Abstract
In the title coordination polymer, [Pb(C7H3NO4)]n, the PbII ion is eight-coordinated in a distorted square-antiprismatic geometry formed by one pyridine N atom and seven carboxylate O atoms from four pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylate (pda) anions. In the pda anion, the dihedral angles between the pyridine ring and carboxylate groups are 19.5 (6) and 73.3 (6)°. The carboxylate groups of the pda anions bridge the Pb ions, forming a two-dimensional coordination polymer parallel to (100). Weak intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen boning is present in the crystal structure.
Related literature
For the coordination modes of the pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylate anion, see: Aghabozorg et al. (2007 ▶); Baruah et al. (2007 ▶); Li et al. (2006 ▶). For the biological activity of pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid, see: Xiang et al. (2006 ▶); Yang et al. (2006 ▶); Zhang et al. (2008 ▶). For the inert lone-pair effect, see: Liat et al. (1998 ▶). For longer Pb—O bonds, see: Mao et al. (2006 ▶); Yang et al. (2010 ▶).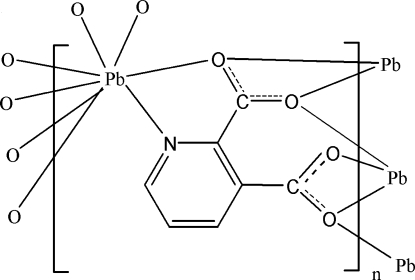
Experimental
Crystal data
[Pb(C7H3NO4)]
M r = 372.30
Monoclinic,
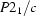
a = 11.6943 (9) Å
b = 4.5392 (4) Å
c = 14.1636 (12) Å
β = 90.046 (2)°
V = 751.84 (11) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 22.42 mm−1
T = 297 K
0.54 × 0.23 × 0.04 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2001 ▶) T min = 0.659, T max = 1.000
4013 measured reflections
1484 independent reflections
1336 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.125
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.073
wR(F 2) = 0.204
S = 1.13
1484 reflections
118 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 4.56 e Å−3
Δρmin = −5.06 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2000 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 1999 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811000419/xu5124sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811000419/xu5124Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected bond lengths (Å).
| Pb—N | 2.651 (7) |
| Pb—O1i | 2.816 (7) |
| Pb—O1ii | 2.911 (6) |
| Pb—O2 | 2.592 (7) |
| Pb—O2i | 2.566 (9) |
| Pb—O3iii | 2.397 (9) |
| Pb—O3ii | 2.754 (9) |
| Pb—O4ii | 2.845 (7) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 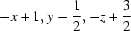 ; (ii)
; (ii) 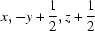 ; (iii)
; (iii) 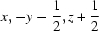 .
.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C5—H5A⋯O3iii | 0.93 | 2.57 | 3.164 (13) | 122 |
Symmetry code: (iii) 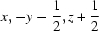 .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported financially by Yuanpei University, Taiwan.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
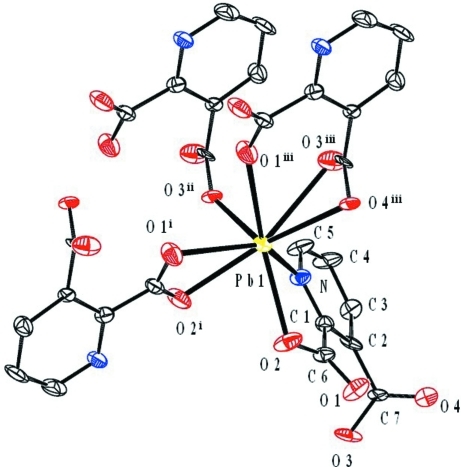
The pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid (pdaH2) is a typical chealated-form ligand. Its biological importance has been described in several literatures (Xiang et al., 2006; Yang et al., 2006; Zhang et al., 2008). Pda shows diverse coordination modes, such as monodentate (Baruah et al., 2007), µ2-bridging (Aghabozorg et al., 2007), µ3-bridging (Li et al., 2006). Here we describe the title compound in which the pda is a µ4-bridging ligand (Fig. 1).
The structure of a coordination polymer [Pb(C7H3NO4)]n, the lead ion is eight-coordinated with a distorted square-antiprismatic geometry formed by one O-monodentate pda-2 ligand, one N,O-bidentate pda-2 ligand, one O,O'-bidentate pda-2 ligand and one O,O',O''-tridentate pda-2 ligand (Table 1). According to "inert-pair effect", the coordination number of PbII is variable, and the lengths of bonds to PbII vary in a wide range (Liat et al., 1998). Longer distance is observed between Pb and O1 (2.911 (6) Å); some long Pb—O weak bonds have also been reported in reported lead complexes (Mao et al., 2006; Yang et al., 2010). The carboxylate group of pda-2ligand bridges four PbII ion forming a 2-D framework is constructed.
There are no classic intermolecular hydrogen-bonding in the title compound, but intermolecular C—H···O weak interaction (Table 2) and ring···metal interaction help to stabilize the crystal structure, the Cg3 (Pb/O1—O2—C6)···Pb interaction is 3.877 Å (symmetry code: 1 - x,-1/2 + y,3/2 - z).
Experimental
An aqueous solution (5 ml) containing Pb(NO3)2 (0.164 g, 0.50 mmol) and 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane (0.0934 g, 0.50 mmol) was added to an aqueous solution (5 ml) of pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid (0.0838 g, 0.50 mmol), and the mixture was stirred for 30 minutes and then filtered. The solution was placed in a 23 ml Teflon-lined reactor, heated at 423 K for 3 days, then cooled slowly to room temperature. The colorless transparent single crystals of the title compound were obtained in 45.67% yield (based on Pb).
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically with C—H = 0.93 (aromatic), and were refined using a riding model with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
View of the title compound with the atom numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms have been omitted for clarity.[Symmetry codes: (i) -x + 1, y - 1/2, -z + 3/2; (ii) x, -y - 1/2, z + 1/2; (iii) x, -y + 1/2].
Crystal data
| [Pb(C7H3NO4)] | F(000) = 664 |
| Mr = 372.30 | Dx = 3.289 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 2856 reflections |
| a = 11.6943 (9) Å | θ = 2.3–26.0° |
| b = 4.5392 (4) Å | µ = 22.42 mm−1 |
| c = 14.1636 (12) Å | T = 297 K |
| β = 90.046 (2)° | Parallelepiped, colorless |
| V = 751.84 (11) Å3 | 0.54 × 0.23 × 0.04 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 1484 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1336 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.125 |
| Detector resolution: 9 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 1.7° |
| ω scan | h = −14→10 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2001) | k = −5→5 |
| Tmin = 0.659, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −17→17 |
| 4013 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.073 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.204 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.13 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.1477P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1484 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 118 parameters | Δρmax = 4.56 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −5.06 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. Elemental analysis: calculated for C7H3NO4Pb: (Mr=372.29) C, 22.56; H, 0.81; N, 3.76%. Found:C,22.47; H, 0.89; N, 3.85%. IR data (cm-1): 3429(s), 1602(s), 1579(s), 1551(s), 1459(w), 1385(s), 1276(w), 1236(w), 1105(m), 871(m), 825(m), 779(m), 711(s), 700(m), 660(m), 603(w), 534(w), 443(w). |
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement on F2 for ALL reflections except those flagged by the user for potential systematic errors. Weighted R-factors wR and all goodnesses of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The observed criterion of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating -R-factor-obs etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Pb | 0.60762 (4) | 0.01636 (10) | 0.85892 (3) | 0.0213 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.6007 (6) | 0.3400 (19) | 0.5591 (4) | 0.035 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.5381 (7) | 0.120 (2) | 0.6883 (5) | 0.037 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.6905 (9) | −0.061 (2) | 0.4106 (6) | 0.032 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.8222 (6) | 0.2863 (17) | 0.4294 (4) | 0.038 (2) | |
| N | 0.7437 (6) | −0.1315 (19) | 0.7170 (5) | 0.024 (2) | |
| C1 | 0.7208 (12) | −0.0178 (18) | 0.6321 (9) | 0.021 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.7951 (11) | −0.058 (3) | 0.5526 (9) | 0.021 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.8932 (8) | −0.216 (2) | 0.5715 (6) | 0.027 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.9192 (9) | −0.325 (3) | 0.6603 (7) | 0.038 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.8383 (9) | −0.288 (3) | 0.7300 (6) | 0.036 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.6141 (8) | 0.163 (3) | 0.6231 (6) | 0.023 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.7687 (9) | 0.068 (2) | 0.4580 (7) | 0.019 (3) | |
| H3A | 0.94410 | −0.25180 | 0.52240 | 0.0320* | |
| H4A | 0.98820 | −0.41980 | 0.67230 | 0.0450* | |
| H5A | 0.85060 | −0.37490 | 0.78850 | 0.0430* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Pb | 0.0207 (5) | 0.0242 (5) | 0.0189 (5) | −0.0031 (1) | −0.0051 (3) | −0.0016 (1) |
| O1 | 0.035 (4) | 0.045 (5) | 0.026 (3) | 0.015 (4) | 0.007 (3) | 0.012 (3) |
| O2 | 0.027 (4) | 0.061 (6) | 0.024 (3) | 0.017 (5) | 0.001 (3) | 0.013 (4) |
| O3 | 0.039 (5) | 0.031 (4) | 0.027 (4) | 0.006 (4) | −0.022 (4) | −0.013 (4) |
| O4 | 0.044 (4) | 0.041 (5) | 0.030 (3) | −0.007 (4) | −0.010 (3) | 0.009 (3) |
| N | 0.018 (4) | 0.032 (5) | 0.021 (3) | 0.004 (3) | −0.003 (3) | 0.004 (3) |
| C1 | 0.018 (7) | 0.028 (6) | 0.017 (6) | −0.002 (3) | 0.000 (5) | −0.001 (3) |
| C2 | 0.006 (5) | 0.037 (5) | 0.021 (5) | 0.002 (4) | −0.004 (4) | −0.010 (5) |
| C3 | 0.023 (5) | 0.032 (6) | 0.026 (4) | 0.006 (4) | 0.003 (4) | 0.003 (4) |
| C4 | 0.029 (6) | 0.054 (8) | 0.031 (5) | 0.018 (6) | −0.013 (4) | 0.010 (5) |
| C5 | 0.041 (6) | 0.046 (7) | 0.021 (4) | 0.009 (5) | −0.009 (4) | 0.011 (4) |
| C6 | 0.018 (5) | 0.031 (5) | 0.021 (4) | 0.006 (4) | −0.005 (3) | 0.002 (4) |
| C7 | 0.008 (5) | 0.030 (5) | 0.019 (4) | 0.006 (4) | −0.007 (4) | 0.004 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Pb—N | 2.651 (7) | N—C1 | 1.336 (14) |
| Pb—O1i | 2.816 (7) | N—C5 | 1.327 (14) |
| Pb—O1ii | 2.911 (6) | C1—C2 | 1.435 (18) |
| Pb—O2 | 2.592 (7) | C1—C6 | 1.499 (17) |
| Pb—O2i | 2.566 (9) | C2—C3 | 1.379 (16) |
| Pb—O3iii | 2.397 (9) | C2—C7 | 1.489 (16) |
| Pb—O3ii | 2.754 (9) | C3—C4 | 1.385 (14) |
| Pb—O4ii | 2.845 (7) | C4—C5 | 1.378 (14) |
| O1—C6 | 1.221 (13) | C3—H3A | 0.9300 |
| O2—C6 | 1.297 (12) | C4—H4A | 0.9300 |
| O3—C7 | 1.276 (14) | C5—H5A | 0.9300 |
| O4—C7 | 1.240 (12) | ||
| O2—Pb—N | 61.8 (2) | Pbv—O1—C6 | 150.1 (7) |
| O1i—Pb—O2 | 99.5 (2) | Pbiv—O1—Pbv | 111.3 (2) |
| O2—Pb—O2i | 71.1 (3) | Pb—O2—C6 | 118.5 (6) |
| O2—Pb—O3iii | 124.6 (3) | Pb—O2—Pbiv | 125.3 (3) |
| O1ii—Pb—O2 | 149.2 (2) | Pbiv—O2—C6 | 99.5 (7) |
| O2—Pb—O3ii | 101.2 (3) | Pbvi—O3—C7 | 147.7 (8) |
| O2—Pb—O4ii | 123.1 (2) | Pbv—O3—C7 | 88.8 (6) |
| O2—Pb—C7ii | 121.1 (3) | Pbvi—O3—Pbv | 123.4 (4) |
| O1i—Pb—N | 139.5 (2) | Pbv—O4—C7 | 85.5 (6) |
| O2i—Pb—N | 91.4 (2) | Pb—N—C1 | 117.7 (7) |
| O3iii—Pb—N | 76.7 (3) | Pb—N—C5 | 122.1 (6) |
| O1ii—Pb—N | 144.3 (2) | C1—N—C5 | 119.9 (9) |
| O3ii—Pb—N | 102.6 (3) | N—C1—C2 | 122.4 (11) |
| O4ii—Pb—N | 79.4 (2) | N—C1—C6 | 117.0 (10) |
| N—Pb—C7ii | 97.8 (3) | C2—C1—C6 | 120.5 (10) |
| O1i—Pb—O2i | 48.2 (2) | C1—C2—C3 | 114.7 (11) |
| O1i—Pb—O3iii | 88.8 (3) | C1—C2—C7 | 122.2 (11) |
| O1i—Pb—O1ii | 68.73 (19) | C3—C2—C7 | 123.1 (10) |
| O1i—Pb—O3ii | 116.7 (3) | C2—C3—C4 | 123.0 (10) |
| O1i—Pb—O4ii | 135.08 (17) | C3—C4—C5 | 117.2 (10) |
| O1i—Pb—C7ii | 121.8 (2) | N—C5—C4 | 122.6 (9) |
| O2i—Pb—O3iii | 75.1 (3) | O1—C6—O2 | 122.7 (10) |
| O1ii—Pb—O2i | 113.1 (2) | O1—C6—C1 | 122.0 (9) |
| O2i—Pb—O3ii | 158.7 (3) | O2—C6—C1 | 115.3 (10) |
| O2i—Pb—O4ii | 153.8 (2) | O3—C7—O4 | 123.8 (9) |
| O2i—Pb—C7ii | 167.3 (2) | O3—C7—C2 | 116.4 (9) |
| O1ii—Pb—O3iii | 84.7 (3) | Pbv—C7—O3 | 66.1 (6) |
| O3iii—Pb—O3ii | 123.4 (3) | O4—C7—C2 | 119.8 (9) |
| O3iii—Pb—O4ii | 78.9 (3) | Pbv—C7—O4 | 70.3 (5) |
| O3iii—Pb—C7ii | 98.4 (3) | Pbv—C7—C2 | 142.1 (7) |
| O1ii—Pb—O3ii | 63.3 (2) | C2—C3—H3A | 119.00 |
| O1ii—Pb—O4ii | 67.22 (18) | C4—C3—H3A | 118.00 |
| O1ii—Pb—C7ii | 54.8 (2) | C3—C4—H4A | 121.00 |
| O3ii—Pb—O4ii | 46.7 (3) | C5—C4—H4A | 121.00 |
| O3ii—Pb—C7ii | 25.1 (3) | N—C5—H5A | 119.00 |
| O4ii—Pb—C7ii | 24.2 (2) | C4—C5—H5A | 119.00 |
| Pbiv—O1—C6 | 89.5 (6) | ||
| N—Pb—O2—C6 | −27.3 (8) | O2—Pb—O4ii—C7ii | 93.1 (6) |
| N—Pb—O2—Pbiv | −155.1 (5) | N—Pb—O4ii—C7ii | 138.9 (6) |
| O1i—Pb—O2—C6 | −169.0 (9) | O2—Pb—C7ii—O3ii | 41.3 (7) |
| O1i—Pb—O2—Pbiv | 63.2 (4) | O2—Pb—C7ii—O4ii | −102.4 (5) |
| O2i—Pb—O2—C6 | −129.5 (9) | O2—Pb—C7ii—C2ii | 144.2 (11) |
| O2i—Pb—O2—Pbiv | 102.7 (4) | N—Pb—C7ii—O3ii | 102.9 (6) |
| O3iii—Pb—O2—C6 | −73.9 (10) | N—Pb—C7ii—O4ii | −40.7 (6) |
| O3iii—Pb—O2—Pbiv | 158.3 (4) | N—Pb—C7ii—C2ii | −154.2 (12) |
| O1ii—Pb—O2—C6 | 126.9 (9) | Pbv—O1—C6—O2 | −131.7 (11) |
| O1ii—Pb—O2—Pbiv | −0.9 (7) | Pbiv—O1—C6—C1 | −175.5 (10) |
| O3ii—Pb—O2—C6 | 71.1 (9) | Pbiv—O1—C6—O2 | 3.8 (11) |
| O3ii—Pb—O2—Pbiv | −56.7 (4) | Pbv—O1—C6—C1 | 49.0 (19) |
| O4ii—Pb—O2—C6 | 25.9 (10) | Pbiv—O2—C6—C1 | 175.1 (8) |
| O4ii—Pb—O2—Pbiv | −101.9 (4) | Pb—O2—C6—C1 | 36.0 (13) |
| C7ii—Pb—O2—C6 | 54.5 (10) | Pb—O2—C6—O1 | −143.4 (9) |
| C7ii—Pb—O2—Pbiv | −73.3 (5) | Pbiv—O2—C6—O1 | −4.2 (12) |
| O2—Pb—N—C1 | 15.4 (7) | Pbvi—O3—C7—O4 | 136.7 (11) |
| O2—Pb—N—C5 | −171.4 (9) | Pbv—O3—C7—O4 | −42.2 (10) |
| O1i—Pb—N—C1 | 85.5 (8) | Pbvi—O3—C7—C2 | −43.1 (19) |
| O1i—Pb—N—C5 | −101.3 (8) | Pbv—O3—C7—C2 | 138.0 (9) |
| O2i—Pb—N—C1 | 83.0 (7) | Pbvi—O3—C7—Pbv | 178.9 (15) |
| O2i—Pb—N—C5 | −103.8 (9) | Pbv—O4—C7—O3 | 40.7 (10) |
| O3iii—Pb—N—C1 | 157.4 (8) | Pbv—O4—C7—C2 | −139.5 (9) |
| O3iii—Pb—N—C5 | −29.4 (9) | C5—N—C1—C2 | 0.1 (16) |
| O1ii—Pb—N—C1 | −142.1 (7) | Pb—N—C1—C2 | 173.5 (8) |
| O1ii—Pb—N—C5 | 31.1 (10) | Pb—N—C1—C6 | −5.1 (12) |
| O3ii—Pb—N—C1 | −80.8 (7) | C1—N—C5—C4 | 4.1 (17) |
| O3ii—Pb—N—C5 | 92.4 (9) | C5—N—C1—C6 | −178.5 (10) |
| O4ii—Pb—N—C1 | −121.6 (7) | Pb—N—C5—C4 | −169.0 (9) |
| O4ii—Pb—N—C5 | 51.6 (8) | C6—C1—C2—C3 | 176.8 (10) |
| C7ii—Pb—N—C1 | −105.8 (7) | N—C1—C2—C3 | −1.7 (16) |
| C7ii—Pb—N—C5 | 67.4 (9) | N—C1—C2—C7 | 179.7 (10) |
| O2—Pb—O1i—C6i | 51.7 (7) | C6—C1—C2—C7 | −1.9 (17) |
| O2—Pb—O1i—Pbvii | −150.3 (3) | N—C1—C6—O1 | 159.4 (10) |
| N—Pb—O1i—C6i | −5.4 (8) | N—C1—C6—O2 | −20.0 (15) |
| N—Pb—O1i—Pbvii | 152.5 (3) | C2—C1—C6—O1 | −19.2 (17) |
| O2—Pb—O2i—Pbi | 14.6 (4) | C2—C1—C6—O2 | 161.5 (10) |
| O2—Pb—O2i—C6i | −120.6 (7) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.7 (17) |
| N—Pb—O2i—Pbi | −44.8 (4) | C7—C2—C3—C4 | 177.9 (11) |
| N—Pb—O2i—C6i | 179.9 (7) | C1—C2—C7—O3 | −74.7 (15) |
| O2—Pb—O3iii—C7iii | 136.3 (13) | C1—C2—C7—O4 | 105.5 (13) |
| N—Pb—O3iii—C7iii | 95.1 (14) | C1—C2—C7—Pbv | 10 (2) |
| O2—Pb—O1ii—Pbvii | 72.2 (6) | C3—C2—C7—O3 | 106.7 (13) |
| O2—Pb—O1ii—C6ii | −59.0 (14) | C3—C2—C7—O4 | −73.0 (15) |
| N—Pb—O1ii—Pbvii | −149.1 (3) | C3—C2—C7—Pbv | −168.9 (8) |
| N—Pb—O1ii—C6ii | 79.8 (14) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 4.5 (18) |
| O2—Pb—O3ii—C7ii | −144.8 (6) | C3—C4—C5—N | −6.3 (18) |
| N—Pb—O3ii—C7ii | −81.6 (6) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+3/2; (ii) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (iii) x, −y−1/2, z+1/2; (iv) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+3/2; (v) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (vi) x, −y−1/2, z−1/2; (vii) −x+1, −y, −z+2.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C5—H5A···O3iii | 0.93 | 2.57 | 3.164 (13) | 122 |
Symmetry codes: (iii) x, −y−1/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: XU5124).
References
- Aghabozorg, H., Daneshvar, S., Motyeian, E., Ghadermazi, M. & Attar Gharamaleki, J. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, m2468–m2469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Baruah, A. M., Karmakar, A. & Baruah, J. B. (2007). Polyhedron, 26, 4518–4524.
- Bruker (1999). SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2000). SMART Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2001). SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Li, M., Xiang, J.-F., Yuan, L.-J., Wu, S.-M., Chen, S.-P. & Sun, J.-T. (2006). Cryst. Growth Des. 6, 2036–2040.
- Liat, S. L., Glusker, J. P. & Bock, C. W. (1998). Inorg. Chem. 37, 1853–1867.
- Mao, J.-G., Wang, Z. & Gearfield, A. (2006). Inorg. Chem. 41, 6106–6111.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Xiang, J.-F., Li, M., Wu, S.-M., Yuan, L.-J. & Sun, J.-T. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, m1122–m1123.
- Yang, J., Dai, J. & Wang, X. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, m1686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Yang, H., Zhang, Z.-H., Guo, J.-H. & Lu, Y.-C. (2006). Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 25, 689–693.
- Zhang, C.-X., Ma, C.-B., Wang, M. & Chen, C.-N. (2008). Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 27, 1370–1374.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811000419/xu5124sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811000419/xu5124Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report