Abstract
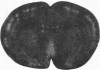
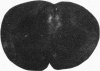
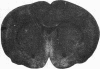
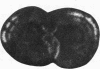
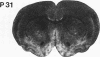
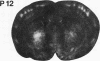
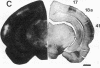
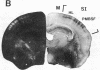
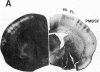
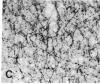
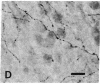
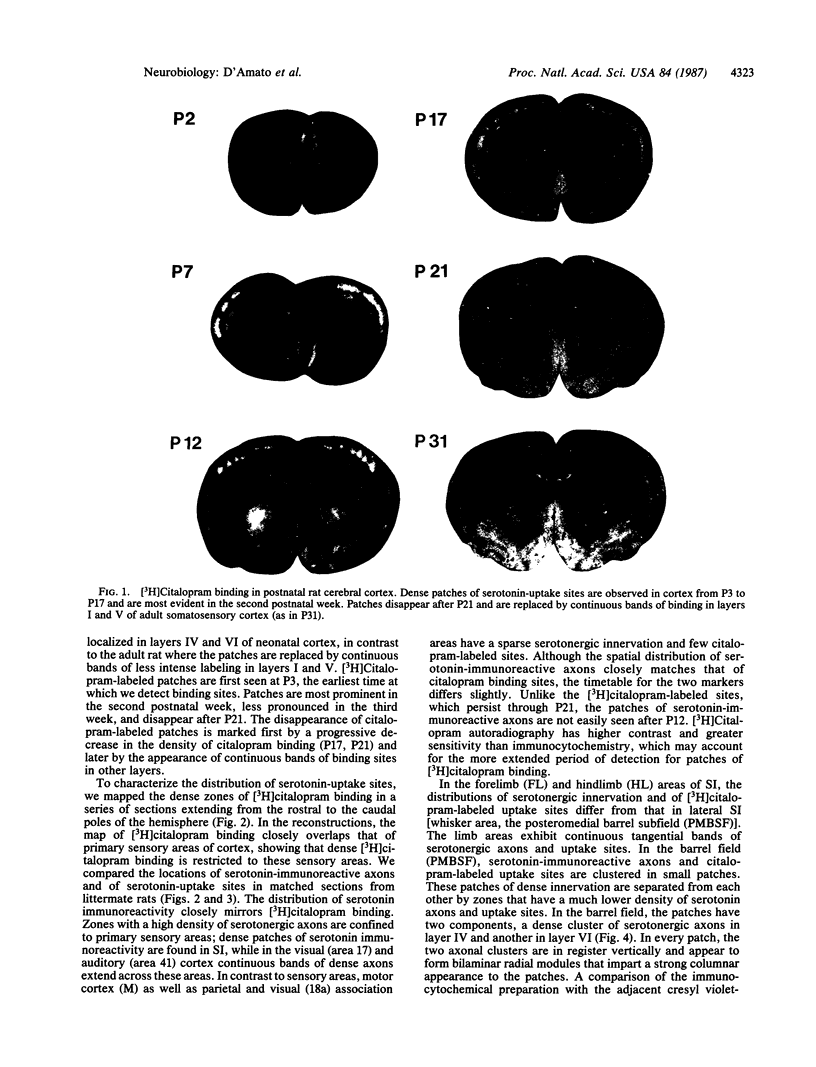
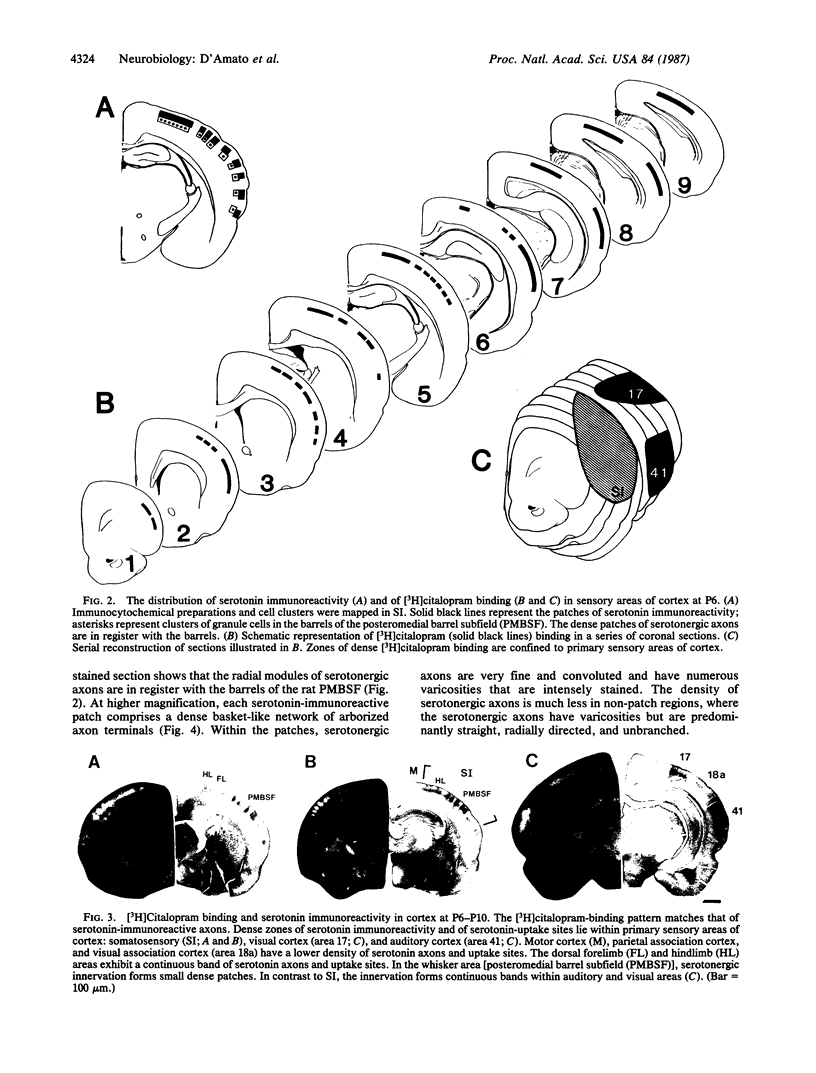
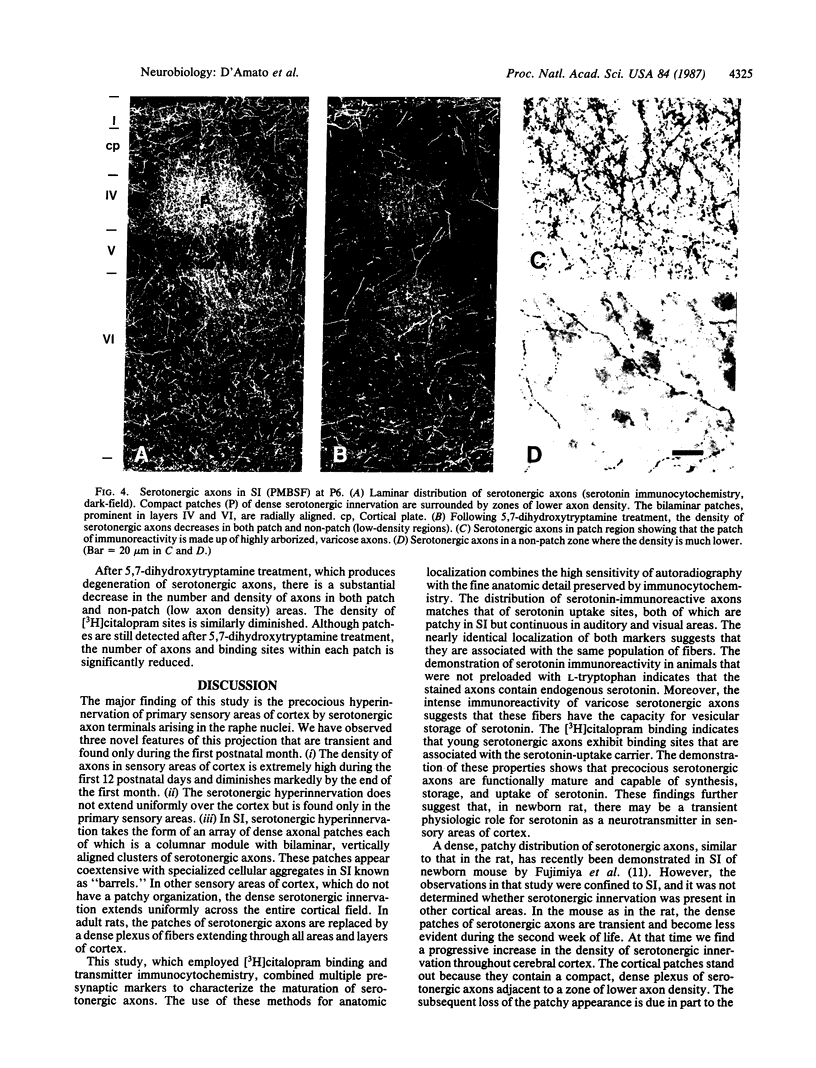
The development of serotonergic innervation to rat cerebral cortex was characterized by immunohistochemical localization of serotonin combined with autoradiographic imaging of serotonin-uptake sites. In neonatal rat, a transient, dense, serotonergic innervation appears in all primary sensory areas of cortex. In somatosensory cortex, dense patches of serotonergic innervation are aligned with specialized cellular aggregates called barrels. The dense patches are not apparent after 3 weeks of age, and the serotonergic innervation becomes more uniform in adult neocortex. This precocious neonatal serotonergic innervation may play a transient physiologic role in sensory areas of cortex or may exert a trophic influence on the development of cortical circuitry and thalamocortical connections.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akers R. M., Killackey H. P. Organization of corticocortical connections in the parietal cortex of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Oct 1;181(3):513–537. doi: 10.1002/cne.901810305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björklund A., Baumgarten H. G., Rensch A. 5,7-Dihydroxytryptamine: improvement of its selectivity for serotonin neurons in the CNS by pretreatment with desipramine. J Neurochem. 1975 Apr;24(4):833–835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blue M. E., Parnavelas J. G. The formation and maturation of synapses in the visual cortex of the rat. II. Quantitative analysis. J Neurocytol. 1983 Aug;12(4):697–712. doi: 10.1007/BF01181531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chubakov A. R., Gromova E. A., Konovalov G. V., Sarkisova E. F., Chumasov E. I. The effects of serotonin on the morpho-functional development of rat cerebral neocortex in tissue culture. Brain Res. 1986 Mar 26;369(1-2):285–297. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90537-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimiya M., Kimura H., Maeda T. Postnatal development of serotonin nerve fibers in the somatosensory cortex of mice studied by immunohistochemistry. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Apr 8;246(2):191–201. doi: 10.1002/cne.902460205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerfen C. R. The neostriatal mosaic. I. Compartmental organization of projections from the striatum to the substantia nigra in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Jun 22;236(4):454–476. doi: 10.1002/cne.902360404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey J. A. Neurotoxic action of halogenated amphetamines. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 12;305:289–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb31530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L. Protein A, avidin, and biotin in immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Nov;29(11):1349–1353. doi: 10.1177/29.11.6172466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innocenti G. M. Growth and reshaping of axons in the establishment of visual callosal connections. Science. 1981 May 15;212(4496):824–827. doi: 10.1126/science.7221566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killackey H. P. Anatomical evidence for cortical subdivisions based on vertically discrete thalamic projections from the ventral posterior nucleus to cortical barrels in the rat. Brain Res. 1973 Mar 15;51:326–331. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90383-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killackey H. P., Leshin S. The organization of specific thalamocortical projections to the posteromedial barrel subfield of the rat somatic sensory cortex. Brain Res. 1975 Mar 28;86(3):469–472. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90897-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidov H. G., Grzanna R., Molliver M. E. The serotonin innervation of the cerebral cortex in the rat--an immunohistochemical analysis. Neuroscience. 1980;5(2):207–227. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90099-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidov H. G., Molliver M. E. An immunohistochemical study of serotonin neuron development in the rat: ascending pathways and terminal fields. Brain Res Bull. 1982 Apr;8(4):389–430. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(82)90077-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidov H. G., Molliver M. E. Immunohistochemical study of the development of serotonergic neurons in the rat CNS. Brain Res Bull. 1982 Jul-Dec;9(1-6):559–604. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(82)90164-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund R. D., Mustari M. J. Development of the geniculocortical pathway in rats. J Comp Neurol. 1977 May 15;173(2):289–306. doi: 10.1002/cne.901730206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary D. D., Stanfield B. B., Cowan W. M. Evidence that the early postnatal restriction of the cells of origin of the callosal projection is due to the elimination of axonal collaterals rather than to the death of neurons. Brain Res. 1981 Jul;227(4):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(81)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakic P. Prenatal development of the visual system in rhesus monkey. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Apr 26;278(961):245–260. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1977.0040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricaurte G., Bryan G., Strauss L., Seiden L., Schuster C. Hallucinogenic amphetamine selectively destroys brain serotonin nerve terminals. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):986–988. doi: 10.1126/science.4023719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice F. L., Gomez C., Barstow C., Burnet A., Sands P. A comparative analysis of the development of the primary somatosensory cortex: interspecies similarities during barrel and laminar development. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Jun 22;236(4):477–495. doi: 10.1002/cne.902360405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C. J., Wu L., Lovenberg W. Methylenedioxymethamphetamine: a potentially neurotoxic amphetamine analogue. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 May 13;124(1-2):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90140-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welker C. Microelectrode delineation of fine grain somatotopic organization of (SmI) cerebral neocortex in albino rat. Brain Res. 1971 Mar 5;26(2):259–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welker C. Receptive fields of barrels in the somatosensory neocortex of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1976 Mar 15;166(2):173–189. doi: 10.1002/cne.901660205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E. L. Identified neurons in mouse Sml cortex which are postsynaptic to thalamocortical axon terminals: a combined Golgi-electron microscopic and degeneration study. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Oct 1;181(3):627–661. doi: 10.1002/cne.901810310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise S. P., Jones E. G. Developmental studies of thalamocortical and commissural connections in the rat somatic sensory cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Mar 15;178(2):187–208. doi: 10.1002/cne.901780202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise S. P., Jones E. G. The organization and postnatal development of the commissural projection of the rat somatic sensory cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1976 Aug 1;168(3):313–343. doi: 10.1002/cne.901680302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolsey T. A., Van der Loos H. The structural organization of layer IV in the somatosensory region (SI) of mouse cerebral cortex. The description of a cortical field composed of discrete cytoarchitectonic units. Brain Res. 1970 Jan 20;17(2):205–242. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Praag H. M. Depression. Lancet. 1982 Dec 4;2(8310):1259–1264. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]