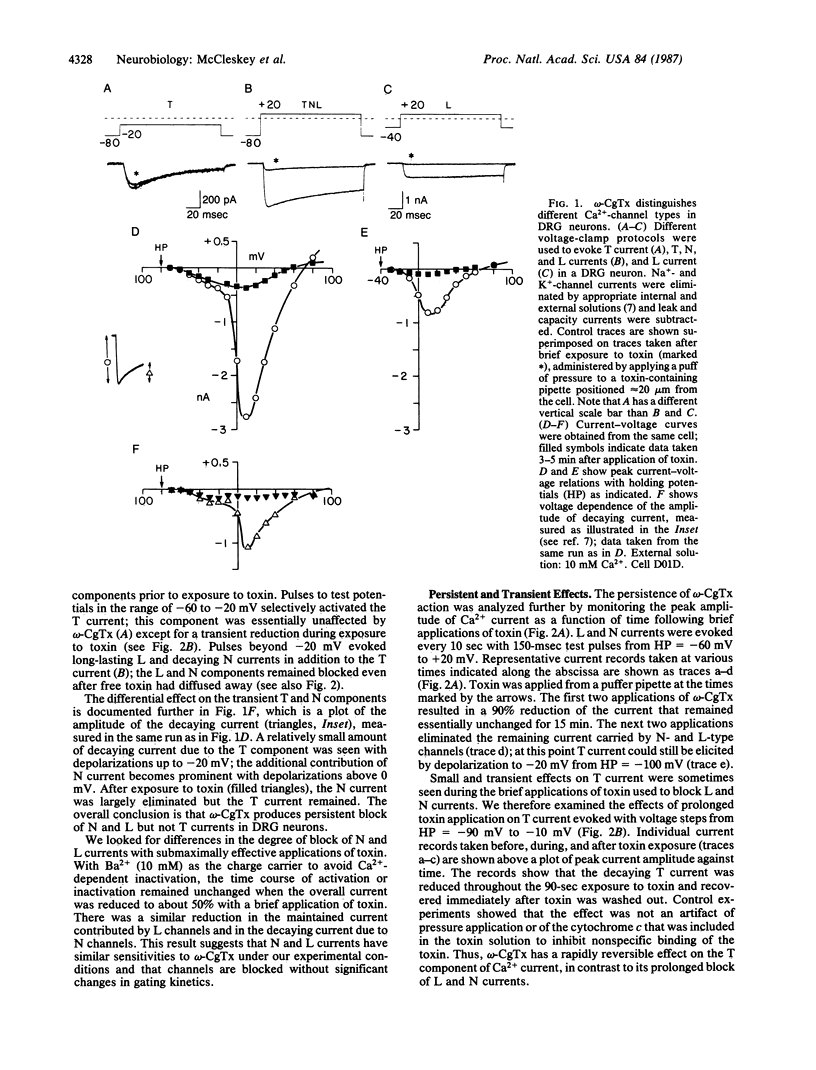
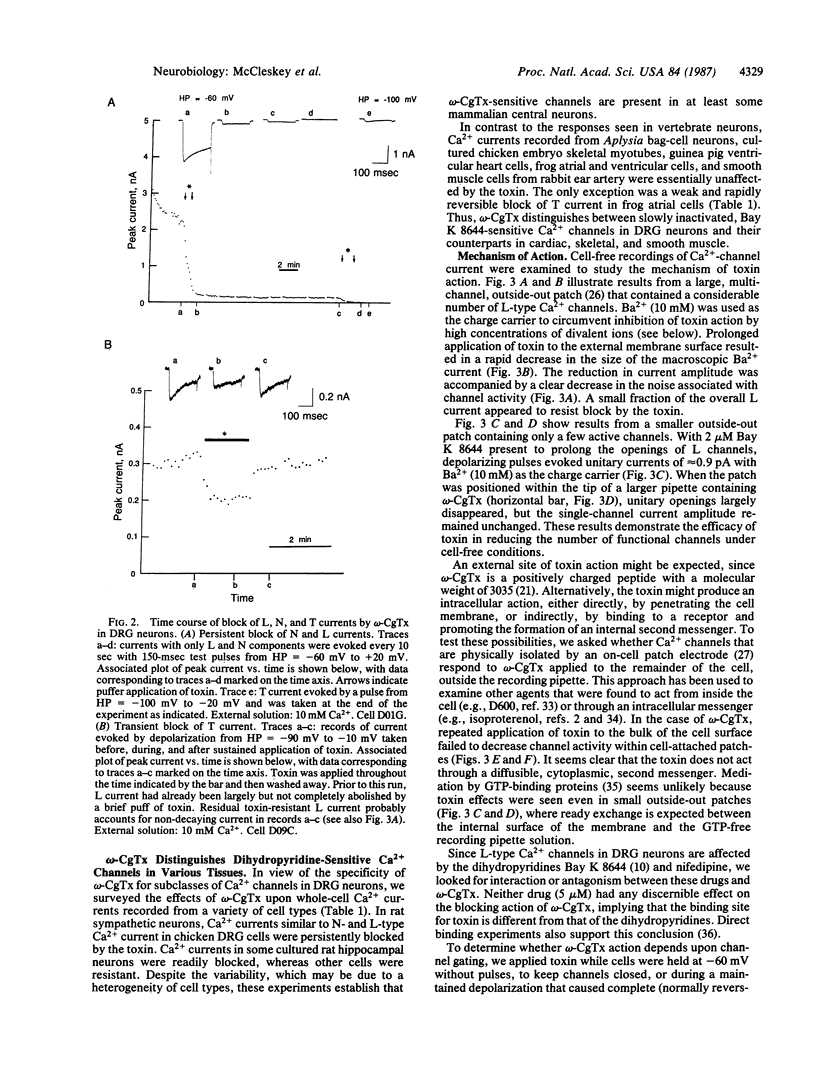
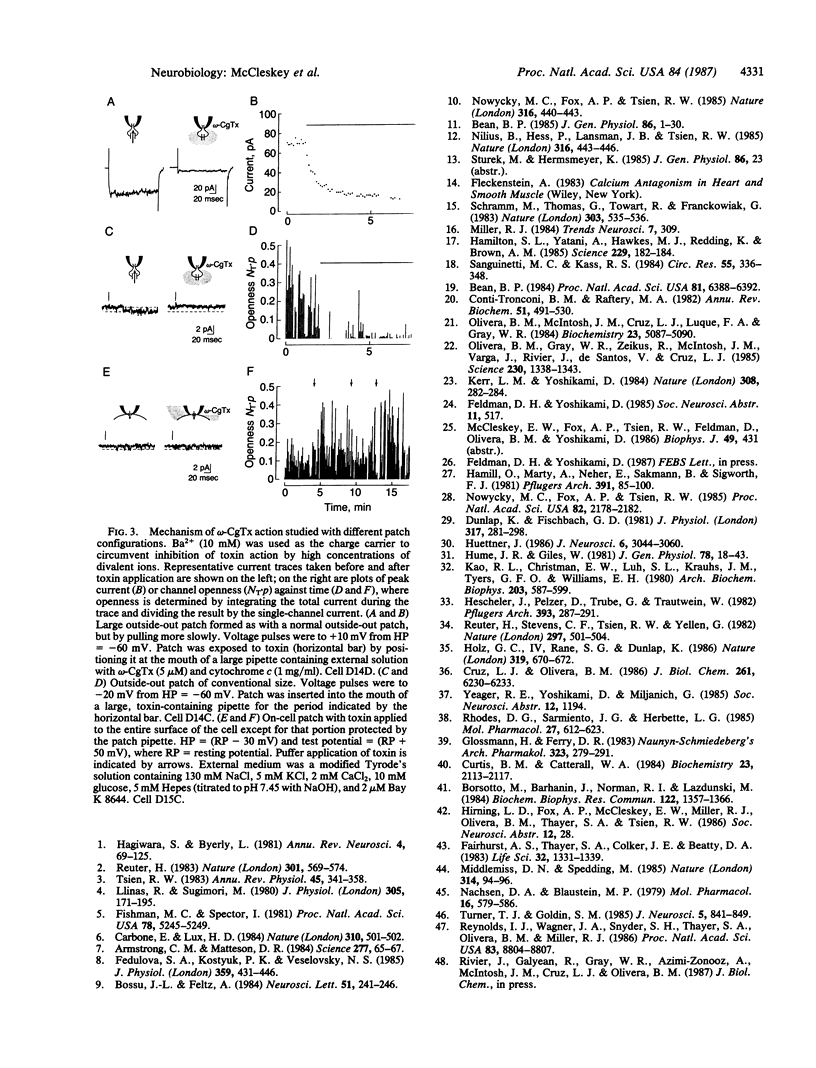
Abstract
Blockade of Ca2+ channels by omega-conotoxin GVIA, a 27 amino acid peptide from the venom of the marine snail Conus geographus, was investigated with patch-clamp recordings of whole-cell and unitary currents in a variety of cell types. In dorsal root ganglion neurons, the toxin produces persistent block of L- and N-type Ca2+ channels but only transiently inhibits T-type channels. Its actions appear to be neuron-specific, since it blocks high-threshold Ca2+ channels in sensory, sympathetic, and hippocampal neurons of vertebrates but not in cardiac, skeletal, or smooth muscle cells. Block occurs through direct interaction of the toxin with an external site closely associated with the Ca2+ channel, without apparent involvement of a second messenger or dependence on channel gating. The tissue and channel-type specificity and the directness and slow reversibility of the block are features that favor use of omega-conotoxin as a tool for purifying particular neuronal Ca2+ channels and defining their physiological function.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean B. P. Nitrendipine block of cardiac calcium channels: high-affinity binding to the inactivated state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6388–6392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Two kinds of calcium channels in canine atrial cells. Differences in kinetics, selectivity, and pharmacology. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Jul;86(1):1–30. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsotto M., Barhanin J., Norman R. I., Lazdunski M. Purification of the dihydropyridine receptor of the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel from skeletal muscle transverse tubules using (+) [3H]PN 200-110. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):1357–1366. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91241-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossu J. L., Feltz A. Patch-clamp study of the tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium current in group C sensory neurones. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Oct 12;51(2):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90558-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Lux H. D. A low voltage-activated, fully inactivating Ca channel in vertebrate sensory neurones. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):501–502. doi: 10.1038/310501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti-Tronconi B. M., Raftery M. A. The nicotinic cholinergic receptor: correlation of molecular structure with functional properties. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:491–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz L. J., Olivera B. M. Calcium channel antagonists. Omega-conotoxin defines a new high affinity site. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6230–6233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Catterall W. A. Purification of the calcium antagonist receptor of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel from skeletal muscle transverse tubules. Biochemistry. 1984 May 8;23(10):2113–2118. doi: 10.1021/bi00305a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairhurst A. S., Thayer S. A., Colker J. E., Beatty D. A. A calcium antagonist drug binding site in skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum: evidence for a calcium channel. Life Sci. 1983 Mar 21;32(12):1331–1339. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedulova S. A., Kostyuk P. G., Veselovsky N. S. Two types of calcium channels in the somatic membrane of new-born rat dorsal root ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Feb;359:431–446. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman M. C., Spector I. Potassium current suppression by quinidine reveals additional calcium currents in neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5245–5249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glossmann H., Ferry D. R. Solubilization and partial purification of putative calcium channels labelled with [3H]-nimodipine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Aug;323(4):279–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00512465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Byerly L. Calcium channel. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:69–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton S. L., Yatani A., Hawkes M. J., Redding K., Brown A. M. Atrotoxin: a specific agonist for calcium currents in heart. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):182–184. doi: 10.1126/science.3160111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Pelzer D., Trube G., Trautwein W. Does the organic calcium channel blocker D600 act from inside or outside on the cardiac cell membrane? Pflugers Arch. 1982 Jun;393(4):287–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00581411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz G. G., 4th, Rane S. G., Dunlap K. GTP-binding proteins mediate transmitter inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium channels. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):670–672. doi: 10.1038/319670a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huettner J. E., Baughman R. W. Primary culture of identified neurons from the visual cortex of postnatal rats. J Neurosci. 1986 Oct;6(10):3044–3060. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-10-03044.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao R. L., Christman E. W., Luh S. L., Krauhs J. M., Tyers G. F., Williams E. H. The effects of insulin and anoxia on the metabolism of isolated mature rat cardiac myocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Sep;203(2):587–599. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. M., Yoshikami D. A venom peptide with a novel presynaptic blocking action. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):282–284. doi: 10.1038/308282a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M. Electrophysiological properties of in vitro Purkinje cell somata in mammalian cerebellar slices. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:171–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlemiss D. N., Spedding M. A functional correlate for the dihydropyridine binding site in rat brain. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):94–96. doi: 10.1038/314094a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachshen D. A., Blaustein M. P. The effects of some organic "calcium antagonists" on calcium influx in presynaptic nerve terminals. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Sep;16(2):576–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilius B., Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. A novel type of cardiac calcium channel in ventricular cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):443–446. doi: 10.1038/316443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Long-opening mode of gating of neuronal calcium channels and its promotion by the dihydropyridine calcium agonist Bay K 8644. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2178–2182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):440–443. doi: 10.1038/316440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivera B. M., Gray W. R., Zeikus R., McIntosh J. M., Varga J., Rivier J., de Santos V., Cruz L. J. Peptide neurotoxins from fish-hunting cone snails. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1338–1343. doi: 10.1126/science.4071055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivera B. M., McIntosh J. M., Cruz L. J., Luque F. A., Gray W. R. Purification and sequence of a presynaptic peptide toxin from Conus geographus venom. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 23;23(22):5087–5090. doi: 10.1021/bi00317a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Calcium channel modulation by neurotransmitters, enzymes and drugs. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):569–574. doi: 10.1038/301569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H., Stevens C. F., Tsien R. W., Yellen G. Properties of single calcium channels in cardiac cell culture. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):501–504. doi: 10.1038/297501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds I. J., Wagner J. A., Snyder S. H., Thayer S. A., Olivera B. M., Miller R. J. Brain voltage-sensitive calcium channel subtypes differentiated by omega-conotoxin fraction GVIA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8804–8807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D. G., Sarmiento J. G., Herbette L. G. Kinetics of binding of membrane-active drugs to receptor sites. Diffusion-limited rates for a membrane bilayer approach of 1,4-dihydropyridine calcium channel antagonists to their active site. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Jun;27(6):612–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanguinetti M. C., Kass R. S. Voltage-dependent block of calcium channel current in the calf cardiac Purkinje fiber by dihydropyridine calcium channel antagonists. Circ Res. 1984 Sep;55(3):336–348. doi: 10.1161/01.res.55.3.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm M., Thomas G., Towart R., Franckowiak G. Novel dihydropyridines with positive inotropic action through activation of Ca2+ channels. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):535–537. doi: 10.1038/303535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson D. G., Williams D. A. Calcium-activated force responses in fast- and slow-twitch skinned muscle fibres of the rat at different temperatures. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:281–302. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W. Calcium channels in excitable cell membranes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:341–358. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner T. J., Goldin S. M. Calcium channels in rat brain synaptosomes: identification and pharmacological characterization. High affinity blockade by organic Ca2+ channel blockers. J Neurosci. 1985 Mar;5(3):841–849. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-03-00841.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



