Abstract
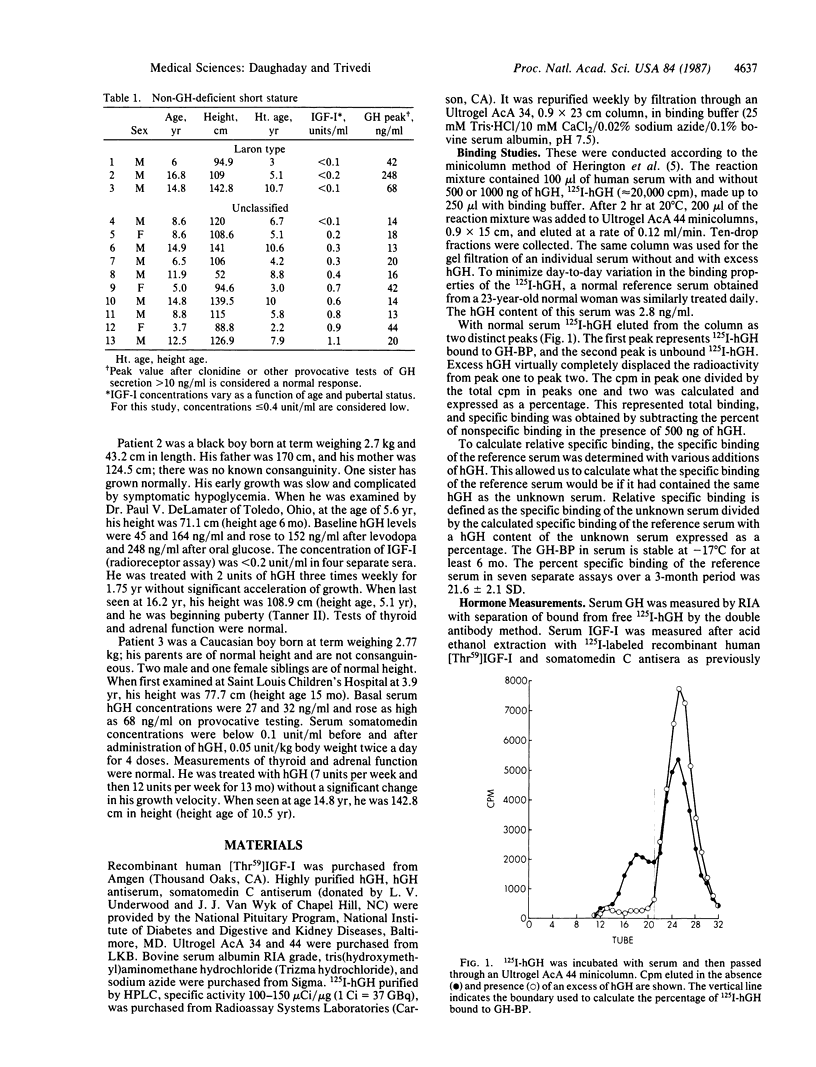
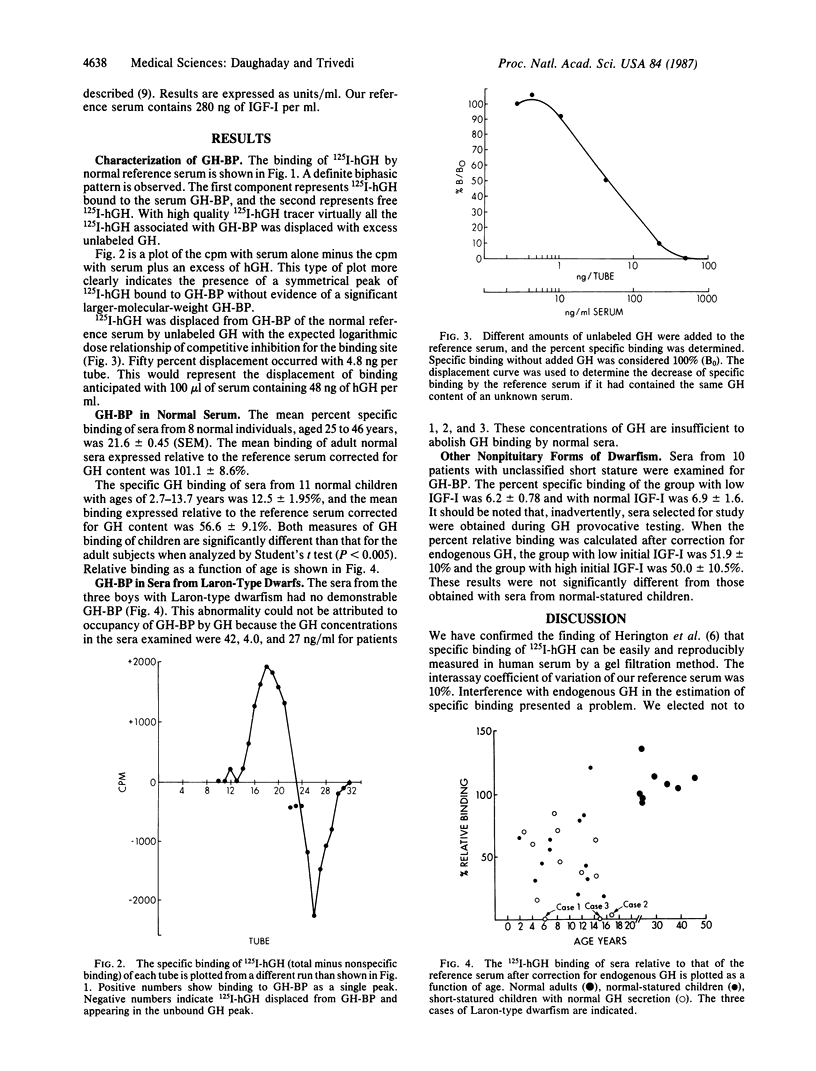
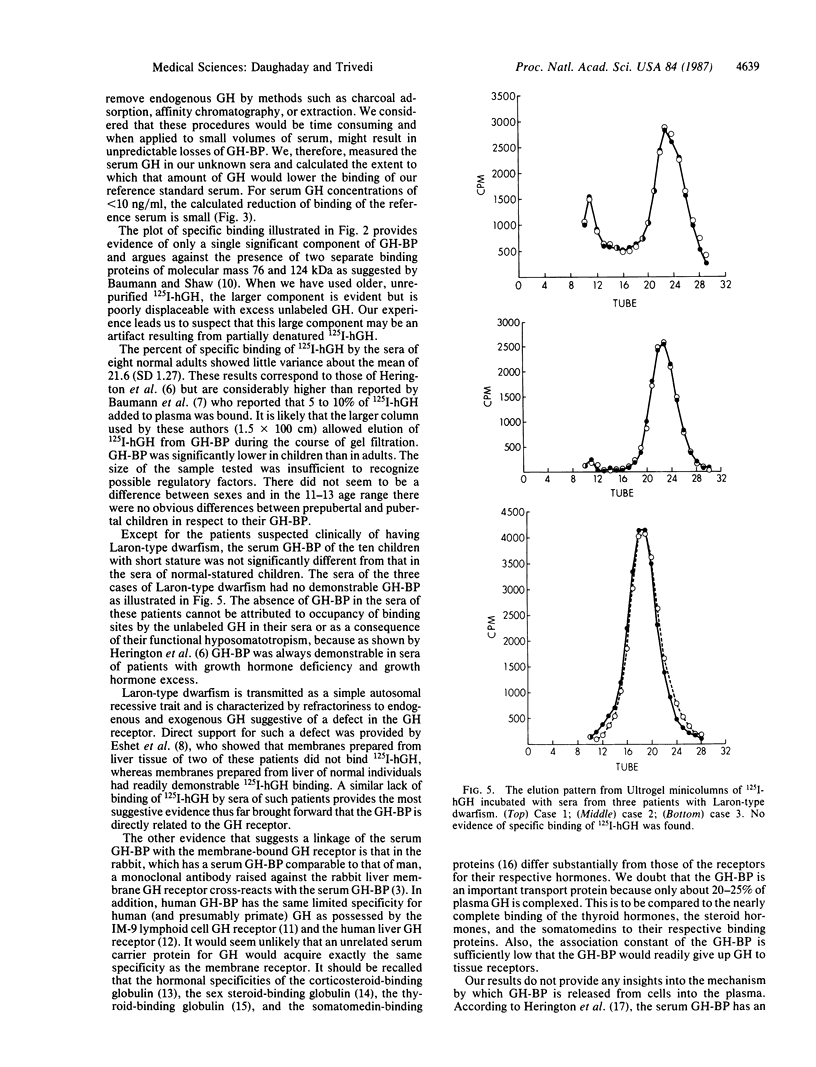
It has recently been recognized that human serum contains a protein that specifically binds human growth hormone (hGH). This protein has the same restricted specificity for hGH as the membrane-bound GH receptor. To determine whether the GH-binding protein is a derivative of, or otherwise related to, the GH receptor, we have examined the serum of three patients with Laron-type dwarfism, a condition in which GH refractoriness has been attributed to a defect in the GH receptor. The binding of 125I-labeled hGH incubated with serum has been measured after gel filtration of the serum through an Ultrogel AcA 44 minicolumn. Nonspecific binding was determined when 125I-hGH was incubated with serum in the presence of an excess of GH. Results are expressed as percent of specifically bound 125I-hGH and as specific binding relative to that of a reference serum after correction is made for endogenous GH. The mean +/- SEM of specific binding of sera from eight normal adults (26-46 years of age) was 21.6 +/- 0.45%, and the relative specific binding was 101.1 +/- 8.6%. Sera from 11 normal children had lower specific binding of 12.5 +/- 1.95% and relative specific binding of 56.6 +/- 9.1%. Sera from three children with Laron-type dwarfism lacked any demonstrable GH binding, whereas sera from 10 other children with other types of nonpituitary short stature had normal relative specific binding. We suggest that the serum GH-binding protein is a soluble derivative of the GH receptor. Measurement of the serum GH-binding protein may permit recognition of other abnormalities of the GH receptor.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumann G., Stolar M. W., Amburn K., Barsano C. P., DeVries B. C. A specific growth hormone-binding protein in human plasma: initial characterization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Jan;62(1):134–141. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-1-134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton R. M., Westphal U. Steroid hormone-binding proteins in blood plasma. Metabolism. 1972 Mar;21(3):253–276. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(72)90048-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr D., Friesen H. G. Growth hormone and insulin binding to human liver. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Mar;42(3):484–493. doi: 10.1210/jcem-42-3-484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cody V. Thyroid hormone interactions: molecular conformation, protein binding, and hormone action. Endocr Rev. 1980 Spring;1(2):140–166. doi: 10.1210/edrv-1-2-140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Mariz I. K., Blethen S. L. Inhibition of access of bound somatomedin to membrane receptor and immunobinding sites: a comparison of radioreceptor and radioimmunoassay of somatomedin in native and acid-ethanol-extracted serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Oct;51(4):781–788. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-4-781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshet R., Laron Z., Pertzelan A., Arnon R., Dintzman M. Defect of human growth hormone receptors in the liver of two patients with Laron-type dwarfism. Isr J Med Sci. 1984 Jan;20(1):8–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Buell D. N., Roth J. Water-soluble insulin receptors from human lymphocytes. Science. 1972 Oct 13;178(4057):168–169. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4057.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P., Hendricks C. M., Roth J. Evidence for "big" and "little" components of human plasma and pituitary growth hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Jan;36(1):178–184. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-1-178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herington A. C., Ymer S. I., Stevenson J. L. Affinity purification and structural characterization of a specific binding protein for human growth hormone in human serum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 29;139(1):150–155. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herington A. C., Ymer S., Roupas P., Stevenson J. Growth hormone-binding proteins in high-speed cytosols of multiple tissues of the rabbit. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Apr 11;881(2):236–240. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herington A. C., Ymer S., Stevenson J. Identification and characterization of specific binding proteins for growth hormone in normal human sera. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1817–1823. doi: 10.1172/JCI112507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L. Plasma forms of somatomedin and the binding protein phenomenon. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Mar;13(1):31–42. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(84)80007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. P., Simpson J. S., Friesen H. G. Analysis of growth hormone and lactogenic binding sites cross-linked to iodinated human growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1983 Jun;112(6):1980–1985. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-6-1980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. A., Posner B. I., Tsushima T., Friesen H. G. Studies of insulin, growth hormone and prolactin binding: ontogenesis, effects of sex and pregnancy. Endocrinology. 1974 Aug;95(2):532–539. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-2-532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiess W., Butenandt O. Specific growth hormone receptors on human peripheral mononuclear cells: reexpression, identification, and characterization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Apr;60(4):740–746. doi: 10.1210/jcem-60-4-740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Schneider W. J., Südhof T. C., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. Mutation in LDL receptor: Alu-Alu recombination deletes exons encoding transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):140–146. doi: 10.1126/science.3155573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesniak M. A., Gorden P., Roth J. Reactivity of non-primate growth hormones and prolactins with human growth hormone receptors on cultured human lymphocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 May;44(5):838–849. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-5-838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuffin W. L., Jr, Gavin J. R., 3rd, Lesniak M. A., Gorden P., Roth J. Water-soluble specific growth hormone binding sites from cultured human lymphocytes: preparation and partial characterization. Endocrinology. 1976 Jun;98(6):1401–1407. doi: 10.1210/endo-98-6-1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy L. J., Vrhovsek E., Lazarus L. Identification and characterization of specific growth hormone receptors in cultured human fibroblasts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Dec;57(6):1117–1124. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-6-1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson J. S., Hughes J. P., Friesen H. G. A monoclonal antibody to the growth hormone receptor of rabbit liver membranes. Endocrinology. 1983 Jun;112(6):2137–2141. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-6-2137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soman V., Goodman A. D. Studies of the composition and radioreceptor activity of "big" and "little" human growth hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Mar;44(3):569–581. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-3-569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigersky R. A., Loriaux D. L., Howards S. S., Hodgen G. B., Lipsett M. B., Chrambach A. Androgen binding proteins of testis, epididymis, and plasma in man and monkey. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1061–1068. doi: 10.1172/JCI108557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ymer S. I., Herington A. C. Evidence for the specific binding of growth hormone to a receptor-like protein in rabbit serum. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1985 Jul;41(2-3):153–161. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(85)90018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



