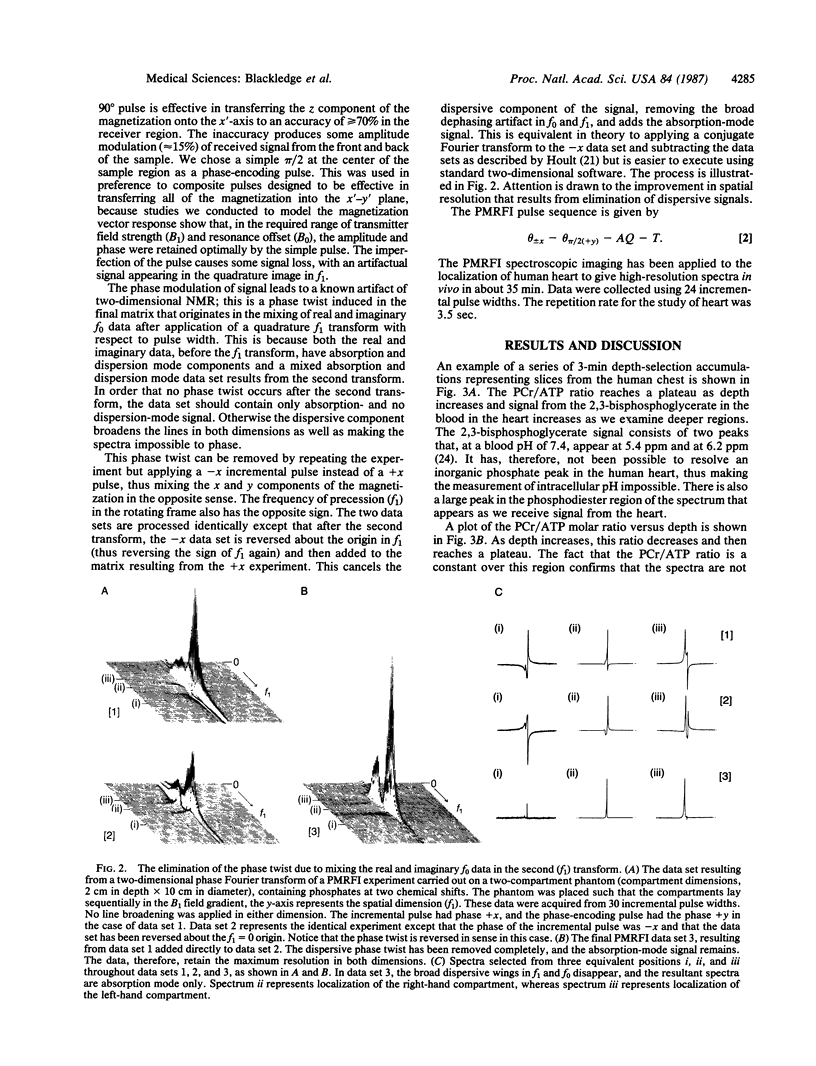
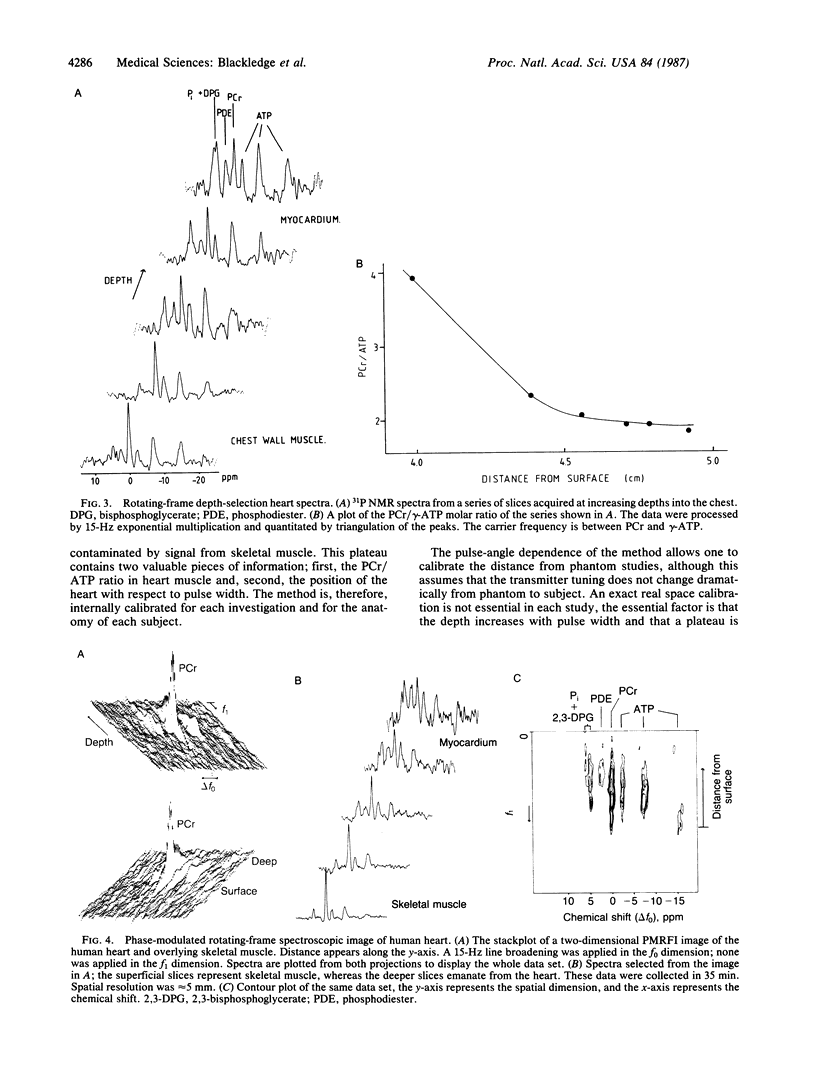
Abstract
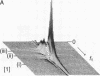
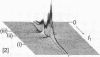
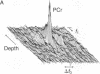
We have developed 31P NMR spectroscopic methods to determine quantitatively relative levels of phosphorous-containing metabolites in the human myocardium. We have used localization techniques based on the rotating-frame imaging experiment and carried out with a double-surface coil probe. Information is obtained from selected slices by rotating-frame depth selection and from a complete one-dimensional spectroscopic image using phase-modulated rotating-frame imaging. The methods collect biochemical information from metabolites in human heart, and we use the fact that the phosphocreatine/ATP molar ratio in skeletal muscle at rest is higher than that in working heart to demonstrate that localization has been achieved for each investigation. The phosphocreatine/ATP molar ratio in normal human heart has been measured as 1.55 +/- 0.20 (mean +/- SD) (3.5-sec interpulse delay) in six subjects using depth selection and as 1.53 +/- 0.25 (mean +/- SD) in four subjects using spectroscopic imaging. Measurement of this ratio is expected to give a useful and reproducible index of myocardial energetics in normal and pathological states.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bendall M. R., Connelly A., McKendry J. M. Elimination of coupling between cylindrical transmit coils and surface-receive coils for in vivo NMR. Magn Reson Med. 1986 Feb;3(1):157–163. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910030124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley P. A. Noninvasive study of high-energy phosphate metabolism in human heart by depth-resolved 31P NMR spectroscopy. Science. 1985 Aug 23;229(4715):769–772. doi: 10.1126/science.4023711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadian D. G., Hoult D. I., Radda G. K., Seeley P. J., Chance B., Barlow C. Phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance studies on normoxic and ischemic cardiac tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4446–4448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick P. B., Radda G. K., Seeley P. J. Phosphorus NMR studies on perfused heart. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Feb 7;74(3):1256–1262. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91653-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. E., Hanley P. E., Shaw D., Gadian D. G., Radda G. K., Styles P., Bore P. J., Chan L. Localization of metabolites in animals using 31P topical magnetic resonance. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):736–738. doi: 10.1038/287736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove T. H., Ackerman J. J., Radda G. K., Bore P. J. Analysis of rat heart in vivo by phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):299–302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobus W. E., Taylor G. J., 4th, Hollis D. P., Nunnally R. L. Phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance of perfused working rat hearts. Nature. 1977 Feb 24;265(5596):756–758. doi: 10.1038/265756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor H. L., Briggs R. W., Balaban R. S. In vivo 31P nuclear magnetic resonance measurements in canine heart using a catheter-coil. Circ Res. 1984 Aug;55(2):261–266. doi: 10.1161/01.res.55.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komaki R., Wilson J. F., Cox J. D., Kline R. W. Carcinoma of the pancreas: results of irradiation for unresectable lesions. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1980 Feb;6(2):209–212. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(80)90039-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon R. B., Richards J. H. Determination of intracellular pH by 31P magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7276–7278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radda G. K. The use of NMR spectroscopy for the understanding of disease. Science. 1986 Aug 8;233(4764):640–645. doi: 10.1126/science.3726553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Styles P., Scott C. A., Radda G. K. A method for localizing high-resolution NMR spectra from human subjects. Magn Reson Med. 1985 Aug;2(4):402–409. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910020408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. J., Bore P. J., Styles P., Gadian D. G., Radda G. K. Bioenergetics of intact human muscle. A 31P nuclear magnetic resonance study. Mol Biol Med. 1983 Jul;1(1):77–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman G. J., Chance B., Bode H., Maris J., Haselgrove J., Kelley R., Clark B. J., Harken A. H. Diagnosis and therapeutic evaluation of a pediatric case of cardiomyopathy using phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1985 Mar;5(3):745–749. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(85)80405-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]