Abstract
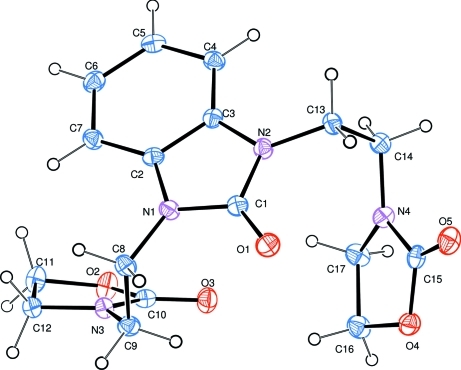
The molecular structure of the title compound, C17H20N4O5, contains a central fused-ring system, comprised of six- and five-membered rings. This unit is linked by C2 chains to two 2-oxo-1,3-oxazolidine five-membered rings. The central fused-ring system is essentially planar, with a maximum deviation of 0.008 (1) Å from the mean plane. Both oxazolidine five-membered rings are also nearly planar, with maximum deviations of 0.090 (1) and 0.141 (1) Å.
Related literature
For the pharmacological and biochemical properties of oxazolidin-2-ones, see: Gribkoff et al. (1994 ▶); Olesen et al. (1994 ▶); Soderlind et al. (1999 ▶). For their antibacterial activity, see: Diekema & Jones (2000 ▶); Mukhtar & Wright (2005 ▶). For related structures, see: Ouzidan et al. (2010 ▶); Matsunaga et al. (2005 ▶); Evans et al. (1993 ▶); Caleb et al. (2009 ▶); Ahoya et al. (2010 ▶); Bel-Ghacham et al. (2010 ▶); Alsubari et al. (2009 ▶).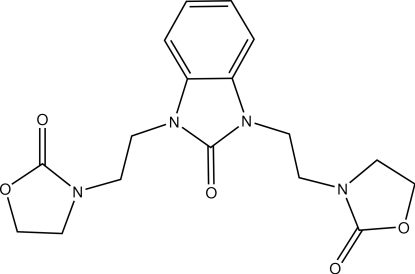
Experimental
Crystal data
C17H20N4O5
M r = 360.37
Monoclinic,
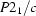
a = 10.5331 (10) Å
b = 10.9647 (10) Å
c = 14.5541 (14) Å
β = 103.258 (5)°
V = 1636.1 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 0.92 mm−1
T = 90 K
0.30 × 0.28 × 0.18 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.770, T max = 0.852
15549 measured reflections
2914 independent reflections
2842 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.024
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.030
wR(F 2) = 0.074
S = 1.05
2914 reflections
235 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.23 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2005 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810052141/fj2373sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810052141/fj2373Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Benzimidazol-2-one derivatives are useful heterocyclic building blocks and are prominent structural elements of compounds presenting a wide variety of pharmacological and biochemical properties(Gribkoff et al. (1994); Olesen et al. (1994); Soderlind et al. (1999).
Also oxazolidin-2-ones are a very important class of heterocyclic compounds and their derivatives have attracted attention in various areas of drug development for antibacterial activity (Diekema & Jones, 2000); Mukhtar & Wright (2005). Some oxazolidin-2-ones have been used as chiral auxiliaries in a wide range of asymmetric reactions (Evans et al., 1993); Matsunaga et al. (2005).
In the previous works, we have studied the crystal structure of several heterocyclic systems containng oxazolidin-2-one (Ouzidan et al. (2010); Caleb et al. (2009); Ahoya et al. (2010); Bel-Ghacham et al. (2010); Alsubari et al. (2009)). In this work, we have synthesized benzimidazol-2-one possessing Oxazolidin-2-one ring by action of bis(2-chloroethyl)amine hydrochloride with 1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one using same conditions, the reaction provided the title compound (Scheme 1).
The 1,3-bis(2-(2-oxo-oxazolidin-3-yl)ethyl)-1H-benzimidazol -\2(3H)-one molecule structure is built up from two fused six-and five-membered rings linked to two chains of five-membered rings by ethylene groups as schown in Fg.1. The fused-ring system is essentially planar, with a maximum deviation of 0.008 (1) Å and -0.008 (1) Å for C1 and C7 or N2 respectyvely. The dihedral angle between them does not exceed 0.23 (6)°. The both five-membered rings (2-oxo-oxazolidine) are almost planar with maximum deviation of -0.090 (1) Å and -0.141 (1) Å for C11 and C16 respectyvely. Their puckering parameters are Q2 = 0.1498 (2) Å and φ2 = 131.6 (5)° for (O2C10N3C12C11) and Q2 = 0.2343 (2) Å and φ2 = -49.4 (3)° for (O4C15N4C17C16). The dihedral angles between each of them and the fused rings are 43.02 (5)° (O2C10N3C12C11) and 49.12 (6)° (O4C15N4C17C16). The torsion angles C1 N1 C8 C9 and C1 N2 C13 C14 are -87.85 (2)° and 101.00 (2)° respectively. These values show the strong asymmetry of the molecule.
Experimental
To 1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one (0,2 g, 1,5 mmol), potassium carbonate (0,82 g, 6 mmol), and tetra-n-butylammonium bromide (0.1 g, 0,3 mmol) in DMF (15 ml) was added bis(2-chloroethyl)amine hydrochloride (0,64 g, 3,58 mmol). The mixture was heated for 48 h. After the completion of the reaction (as monitored by TLC), the inorganic material salt was filtered and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by column chromatography on silica gel by using (ethanol/ethyl acetate: 1/4) as eluent. Colorless crystals were isolated when the solvent was allowed to evaporate.
Refinement
H atoms were located in a difference map and treated as riding with C—H = 0.93 Å for all H atoms with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(aromatic, methine).
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound with the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are represented as small circles.
Crystal data
| C17H20N4O5 | F(000) = 760 |
| Mr = 360.37 | Dx = 1.463 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 9916 reflections |
| a = 10.5331 (10) Å | θ = 4.0–68.1° |
| b = 10.9647 (10) Å | µ = 0.92 mm−1 |
| c = 14.5541 (14) Å | T = 90 K |
| β = 103.258 (5)° | Fragment, colourless |
| V = 1636.1 (3) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.28 × 0.18 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2914 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2842 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.024 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 68.2°, θmin = 4.3° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | h = −12→9 |
| Tmin = 0.770, Tmax = 0.852 | k = −12→13 |
| 15549 measured reflections | l = −17→17 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.030 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.074 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0315P)2 + 0.8105P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2914 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 235 parameters | Δρmax = 0.23 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.51156 (8) | 0.90454 (8) | 0.65034 (6) | 0.01864 (19) | |
| O2 | 0.81349 (8) | 0.63845 (8) | 0.39970 (6) | 0.0221 (2) | |
| O3 | 0.61653 (8) | 0.68768 (8) | 0.42496 (6) | 0.0209 (2) | |
| O4 | 0.22108 (8) | 0.77982 (8) | 0.47938 (6) | 0.01792 (19) | |
| O5 | 0.18927 (8) | 0.77876 (8) | 0.62760 (6) | 0.0217 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.71846 (9) | 0.83091 (9) | 0.64775 (7) | 0.0145 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.58627 (9) | 0.71116 (9) | 0.70549 (7) | 0.0143 (2) | |
| N3 | 0.79091 (9) | 0.81926 (9) | 0.46197 (7) | 0.0149 (2) | |
| N4 | 0.33456 (9) | 0.64839 (9) | 0.58183 (7) | 0.0158 (2) | |
| C1 | 0.59511 (11) | 0.82469 (11) | 0.66601 (8) | 0.0143 (2) | |
| C2 | 0.78498 (11) | 0.72200 (10) | 0.67384 (8) | 0.0142 (2) | |
| C3 | 0.70112 (11) | 0.64616 (11) | 0.71027 (7) | 0.0137 (2) | |
| C4 | 0.73829 (11) | 0.52998 (11) | 0.74338 (8) | 0.0157 (2) | |
| H4 | 0.6828 | 0.4800 | 0.7679 | 0.019* | |
| C5 | 0.86290 (11) | 0.49150 (11) | 0.73819 (8) | 0.0174 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.8907 | 0.4137 | 0.7591 | 0.021* | |
| C6 | 0.94645 (11) | 0.56687 (11) | 0.70237 (8) | 0.0176 (3) | |
| H6 | 1.0288 | 0.5384 | 0.7000 | 0.021* | |
| C7 | 0.90915 (11) | 0.68422 (11) | 0.66999 (8) | 0.0162 (2) | |
| H7 | 0.9653 | 0.7350 | 0.6468 | 0.019* | |
| C8 | 0.76194 (11) | 0.93510 (10) | 0.60123 (8) | 0.0159 (2) | |
| H8A | 0.8558 | 0.9432 | 0.6227 | 0.019* | |
| H8B | 0.7223 | 1.0086 | 0.6190 | 0.019* | |
| C9 | 0.72673 (11) | 0.92265 (11) | 0.49385 (8) | 0.0162 (2) | |
| H9A | 0.6330 | 0.9132 | 0.4724 | 0.019* | |
| H9B | 0.7516 | 0.9966 | 0.4659 | 0.019* | |
| C10 | 0.72954 (11) | 0.71504 (11) | 0.42958 (8) | 0.0160 (2) | |
| C11 | 0.94356 (12) | 0.69048 (12) | 0.42409 (9) | 0.0210 (3) | |
| H11A | 0.9846 | 0.6861 | 0.3709 | 0.025* | |
| H11B | 0.9977 | 0.6475 | 0.4771 | 0.025* | |
| C12 | 0.92429 (11) | 0.82316 (11) | 0.45003 (8) | 0.0170 (3) | |
| H12A | 0.9852 | 0.8466 | 0.5080 | 0.020* | |
| H12B | 0.9329 | 0.8785 | 0.3998 | 0.020* | |
| C13 | 0.47432 (11) | 0.67173 (11) | 0.74094 (8) | 0.0156 (2) | |
| H13A | 0.4262 | 0.7430 | 0.7533 | 0.019* | |
| H13B | 0.5050 | 0.6290 | 0.8002 | 0.019* | |
| C14 | 0.38313 (11) | 0.58849 (11) | 0.67225 (8) | 0.0169 (2) | |
| H14A | 0.4293 | 0.5147 | 0.6628 | 0.020* | |
| H14B | 0.3102 | 0.5655 | 0.6989 | 0.020* | |
| C15 | 0.24555 (11) | 0.73773 (11) | 0.57032 (8) | 0.0159 (2) | |
| C16 | 0.31809 (12) | 0.72690 (11) | 0.43458 (9) | 0.0198 (3) | |
| H16A | 0.3889 | 0.7837 | 0.4355 | 0.024* | |
| H16B | 0.2794 | 0.7048 | 0.3697 | 0.024* | |
| C17 | 0.36658 (12) | 0.61423 (11) | 0.49327 (8) | 0.0197 (3) | |
| H17A | 0.3204 | 0.5413 | 0.4665 | 0.024* | |
| H17B | 0.4596 | 0.6023 | 0.5006 | 0.024* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0189 (4) | 0.0159 (4) | 0.0217 (4) | 0.0033 (3) | 0.0056 (3) | 0.0003 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0169 (4) | 0.0205 (5) | 0.0288 (5) | −0.0003 (3) | 0.0049 (3) | −0.0081 (4) |
| O3 | 0.0160 (4) | 0.0201 (5) | 0.0261 (5) | −0.0024 (3) | 0.0038 (3) | −0.0008 (4) |
| O4 | 0.0165 (4) | 0.0186 (4) | 0.0190 (4) | 0.0030 (3) | 0.0048 (3) | 0.0007 (3) |
| O5 | 0.0178 (4) | 0.0263 (5) | 0.0222 (4) | 0.0031 (4) | 0.0069 (3) | −0.0052 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0156 (5) | 0.0134 (5) | 0.0151 (5) | 0.0001 (4) | 0.0047 (4) | 0.0010 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0135 (5) | 0.0143 (5) | 0.0155 (5) | 0.0002 (4) | 0.0044 (4) | 0.0001 (4) |
| N3 | 0.0145 (5) | 0.0147 (5) | 0.0159 (5) | −0.0007 (4) | 0.0042 (4) | −0.0003 (4) |
| N4 | 0.0161 (5) | 0.0158 (5) | 0.0155 (5) | 0.0018 (4) | 0.0037 (4) | −0.0017 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0158 (6) | 0.0145 (6) | 0.0123 (5) | −0.0005 (5) | 0.0025 (4) | −0.0022 (4) |
| C2 | 0.0164 (6) | 0.0143 (6) | 0.0108 (5) | −0.0001 (5) | 0.0010 (4) | −0.0011 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0139 (5) | 0.0159 (6) | 0.0111 (5) | −0.0006 (4) | 0.0020 (4) | −0.0023 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0184 (6) | 0.0160 (6) | 0.0125 (5) | −0.0018 (5) | 0.0031 (4) | 0.0001 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0211 (6) | 0.0153 (6) | 0.0148 (5) | 0.0034 (5) | 0.0019 (4) | 0.0014 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0157 (6) | 0.0212 (6) | 0.0158 (5) | 0.0038 (5) | 0.0033 (4) | −0.0002 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0163 (6) | 0.0188 (6) | 0.0141 (5) | −0.0013 (5) | 0.0047 (4) | 0.0001 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0181 (6) | 0.0118 (6) | 0.0183 (6) | −0.0016 (5) | 0.0054 (4) | −0.0003 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0179 (6) | 0.0133 (6) | 0.0175 (6) | 0.0020 (5) | 0.0042 (4) | 0.0017 (4) |
| C10 | 0.0177 (6) | 0.0163 (6) | 0.0136 (5) | 0.0017 (5) | 0.0024 (4) | 0.0017 (4) |
| C11 | 0.0149 (6) | 0.0240 (7) | 0.0241 (6) | 0.0000 (5) | 0.0049 (5) | −0.0046 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0146 (6) | 0.0201 (6) | 0.0169 (6) | −0.0007 (5) | 0.0046 (4) | 0.0016 (5) |
| C13 | 0.0147 (6) | 0.0172 (6) | 0.0159 (5) | −0.0010 (5) | 0.0057 (4) | −0.0003 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0166 (6) | 0.0161 (6) | 0.0179 (6) | −0.0008 (5) | 0.0038 (4) | 0.0012 (5) |
| C15 | 0.0121 (5) | 0.0165 (6) | 0.0183 (6) | −0.0028 (5) | 0.0020 (4) | −0.0030 (5) |
| C16 | 0.0215 (6) | 0.0197 (6) | 0.0206 (6) | 0.0029 (5) | 0.0097 (5) | 0.0006 (5) |
| C17 | 0.0246 (6) | 0.0175 (6) | 0.0197 (6) | 0.0033 (5) | 0.0106 (5) | −0.0001 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C1 | 1.2252 (14) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| O2—C10 | 1.3612 (14) | C6—C7 | 1.3955 (17) |
| O2—C11 | 1.4510 (15) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| O3—C10 | 1.2144 (14) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| O4—C15 | 1.3692 (14) | C8—C9 | 1.5273 (16) |
| O4—C16 | 1.4531 (14) | C8—H8A | 0.9700 |
| O5—C15 | 1.2147 (14) | C8—H8B | 0.9700 |
| N1—C1 | 1.3862 (15) | C9—H9A | 0.9700 |
| N1—C2 | 1.3926 (15) | C9—H9B | 0.9700 |
| N1—C8 | 1.4545 (15) | C11—C12 | 1.5282 (17) |
| N2—C1 | 1.3831 (15) | C11—H11A | 0.9700 |
| N2—C3 | 1.3921 (15) | C11—H11B | 0.9700 |
| N2—C13 | 1.4570 (14) | C12—H12A | 0.9700 |
| N3—C10 | 1.3439 (16) | C12—H12B | 0.9700 |
| N3—C9 | 1.4496 (15) | C13—C14 | 1.5215 (16) |
| N3—C12 | 1.4552 (14) | C13—H13A | 0.9700 |
| N4—C15 | 1.3396 (15) | C13—H13B | 0.9700 |
| N4—C17 | 1.4542 (15) | C14—H14A | 0.9700 |
| N4—C14 | 1.4546 (15) | C14—H14B | 0.9700 |
| C2—C7 | 1.3853 (16) | C16—C17 | 1.5220 (17) |
| C2—C3 | 1.4027 (16) | C16—H16A | 0.9700 |
| C3—C4 | 1.3862 (17) | C16—H16B | 0.9700 |
| C4—C5 | 1.3971 (17) | C17—H17A | 0.9700 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C17—H17B | 0.9700 |
| C5—C6 | 1.3927 (17) | ||
| C10—O2—C11 | 108.99 (9) | C8—C9—H9B | 109.2 |
| C15—O4—C16 | 107.65 (9) | H9A—C9—H9B | 107.9 |
| C1—N1—C2 | 109.92 (9) | O3—C10—N3 | 128.03 (11) |
| C1—N1—C8 | 122.48 (10) | O3—C10—O2 | 122.02 (11) |
| C2—N1—C8 | 127.44 (10) | N3—C10—O2 | 109.95 (10) |
| C1—N2—C3 | 109.94 (9) | O2—C11—C12 | 105.27 (9) |
| C1—N2—C13 | 123.46 (9) | O2—C11—H11A | 110.7 |
| C3—N2—C13 | 126.51 (10) | C12—C11—H11A | 110.7 |
| C10—N3—C9 | 123.71 (10) | O2—C11—H11B | 110.7 |
| C10—N3—C12 | 112.52 (10) | C12—C11—H11B | 110.7 |
| C9—N3—C12 | 123.31 (10) | H11A—C11—H11B | 108.8 |
| C15—N4—C17 | 112.04 (10) | N3—C12—C11 | 100.84 (9) |
| C15—N4—C14 | 122.29 (10) | N3—C12—H12A | 111.6 |
| C17—N4—C14 | 125.49 (10) | C11—C12—H12A | 111.6 |
| O1—C1—N2 | 127.34 (11) | N3—C12—H12B | 111.6 |
| O1—C1—N1 | 126.44 (11) | C11—C12—H12B | 111.6 |
| N2—C1—N1 | 106.22 (9) | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.4 |
| C7—C2—N1 | 131.76 (11) | N2—C13—C14 | 112.67 (9) |
| C7—C2—C3 | 121.35 (11) | N2—C13—H13A | 109.1 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 106.88 (10) | C14—C13—H13A | 109.1 |
| C4—C3—N2 | 131.36 (11) | N2—C13—H13B | 109.1 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.60 (11) | C14—C13—H13B | 109.1 |
| N2—C3—C2 | 107.03 (10) | H13A—C13—H13B | 107.8 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 116.91 (11) | N4—C14—C13 | 111.20 (10) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 121.5 | N4—C14—H14A | 109.4 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 121.5 | C13—C14—H14A | 109.4 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.54 (11) | N4—C14—H14B | 109.4 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.2 | C13—C14—H14B | 109.4 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.2 | H14A—C14—H14B | 108.0 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 121.36 (11) | O5—C15—N4 | 128.51 (11) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.3 | O5—C15—O4 | 121.68 (11) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 119.3 | N4—C15—O4 | 109.79 (10) |
| C2—C7—C6 | 117.21 (11) | O4—C16—C17 | 104.61 (9) |
| C2—C7—H7 | 121.4 | O4—C16—H16A | 110.8 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 121.4 | C17—C16—H16A | 110.8 |
| N1—C8—C9 | 112.19 (9) | O4—C16—H16B | 110.8 |
| N1—C8—H8A | 109.2 | C17—C16—H16B | 110.8 |
| C9—C8—H8A | 109.2 | H16A—C16—H16B | 108.9 |
| N1—C8—H8B | 109.2 | N4—C17—C16 | 99.92 (9) |
| C9—C8—H8B | 109.2 | N4—C17—H17A | 111.8 |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 107.9 | C16—C17—H17A | 111.8 |
| N3—C9—C8 | 112.07 (9) | N4—C17—H17B | 111.8 |
| N3—C9—H9A | 109.2 | C16—C17—H17B | 111.8 |
| C8—C9—H9A | 109.2 | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| N3—C9—H9B | 109.2 |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: FJ2373).
References
- Ahoya, C. A., Bouhfid, R., Daouda, B., Essassi, E. M. & El Ammari, L. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Alsubari, A., Bouhfid, R. & Essassi, E. M. (2009). Arkivoc, xii, 337–346.
- Bel-Ghacham, H., Kandri Rodi, Y., Saffon, N., Essassi, E. M. & Ng, S. W. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2005). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Caleb, A. A., Bouhfid, R., Essassi, E. M. & El Ammari, L. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o2024–o2025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Diekema, D. J. & Jones, R. N. (2000). Drugs, 59, 7–16. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Evans, D. A., Ny, H. P. & Rieger, D. L. (1993). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115, 11446–11459.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Gribkoff, V. K., Champigny, G., Barbry, P., Dworetzky, S. I., Meanwell, N. A. & Lazdunski, M. (1994). J. Biol. Chem. 269, 10983–10986. [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, H., Ishizuka, T. & Kunieda, T. (2005). Tetrahedron, 61, 8073–8094.
- Mukhtar, T. A. & Wright, G. D. (2005). Chem. Rev. 105, 529–542. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Olesen, S. P., Munch, E., Moldt, P. & Drejer, J. (1994). Eur. J. Pharmacol. 251, 53–59. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ouzidan, Y., Obbade, S., Capet, F., Essassi, E. M. & Ng, S. W. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Soderlind, K. J., Gorodetsky, B., Singh, A. K., Bachur, N., Miller, G. G. & Lown, J. W. (1999). Anticancer Drug Des. 14, 19–36. [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810052141/fj2373sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810052141/fj2373Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report