Abstract
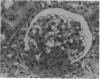
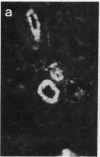
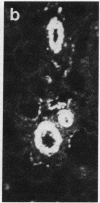
Primate renins (human and monkey) are very similar. We used pure human renin to immunize marmosets (Callithrix jacchus) and thereby produce a chronic blockade of the renin-angiotensinogen reaction. After a control period of 2 months, five male marmosets, on their usual sodium-poor diet, were immunized against pure human renin by three subcutaneous injections of 30 micrograms each, with complete and then incomplete Freund's adjuvant. Three marmosets were injected with adjuvant only and served as controls. Blood sampling and blood pressure measurements were performed weekly. After the third injection, the five marmosets immunized against renin developed a high titer of renin antibodies (50% binding of 125I-labeled human renin at a dilution of greater than or equal to 1:10,000). The antibodies inhibited the enzymatic activity of both marmoset and human renins. At the same time, systolic blood pressure decreased significantly from 125 +/- 13 mm Hg to 87 +/- 8 mm Hg (mean +/- SD; 1 mm Hg = 133 Pa). Plasma renin enzyme activity was undetectable in three animals. Plasma aldosterone decreased significantly. After 1-4 months with low blood pressure, a normal urinary output, and a normal plasma creatinine, the five marmosets became sick and died within one month. At autopsy an immunological renal disease, characterized by the presence of immunoglobulin and macrophage infiltration colocalized with renin, was found. Granulomatous formations, probably due to Freund's adjuvant, could be seen in the lungs and in the kidney. No immunoglobulin was detectable in extrarenal vessels or in other organs. These experiments demonstrate that, in this primate, a chronic blockade of the renin-angiotensin system can be achieved by active immunization against homologous renin, but this blockade is associated with the development of an autoimmune disease localized in the kidney.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burton J., Cody R. J., Jr, Herd J. A., Haber E. Specific inhibition of renin by an angiotensinogen analog: studies in sodium depletion and renin-dependent hypertension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5476–5479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilleri J. P., Phat V. N., Bariety J., Corvol P., Menard J. Use of a specific antiserum for renin detection in human kidney. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Dec;28(12):1343–1346. doi: 10.1177/28.12.7014714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEODHAR S. D., HAAS E., GOLDBLATT H. PRODUCTION OF ANTIRENIN TO HOMOLOGOUS RENIN AND ITS EFFECT OF EXPERIMENTAL RENAL HYPERTENSION. J Exp Med. 1964 Mar 1;119:425–432. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.3.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzau V. J., Brenner A., Wolfsohn S., Haber E. Characterization of antibodies to canine renal renin. Studies of interspecies homology of renin using antibodies as probe. Hypertension. 1982 May-Jun;4(3):341–347. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.4.3.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK M. H. Renin in experimental renal hypertension in monkeys. Circ Res. 1963 Mar;12:241–255. doi: 10.1161/01.res.12.3.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara H., Sakata M., Tomooka Y., Tanaka M., Torisu M. Macrophage locomotion in experimental allergic thyroiditis of the rat. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Mar;22(3):375–383. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GANONG W. F., LEE T. C., VANBRUNT E. E., BIGLIERI E. G. ALDOSTERONE SECRETION IN DOGS IMMUNIZED WITH HOG RENIN. Endocrinology. 1965 Jun;76:1141–1149. doi: 10.1210/endo-76-6-1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galen F. X., Devaux C., Atlas S., Guyenne T., Menard J., Corvol P., Simon D., Cazaubon C., Richer P., Badouaille G. New monoclonal antibodies directed against human renin. Powerful tools for the investigation of the renin system. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):723–735. doi: 10.1172/JCI111488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomoll A. W., Schmid H. E., Jr Urinary excretion of aldosterone in dogs with elevated plasma titers of antirenin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Nov;120(2):326–330. doi: 10.3181/00379727-120-30526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTROFT P. M. Juxtaglomerular cells. Circ Res. 1963 May;2:525–538. doi: 10.1161/01.res.12.5.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELMER O. M. Studies on renin antibodies. Circulation. 1958 Apr;17(4 Pt 2):648–652. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.17.4.648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas E., Goldblatt H., Gipson E. C. Extraction, purification, and acetylation of human renin and the production of antirenin to human renin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Jun;110(3):534–543. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90447-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges J. K., Hearn J. P. Effects of immunisation against luteinising hormone releasing hormone on reproduction of the marmoset monkey Callithrixjacchus. Nature. 1977 Feb 24;265(5596):746–748. doi: 10.1038/265746b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREMEN S. H., WAKERLIN G. E. Renin and antirenin in treatment of long term experimental renal hypertension in the dog. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):99–104. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-21951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Pearson G., Rabson A., Ablashi D. V., Falk L., Wolfe L., Dienhardt F., Rabin H. Antibody reactions to herpesvirus saimiri (HVS)-induced early and late antigens (EA and LA) in HVS-infected squirrel, marmoset and owl monkeys. Int J Cancer. 1973 Jul 15;12(1):270–289. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910120128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMFROM H., HAAS E., GOLDBLATT H. Studies on antirenin. Am J Physiol. 1954 Apr;177(1):55–64. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.177.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAUFER A., TAL C., BEHAR A. J. Effect of adjuvant (Freund's type) and its components on the organs of various animal species; a comparative study. Br J Exp Pathol. 1959 Feb;40(1):1–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel J. B., Wood J., Hofbauer K., Corvol P., Menard J. Blood pressure effects of renin inhibition by human renin antiserum in normotensive marmosets. Am J Physiol. 1984 Mar;246(3 Pt 2):F309–F316. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.3.F309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMID H. E., Jr, GRAHAM L., BRENNAN B. B., WAKERLIN G. E. Renin concentration of normotensive and hypertensive dog kidney: its relation to serum antirenin titer. Circ Res. 1962 Apr;10:696–703. doi: 10.1161/01.res.10.4.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMID H. E., Jr, GRAHAMLA Juxtaglomerular cell changes in dogs with antirenin titers. Circ Res. 1962 Nov;11:853–856. doi: 10.1161/01.res.11.5.853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skeggs L. T., Kahn J. R., Levine M., Dorer F. E., Lentz K. E. Chronic one-kidney hypertension in rabbits. II. Evidence for a new factor. Circ Res. 1976 Sep;39(3):400–406. doi: 10.1161/01.res.39.3.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAKERLIN G. E. Antibodies to renin as proof of the pathogenesis of sustained renal hypertension. Circulation. 1958 Apr;17(4 Pt 2):653–657. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.17.4.653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigle W. O. Analysis of autoimmunity through experimental models of thyroiditis and allergic encephalomyelitis. Adv Immunol. 1980;30:159–273. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60196-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser R. A., Johnson A. G., Hoobler S. W. The effect of antirenin on the blood pressure of the rat with exprimental renal hypertension. Lab Invest. 1969 Apr;20(4):326–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. M., Gulati N., Forgiarini P., Fuhrer W., Hofbauer K. G. Effects of a specific and long-acting renin inhibitor in the marmoset. Hypertension. 1985 Sep-Oct;7(5):797–803. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.7.5.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. M., Gulati N., Michel J. B., Hofbauer K. G. Two-kidney, one clip renal hypertension in the marmoset. J Hypertens. 1986 Apr;4(2):251–254. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198604000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]