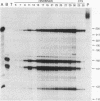
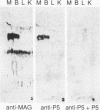
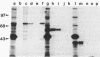
Abstract
The structures of two rat brain-specific 1B236 mRNAs, alternative splice products from a single gene regulated differently during postnatal brain development, were deduced from full-length cDNA clones. The 626- and 582-amino acid-long encoded proteins are indistinguishable from two forms of myelin-associated glycoprotein, a cell adhesion molecule involved in axonal-glial and glial-glial interactions in postnatal brain development, particularly in myelination. The two proteins share a single membrane-spanning domain and a glycosylated N terminus but differ in the structures of their C termini. The N terminus consists of five domains related in sequence to each other and to immunoglobulin-like molecules, especially the neural cell adhesion molecule N-CAM, suggesting a common structure for cell adhesion molecules.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arquint M., Roder J., Chia L. S., Down J., Wilkinson D., Bayley H., Braun P., Dunn R. Molecular cloning and primary structure of myelin-associated glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):600–604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F. E., Battenberg E. L., Milner R. J., Sutcliffe J. G. Immunocytochemical mapping of 1B236, a brain-specific neuronal polypeptide deduced from the sequence of a cloned mRNA. J Neurosci. 1985 Jul;5(7):1781–1802. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-07-01781.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobersen M. J., Hammer J. A., Noronha A. B., MacIntosh T. D., Trapp B. D., Brady R. O., Quarles R. H. Generation and characterization of mouse monoclonal antibodies to the myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG). Neurochem Res. 1985 Apr;10(4):499–513. doi: 10.1007/BF00964654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Cell adhesion molecules in the regulation of animal form and tissue pattern. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:81–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frail D. E., Braun P. E. Two developmentally regulated messenger RNAs differing in their coding region may exist for the myelin-associated glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14857–14862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander D. R., Grumet M., Edelman G. M. Nerve growth factor enhances expression of neuron-glia cell adhesion molecule in PC12 cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):413–419. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampe A., Gobet M., Sherr C. J., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of the feline retroviral oncogene v-fms shows unexpected homology with oncogenes encoding tyrosine-specific protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):85–89. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemperly J. J., Murray B. A., Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. Sequence of a cDNA clone encoding the polysialic acid-rich and cytoplasmic domains of the neural cell adhesion molecule N-CAM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):3037–3041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.3037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoyama Y., Sternberger N. H., Webster H. D., Quarles R. H., Cohen S. R., Richardson E. P., Jr Immunocytochemical observations on the distribution of myelin-associated glycoprotein and myelin basic protein in multiple sclerosis lesions. Ann Neurol. 1980 Feb;7(2):167–177. doi: 10.1002/ana.410070212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D., Quarles R. H., Brady R. O. A radioimmunoassay for the myelin-associated glycoprotein. J Neurochem. 1982 Nov;39(5):1356–1362. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb12578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D., Sato S., Quarles R. H., Inuzuka T., Brady R. O., Tourtellotte W. W. Quantitation of the myelin-associated glycoprotein in human nervous tissue from controls and multiple sclerosis patients. J Neurochem. 1986 Apr;46(4):1086–1093. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb00622.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse J., Mailhammer R., Wernecke H., Faissner A., Sommer I., Goridis C., Schachner M. Neural cell adhesion molecules and myelin-associated glycoprotein share a common carbohydrate moiety recognized by monoclonal antibodies L2 and HNK-1. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):153–155. doi: 10.1038/311153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemke G., Axel R. Isolation and sequence of a cDNA encoding the major structural protein of peripheral myelin. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):501–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90198-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenoir D., Battenberg E., Kiel M., Bloom F. E., Milner R. J. The brain-specific gene 1B236 is expressed postnatally in the developing rat brain. J Neurosci. 1986 Feb;6(2):522–530. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-02-00522.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Bakhit C., Bloom F. E., Sutcliffe J. G., Milner R. J. Brain-specific polypeptide 1B236 exists in multiple molecular forms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2009–2013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martini R., Schachner M. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of neural cell adhesion molecules (L1, N-CAM, and MAG) and their shared carbohydrate epitope and myelin basic protein in developing sciatic nerve. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2439–2448. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner R. J., Sutcliffe J. G. Gene expression in rat brain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5497–5520. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noronha A. B., Ilyas A., Antonicek H., Schachner M., Quarles R. H. Molecular specificity of L2 monoclonal antibodies that bind to carbohydrate determinants of neural cell adhesion molecules and their resemblance to other monoclonal antibodies recognizing the myelin-associated glycoprotein. Brain Res. 1986 Oct 22;385(2):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarles R. H., Barbarash G. R., Figlewicz D. A., McIntyre L. J. Purification and partial characterization of the myelin-associated glycoprotein from adult rat brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 4;757(1):140–143. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarles R. H., Johnson D., Brady R. O., Sternberger N. H. Preparation and characterization of antisera to the myelin-associated glycoprotein. Neurochem Res. 1981 Oct;6(10):1115–1127. doi: 10.1007/BF00964417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarles R. H. Myelin-associated glycoprotein in development and disease. Dev Neurosci. 1983;6(6):285–303. doi: 10.1159/000112356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. Arg-Gly-Asp: a versatile cell recognition signal. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):517–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger N. H., Quarles R. H., Itoyama Y., Webster H. D. Myelin-associated glycoprotein demonstrated immunocytochemically in myelin and myelin-forming cells of developing rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1510–1514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G., Milner R. J., Bloom F. E. Cellular localization and function of the proteins encoded by brain-specific mRNAs. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 2):477–484. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G., Milner R. J., Shinnick T. M., Bloom F. E. Identifying the protein products of brain-specific genes with antibodies to chemically synthesized peptides. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):671–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapp B. D., Quarles R. H., Suzuki K. Immunocytochemical studies of quaking mice support a role for the myelin-associated glycoprotein in forming and maintaining the periaxonal space and periaxonal cytoplasmic collar of myelinating Schwann cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):594–606. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Escobedo J. A., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T. L., Daniel T. O., Tremble P. M., Chen E. Y., Ando M. E., Harkins R. N., Francke U. Structure of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor helps define a family of closely related growth factor receptors. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):226–232. doi: 10.1038/323226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]