Abstract
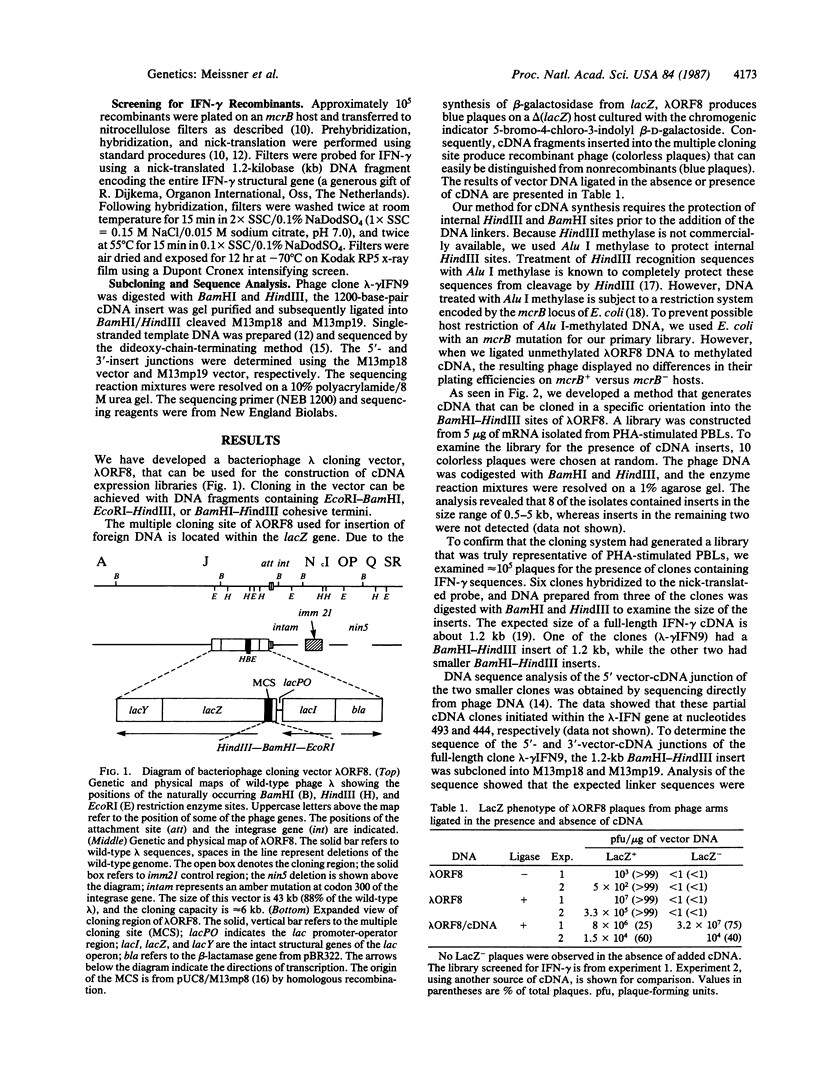
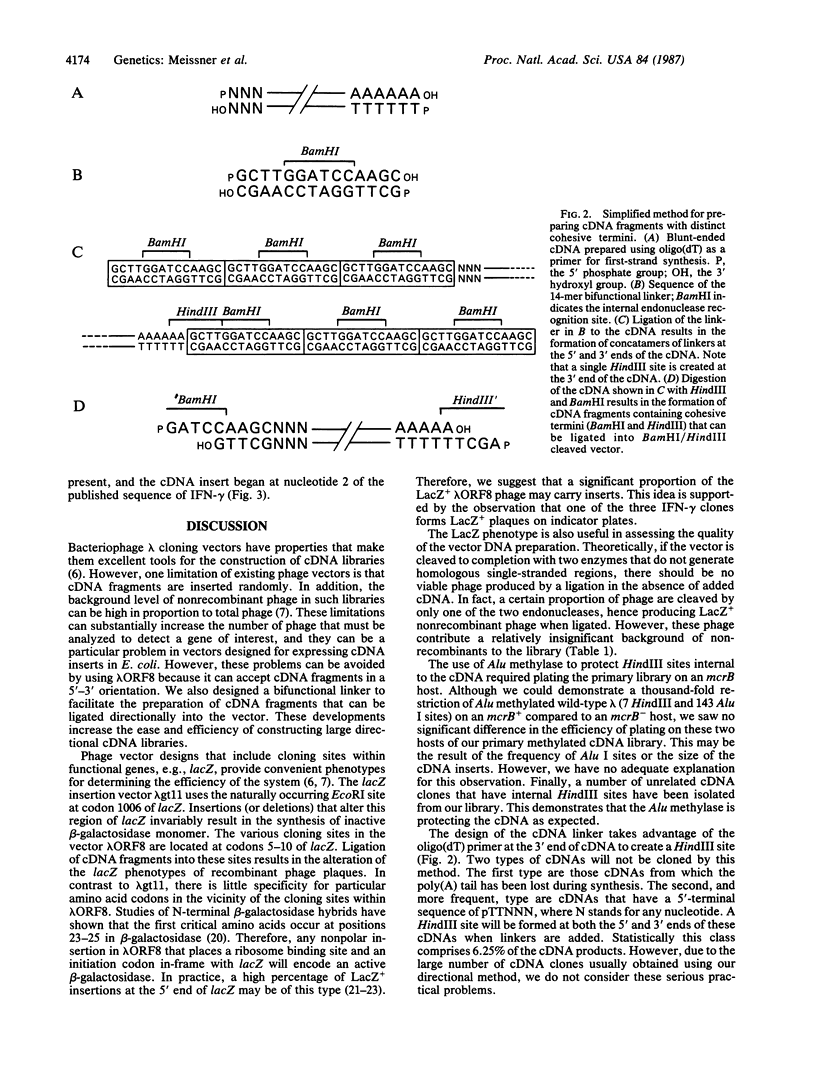
We have developed a bacteriophage lambda cloning vector, lambda ORF8, that can be used for the construction of cDNA libraries. The wild-type lambda genome contains five BamHI, five EcoRI, and seven HindIII restriction sites that have all been removed from the genome of lambda ORF8. Sites for these endonucleases are present within the multiple cloning site of lambda ORF8. We report a method for preparing cDNAs that can be cloned in a single orientation in our phage vector. The method utilizes the synthesis of double-stranded cDNA, including priming of first-strand synthesis by oligo(dT). After completion of second-strand synthesis, a bifunctional oligodeoxynucleotide linker is ligated to the cDNA fragments. This linker, which contains a BamHI restriction site, will create a HindIII restriction site when ligated to the 3' end of cDNA fragments. Subsequent treatment of methylated cDNA with HindIII and BamHI endonucleases allows these fragments to be cloned directionally into lambda ORF8. To demonstrate the utility of this cloning system, we prepared a library from 5 micrograms of mRNA isolated from phytohemagglutinin-stimulated human peripheral blood lymphocytes. The primary library contained 2 X 10(8) plaque-forming phage, at least 80% of which contain inserts. A portion of the library was examined for the presence of gamma-interferon-related clones to verify the method had generated a library that was representative of phytohemagglutinin-stimulated peripheral blood lymphocytes. This simple and efficient cDNA cloning system significantly reduces the amount of RNA and effort required for the preparation of large directionally cloned libraries.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander D. C., McKnight T. D., Williams B. G. A simplified and efficient vector-primer cDNA cloning system. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90197-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celada F., Zabin I. A dimer--dimer binding region in beta-galactosidase. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 6;18(3):404–406. doi: 10.1021/bi00570a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Kafatos F. C., Maxam A. M., Maniatis T. Enzymatic in vitro synthesis of globin genes. Cell. 1976 Feb;7(2):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. R., Colot H. V., Guarente L., Rosbash M. Open reading frame cloning: identification, cloning, and expression of open reading frame DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6598–6602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Leung D. W., Pennica D., Yelverton E., Najarian R., Simonsen C. C., Derynck R., Sherwood P. J., Wallace D. M., Berger S. L. Expression of human immune interferon cDNA in E. coli and monkey cells. Nature. 1982 Feb 11;295(5849):503–508. doi: 10.1038/295503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Feramisco J. R., Fiddes J. C., Thomas G. P., Hughes S. H. Identification of clones that encode chicken tropomyosin by direct immunological screening of a cDNA expression library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):31–35. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenen M., Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Immunoenzymatic detection of expressed gene fragments cloned in the lac Z gene of E. coli. EMBO J. 1982;1(4):509–512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01199.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus J. P., Williamson C. L., Firgaira F. A., Yang-Feng T. L., Münke M., Francke U., Rosenberg L. E. Cloning and screening with nanogram amounts of immunopurified mRNAs: cDNA cloning and chromosomal mapping of cystathionine beta-synthase and the beta subunit of propionyl-CoA carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2047–2051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M., Nelson M. The effect of site specific methylation on restriction endonuclease digestion. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985;13 (Suppl):r201–r207. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.suppl.r201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raleigh E. A., Wilson G. Escherichia coli K-12 restricts DNA containing 5-methylcytosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9070–9074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom J. H., Evans C. H., McCabe R. P., Pomato N., Heinbaugh J. A., Chin M., Hanna M. G., Jr Leukoregulin, a direct-acting anticancer immunological hormone that is distinct from lymphotoxin and interferon. Cancer Res. 1985 Feb;45(2):851–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougeon F., Mach B. Stepwise biosynthesis in vitro of globin genes from globin mRNA by DNA polymerase of avian myeloblastosis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3418–3422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock G. M., ap Rhys C., Berman M. L., Hampar B., Jackson D., Silhavy T. J., Weisemann J., Zweig M. Open reading frame expression vectors: a general method for antigen production in Escherichia coli using protein fusions to beta-galactosidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4432–4436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]