Abstract
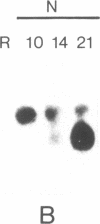
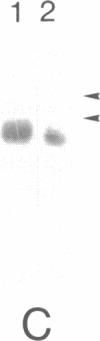
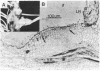
Establishment of a nitrogen-fixing root nodule is accompanied by a developmentally regulated expression of nodulin genes, only some of which, the so-called early nodulin genes, are expressed in stages preceding actual nitrogen fixation. We have isolated soybean cDNA clones representing early nodulin genes and have studied clone pENOD2 in detail. The cDNA insert of this clone hybridizes to nodule-specific RNA of 1200 nucleotides in length. The RNA that was hybrid-selected by the cloned ENOD2 DNA was in vitro translated to produce two nodulins with an apparent Mr of 75,000, the N-75 nodulins. These two nodulins differ slightly in charge and one does not contain methionine. The amino acid sequence deduced from the DNA sequence shows that proline accounts for 45% of the 240 residues in these nodulins and the sequence contains at least 20 repeating heptapeptide units. The amino acid composition of none of the (hydroxy)proline-rich (glyco)proteins described in plants resembles the composition of the N-75 nodulins, especially with respect to the high glutamic acid and the low serine content. This suggests that the N-75 nodulins belong to a hitherto unidentified class of presumably structural proteins. The genes encoding the N-75 nodulins were found to be expressed in nodule-like structures devoid of intracellular bacteria and infection threads, indicating that these nodulins do not function in the infection process but more likely function in nodule morphogenesis.
Keywords: Rhizobium, nodule-like structures, proline-rich proteins, DNA sequence
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen A. K., Desai N. N., Neuberger A., Creeth J. M. Properties of potato lectin and the nature of its glycoprotein linkages. Biochem J. 1978 Jun 1;171(3):665–674. doi: 10.1042/bj1710665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhuvaneswari T. V., Turgeon B. G., Bauer W. D. Early Events in the Infection of Soybean (Glycine max L. Merr) by Rhizobium japonicum: I. LOCALIZATION OF INFECTIBLE ROOT CELLS. Plant Physiol. 1980 Dec;66(6):1027–1031. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.6.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisseling T., van den Bos R. C., van Kammen A. The effect of ammonium nitrate on the synthesis of nitrogenase and the concentration of leghemoglobin in pea root nodules induced by Rhizobium leguminosarum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 13;539(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Varner J. E. An extracellular matrix protein in plants: characterization of a genomic clone for carrot extensin. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2145–2151. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03908.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Varner J. E. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for carrot extensin and a proline-rich 33-kDa protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4399–4403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freytag J. W., Noelken M. E., Hudson B. G. Physical properties of collagen--sodium dodecyl sulfate complexes. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4761–4768. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller F., Künstner P. W., Nguyen T., Verma D. P. Soybean nodulin genes: Analysis of cDNA clones reveals several major tissue-specific sequences in nitrogen-fixing root nodules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2594–2598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govers F., Gloudemans T., Moerman M., van Kammen A., Bisseling T. Expression of plant genes during the development of pea root nodules. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):861–867. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03711.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang-Unnasch N., Ausubel F. M. Nodule-specific polypeptides from effective alfalfa root nodules and from ineffective nodules lacking nitrogenase. Plant Physiol. 1985 Apr;77(4):833–839. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.4.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach J. E., Cantrell M. A., Sequeira L. Hydroxyproline-rich bacterial agglutinin from potato : extraction, purification, and characterization. Plant Physiol. 1982 Nov;70(5):1353–1358. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.5.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim V. I. Algorithms for prediction of alpha-helical and beta-structural regions in globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 5;88(4):873–894. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90405-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil M., Darvill A. G., Fry S. C., Albersheim P. Structure and function of the primary cell walls of plants. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:625–663. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter A. M., Bell J. N., Cramer C. L., Bailey J. A., Varner J. E., Lamb C. J. Accumulation of hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein mRNAs in response to fungal elicitor and infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6551–6555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Graphic methods to determine the function of nucleic acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):521–538. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Holst G. J., Klis F. M., de Wildt P. J., Hazenberg C. A., Buijs J., Stegwee D. Arabinogalactan Protein from a Crude Cell Organelle Fraction of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Physiol. 1981 Oct;68(4):910–913. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.4.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Holst G. J., Varner J. E. Reinforced Polyproline II Conformation in a Hydroxyproline-Rich Cell Wall Glycoprotein from Carrot Root. Plant Physiol. 1984 Feb;74(2):247–251. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]