Abstract
We assessed the role of promotoras—briefly trained community health workers—in depression care at community health centers. The intervention focused on four contextual sources of depression in underserved, low-income communities: underemployment, inadequate housing, food insecurity, and violence. A multi-method design included quantitative and ethnographic techniques to study predictors of depression and the intervention’s impact. After a structured training program, primary care practitioners (PCPs) and promotoras collaboratively followed a clinical algorithm in which PCPs prescribed medications and/or arranged consultations by mental health professionals and promotoras addressed the contextual sources of depression. Based on an intake interview with 464 randomly recruited patients, 120 patients with depression were randomized to enhanced care plus the promotora contextual intervention, or to enhanced care alone. All four contextual problems emerged as strong predictors of depression (chi square, p < .05); logistic regression revealed housing and food insecurity as the most important predictors (odds ratios both 2.40, p < .05). Unexpected challenges arose in the intervention’s implementation, involving infrastructure at the health centers, boundaries of the promotoras’ roles, and “turf” issues with medical assistants. In the quantitative assessment, the intervention did not lead to statistically significant improvements in depression (odds ratio 4.33, confidence interval overlapping 1). Ethnographic research demonstrated a predominantly positive response to the intervention among stakeholders, including patients, promotoras, PCPs, non-professional staff workers, administrators, and community advisory board members. Due to continuing unmet mental health needs, we favor further assessment of innovative roles for community health workers.
Keywords: Mental health, Health services accessibility, Primary health care, Community health aides, Community health centers
Introduction
Substantial barriers to adequate services affect people with mental health problems [1]. When people seek mental health services, they tend to do so in the primary care sector [2, 3]. However, primary care practitioners (PCPs) often do not recognize mental health disorders, do not provide adequate treatment, and report difficulties in responding to patients’ psychosocial needs [1, 4–6].
We report here the results of an intervention in which promotoras (community health workers) assisted in the identification and treatment of depression within community health centers (CHCs). Our aims were: (1) to educate promotoras about depression; (2) to implement and evaluate a procedure for promotoras to identify depression among patients who sought primary care services; (3) to implement and evaluate a procedure by which patients identified with depression received treatment through the collaboration of promotoras and PCPs; and (4) to assess the value achieved by this intervention, as determined by outcome measures and as perceived by key stakeholders. The main research question, focusing on the fourth aim, asked: To what extent can an intervention that uses promotoras to address social contextual sources of depression achieve improved outcomes in patients and acceptance by stakeholders?
Our project focused specifically on efforts by promotoras to address four sources of depression in patients’ social context: underemployment, inadequate housing, food insecurity, and violence. We used a multi-method research design, with quantitative methods to determine the predictors of depression and the impact of the intervention on outcomes, and ethnographic methods to assess the intervention’s implementation and impact as perceived by key stakeholders. To our knowledge, our project was the first multi-method evaluation of promotoras focusing on depression among patients in primary care.
Diagnosing and Improving Services for Depression in Primary Care
Screening for Mental Disorders and Intervention Trials
When patients who present to primary care settings receive screening, the prevalence of depression generally ranges from 20 to 50%. These prevalence rates vary considerably according to setting, method of assessment, language used, and race/ethnicity [7–12].
Intervention trials for psychiatric disorders in large primary care settings such as managed care organizations [13–18] have included improved depression treatment by systems modification or quality improvement programs to foster evidence-based care [19–23]. In the Partners in Care study, guideline-informed interventions resulted in improved quality of care, quality of life, clinical outcomes, and employment retention; cost effectiveness analysis also showed substantial benefits [24–26]. Enhanced depression care for minorities has led to long-term improvements in outcomes [27]. Most intervention strategies include guideline-informed “best practices” for recognition and treatment of depression [28–32]. Recent intervention research demonstrates the value of enhanced, collaborative approaches [33–41]. Several studies substantiate the efficacy of collaborative interventions for depression in primary care for ethnically diverse and underserved populations [42–48]. Nevertheless, disparities remain in the care of patients treated in primary care settings, especially for minorities [49].
Promotoras and the Challenges of Underserved Areas
Promotoras have become a widely adopted work role in underserved communities [50, 51]. Our definition of promotora refers to her or his role as a trusted community member, who provides health-related services for underserved individuals in community settings and helps fortify the relationship between patients and PCPs [52–55]. Community health workers are known by nearly 30 titles such as: promotoras de salud (Spanish for “health promoters”), community health advocates, outreach workers, indigenous health workers, lay health educators, and community health aides [56, 57].
Other than mental health services, promotoras have performed a variety of duties: first aid, nutrition education, blood pressure screenings, midwifery, translation, environmental work, patient transportation, case management, breast cancer screening, diabetes education, asthma management, social work, and peer counseling [58–61]. The Diabetes Initiative of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation has included promotoras focusing in part on depression [62, 63]. Promotoras may help PCPs to identify patients’ health needs and to consider the cultural relevance of treatments provided [64].
Researchers have assessed the efficacy of promotora interventions focusing on heart disease [65], diabetes [66], tobacco [67], general chronic diseases [68], breast and cervical cancer [69, 70], and nutrition [71]. These studies generally showed favorable intervention effects. Regarding applicability to diverse cultures and ethnicities, studies in Panama [72], Uganda [73], and Chile [74] showed positive results from training non-physicians for depression interventions in rural settings. A curriculum “toolbox” was developed for promotoras to use for English and Spanish-speaking diabetic patients with depression [75].
Public Health, Risk Factors for Mental Disorders, and Contextual Conditions
Efforts by NIMH, the Surgeon General, the World Health Organization, the President’s New Freedom Commission on Mental Health, and the Institute of Medicine have emphasized interventions to impact risk factors for mental illness [76–79]. Social risk factors for depression include domestic violence, traumatic life events, marital discord, unmarried status, job stress, underemployment, poverty, and social isolation [80–84]. We documented the relationship of contextual problems, such as violence, to depression and other mental disorders among Latino and American Indian patients seen in primary care settings [85–87]. Long-term outcomes may improve through reducing social risk factors for stressful life events [88]. The “behavioral model for vulnerable populations” also has addressed some of these contextual influences on health outcomes, for example regarding issues of violence as well as financial, nutritional, and housing insecurity among homeless women [89–91].
Conceptual Framework, Objectives, and Significance
In recent research, social contextual conditions such as underemployment [92–97], inadequate housing [98–101], and food insecurity [102–109] figure as important risk factors in depression. Depression-causing violence, another risk factor, can arise in the family, between intimate partners, in child abuse, and or in the community [110–119].
Remarkably little research has examined the impact of interventions designed to modify such contextual difficulties, especially in primary care. In non-medical settings, experimental or quasi-experimental research has shown that contextual interventions directed toward underemployment [120–122], inadequate housing [123–126], domestic violence [127], and poverty [128] exerted favorable effects on mental health outcomes. From an extensive review, however, we located only one intervention trial that specifically addressed contextual problems in primary care. For a randomized urban trial, Miranda et al. compared group cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) alone, versus CBT plus clinical care management. In the CBT plus clinical care management group, social work care managers addressed problems in housing, employment, recreation, and interpersonal relationships, which resulted in better mental health outcomes [129].
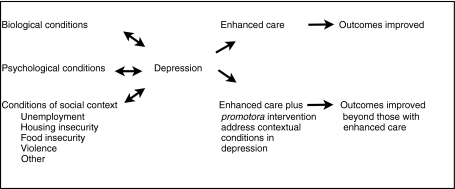
Figure 1 shows our conceptual framework. Adopting Engel’s “biopsychosocial” approach [130, 131], we considered the importance of biological and psychological conditions in the etiology and treatment of depression. However, we also emphasized social conditions as causative elements in depression, recognizing that contextual conditions not only can affect depression but that depression can contribute to worsening social conditions, especially in such arenas as unemployment, housing insecurity, food insecurity, and violence. For that reason, we depicted the relationships between depression and contextual conditions as bidirectional.
Fig. 1.
Conceptual framework for the proposed research
Methods
Research Setting
At the time of the study, New Mexico ranked 47th among the 50 states in personal income per capita ($24,291) [132], 3rd in persons below the poverty level (18.4%) [133], 2nd in lack of health insurance (22.1%) [134], and 1st to 11th in underemployment, reflecting the economy’s volatility [135, 136]. Latinos and American Indians made up 51.6% of the state’s population [136]. The state’s drug- and alcohol-induced death rates per population ranked 1st and 2nd highest respectively, the suicide death rate 5th highest, and the homicide death rate 6th highest in the United States [137].
Recruitment of Promotoras and Educational Approach
We initially hired two applicants: a receptionist at a CHC and a security guard. Both promotoras, bilingual in English and Spanish, were high school graduates with roots in the community. When 1 of the original promotoras left because of major health and financial problems, we recruited another promotora.
Five training sessions took place at each of the two participating CHCs. A prior mentorship program served as a model for the educational program [138]. Conferences for promotoras, PCPs, and other staff members took place over the lunch hour at the CHCs. Promotoras also took part in an educational program on depression for community health workers.
Assessment Instruments
Demographic Data
An initial instrument assessed age, gender, income, employment status, socioeconomic status, marital status and children, immigration status, and number of years in the United States.
Mental Health Disorders
We used the extensively validated Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ), whose 16 questions identified threshold DSM-IV diagnoses of major depressive disorder, panic disorder, other anxiety disorder, and bulimia nervosa, and subthreshold diagnoses (encompassing fewer symptoms than required for specific DSM-IV disorders) of other depressive disorder, probable alcohol abuse or dependence, somatoform disorder, and binge eating disorder [139–147]. We added a section assessing drug abuse or dependence, patterned on the PHQ alcohol section [148]. For Spanish-speaking patients, we used the Spanish version of the PHQ, previously validated in primary care settings [149, 150].
Contextual Risk Factors
Additional instruments elicited information about marital or partnership change, geographical relocation, job loss, job change, housing problems, and food insecurity. We used the Trauma Screening Questionnaire and StaT instruments to measure trauma exposure and intimate partner violence [151, 152].
Pre-Test
We pre-tested the PHQ instrument with 150 patients and then made limited modifications so the intake interview took less than 1 h. No modifications in the Spanish PHQ proved necessary for the local setting.
Promotora-PCP Consultation
Before patients entered the study, we provided the PCPs with clinical guidelines on “best practice” diagnosis and treatment of depression [153]. The medications and frequency of recommended follow-up in the guidelines were modified slightly, based on medications available in the CHCs’ formulary and practitioners’ schedules. For each patient recruited, the PCP received the PHQ results from the promotora. The PCP did not receive reminders or inducements, with a rationale of restricting the experimental variable to the promotora-based algorithm described below.
Subjects, Sample Size
Recruitment
The promotoras recruited patients from the list of scheduled patients for each day, using a table of random numbers to determine which patients to approach for participation in the study. We randomized recruitment activities at the CHCs by day of the week and by morning versus afternoon sessions. To ensure adequate follow-up, patients were informed at intake that they would be invited to participate in one or more follow-up interviews. Re-contact information was collected on all participants, including the names, addresses, and phone numbers of at least two other relatives or close friends who would know the subjects’ whereabouts.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Patients were included if they met the criteria for a diagnosis of depression on the PHQ. The exclusion criteria were: (a) suicidal or homicidal ideation (emergency care was provided to such patients); (b) acute bereavement; (c) psychotic or bipolar depression; (d) age under 18; and (e) general health status precluding the interview.
Sample Size Determination, Statistical Power
In determining sample size, we made the following assumptions. The significance level was set at 0.05 and the desired statistical power at 0.80. Based on prior interventions, we anticipated medium effect size (0.3) for the intervention. We assumed conservatively a 10% prevalence of depression. With an anticipated attrition rate of 15%, a sample size of 1,040 respondents would detect all relevant effects of the intervention [154–156]. Because the prevalence of depression observed in the study itself was higher, 28%, we were able to reduce the total number of enrolled subjects from 1,040 to 464. From the intake, we recruited 120 patients with depression.
Intervention
Intervention Algorithm
We developed an algorithm that the promotoras and PCPs applied collaboratively (Fig. 2). If the PHQ indicated a depression diagnosis, the promotoras provided this information to the PCP, who initiated treatment with medication and/or arranged psychiatric or psychological consultation as warranted. The promotoras tried to address problems in four contextual areas: underemployment, inadequate housing, food insecurity, and violence. PCPs and promotoras communicated orally at least monthly. The algorithm also included follow-up PHQ assessments at 6 months and 12 months after diagnosis to determine changes in depression.
Fig. 2.
Primary care practitioner–promotora algorithm
When the intake process revealed a contextual problem, the promotoras offered to seek a resolution. Promotoras used a resource directory that the CHC system had developed previously and which the research team updated and expanded. For instance, if a depressed patient reported a problem of unemployment or unstable employment, the promotora contacted one or more community based organizations that dealt with vocational training, rehabilitation, tracking jobs, advising about job interviews, and similar employment-related services. If a patient reported a problem of insecure housing or homelessness, the promotora helped contact organizations that focused on housing. For problems of food insecurity, the promotora facilitated contacts with churches, food banks, and government agencies that provided food stamps or helped clients obtain suitable foods. If a patient suffered from violence, the promotora helped seek assistance from shelters, programs focusing on abuse, etc. The promotora tracked the referral through monthly follow-up telephone calls with the patient and the organizations.
Promotora Intervention Contact Form
After each encounter with a patient, the promotoras wrote case notes and completed a form that specified the referrals and other actions taken to address contextual sources of depression that the patient reported.
Intervention Implementation
As in prior intervention trials such as the Partners in Care study, we randomized CHCs rather than patients within CHCs. We chose this approach to avoid the well documented problem of “contamination,” which refers to an intervention’s impact on control subjects at a clinical site [23–27].
Therefore, the algorithm was implemented at one “experimental” CHC in the network. At a “control” CHC, depression also was assessed by the PHQ and the findings were provided to PCPs, but the promotora algorithm was not implemented. At both CHCs, depression care was enhanced through the education program described above. We determined which CHC received the promotora algorithm by a three out of five heads or tails coin flip. If the promotora intervention achieved positive outcomes at the experimental CHC, the design called for its later implementation at the control CHC (Table 1).
Table 1.
Research design for the promotora intervention
| Intake interview by promotoras | PCP Dx & Rx | Promotora algorithm (employment, housing, food, violence) | 6-month assessment | 12-month assessment | Promotora algorithm (housing, food, employment, violence) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental CHC | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Control CHC | X | X | X | X | (X) |
PCP primary care practitioner, Dx diagnosis, Rx treatment
Quantitative Data Analysis
Predictors of Depression
We first examined the univariate distributions of depression and other mental health disorders, risk factors, and contextual problems. Depression was treated as a dichotomous dependent variable (present or absent), based on the standard PHQ scoring scheme. Independent variables included risk factors and contextual problems. Demographic characteristics and CHC site were intervening variables. Missing values for independent variables were imputed via a multiple imputation routine [157]. Multiple logistic regression determined the degree to which the independent variables predicted depression, controlling for intervening variables. We calculated odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals. Although not a standard use of the PHQ, we created a variable to indicate severity of depression by counting depressive symptoms and performed multiple regression analysis on this variable as well.
Quantitative Assessment of the Intervention’s Impact
The unit of analysis was the individual patient. A two by two chi-square analysis assessed the effectiveness of the intervention for depression. Differences in other measures between the experimental and control CHCs were assessed with chi-square analyses (for nominal data) or multivariate analysis of variance (for interval data). We also assessed outcomes for patients served by each promotora through chi-square analyses. To determine the statistical significance of findings, we used two-tailed tests and a significance level of 0.05.
Multivariate logistic regression models determined the relative importance of the intervention versus other key variables in predicting change in depression and other outcome indicators. Independent variables significantly associated with depression in the univariate and bivariate analyses were selected for the multivariate regression modeling procedures. For this analysis, improvement in depression was operationally defined as a transition from presence to absence, as assessed by the PHQ instrument.
To address non-independence of repeated observations for the same subjects, we used random effects in subjects and fixed effects in time [157]. Data were analyzed with SAS software (Cary, NC).
Ethnographic Assessment
Participant Observation
Four ethnographers completed more than 200 h of participant observation at the two CHC sites. The ethnographers “shadowed” the promotoras as they went about their workdays. We randomized observation periods by ethnographer, promotora observed, CHC site, day of the week, and time of day (morning or afternoon shift).
Semi-Structured Interviews
Interviews with stakeholders (patients, PCPs, and promotoras) permitted assessment of intervention implementation, barriers and facilitators that affected fidelity to the algorithm, and perceived value of the intervention. Interview guides followed a standardized structure, tailored to capture the experiences of each respondent group. The ethnographers interviewed the promotoras and a random selection of PCPs, patients, non-professional staff members, CHC administrators, and community board members. In all, the ethnographers conducted 35 semi-structured interviews.
Ethnographic Data Analysis
The ethnographers took extensive field notes and transcribed all interviews, inputting both sets of documents into NVivo [158], a software package for iterative coding and data analysis. They also reviewed the promotora intervention contact forms. Qualitative analysis identified common themes across and within respondent groups. Data were analyzed through iterative codings: “open coding” to uncover general themes, ideas, and issues; and “focused coding” to determine which of the themes, ideas, and issues were repeated often and which represented unusual or particular concerns [159].
To triangulate the data analysis, the ethnographers checked the consistency of information collected at different times and through different methods. This work compared observational data with medical chart data and interview data, checked for consistency in what respondents said about the intervention over time, and compared perspectives of the stakeholder groups [160].
Results
Identification, Correlates, and Predictors of Depression
Table 2A presents the prevalences of depression and other mental health disorders at baseline. The PHQ instrument revealed depression in 28% of the patients screened. Somatoform disorders and anxiety disorders (including panic disorder) also occurred frequently, 16 and 17% respectively.
Table 2.
Prevalence of mental disorders and predictors of depression
| Diagnosis | Present N (%) |
Absent N (%) |
Total N† |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. Mental disorders | |||
| Major depression | 82 (18) | 382 (82) | 464 |
| Other depression | 48 (10) | 416 (90) | 464 |
| Panic disorder | 29 (6) | 431 (94) | 460 |
| Other anxiety | 52 (11) | 403 (89) | 455 |
| Alcohol disorder | 40 (9) | 419 (91) | 459 |
| Somatoform disorder | 74 (16) | 390 (84) | 464 |
| Bulimia nervosa | 4 (1) | 453 (99) | 457 |
| Binge eating disorder | 12 (3) | 445 (97) | 457 |
| Depressed N (%) |
Not depressed N (%) |
Chi-square (p value) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| B. Demographic characteristics and depression | |||
| Gender | (0.07) | ||
| Male | 38 (23) | 127 (77) | |
| Female | 92 (31) | 207 (69) | |
| Marital status | (0.25) | ||
| Married | 53 (25) | 156 (75) | |
| Not-married | 77 (30) | 178 (70) | |
| Ethnicity | (0.13) | ||
| Hispanic | 118 (29) | 284 (71) | |
| Non-Hispanic | 12 (20) | 48 (80) | |
| Citizenship | (0.05) | ||
| US citizen | 79 (26) | 226 (74) | |
| Non-US citizen | 49 (35) | 92 (65) | |
| Age | (0.04) | ||
| Less than 30 years | 30 (29) | 74 (71) | |
| Between 30 and 59 years | 85 (31) | 187 (69) | |
| 60 years and over | 15 (17) | 73 (83) | |
| C. Contextual risk factors and depression | |||
| Marital status change | (0.18) | ||
| Present | 17 (36) | 30 (64) | |
| Absent | 107 (27) | 290 (73) | |
| Move | (0.01) | ||
| Present | 24 (41) | 34 (59) | |
| Absent | 100 (26) | 287 (74) | |
| Job change | (0.02) | ||
| Present | 39 (37) | 66 (63) | |
| Absent | 85 (25) | 255 (75) | |
| Job loss | (0.001) | ||
| Present | 35 (43) | 46 (57) | |
| Absent | 89 (25) | 273 (75) | |
| Housing problem | (<.0001) | ||
| Present | 52 (56) | 41 (44) | |
| Absent | 71 (20) | 280 (80) | |
| Food problem | (<.0001) | ||
| Present | 44 (61) | 28 (39) | |
| Absent | 79 (21) | 292 (79) | |
| Employment | (0.91) | ||
| Employed | 67 (28) | 171 (72) | |
| Unemployed | 62 (28) | 162 (72) | |
| D. Traumatic life events and depression | |||
| Major accident or disaster | (0.88) | ||
| Present | 28 (29) | 70 (71) | |
| Absent | 93 (28) | 242 (72) | |
| General violence | (0.002) | ||
| Present | 29 (43) | 38 (57) | |
| Absent | 91 (25) | 274 (75) | |
| Intimate partner violence/threat | (<.0001) | ||
| Present | 44 (44) | 20 (57) | |
| Absent | 76 (23) | 255 (77) | |
| Adult sexual violence | (0.04) | ||
| Present | 15 (43) | 20 (57) | |
| Absent | 105 (27) | 289 (73) | |
| Childhood sexual violence | (0.01) | ||
| Present | 20 (43) | 26 (57) | |
| Absent | 98 (26) | 283 (74) | |
| B‡ | Standard error of B | Odds ratio | Confidence interval†† | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower bound | Upper bound | ||||
| E. Logistic regression analysis for predictors of depression | |||||
| Demographic characteristics | |||||
| Male | −0.32 | 0.26 | 0.73 | 0.43 | 1.22 |
| Marrieda | 0.00 | 0.25 | 1.00 | 0.61 | 1.65 |
| Latinob | 0.64 | 0.39 | 1.90 | 0.88 | 4.11 |
| US citizenc | −0.27 | 0.27 | 0.76 | 0.45 | 1.29 |
| Age | 0.00 | 0.01 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.02 |
| Contextual risk factors | |||||
| Marital status change | −0.10 | 0.43 | 0.90 | 0.39 | 2.11 |
| Move | 0.32 | 0.38 | 1.37 | 0.65 | 2.88 |
| Job change | 0.19 | 0.33 | 1.20 | 0.63 | 2.32 |
| Job loss | 0.29 | 0.36 | 1.33 | 0.66 | 2.72 |
| Housing problem** | 0.88 | 0.33 | 2.40 | 1.26 | 4.58 |
| Food problem* | 0.88 | 0.36 | 2.40 | 1.18 | 4.87 |
| Employedd | 0.12 | 0.25 | 1.12 | 0.69 | 1.84 |
| Traumatic life event | |||||
| Major accident or disaster | −0.16 | 0.30 | 0.85 | 0.47 | 1.54 |
| General violence | 0.39 | 0.35 | 1.48 | 0.74 | 2.97 |
| Intimate partner violence/threat | 0.60 | 0.33 | 1.83 | 0.97 | 3.46 |
| Adult sexual violence | −0.22 | 0.48 | 0.80 | 0.31 | 2.05 |
| Childhood sexual violence | 0.55 | 0.37 | 1.73 | 0.84 | 3.58 |
* p < .05
** p < .01
†Missing data are excluded
‡B is the unstandardized regression coefficient
††95% confidence intervals are shown. N = 464
aReference category is not married
bReference category is non-Latino
cReference category is non-US citizen
dReference category is unemployed
We used chi-square tests to examine associations between depression and demographic characteristics, contextual risk factors, and traumatic life events (Table 2B–D). A higher proportion of non-US citizens was depressed, compared to US citizens (35 vs. 26%). Subjects who experienced a recent move, job change, or job loss were much more likely to manifest depression. A much higher proportion of subjects who reported difficulties paying for housing or food was depressed. Depression was significantly more prevalent among subjects who had experienced traumatic life events, including general violence, intimate partner violence or threat, adult sexual violence, or childhood sexual violence.
With multiple logistic regression analysis, we examined the relative importance of demographic characteristics, contextual risk factors, and traumatic life events in predicting depression (Table 2E). From this analysis, significant predictors of depression included inadequate housing and food insecurity.
Implementation and Impact of the Intervention
Quantitative Assessment of Outcomes
Subjects in the experimental and control groups did not differ significantly by gender, marital status, marital status, employment, housing problems, food problems, or violence; subjects at the experimental site were slightly older and at the control site slightly more Hispanic in ethnicity (data not shown).
Chi-square analyses did not show a significant effect of the intervention on depression between baseline and 6 months, between baseline and 12 months, or between 6 and 12 months. In the multiple logistic regression analysis, which took into account the pertinent demographic and contextual variables, the intervention effect also did not reach significance in (Table 3). Multiple regression analysis using the measure of depression severity based on symptom count led to substantially similar results (data not shown).
Table 3.
Logistic regression analysis for impact of intervention on depression†
| B‡ | Standard error of B | Odds ratio | Confidence interval†† | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower bound | Upper bound | ||||
| Intervention | |||||
| Group (Intervention = 1) | 1.47 | 0.92 | 4.33 | 0.70 | 26.66 |
| Time period (12 months = 1) | −0.71 | 0.70 | 0.49 | 0.12 | 1.94 |
| Interaction: group × period | −1.27 | 0.92 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 1.73 |
| Demographic characteristics | |||||
| Male | 0.74 | 0.88 | 2.09 | 0.37 | 11.82 |
| Marrieda | 0.43 | 0.78 | 1.53 | 0.33 | 7.13 |
| US citizenb | −0.36 | 0.76 | 0.70 | 0.16 | 3.14 |
| Age | 0.05 | 0.03 | 1.05 | 0.99 | 1.11 |
| Contextual risk factors | |||||
| Job change | −0.70 | 0.99 | 0.50 | 0.07 | 3.47 |
| Housing problem | 1.21 | 0.94 | 3.34 | 0.52 | 21.47 |
| Food problem | −0.09 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 0.14 | 6.08 |
| Employedc | −1.21 | 0.71 | 0.30 | 0.07 | 1.22 |
| Traumatic life event | |||||
| Major accident or disaster | −0.29 | 0.90 | 0.75 | 0.13 | 4.39 |
| General violence | 0.54 | 1.04 | 1.71 | 0.22 | 13.44 |
| Intimate partner violence/threat | 1.26 | 0.94 | 3.52 | 0.54 | 22.70 |
| Adult sexual violence | 0.61 | 1.10 | 1.84 | 0.21 | 16.29 |
| Childhood sexual violence | 0.88 | 0.82 | 2.42 | 0.48 | 12.26 |
†Missing data are excluded
‡B is the unstandardized regression coefficient
††95% confidence intervals are shown. N = 165
aReference category is not married
bReference category is non-US citizen
cReference category is unemployed
We analyzed changes in the key contextual areas that the promotoras were to address in the intervention. At 12 months, the proportion of subjects with difficulty paying for housing decreased from 44 to 28% in the intervention group, and from 41 to 35% in the control group—not a significant difference by Chi square. The proportion of unemployed remain about the same in the intervention group (47 vs. 45%) but deteriorated in the control group (49 vs. 56%), again not a significant difference.
No significant differences in the intervention’s impact emerged when analyzed by promotora.
Ethnographic Assessment of Intervention Implementation and Outcomes
The ethnographic assessment revealed certain issues regarding fidelity of the implementation process [161]. First, some differences between the clinical sites became apparent. The randomly selected experimental site manifested space constraints, more staff turnover, and lower staff morale—all creating challenges for promotoras’ work. The control site provided an office for the promotoras, maintained more continuity of staffing, and welcomed the promotoras more enthusiastically.
Confusion about the boundaries of promotoras’ role affected the intervention’s implementation. Promotoras became so closely associated with mental health that they received frequent requests to intervene in crises of patients who were not participating in the intervention. Staff members tried to refer additional patients to the promotoras, although the promotoras could not accept these referrals because of the random study design. Members of the research team met several times with staff members at both CHCs to clarify the limitations of the promotoras’ training and responsibilities.
The roles of CHC staff members affected the algorithm’s implementation. Medical assistants (MAs) unexpectedly became key players in the intervention. The MAs functioned as gatekeepers because they controlled the promotoras’ access to medical files, exam rooms, and patients. Low-grade “turf wars” ensued in the initial phases at the experimental CHC site, where some MAs felt threatened by the promotoras. Due to this tension, the promotoras spent considerable time doing favors for the MAs, such as bringing patients into exam rooms, translating, or retrieving charts.
Regarding the intervention’s impact, the ethnographic assessment revealed that key stakeholders perceived the intervention as a useful and cost-effective way to identify and treat depression. Patients, selected randomly to participate in the evaluation, conveyed a perception that the promotoras gave them more time than the PCPs and listened more attentively. Viewing the promotoras as peers, patients emphasized their rapport with them. Overall, interviewed patients viewed the promotoras’ involvement in their care as positive.
The promotoras highlighted the additional time that they could spend with patients; their own ability in diagnosing depression and in addressing contextual sources of depression; and rapport based upon their ability to speak Spanish and to understand cultural differences. They also emphasized the project’s value in raising depression awareness among patients, PCPs, and the community at large.
PCPs perceived the intervention’s value in the greater amount of time that promotoras could spend with patients, improved access to bilingual and culturally appropriate services, patients’ increased comfort in discussing difficult issues, and staff members’ enhanced awareness of depression. All interviewed PCPs favorably assessed the value of promotora services for depression.
Other stakeholders also expressed generally favorable evaluative comments about the intervention. Non-professional staff members emphasized improvement of services for depressed patients. CHC administrators conveyed a positive perception of the intervention’s value. For instance, the CHC network’s chief executive officer used the study to obtain third-party reimbursements for mental health services provided by promotoras. Community advisory board members approved an extension of the promotora model to additional CHCs in the network.
Challenges and Opportunities
An unexpected internal challenge involved turnover of clinical staff members, especially at the experimental CHC site. All six PCPs at the experimental CHC who received training about the intervention left the CHC during the project. This turnover reflected transitions in careers and/or family circumstances that did not relate to the intervention. Four new PCPs who joined the staff at the experimental CHC received individualized training from project team members. At the control CHC, four of the six PCPs remained throughout the project.
For two promotoras, the project provided opportunities for career advancement. One promotora re-entered college studies and eventually finished graduate school in social work. Another promotora continued working at a CHC, supported by funding to expand behavioral health services.
On the other hand, one of the original promotoras left the project due to serious health and financial problems. Eventually he chose to work in the field of used car refurbishment—an occupation that he viewed as more financially lucrative.
Ethnographic analysis of the intervention contact forms showed that the promotoras did identify contextual sources of depression in underemployment, inadequate housing, food insecurity, and violence and intervened appropriately in making referrals and providing other forms of assistance. However, patients of the promotora who experienced health and financial problems received these measures less promptly and less consistently than those followed by the promotora who remained throughout the project.
Discussion
Overview and Interpretation of Findings
Our research led to mixed findings. The project showed that the promotora model for depression care can achieve implementation at CHCs and can generate perceptions of value among a wide cross-section of stakeholders. Despite the favorable observations from the ethnographic evaluation, the quantitative assessment did not reveal a statistically significant impact of the promotora intervention on depression, the key targeted outcome.
Several issues may help explain the lack of significant impact in the quantitative assessment. First, as observed in the ethnographic research, sources of clinic “noise” impinged on the fidelity of the intervention’s implementation. Unexpected differences between the clinical sites, including a more favorable environment at the control site, may have reduced the intervention’s impact as assessed quantitatively. Because the promotoras’ role remained unclear to some staff members, expectations exceeded the promotoras’ training or job description. Finally, unpredicted “turf” conflicts arose between MAs and promotoras.
Secondly, due to serious illness and financial crisis, one promotora could not work with patients for approximately 5 months. After he eventually left the project, substantial delays occurred in hiring a suitable replacement.
Despite extensive re-contact information to assure adequate follow-up, subjects proved more mobile than expected. While the final number of subjects remained large enough to assure adequate statistical power, we remain uncertain if the lack of statistically significant differences reflected issues of fidelity and discontinuity, rather than an ineffective intervention.
Policy Implications
The CHC network followed federal guidelines for integrating behavioral health services within the primary care setting [78]. After this project, the CHC network modified the guidelines to include a promotora as a team member. The promotora’s activities focused on access, contextual problems, and sources of non-adherence.
Negotiations continued between the CHC network and third-party payers for reimbursement of promotora services. This process proved partly successful, as one of the 3 for-profit managed care organizations contracting under Medicaid agreed to reimburse specified mental health services offered by promotoras. Later, a major behavioral health initiative of state government included a role for promotoras as service providers, and the state’s Department of Health organized an office focusing on community health workers in primary care and mental health. Such policy changes may provide a precedent for consideration in other geographical areas.
Implications for Research
To assist in policy decisions regarding promotora services, we argue for additional research that addresses some issues that we clarified in this study. Such research should take place on a scale large enough and with enough attention to variations in clinical settings to permit more definitive conclusions about the efficacy of promotoras as full-fledged members of clinical teams.
Differences in initial CHC environments should receive attention in interventions with promotoras or similar community health workers. Selection of clinical sites should consider differences in history and institutional culture. Although budgetary considerations influenced our decision to compare only two CHCs, we now recognize the importance of randomizing an intervention like this one to a larger number of intervention and control CHCs, to address variability among clinical sites.
Research in CHCs should anticipate constraints of clinical staffing. Non-PCP and non-promotora staff members should take part in planning research activities. Predictable turnover of PCPs and promotoras should receive attention in planning. For instance, we might have identified the problems experienced by one promotora earlier and addressed them more effectively. Despite budgetary limitations, we probably should have have employed more than two promotoras to reduce the likelihood that unanticipated difficulties experienced by one promotora would hinder the intervention and its assessment.
Conclusion
This project aimed to assess the role of promotoras in depression care at primary care clinics. Despite unexpected challenges, the promotoras achieved wide acceptance and support among stakeholders such as patients, PCPs, and administrators. The ethnographic assessment reached mainly favorable conclusions about the role of promotoras and the value of their work in addressing contextual sources of depression. Nevertheless, the quantitative assessment did not confirm the intervention’s favorable impact on depression outcomes.
We remain uncertain about the future role of promotoras in depression care. Due to the differences that emerged from the ethnographic and quantitative assessments, the lack of significant quantitative findings to demonstrate the intervention’s efficacy becomes less convincing than it otherwise might. Overall, the research effort revealed some of the vicissitudes of implementing and evaluating an intervention that addresses an important problem and that seems on face value to be a good idea.
Given the dire gaps in services that persist in underserved inner cities and rural areas, we favor a further assessment of innovative roles for new mental health practitioners who are firmly rooted in their communities. In such efforts, the sources of depression in contextual problems like underemployment, inadequate housing, food insecurity, and violence—whose importance as predictors of depression this study confirmed—warrant more attention than they have received so far.
Acknowledgments
This project was funded in part by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (grant 048127). The Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Center for Health Policy at the University of New Mexico provided additional support for statistical analyses. We thank the rest of the research team (Maureen Kelly, Margaret Menache, Jesse Méndez, D. Imelda Padilla-Frausto, Linda Pérez, and Aki Roberts). Christopher Lyons provided expert statistical consultation. Most importantly, we express our gratitude to the patients, practitioners, staff members, and community advisory board members who participated in the study.
References
- 1.Kessler R, Demler O, Frank R, et al. Prevalence and treatment of mental disorders, 1990 to 2003. New England Journal of Medicine. 2005;352(24):2515–2523. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa043266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.National Institute of Mental Health. (2010). Strategic plan. Retrieved August 23, 2010 at http://www.nimh.nih.gov/about/strategic-planning-reports/index.shtml.
- 3.Wang PS, Lane M, Olfson M, et al. Twelve-month use of mental health services in the United States: Results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Archives of General Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):629–640. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.62.6.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Borowsky SJ, Rubenstein LV, Meredith LS, et al. Who is at risk of nondetection of mental health problems in primary care? Journal of General Internal Medicine. 2000;15(6):381–388. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.2000.12088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Holman EA, Silver RC, Waitzkin H. Traumatic life events in primary care patients: A study in an ethnically diverse sample. Archives of Family Medicine. 2000;9(9):802–810. doi: 10.1001/archfami.9.9.802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rizzo VM, Mizrahi T, Kirkland K. Psychosocial problems among patients in neighborhood health centers: Perspectives from health care providers. Journal of Community Health. 2005;30(2):125–140. doi: 10.1007/s10900-004-1096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gallo JJ, Bogner HR, Morales KH, et al. Patient ethnicity and the identification and active management of depression in late life. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2005;165(17):1962–1968. doi: 10.1001/archinte.165.17.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hansson M, Chotai J, Nordstom A, et al. Comparison of two self-rating scales to detect depression: HADS and PHQ-9. British Journal of General Practice. 2009;59(566):650–654. doi: 10.3399/bjgp09X454070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hauenstein EJ, Peddada S. Prevalence of major depressive episodes in rural women using primary care. Journal of Health Care for the Poor and Underserved. 2007;18(1):185–202. doi: 10.1353/hpu.2007.0010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mitchell AJ, Vaze A, Rao S. Clinical diagnosis of depression in primary care: A meta-analysis. Lancet. 2009;374(9690):609–619. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60879-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Reuland DS, Cherrington A, Watkins GS, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of Spanish language depression-screening instruments. Annals of Family Medicine. 2009;7(5):455–462. doi: 10.1370/afm.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Schmaling KB, Hernandez DV. Detection of depression among low-income Mexican Americans in primary care. Journal of Health Care for the Poor and Undeserved. 2005;16(4):780–790. doi: 10.1353/hpu.2005.0105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fleming MF, Barry KL, Manwell LB, et al. Brief physician advice for problem alcohol drinkers: A randomized controlled trial in community-based primary care practices. JAMA. 1997;277(13):1039–1045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fleming MF, Mundt MP, French MT, et al. Benefit-cost analysis of brief physician advice with problem drinkers in primary care settings. Medical Care. 2000;38(1):7–18. doi: 10.1097/00005650-200001000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Harvey I, Nelson SJ, Lyons RA, et al. A randomized controlled trial and economic evaluation of counselling in primary care. British Journal of General Practice. 1998;48(428):1043–1048. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rollman BL, Hanusa BH, Gilbert T, et al. The electronic medical record. A randomized trial of its impact on primary care physicians’ initial management of major depression [corrected] Archives of Internal Medicine. 2001;161(2):189–197. doi: 10.1001/archinte.161.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Simon GE, VonKorff M, Heiligenstein JH, et al. Initial antidepressant choice in primary care: Effectiveness and cost of fluoxetine vs tricyclic antidepressants. JAMA. 1996;275(24):1897–1902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Williams JW, Barrett J, Oxman T, et al. Treatment of dysthymia and minor depression in primary care: A randomized controlled trial in older adults. JAMA. 2000;284(12):1519–1526. doi: 10.1001/jama.284.12.1519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Katon W, Korff M, Lin E, et al. Stepped collaborative care for primary care patients with persistent symptoms of depression: A randomized trial. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1999;56(12):1109–1115. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.56.12.1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rost K, Nutting P, Smith J, et al. Improving depression outcomes in community primary care practice: A randomized trial of the QuEST intervention. Journal of General Internal Medicine. 2001;16(3):143–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1497.2001.00537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rubenstein LV, Jackson-Triche M, Unutzer J, et al. Evidence-based care for depression in managed primary care practices. Health Affairs. 1999;18(5):89–105. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.18.5.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Unutzer J, Rubenstein L, Katon WJ, et al. Two-year effects of quality improvement programs on medication management for depression. Archives of General Psychiatry. 2001;58(10):935–942. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.58.10.935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wells KB, Sherbourne C, Schoenbaum M, et al. Impact of disseminating quality improvement programs for depression in managed primary care: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2000;283(2):212–220. doi: 10.1001/jama.283.2.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Schoenbaum M, Unutzer J, Sherbourne C, et al. Cost-effectiveness of practice-initiated quality improvement for depression: Results of a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2001;286(11):1325–1330. doi: 10.1001/jama.286.11.1325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sherbourne CD, Weiss R, Duan N, et al. Do the effects of quality improvement for depression care differ for men and women? Results of a group-level randomized controlled trial. Medical Care. 2004;42(12):1186–1193. doi: 10.1097/00005650-200412000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wells KB, Schoenbaum M, Duan N, et al. Cost-effectiveness of quality improvement programs for patients with subthreshold depression or depressive disorder. Psychiatric Services. 2007;58(10):1269–1278. doi: 10.1176/ps.2007.58.10.1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wells KB, Sherbourne CD, Miranda J, et al. The cumulative effects of quality improvement for depression on outcome disparities over 9 years: Results from a randomized, controlled group-level trial. Medical Care. 2007;45(11):1052–1059. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0b013e31813797e5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Clarke GN. Improving the transition from basic efficacy research to effectiveness studies: Methodological issues and procedures. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 1995;63(5):718–725. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.63.5.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Dietrich AJ, Oxman TE, Williams JW, et al. Re-engineering systems for the treatment of depression in primary care: Cluster randomised controlled trial. British Medical Journal. 2004;329(7466):602–605. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38219.481250.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Essock SM, Goldman HH, Anthony WA, et al. Evidence-based practices: Setting the context and responding to concerns. Psychiatric Clinics of North America. 2003;26(4):919. doi: 10.1016/s0193-953x(03)00069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gray GE, Pinson LA. Evidence-based medicine and psychiatric practice. Psychiatric Quarterly. 2003;74(4):387–399. doi: 10.1023/a:1026091611425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Klinkman MS. The role of algorithms in the detection and treatment of depression in primary care. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2003;64:19–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bruce ML, Ten Have TR, Reynolds CF, et al. Reducing suicidal ideation and depressive symptoms in depressed older primary care patients: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2004;291(9):1081–1091. doi: 10.1001/jama.291.9.1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Craven, M. A., & Bland, R. (2006). Better practices in collaborative mental health care: An analysis of the evidence base.Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 51(6 Suppl 1), 7S–72S. [PubMed]
- 35.Hegel MT, Unutzer J, Tang LQ, et al. Impact of comorbid panic and posttraumatic stress disorder on outcomes of collaborative care for late-life depression in primary care. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. 2005;13(1):48–58. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajgp.13.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hunkeler EM, Katon W, Tang L, et al. Long-term outcomes from the IMPACT randomised trial for depressed elderly patients in primary care. British Medical Journal. 2006;332(7536):259–263. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38683.710255.BE. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Katon W, Unutzer J, Fan MY, et al. Cost-effectiveness and net benefit of enhanced treatment of depression for older adults with diabetes and depression. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(2):265–270. doi: 10.2337/diacare.29.02.06.dc05-1572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Nutting PA, Gallagber K, Riley K, et al. Care management for depression in primary care practice: Findings from the RESPECT-depression trial. Annals of Family Medicine. 2008;6(1):30–37. doi: 10.1370/afm.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nutting PA, Gallagher KM, Riley K, et al. Implementing a depression improvement intervention in five health care organizations: Experience from the RESPECT-depression trial. Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research. 2007;34(2):127–137. doi: 10.1007/s10488-006-0090-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Oxman TE, Schulberg HC, Greenberg RL, et al. A fidelity measure for integrated management of depression in primary care. Medical Care. 2006;44(11):1030–1037. doi: 10.1097/01.mlr.0000233683.82254.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Williams JW, Katon W, Lin EHB, et al. The effectiveness of depression care management on diabetes-related outcomes in older patients. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2004;140(12):1015–1024. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-140-12-200406150-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ayalon L, Arean PA, Linkins K, et al. Integration of mental health services into primary care overcomes ethnic disparities in access to mental health services between black and white elderly. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. 2007;15(10):906–912. doi: 10.1097/JGP.0b013e318135113e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Cooper LA, Gonzales JJ, Gallo JJ, et al. The acceptability of treatment for depression among African-American, Hispanic, and white primary care patients. Medical Care. 2003;41(4):479–489. doi: 10.1097/01.MLR.0000053228.58042.E4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Miranda J, Bernal G, Lau A, et al. State of the science on psychosocial interventions for ethnic minorities. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology. 2005;1:113–142. doi: 10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.1.102803.143822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Miranda J, Chung JY, Green BL, et al. Treating depression in predominantly low-income young minority women: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2003;290(1):57–65. doi: 10.1001/jama.290.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Miranda J, Duan NH, Sherbourne C, et al. Improving care for minorities: Can quality improvement interventions improve care and outcomes for depressed minorities? Results of a randomized, controlled trial. Health Services Research. 2003;38(2):613–630. doi: 10.1111/1475-6773.00136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Rojas G, Fritsch R, Solis J, et al. Treatment of postnatal depression in low-income mothers in primary-care clinics in Santiago, Chile: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2007;370(9599):1629–1637. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61685-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wells K, Sherbourne C, Schoenbaum M, et al. Five-year impact of quality improvement for depression: Results of a group-level randomized controlled trial. Archives of General Psychiatry. 2004;61(4):378–386. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.61.4.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Stockdale SE, Lagomasino IT, Siddique J, et al. Racial and ethnic disparities in detection and treatment of depression and anxiety among psychiatric and primary health care visits, 1995–2005. Medical Care. 2008;46(7):668–677. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0b013e3181789496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ramos IN, May M, Ramos KS. Environmental health training of promotoras in colonias along the Texas-Mexico border. American Journal of Public Health. 2001;91(4):568–570. doi: 10.2105/ajph.91.4.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Williams DM. La promotora: Linking disenfranchised residents along the border to the U.S. healthcare system. Health Affairs. 2001;20(3):212–218. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.20.3.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hanscom KL. Treating survivors of war trauma and torture. American Psychologist. 2001;56(11):1032–1039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.McElmurry BJ, Park CG, Buseh AG. The nurse-community health advocate team for urban immigrant primary health care. Journal of Nursing Scholarship. 2003;35(3):275–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1547-5069.2003.00275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Nemcek MA, Sabatier R. State of evaluation: Community health workers. Public Health Nursing. 2003;20(4):260–270. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1446.2003.20403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Zuvekas A, Nolan L, Tumaylle C, et al. Impact of community health workers on access, use of services, and patient knowledge and behavior. Journal of Ambulatory Care Management. 1999;22(4):33–44. doi: 10.1097/00004479-199910000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Balcázar H, Alvarado M, Cantu F, et al. A promotora de salud model for addressing cardiovascular disease risk factors in the US-Mexico border region. Preventing Chronic Disease. 2009;6(1):A02. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Rodríguez VM, Conway TL, Woodruff SI, et al. Pilot test of an assessment instrument for Latina community health advisors conducting an ETS intervention. Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health. 2003;5(3):129–137. doi: 10.1023/a:1023991818829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Berg J, Anderson NL, Tichacek MJ, et al. One gets so afraid: Latino families and asthma management: An exploratory study. Journal of Pediatric Health Care. 2007;21:361–371. doi: 10.1016/j.pedhc.2006.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Joshu CE, Rangel L, Garcia O, et al. Integration of a promotora-led self-management program into a system of care. Diabetes Educator. 2007;33:151S–158S. doi: 10.1177/0145721707304076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Lujan J, Ostwald SK, Ortiz M. Promotora diabetes interventions for Mexican Americans. Diabetes Education. 2007;33(4):660–670. doi: 10.1177/0145721707304080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Sauaia A, Min SJ, Lack D, et al. Church-based breast cancer screening education: impact of two approaches on Latinas enrolled in public and private health insurance plans. Preventing Chronic Disease. 2007;4(4):A99. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Anderson D, O’Toole ML, Brownson CA, et al. Integrating depression care with diabetes care in real-world settings: Lessons from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Diabetes Initiative. Diabetes Spectrum. 2007;20(1):10–16. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Robert Wood Foundation. (2006). The diabetes initiative of the robert wood foundation. Retrieved August 23, 2010 from http://rwjf.org/files/research/diabetesinitiativeoverview.pdf.
- 64.Center for Disease Control and Prevention. (2010). Community health workers/promotores de salud: Critical connections in communities. Retrieved August 23, 2010 from http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/projects/comm.htm.
- 65.Balcázar H, Alvarado M, Hollen ML, et al. Salud para su corazón–NCLR: A comprehensive promotora outreach program to promote heart-healthy behaviors among hispanics. Health Promotion Practice. 2006;7(1):68–77. doi: 10.1177/1524839904266799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Teufel-Shone NI, Drummond R, Rawiel U. Developing and adapting a family-based diabetes program at the US-Mexico border. Preventing Chronic Disease. 2005;2(1):A20. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Conway TL, Woodruff SI, Edwards CC, et al. Intervention to reduce environmental tobacco smoke exposure in Latino children: Null effects on hair biomarkers and parent reports. Tobacco Control. 2004;13(1):90–92. doi: 10.1136/tc.2003.004440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Hunter JB, Zapien JG, Papenfuss M, et al. The impact of a promotora on increasing routine chronic disease prevention among women aged 40 and older at the US-Mexico border. Health Education Behavior. 2004;31(4 Suppl):18S–28S. doi: 10.1177/1090198104266004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Hansen LK, Feigl P, Modiano MR, et al. An educational program to increase cervical and breast cancer screening in Hispanic women: A southwest oncology group study. Cancer Nursing. 2005;28(1):47–53. doi: 10.1097/00002820-200501000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Welsh, A. L., Sauaia, A., Jacobellis, J., et al. (2005). The effect of two church-based interventions on breast cancer screening rates among Medicaid-insured Latinas.Preventing Chronic Disease, 2(4). [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 71.Elder JP, Ayala GX, Campbell NR, et al. Interpersonal and print nutrition communication for a Spanish-dominant Latino population: Secretos de la buena vida. Health Psychology. 2005;24(1):49–57. doi: 10.1037/0278-6133.24.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Moreno P, Saravanan Y, Levav I, et al. Evaluation of the PAHO/WHO training program on the detection and treatment of depression for primary care nurses in Panama. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. 2003;108(1):61–65. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0447.2003.00133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Bolton P, Bass J, Neugebauer R, et al. Group interpersonal psychotherapy for depression in rural Uganda: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2003;289(23):3117–3124. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.23.3117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Araya R, Rojas G, Fritsch R, et al. Treating depression in primary care in low-income women in Santiago, Chile: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2003;361(9362):995–1000. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12825-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Reinschmidt, K. M. & Chong, J. (2007). SONRISA: A curriculum toolbox for promotores to address mental health and diabetes. Preventing Chronic Disease, 4(4): A101. Electronic publication September 15. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 76.Quality through collaboration: The future of rural health care. Washington, DC: National Academy of Sciences; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 77.President’s New Freedom Commission on Mental Health. (2003). Achieving the promise: Transforming mental health care in America. Final Report. Rockville, MD: Department of Health and Human Services.
- 78.U.S. Health Resources and Service Administration. Mental health. Retrieved August 23, 2010 from http://www.hrsa.gov/mentalhealth/default.htm.
- 79.World Health Organization. (2001). Mental health: New understanding, new hope. World health report. Geneva: World Health Organization.
- 80.Brown GW. A psychosocial perspective and the aetiology of depression. In: Honig A, Praag HM, editors. Depression: Neurobiological, psychopathological & therapeutic advances. New York: Wiley; 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 81.Brown GW, Moran P. Clinical and psychosocial origins of chronic depressive episodes I: A community survey. British Journal of Psychiatry. 1994;165:447–456. doi: 10.1192/bjp.165.4.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Brown GW, Moran PM. Single mothers, poverty and depression. Psychological Medicine. 1997;27(1):21–33. doi: 10.1017/s0033291796004060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Eaton WW, Muntaner C, Bovasso G, et al. Socioeconomic status and depressive syndrome: The role of inter- and intra-generational mobility, government assistance, and work environment. Journal of Health and Social Behavior. 2001;42(3):277–294. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Tiwari A, Chan KL, Fong D, et al. The impact of psychological abuse by an intimate partner on the mental health of pregnant women. BJOG. 2008;115(3):377–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2007.01593.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Duran B, Malcoe LH, Sanders M, et al. Child maltreatment prevalence and mental disorders outcomes among American Indian women in primary care. Child Abuse and Neglect. 2004;28(2):131–145. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2003.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Duran B, Sanders M, Skipper B, et al. Prevalence and correlates of mental disorders among native American women in primary care. American Journal of Public Health. 2004;94(1):71–77. doi: 10.2105/ajph.94.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Escobar JI, Waitzkin H, Silver RC, et al. Abridged somatization: A study in primary care. Psychosomatic Medicine. 1998;60(4):466–472. doi: 10.1097/00006842-199807000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Sherbourne CD, Edelen MO, Zhou A, et al. How a therapy-based quality improvement intervention for depression affected life events and psychological well-being over time: A 9-year longitudinal analysis. Medical Care. 2008;46(1):78–84. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0b013e318148478d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Austin EL, Andersen R, Gelberg L. Ethnic differences in the correlates of mental distress among homeless women. Women’s Health Issues. 2008;18(1):26–34. doi: 10.1016/j.whi.2007.08.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Gelberg L, Andersen RM, Leake BD. The behavioral model for vulnerable populations: Application to medical care use and outcomes for homeless people. Health Services Research. 2000;34(6):1273–1302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Stein JA, Andersen R, Gelberg L. Applying the Gelberg-Andersen behavioral model for vulnerable populations to health services utilization in homeless women. Journal of Health Psychology. 2007;12(5):791–804. doi: 10.1177/1359105307080612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Ansseau M, Fischler B, Dierick M, et al. Socioeconomic correlates of generalized anxiety disorder and major depression in primary care: The GADIS II study (Generalized Anxiety and Depression Impact Survey II) Depression and Anxiety. 2008;25(6):506–513. doi: 10.1002/da.20306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Fortney J, Rushton G, Wood S, et al. Community-level risk factors for depression hospitalizations. Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research. 2007;34(4):343–352. doi: 10.1007/s10488-007-0117-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Gallo WT, Bradley EH, Dubin JA, et al. The persistence of depressive symptoms in older workers who experience involuntary job loss: Results from the health and retirement survey. Journals of Gerontology Social Sciences. 2006;61(4):S221–S228. doi: 10.1093/geronb/61.4.s221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Gilchrist G, Gunn J. Observational studies of depression in primary care: What do we know? BioMed Family Practice. 2007;8(28):93. doi: 10.1186/1471-2296-8-28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Mascaro N, Arnette NC, Santana MC, et al. Longitudinal relations between employment and depressive symptoms in low-income, suicidal African American women. Journal of Clinical Psychology. 2007;63(6):541–553. doi: 10.1002/jclp.20365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Stack S, Wasserman I. Economic strain and suicide risk: A qualitative analysis. Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior. 2007;37(1):103–112. doi: 10.1521/suli.2007.37.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Fone D, Dunstan F, Williams G, et al. Places, people and mental health: a multilevel analysis of economic inactivity. Social Science and Medicine. 2007;64(3):633–645. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2006.09.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Galea S, Ahern J, Rudenstine S, et al. Urban built environment and depression: A multilevel analysis. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health. 2005;59(10):822–827. doi: 10.1136/jech.2005.033084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Karim K, Tischler V, Gregory P, et al. Homeless children and parents: Short-term mental health outcome. International Journal of Social Psychiatry. 2006;52(5):447–458. doi: 10.1177/0020764006066830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Siefer K, Finalayson TL, Williams DR, et al. Modifiable risk and protective factors for depressive symptoms in low-income African American mothers. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry. 2007;77(1):113–123. doi: 10.1037/0002-9432.77.1.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Alegría M, Pérez DJ, Williams S. The role of public policies in reducing mental health status disparities for people of color. Health Affairs (Milwood) 2003;22(5):51–64. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.22.5.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Casey P, Goolsby S, Berkowitz C, et al. Maternal depression, changing public assistance, food security, and child health status. Pediatrics. 2004;113(2):298–304. doi: 10.1542/peds.113.2.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Chilton M, Booth S. Hunger of the body and hunger of the mind: African American women’s perceptions of food insecurity, health and violence. Journal of Nutrition, Education and Behavior. 2007;39(3):116–125. doi: 10.1016/j.jneb.2006.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Huddleston-Casas C, Charnigo R, Simmons LA. Food insecurity and maternal depression in rural, low-income families: A longitudinal investigation. Public Health Nutrition. 2009;12(8):1133–1140. doi: 10.1017/S1368980008003650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Kim K, Frongillo EA. Participation in food assistance programs modifies the relation of food insecurity with weight and depression in elders. Journal of Nutrition. 2007;137(4):1005–1010. doi: 10.1093/jn/137.4.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Siefert K, Heflin CM, Corcoran ME, et al. Food insufficiency and physical and mental health in a longitudinal survey of welfare recipients. Journal of Health and Social Behavior. 2004;45(2):171–186. doi: 10.1177/002214650404500204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Weigel MM, Armijos RX, Hall YP, et al. The household food insecurity and health outcomes of U.S.-Mexico border migrant and seasonal farmworkers. Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health. 2007;9(3):157–169. doi: 10.1007/s10903-006-9026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Whitaker RC, Phillips SM, Orzol SM. Food insecurity and the risks of depression and anxiety in mothers and behavior problems in their preschool-aged children. Pediatrics. 2006;118(3):e859–e868. doi: 10.1542/peds.2006-0239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Clark C, Ryan L, Kawachi I, et al. Witnessing community violence in residential neighborhoods: A mental health hazard for urban women. Journal of Urban Health Bulletin of the New York Academy of Medicine. 2008;85(1):22–38. doi: 10.1007/s11524-007-9229-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Coker AL, Smith PH, Fadden MK. Intimate partner violence and disabilities among women attending family practice clinics. Journal of Women’s Health. 2005;14(9):829–838. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2005.14.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Dervic K, Grunebaum MF, Burke AK, et al. Protective factors against suicidal behavior in depressed adults reporting childhood abuse. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease. 2006;194(12):971–974. doi: 10.1097/01.nmd.0000243764.56192.9c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Fedovskiy K, Higgins S, Paranjape A. Intimate partner violence: How does it impact major depressive disorder and post traumatic stress disorder among immigrant Latinas? Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health. 2008;10(1):45–51. doi: 10.1007/s10903-007-9049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Fogarty CT, Fredman L, Heeren TC, et al. Synergistic effects of child abuse and intimate partner violence on depressive symptoms in women. Preventive Medicine. 2008;46(5):463–469. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2007.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Geiger-Brown J, Muntaner C, McPhaul K, et al. Abuse and violence during home care work as predictor of worker depression. Home Health Care Services Quarterly. 2007;26(1):59–77. doi: 10.1300/J027v26n01_05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Goldstein AL, Walton MA, Cunningham RM, et al. Violence and substance use as risk factors for depressive symptoms among adolescents in an urban emergency department. Journal of Adolescent Health. 2007;40(3):276–279. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2006.09.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Hicks MHR, Li ZH. Partner violence and major depression in women: A community study of Chinese Americans. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease. 2003;191(11):722–729. doi: 10.1097/01.nmd.0000095124.05023.e1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Koopman C, Ismailji T, Palesh O, et al. Relationships of depression to child and adult abuse and bodily pain among women who have experienced intimate partner violence. Journal of Interpersonal Violence. 2007;22(4):438–455. doi: 10.1177/0886260506297028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Storr CL, Ialongo NS, Anthony JC, et al. Childhood antecedents of exposure to traumatic events and posttraumatic stress disorder. American Journal of Psychiatry. 2007;164(1):119–125. doi: 10.1176/ajp.2007.164.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Matt GE, Bellardita L, Fischerand G, et al. Psychological resources and mental health among the difficult to employ: Can a pre-employment training program make a difference? Journal of Vocational Rehabilitation. 2006;24(1):33–43. [Google Scholar]
- 121.Vinokur AD, Schul Y, Vuori J, et al. Two years after a job loss: Long-term impact of he JOBS program on re-employment and mental health. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology. 2000;5(1):32–47. doi: 10.1037//1076-8998.5.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Vuori J, Silvonen J. The benefits of a preventive job search program on re-employment and mental health at two-year follow-up. Journal of Occupational & Organizational Psychology. 2005;78:43–52. [Google Scholar]
- 123.Fauth RC, Leventhal T, Brooks-Gunn J. Short-term effects of moving from public housing in poor to middle-class neighborhoods on low-income, minority adults’ outcomes. Social Science and Medicine. 2004;59(11):2271–2284. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2004.03.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Katz LF, Kling JR, Liebman JB. Moving to opportunity in Boston: Early results of a randomized mobility experiment. Quarterly Journal of Economics. 2001;116(2):607–654. [Google Scholar]
- 125.Kling JR, Liebman JB, Katz LF. Experimental analysis of neighborhood effects. Econometrica. 2007;75(1):83–119. [Google Scholar]
- 126.Leventhal T, Brooks-Gunn J. Moving to opportunity: An experimental study of neighborhood effects on mental health. American Journal of Public Health. 2003;93(9):1576–1582. doi: 10.2105/ajph.93.9.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Sullivan CM, Bybee DI, Allen NE. Findings from a community-based program for battered women and their children. Journal of Interpersonal Violence. 2002;17(9):915–936. [Google Scholar]
- 128.Gassman-Pines A, Yoshikawa H. Five-year effects of an anti-poverty program on marriage among never-married mothers. Journal of Policy Analysis and Management. 2006;25(1):11–30. [Google Scholar]
- 129.Miranda J, Azocar F, Organista KC, et al. Treatment of depression among impoverished primary care patients from ethnic minority groups. Psychiatric Services. 2003;54(2):219–225. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.54.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Borrell-Carrio F, Suchman AL, Epstein RM. The biopsychosocial model 25 years later: Principles, practice, and scientific inquiry. Annals of Family Medicine. 2004;2(6):576–582. doi: 10.1370/afm.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Engel GL. Need for a new medical model: Challenge for biomedicine. Science. 1977;196(4286):129–136. doi: 10.1126/science.847460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.U.S. Census Bureau. (2008). Statistical abstract of the United States: 2005. Personal income per capita in constant in dollars, 2007. Retrieved August 23, 2010 from http://www.census.gov/statab/ranks/rank34.html.
- 133.Statistical abstract of the United States: 2005. Persons below poverty level. Washington, DC: Government Printing Office; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 134.Statistical abstract of the United States: 2005. Washington, DC: Government Printing Office; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 135.Statistical abstract of the United States: 1999. Washington, DC: Government Printing Office; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 136.Statistical abstract of the United States: 2006. Washington, DC: Government Printing Office; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 137.Morgan KO, Morgan S. Health care state rankings 2005: Health care in the 50 United States. Lawrence, KS: Morgan Quitno Press; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 138.Waitzkin H, Yager J, Parker T, Duran B. Mentoring partnerships for minority faculty and graduate students in mental health services research. Academic Psychiatry. 2006;30(3):205–217. doi: 10.1176/appi.ap.30.3.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Brody DS, Hahn SR, Spitzer RL, et al. Identifying patients with depression in the primary care setting: A more efficient method. Archives of Internal Medicine. 1998;158(22):2469–2475. doi: 10.1001/archinte.158.22.2469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Connelly JE, Wofford AB, Philbrick JT. Healthy patients who perceive poor health: Why are they worried sick? American Journal of the Medical Sciences. 2000;320(1):36–42. doi: 10.1097/00000441-200007000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Hahn SR. Physical symptoms and physician-experienced difficulty in the physician-patient relationship. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2001;134(9):897–904. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-134-9_part_2-200105011-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Jackson JL, Houston JS, Hanling SR, et al. Clinical predictors of mental disorders among medical outpatients. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2001;161(6):875–879. doi: 10.1001/archinte.161.6.875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Lefevre F, Reifler D, Lee P, et al. Screening for undetected mental disorders in high utilizers of primary care services. Journal of General Internal Medicine. 1999;14(7):425–431. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.1999.07238.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Miranda J, Azocar F, Komaromy M, et al. Unmet mental health needs of women in public-sector gynecologic clinics. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 1998;178(2):212–217. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(98)80002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Schriger DL, Gibbons PS, Langone CA, et al. Enabling the diagnosis of occult psychiatric illness in the emergency department: A randomized, controlled trial of the computerized, self-administered PRIME-MD diagnostic system. Annals of Emergency Medicine. 2001;37(2):132–140. doi: 10.1067/mem.2001.112255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Spitzer RL, Williams JB, Kroenke K, et al. Validity and utility of the PRIME-MD Patient Health Questionnaire in assessment of 3000 obstetric-gynecologic patients: The PRIME-MD Patient Health Questionnaire Obstetrics Gynecology Study. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2000;183(3):759–769. doi: 10.1067/mob.2000.106580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Thompson MA, Unützer J, Katon WJ, et al. Detection and treatment of depressive syndromes in a rural island clinic. Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine. 1999;12(2):120–127. doi: 10.3122/jabfm.12.2.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Olfson M, Shea S, Feder A, et al. Prevalence of anxiety, depression, and substance use disorders in an urban general medicine practice. Archives of Family Medicine. 2000;9(9):876–883. doi: 10.1001/archfami.9.9.876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Baca E, Saiz J, Aguera L, et al. Validation of the Spanish version of PRIME-MD: A procedure for diagnosing mental disorders in primary care. Actas Espanolas De Psiquiatria. 1999;27(6):375–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Baca-Baldomero E, Sáiz-Ruiz J, Agüera-Ortiz LF, et al. Prevalencia de los trastornos psiquiátricos en atención primaria usando el cuestionario PRIME-MD. Actas Españolas de Psiquiatría. 1999;27(6):375–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.McIntyre LM, Butterfield MI, Nanda K, et al. Validation of a trauma questionnaire in veteran women. Journal of General Internal Medicine. 1999;14(3):186–189. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.1999.00311.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Paranjape A, Liebschutz J. STAT: A three-question screen for intimate partner violence. Journal of Women’s Health and Gender-Based Medicine. 2003;12(3):233–239. doi: 10.1089/154099903321667573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. (2009). The treatment and management of depression in adults. Retrieved August 23, 2010 from http://www.guideline.gov/content.aspx?id=15521&search=depression.
- 154.Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2. Hillsdale, NJ: L. Erlbaum Associates; 1988. [Google Scholar]
- 155.Hinlus J. NCCS-PASS. Kaysville, UT: NCSS Statistical Software; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 156.Peduzzi P, Concato J, Kemper E, et al. A simulation study of the number of events per variable in logistic regression analysis. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 1996;49(12):1373–1379. doi: 10.1016/s0895-4356(96)00236-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Menard S. Applied logistic regression analysis. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 158.QSR International. (2010). NVivo 8. Retrieved August 23, 2010 from http://www.qsrinternational.com.
- 159.Emerson RM, Fretz RI, Shaw LL. Writing ethnographic fieldnotes. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 1995. [Google Scholar]
- 160.Patton MQ. Enhancing the quality and credibility of qualitative analysis. Health Services Research. 1999;34(5):1189–1208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Getrich C, Heying S, Willging C, et al. An ethnography of clinic “noise’ in a community-based, promotora-centered mental health intervention. Social Science and Medicine. 2007;65(2):319–330. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2007.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]