Figure 5. Lack of GABA-mediated inhibition to dopamine neurons in Cx36 KO mice.
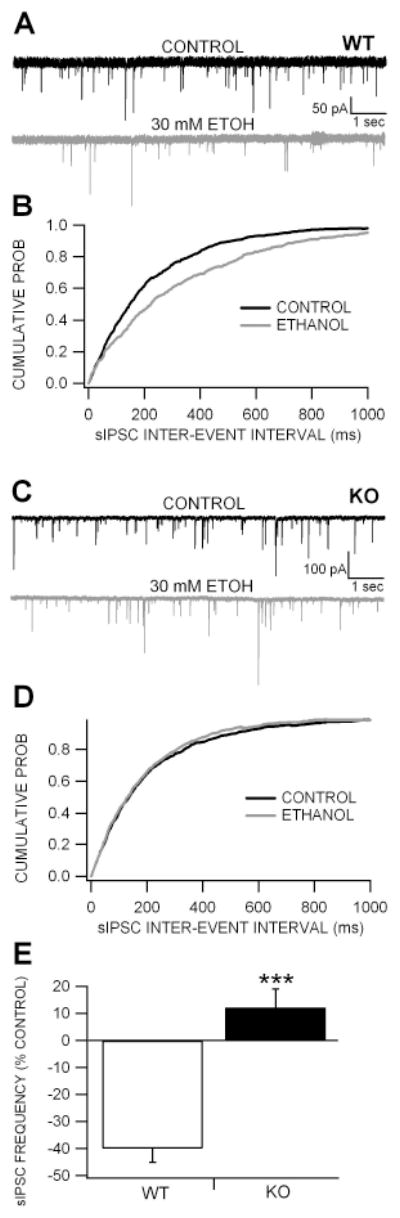
(A) These are representative 10 sec traces of DA neuron sIPSCs recorded in a WT mouse in the presence of APV and CNQX with QX-314 in the pipette to prevent spike events. Superfusion of 30% ethanol reduced sIPSCs approximately 50%. (B) This graph shows the averaged cumulated probability inter-event interval plots for ethanol effects on sIPSCs in WT mice. Note that ethanol shifts the curve to right confirming a slowing in frequency. (C) These are representative traces of DA neuron sIPSCs recorded in a KO mouse. Superfusion of 30 mM ethanol did not affect sIPSC frequency. (D) This graph shows the averaged cumulated probability inter-event interval plots for ethanol effects on sIPSCs in Cx36 KO mice. Note that ethanol has little effect on DA neuron sIPSC frequency. (E) This graph compares the effects of 30 mM ethanol on DA neuron sIPSC frequency in KO vs WT mice. While ethanol significantly reduced sIPSC frequency in WT mice, DA neurons in KO mice were significantly less sensitive to ethanol than WT mice.
