Abstract
Interleukin 1 (IL-1) is a two-member family of proteins (IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta) that mediates a diverse series of immune and inflammatory responses. These two proteins have only 26% amino acid homology yet bind to the same receptor. It is of importance to define the active sites of these molecules in order to understand their receptor interactions and the mechanisms involved in their multiple biological functions. We report here the localization of the biologically active portions within the initial polypeptide translation products. An in vitro transcription and translation system was used to generate specific fragments of each of the IL-1 molecules, which then were assayed for receptor binding capability and biological activity. Using this system, we have demonstrated that core sequences of amino acids for IL-1 beta (numbers 120-266) and 140 amino acids for IL-1 alpha (numbers 128-267) must be left intact to retain full biological activity and further that the biological activities of the IL-1 polypeptides parallel their receptor binding capabilities.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cameron P. M., Limjuco G. A., Chin J., Silberstein L., Schmidt J. A. Purification to homogeneity and amino acid sequence analysis of two anionic species of human interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):237–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron P., Limjuco G., Rodkey J., Bennett C., Schmidt J. A. Amino acid sequence analysis of human interleukin 1 (IL-1). Evidence for biochemically distinct forms of IL-1. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):790–801. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlon P. J. A rapid biologic assay for the detection of interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1280–1282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
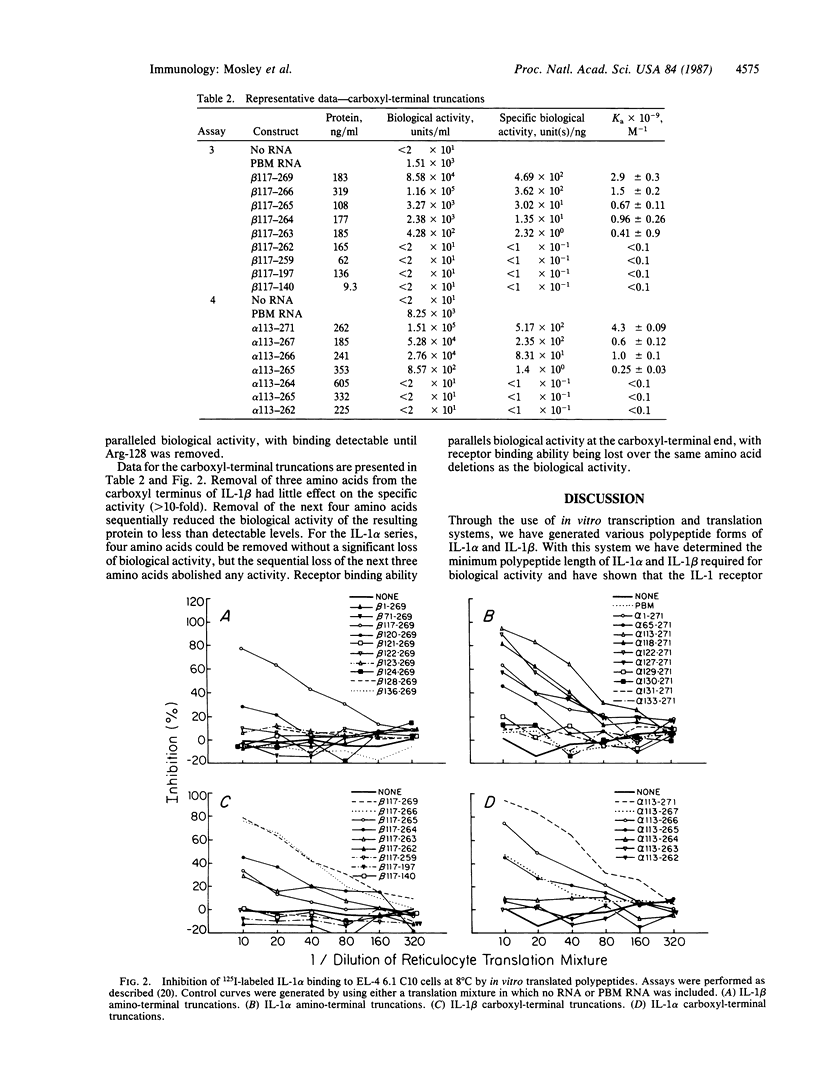
- DeChiara T. M., Young D., Semionow R., Stern A. S., Batula-Bernardo C., Fiedler-Nagy C., Kaffka K. L., Kilian P. L., Yamazaki S., Mizel S. B. Structure-function analysis of murine interleukin 1: biologically active polypeptides are at least 127 amino acids long and are derived from the carboxyl terminus of a 270-amino acid precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8303–8307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhirst F. E., Stashenko P. P., Mole J. E., Tsurumachi T. Purification and partial sequence of human osteoclast-activating factor: identity with interleukin 1 beta. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2562–2568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Clowes G. H., Jr, Gordon A. H., Saravis C. A., Wolff S. M. Cleavage of human interleukin 1: isolation of a peptide fragment from plasma of febrile humans and activated monocytes. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1332–1338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):51–95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower S. K., Call S. M., Gillis S., Urdal D. L. Similarity between the interleukin 1 receptors on a murine T-lymphoma cell line and on a murine fibroblast cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1060–1064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furutani Y., Notake M., Yamayoshi M., Yamagishi J., Nomura H., Ohue M., Furuta R., Fukui T., Yamada M., Nakamura S. Cloning and characterization of the cDNAs for human and rabbit interleukin-1 precursor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 26;13(16):5869–5882. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.16.5869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Mizel S. B. T-Cell lymphoma model for the analysis of interleukin 1-mediated T-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1133–1137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kampschmidt R. F. The numerous postulated biological manifestations of interleukin-1. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Sep;36(3):341–355. doi: 10.1002/jlb.36.3.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball E. S., Pickeral S. F., Oppenheim J. J., Rossio J. L. Interleukin 1 activity in normal human urine. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):256–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P. T., Gubler U., Hellmann C. P., Dukovich M., Giri J. G., Pan Y. C., Collier K., Semionow R., Chua A. O., Mizel S. B. Cloning and expression of murine interleukin-1 cDNA in Escherichia coli. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):458–462. doi: 10.1038/312458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Rousseaux M., Lees R., MacDonald H. R., Bron C. Cell surface glycoproteins involved in the stimulation of interleukin 1-dependent interleukin 2 production by a subline of EL4 thymoma cells. II. Structure, biosynthesis, and maturation. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3951–3957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March C. J., Mosley B., Larsen A., Cerretti D. P., Braedt G., Price V., Gillis S., Henney C. S., Kronheim S. R., Grabstein K. Cloning, sequence and expression of two distinct human interleukin-1 complementary DNAs. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):641–647. doi: 10.1038/315641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Ovalbumin messenger ribonucleic acid translation. Comparable rates of polypeptide initiation and elongation on ovalbumin and globin messenger ribonucleic acid in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2095–2106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenwasser L. J., Webb A. C., Clark B. D., Irie S., Chang L., Dinarello C. A., Gehrke L., Wolff S. M., Rich A., Auron P. E. Expression of biologically active human interleukin 1 subpeptides by transfected simian COS cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5243–5246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp E. A., Cameron P. M., Ranawat C. S., Schmidt J. A., Bayne E. K. Specific bioactivities of monocyte-derived interleukin 1 alpha and interleukin 1 beta are similar to each other on cultured murine thymocytes and on cultured human connective tissue cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):836–839. doi: 10.1172/JCI112649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saklatvala J., Sarsfield S. J., Townsend Y. Pig interleukin 1. Purification of two immunologically different leukocyte proteins that cause cartilage resorption, lymphocyte activation, and fever. J Exp Med. 1985 Oct 1;162(4):1208–1222. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.4.1208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. A. Purification and partial biochemical characterization of normal human interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):772–787. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. J., Bell J. E. An exponential gradient marker for use with minigel polyacrylamide electrophoresis systems. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jan;152(1):74–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90121-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]