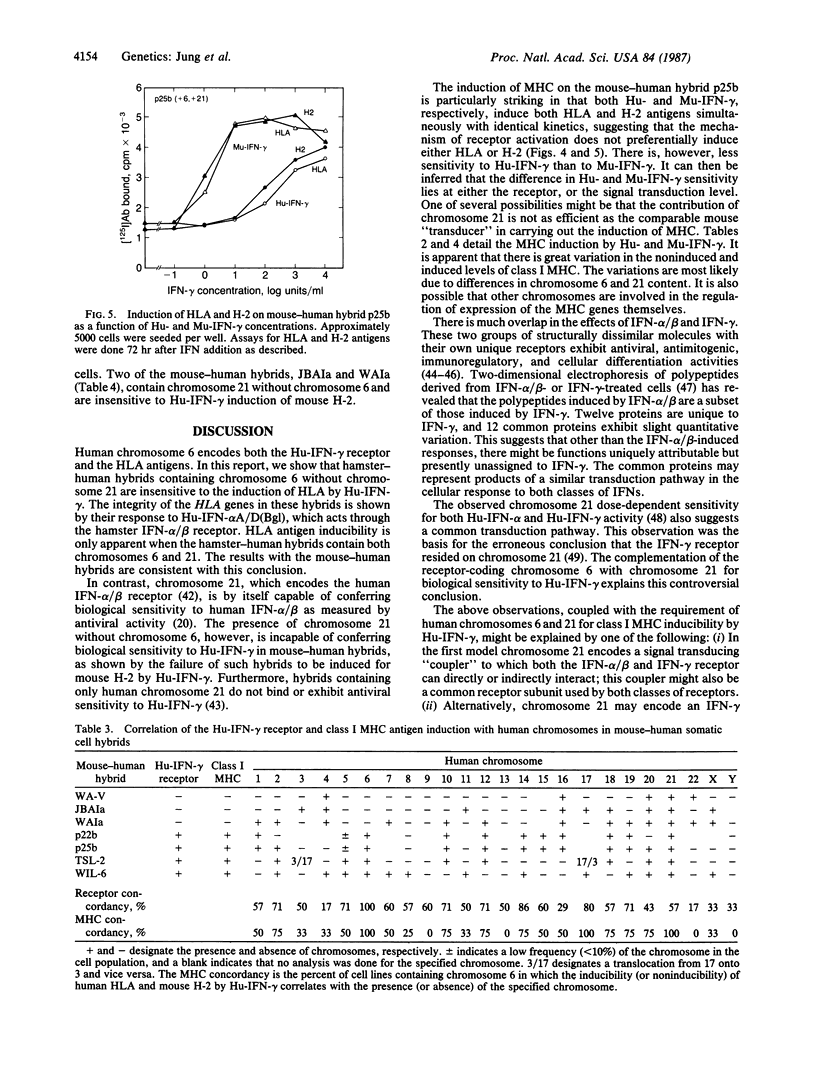
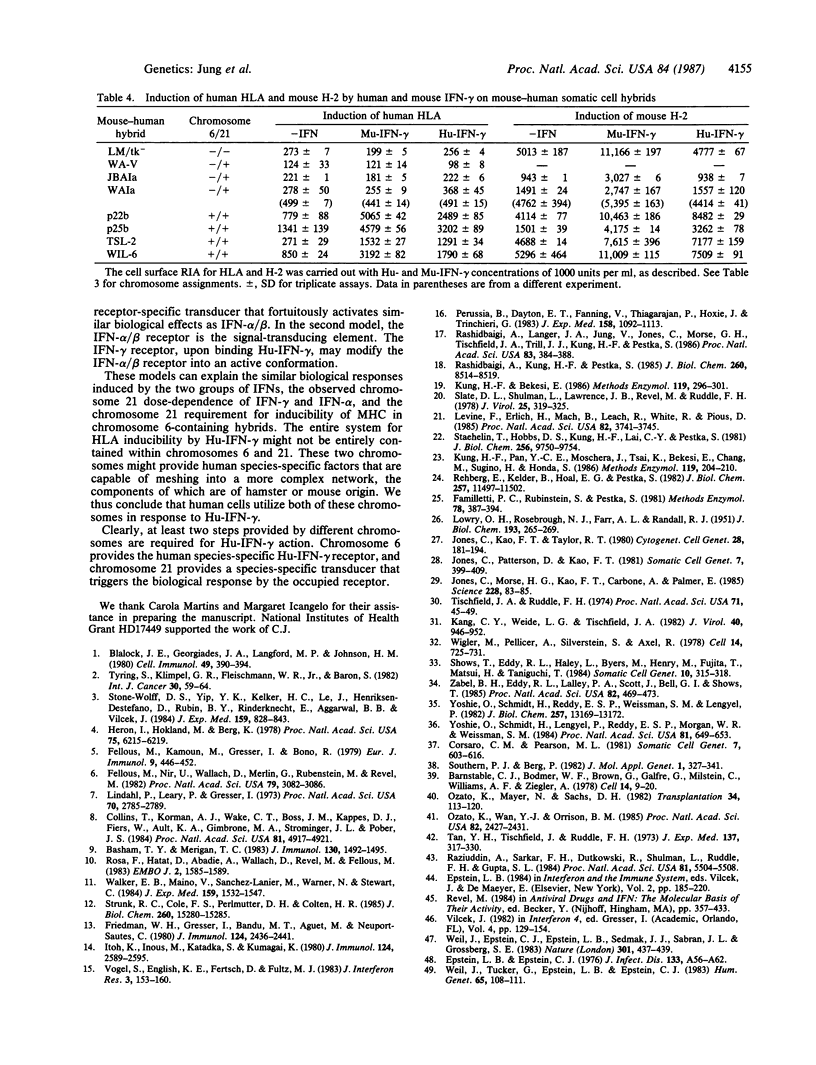
The human interferon gamma receptor has previously been assigned to chromosome 6. Chromosome 6 also encodes HLA, the human class I major histocompatibility antigens. However, the presence of chromosome 6 in hamster-human hybrids is by itself insufficient to confer sensitivity to human immune interferon as measured by the induction of human HLA. Human chromosome 21 was found to be the second chromosome essential for HLA inducibility. Similar results were found with mouse-human somatic cell hybrids. Thus, at least two steps are involved in the action of human interferon gamma: the binding of interferon gamma to its receptor coded by chromosome 6 and the linkage of this binding event through a factor coded by chromosome 21 to trigger biological action. Both of these steps are species-specific.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basham T. Y., Merigan T. C. Recombinant interferon-gamma increases HLA-DR synthesis and expression. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1492–1494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blalock J. E., Georgiades J. A., Langford M. P., Johnson H. M. Purified human immune interferon has more potent anticellular activity than fibroblast or leukocyte interferon. Cell Immunol. 1980 Feb;49(2):390–394. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Korman A. J., Wake C. T., Boss J. M., Kappes D. J., Fiers W., Ault K. A., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Strominger J. L., Pober J. S. Immune interferon activates multiple class II major histocompatibility complex genes and the associated invariant chain gene in human endothelial cells and dermal fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corsaro C. M., Pearson M. L. Enhancing the efficiency of DNA-mediated gene transfer in mammalian cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 Sep;7(5):603–616. doi: 10.1007/BF01549662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. B., Epstein C. J. Localization fo the gene AVG for the antiviral expression of immune and classical interferon to the distal portion of the long arm of chromosome 21. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133 (Suppl):A56–A62. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_2.a56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Familletti P. C., Rubinstein S., Pestka S. A convenient and rapid cytopathic effect inhibition assay for interferon. Methods Enzymol. 1981;78(Pt A):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)78146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellous M., Kamoun M., Gresser I., Bono R. Enhanced expression of HLA antigens and beta 2-microglobulin on interferon-treated human lymphoid cells. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jun;9(6):446–449. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellous M., Nir U., Wallach D., Merlin G., Rubinstein M., Revel M. Interferon-dependent induction of mRNA for the major histocompatibility antigens in human fibroblasts and lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3082–3086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridman W. H., Gresser I., Bandu M. T., Aguet M., Neauport-Sautes C. Interferon enhances the expression of Fc gamma receptors. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2436–2441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heron I., Hokland M., Berg K. Enhanced expression of beta2-microglobulin and HLA antigens on human lymphoid cells by interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6215–6219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh K., Inoue M., Kataoka S., Kumagai K. Differential effect of interferon expression of IgG- and IgM-Fc receptors on human lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2589–2595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C., Kao F. T., Taylor R. T. Chromosomal assignment of the gene for folylpolyglutamate synthetase to human chromosome 9. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1980;28(3):181–194. doi: 10.1159/000131529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C., Morse H. G., Kao F. T., Carbone A., Palmer E. Human T-cell receptor alpha-chain genes: location on chromosome 14. Science. 1985 Apr 5;228(4695):83–85. doi: 10.1126/science.3919444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C., Patterson D., Kao F. T. Assignment of the gene coding for phosphoribosylglycineamide formyltransferase to human chromosome 14. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 Jul;7(4):399–409. doi: 10.1007/BF01542985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y., Weide L. G., Tischfield J. A. Suppression of vesicular stomatitis virus defective intefering particle generation by a function(s) associated with human chromosome 16. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):946–952. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.946-952.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung H. F., Bekesi E. Phosphorylation of human immune interferon (IFN-gamma). Methods Enzymol. 1986;119:296–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)19045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung H. F., Pan Y. C., Moschera J., Tsai K., Bekesi E., Chang M., Sugino H., Honda S. Purification of recombinant human immune interferon. Methods Enzymol. 1986;119:204–210. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)19031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine F., Erlich H., Mach B., Leach R., White R., Pious D. Deletion mapping of HLA and chromosome 6p genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3741–3745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl P., Leary P., Gresser I. Enhancement by interferon of the expression of surface antigens on murine leukemia L 1210 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2785–2788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Mayer N. M., Sachs D. H. Monoclonal antibodies to mouse major histocompatibility complex antigens. Transplantation. 1982 Sep;34(3):113–120. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198209000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Wan Y. J., Orrison B. M. Mouse major histocompatibility class I gene expression begins at midsomite stage and is inducible in earlier-stage embryos by interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2427–2431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Dayton E. T., Lazarus R., Fanning V., Trinchieri G. Immune interferon induces the receptor for monomeric IgG1 on human monocytic and myeloid cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1092–1113. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashidbaigi A., Kung H. F., Pestka S. Characterization of receptors for immune interferon in U937 cells with 32P-labeled human recombinant immune interferon. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8514–8519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashidbaigi A., Langer J. A., Jung V., Jones C., Morse H. G., Tischfield J. A., Trill J. J., Kung H. F., Pestka S. The gene for the human immune interferon receptor is located on chromosome 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):384–388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raziuddin A., Sarkar F. H., Dutkowski R., Shulman L., Ruddle F. H., Gupta S. L. Receptors for human alpha and beta interferon but not for gamma interferon are specified by human chromosome 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5504–5508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehberg E., Kelder B., Hoal E. G., Pestka S. Specific molecular activities of recombinant and hybrid leukocyte interferons. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11497–11502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F., Hatat D., Abadie A., Wallach D., Revel M., Fellous M. Differential regulation of HLA-DR mRNAs and cell surface antigens by interferon. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1585–1589. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01628.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T., Eddy R., Haley L., Byers M., Henry M., Fujita T., Matsui H., Taniguchi T. Interleukin 2 (IL2) is assigned to human chromosome 4. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 May;10(3):315–318. doi: 10.1007/BF01535253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slate D. L., Shulman L., Lawrence J. B., Revel M., Ruddle F. H. Presence of human chromosome 21 alone is sufficient for hybrid cell sensitivity to human interferon. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):319–325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.319-325.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin T., Hobbs D. S., Kung H., Lai C. Y., Pestka S. Purification and characterization of recombinant human leukocyte interferon (IFLrA) with monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9750–9754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone-Wolff D. S., Yip Y. K., Kelker H. C., Le J., Henriksen-Destefano D., Rubin B. Y., Rinderknecht E., Aggarwal B. B., Vilcek J. Interrelationships of human interferon-gamma with lymphotoxin and monocyte cytotoxin. J Exp Med. 1984 Mar 1;159(3):828–843. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.3.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strunk R. C., Cole F. S., Perlmutter D. H., Colten H. R. gamma-Interferon increases expression of class III complement genes C2 and factor B in human monocytes and in murine fibroblasts transfected with human C2 and factor B genes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15280–15285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan Y. H., Tischfield J., Ruddle F. H. The linkage of genes for the human interferon-induced antiviral protein and indophenol oxidase-B traits to chromosome G-21. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):317–330. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischfield J. A., Ruddle F. H. Assignment of the gene for adenine phosphoribosyltransferase to human chromosome 16 by mouse-human somatic cell hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):45–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyring S., Klimpel G. R., Fleischmann W. R., Jr, Baron S. Direct cytolysis by partially-purified preparations of immune interferon. Int J Cancer. 1982 Jul 15;30(1):59–64. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910300111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J. The importance of having gamma. Interferon. 1982;4:129–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., English K. E., Fertsch D., Fultz M. J. Differential modulation of macrophage membrane markers by interferon: analysis of Fc and C3b receptors, Mac-1 and Ia antigen expression. J Interferon Res. 1983;3(2):153–160. doi: 10.1089/jir.1983.3.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker E. B., Maino V., Sanchez-Lanier M., Warner N., Stewart C. Murine gamma interferon activates the release of a macrophage-derived Ia-inducing factor that transfers Ia inductive capacity. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1532–1547. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil J., Epstein C. J., Epstein L. B., Sedmak J. J., Sabran J. L., Grossberg S. E. A unique set of polypeptides is induced by gamma interferon in addition to those induced in common with alpha and beta interferons. Nature. 1983 Feb 3;301(5899):437–439. doi: 10.1038/301437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil J., Tucker G., Epstein L. B., Epstein C. J. Interferon induction of (2'-5') oligoisoadenylate synthetase in diploid and trisomy 21 human fibroblasts: relation to dosage of the interferon receptor gene (IRFC). Hum Genet. 1983;65(2):108–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00286644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshie O., Schmidt H., Lengyel P., Reddy E. S., Morgan W. R., Weissman S. M. Transcripts of human HLA gene fragments lacking the 5'-terminal region in transfected mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):649–653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshie O., Schmidt H., Reddy E. S., Weissman S., Lengyel P. Mouse interferons enhance the accumulation of a human HLA RNA and protein in transfected mouse and hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13169–13172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel B. U., Eddy R. L., Lalley P. A., Scott J., Bell G. I., Shows T. B. Chromosomal locations of the human and mouse genes for precursors of epidermal growth factor and the beta subunit of nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):469–473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



