Abstract
In the title compound, C13H13NO3S, the benzene ring of the benzenesulfonamide moiety is disordered with an occupancy ratio of 0.56 (3):0.44 (3), the disorder components being twisted at and angle of 21 (1)° to each other. The methoxybenzene group is roughly planar (r.m.s. deviation = 0.0144 Å) and the amide N atom is displaced from this plane by 0.090 (6) Å. The dihedral angles between the methoxybenzene group and the major and minor occupancy components of the disordered benzene ring are 54.6 (4) and 62.9 (5)°, respectively. In the crystal, infinite polymeric chains are formed along [100] due to intermolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bonding. Weak C—H⋯π interactions are also present in the crystal.
Related literature
For related structures, see: Kato et al. (2006 ▶); Perlovich et al. (2009 ▶).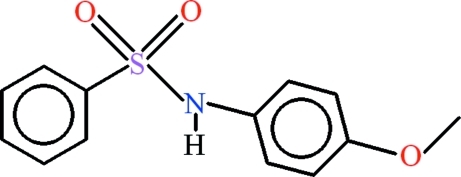
Experimental
Crystal data
C13H13NO3S
M r = 263.30
Orthorhombic,
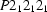
a = 5.3094 (5) Å
b = 8.5309 (10) Å
c = 27.925 (3) Å
V = 1264.8 (2) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.26 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.30 × 0.14 × 0.12 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.961, T max = 0.970
7272 measured reflections
2457 independent reflections
1503 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.060
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.061
wR(F 2) = 0.131
S = 1.02
2457 reflections
138 parameters
1 restraint
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.41 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 961 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: 0.09 (16)
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2009 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811000365/bq2272sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811000365/bq2272Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1, Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the C1A–C6A, C7–C12 and C1B–C6B rings, respectively.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O2i | 0.83 (2) | 2.22 (2) | 3.039 (4) | 170 (4) |
| C8—H8⋯Cg2ii | 0.93 | 2.93 | 3.613 (5) | 132 |
| C13—H13B⋯Cg1iii | 0.96 | 2.98 | 3.766 (6) | 140 |
| C13—H13B⋯Cg3iii | 0.96 | 2.96 | 3.763 (7) | 143 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 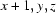 ; (ii)
; (ii) 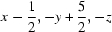 ; (iii)
; (iii) 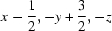 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Professor Dr Islam Ullah Khan for providing research facilities at Government College University, Lahore, Pakistan.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound (I, Fig. 1) is a part of the synthesis of sulfonamides and consequently the study of their bioactivity. The crystal structures of 4-amino-N-(4-methoxyphenyl)benzenesulfonamide (Perlovich et al., 2009) and P-(+)-N-Phenyl-4-methoxybenzenesulfonamide (Kato, et al., 2006) have been published previously which are related to the title compound (I).
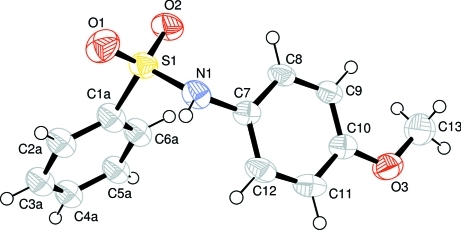
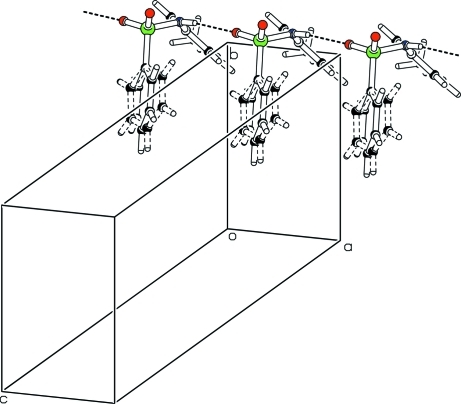
In (I), the phenyl ring of benzenethiol moiety is disordered over two set of sites A (C1A—C6A) and B (C1B—C6B) with occupancy ratio of 0.56 (3):0.44 (3). The dihedral angle between A/B is 21 (1)°. The methoxybenzene group C (C7—C13/O2) is almost planar with r. m. s. deviation of 0.0144 Å and amide atom N1 is at a distance of 0.0897 (55)Å. The dihedral angle between A/C and B/C is 54.63 (35)° and 62.86 (50)°, respectively. The sulfonyl group D (S1/O1/O2) is of course planar. The dihedral angles between A/D, B/D and C/D are 53.37 (43)°, 51.65 (50)° and 24.10 (28)°, respectively. The molecules are stabilized in the form of infinite one-dimensional polymeric chains due to N—H···O type (Table 1, Fig. 2) extending along the crystallographic a-axis. The C—H···π interactions (Table 1) also play important role in stabilizing the molecules.
Experimental
Equal molar (10 mmol) quantity of benzene sulfonyl chloride and para anisidine was mixed in 10 ml distilled water under stirring at room temperature. During the reaction pH was adjusted at 8 using dilute solution of sodium carbonate. The reaction was monitored using TLC. On the completion of reaction the pH was made acidified using 3 N HCl. The crude product was separated by filtration, dried and recrystalized in methanol to afford white needles of (I) after 72 h.
Refinement
The benzene ring of benzenethiol moiety is disordered over two set of sites with occupancy ratio of 0.56 (3):0.44 (3). The rings are fitted in regular hexagons with nearly equal bond distances and bond angles. The thermal parameters of C-atoms within disordered benzene rings are treated to be equal.
The coordinates of amide H-atom were refined. All other H-atoms were positioned geometrically (C–H = 0.93–0.96 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = xUeq(C, N), where x = 1.5 for methyl H-atoms and x = 1.2 for all other H-atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
View of the title compound with the atom numbering scheme having atoms of greater occupancy ratio. The thermal ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
The partial packing (PLATON; Spek, 2009) which shows that molecules form polymeric chains extending along the a axis.
Crystal data
| C13H13NO3S | F(000) = 552 |
| Mr = 263.30 | Dx = 1.383 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 1503 reflections |
| a = 5.3094 (5) Å | θ = 2.5–25.2° |
| b = 8.5309 (10) Å | µ = 0.26 mm−1 |
| c = 27.925 (3) Å | T = 296 K |
| V = 1264.8 (2) Å3 | Needle, white |
| Z = 4 | 0.30 × 0.14 × 0.12 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2457 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1503 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.060 |
| Detector resolution: 8.00 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 2.5° |
| ω scans | h = −4→6 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | k = −9→10 |
| Tmin = 0.961, Tmax = 0.970 | l = −32→31 |
| 7272 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.061 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.131 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0506P)2 + 0.2719P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.02 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2457 reflections | Δρmax = 0.41 e Å−3 |
| 138 parameters | Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 961 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: 0.09 (16) |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| S1 | 0.5888 (2) | 1.17782 (15) | 0.14716 (4) | 0.0434 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.6723 (6) | 1.2938 (4) | 0.18015 (10) | 0.0615 (14) | |
| O2 | 0.3371 (4) | 1.1850 (4) | 0.12785 (9) | 0.0549 (13) | |
| O3 | 0.7036 (6) | 0.8660 (4) | −0.07098 (11) | 0.0570 (12) | |
| N1 | 0.7813 (6) | 1.1858 (5) | 0.10190 (12) | 0.0427 (14) | |
| C1A | 0.6261 (14) | 0.9927 (7) | 0.1750 (2) | 0.0500 (19) | 0.56 (3) |
| C2A | 0.7618 (19) | 0.9727 (8) | 0.2171 (3) | 0.0500 (19) | 0.56 (3) |
| C3A | 0.786 (2) | 0.8243 (10) | 0.2371 (2) | 0.0500 (19) | 0.56 (3) |
| C4A | 0.6743 (17) | 0.6959 (8) | 0.2150 (2) | 0.0500 (19) | 0.56 (3) |
| C5A | 0.5386 (12) | 0.7159 (8) | 0.1729 (3) | 0.0500 (19) | 0.56 (3) |
| C6A | 0.5145 (17) | 0.8643 (9) | 0.1529 (3) | 0.0500 (19) | 0.56 (3) |
| C7 | 0.7490 (7) | 1.0996 (5) | 0.05846 (15) | 0.0353 (16) | |
| C8 | 0.5531 (8) | 1.1329 (5) | 0.02810 (14) | 0.0403 (16) | |
| C9 | 0.5314 (8) | 1.0566 (5) | −0.01519 (16) | 0.0413 (17) | |
| C10 | 0.7056 (8) | 0.9465 (6) | −0.02856 (16) | 0.0407 (17) | |
| C11 | 0.9050 (9) | 0.9139 (5) | 0.00183 (17) | 0.0490 (17) | |
| C12 | 0.9241 (9) | 0.9870 (6) | 0.04544 (16) | 0.0473 (16) | |
| C13 | 0.4974 (11) | 0.8934 (7) | −0.10251 (17) | 0.075 (3) | |
| C3B | 0.879 (3) | 0.8430 (11) | 0.2267 (4) | 0.054 (3) | 0.44 (3) |
| C4B | 0.726 (2) | 0.7133 (10) | 0.2186 (3) | 0.054 (3) | 0.44 (3) |
| C5B | 0.5220 (14) | 0.7245 (11) | 0.1876 (6) | 0.054 (3) | 0.44 (3) |
| C6B | 0.4708 (16) | 0.8655 (12) | 0.1646 (5) | 0.054 (3) | 0.44 (3) |
| C2B | 0.827 (3) | 0.9840 (9) | 0.2037 (5) | 0.054 (3) | 0.44 (3) |
| C1B | 0.6235 (18) | 0.9952 (10) | 0.1726 (3) | 0.054 (3) | 0.44 (3) |
| H6A | 0.42369 | 0.87769 | 0.12470 | 0.0601* | 0.56 (3) |
| H5A | 0.46390 | 0.62998 | 0.15812 | 0.0601* | 0.56 (3) |
| H11 | 1.02714 | 0.84188 | −0.00742 | 0.0589* | |
| H12 | 1.05444 | 0.96101 | 0.06623 | 0.0569* | |
| H13A | 0.34217 | 0.88310 | −0.08517 | 0.1122* | |
| H13B | 0.50147 | 0.81823 | −0.12809 | 0.1122* | |
| H13C | 0.50967 | 0.99726 | −0.11552 | 0.1122* | |
| H8 | 0.43398 | 1.20759 | 0.03680 | 0.0480* | |
| H9 | 0.39767 | 1.08001 | −0.03547 | 0.0494* | |
| H1 | 0.930 (4) | 1.197 (5) | 0.1105 (13) | 0.0514* | |
| H2A | 0.83652 | 1.05863 | 0.23189 | 0.0601* | 0.56 (3) |
| H3A | 0.87672 | 0.81092 | 0.26532 | 0.0601* | 0.56 (3) |
| H4A | 0.69041 | 0.59660 | 0.22843 | 0.0601* | 0.56 (3) |
| H2B | 0.92955 | 1.07075 | 0.20904 | 0.0646* | 0.44 (3) |
| H3B | 1.01505 | 0.83549 | 0.24742 | 0.0646* | 0.44 (3) |
| H4B | 0.76021 | 0.61899 | 0.23400 | 0.0646* | 0.44 (3) |
| H5B | 0.41988 | 0.63775 | 0.18221 | 0.0646* | 0.44 (3) |
| H6B | 0.33438 | 0.87301 | 0.14384 | 0.0646* | 0.44 (3) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0335 (6) | 0.0474 (8) | 0.0494 (7) | 0.0026 (6) | −0.0036 (5) | −0.0007 (7) |
| O1 | 0.060 (2) | 0.060 (3) | 0.0646 (19) | −0.0021 (18) | −0.0064 (16) | −0.022 (2) |
| O2 | 0.0254 (16) | 0.075 (3) | 0.0642 (18) | 0.0085 (17) | −0.0046 (13) | 0.004 (2) |
| O3 | 0.056 (2) | 0.057 (2) | 0.058 (2) | 0.0110 (17) | 0.0010 (17) | −0.0093 (18) |
| N1 | 0.0250 (19) | 0.054 (3) | 0.049 (2) | −0.005 (2) | −0.0056 (17) | 0.005 (2) |
| C1A | 0.042 (3) | 0.056 (4) | 0.052 (3) | −0.004 (2) | −0.001 (2) | 0.014 (2) |
| C2A | 0.042 (3) | 0.056 (4) | 0.052 (3) | −0.004 (2) | −0.001 (2) | 0.014 (2) |
| C3A | 0.042 (3) | 0.056 (4) | 0.052 (3) | −0.004 (2) | −0.001 (2) | 0.014 (2) |
| C4A | 0.042 (3) | 0.056 (4) | 0.052 (3) | −0.004 (2) | −0.001 (2) | 0.014 (2) |
| C5A | 0.042 (3) | 0.056 (4) | 0.052 (3) | −0.004 (2) | −0.001 (2) | 0.014 (2) |
| C6A | 0.042 (3) | 0.056 (4) | 0.052 (3) | −0.004 (2) | −0.001 (2) | 0.014 (2) |
| C7 | 0.025 (2) | 0.034 (3) | 0.047 (3) | −0.0053 (19) | 0.005 (2) | 0.004 (2) |
| C8 | 0.026 (2) | 0.046 (3) | 0.049 (3) | 0.007 (2) | −0.003 (2) | 0.007 (2) |
| C9 | 0.036 (3) | 0.041 (3) | 0.047 (3) | 0.006 (2) | −0.003 (2) | 0.007 (2) |
| C10 | 0.033 (3) | 0.037 (3) | 0.052 (3) | −0.004 (2) | 0.002 (2) | 0.003 (2) |
| C11 | 0.035 (3) | 0.041 (3) | 0.071 (3) | 0.006 (2) | 0.000 (3) | 0.005 (3) |
| C12 | 0.028 (2) | 0.053 (3) | 0.061 (3) | 0.003 (2) | −0.006 (2) | 0.010 (3) |
| C13 | 0.088 (5) | 0.081 (5) | 0.055 (3) | 0.018 (3) | −0.017 (3) | −0.017 (3) |
| C3B | 0.055 (4) | 0.055 (5) | 0.052 (4) | −0.021 (3) | −0.010 (3) | 0.010 (3) |
| C4B | 0.055 (4) | 0.055 (5) | 0.052 (4) | −0.021 (3) | −0.010 (3) | 0.010 (3) |
| C5B | 0.055 (4) | 0.055 (5) | 0.052 (4) | −0.021 (3) | −0.010 (3) | 0.010 (3) |
| C6B | 0.055 (4) | 0.055 (5) | 0.052 (4) | −0.021 (3) | −0.010 (3) | 0.010 (3) |
| C2B | 0.055 (4) | 0.055 (5) | 0.052 (4) | −0.021 (3) | −0.010 (3) | 0.010 (3) |
| C1B | 0.055 (4) | 0.055 (5) | 0.052 (4) | −0.021 (3) | −0.010 (3) | 0.010 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| S1—O1 | 1.423 (3) | C7—C12 | 1.385 (6) |
| S1—O2 | 1.442 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.378 (6) |
| S1—N1 | 1.627 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.370 (6) |
| S1—C1A | 1.771 (6) | C10—C11 | 1.385 (6) |
| S1—C1B | 1.722 (9) | C11—C12 | 1.372 (7) |
| O3—C10 | 1.369 (6) | C2A—H2A | 0.9300 |
| O3—C13 | 1.424 (6) | C2B—H2B | 0.9300 |
| N1—C7 | 1.429 (6) | C3A—H3A | 0.9300 |
| N1—H1 | 0.83 (2) | C3B—H3B | 0.9300 |
| C1A—C6A | 1.390 (10) | C4A—H4A | 0.9300 |
| C1A—C2A | 1.389 (11) | C4B—H4B | 0.9300 |
| C1B—C2B | 1.390 (18) | C5A—H5A | 0.9300 |
| C1B—C6B | 1.390 (13) | C5B—H5B | 0.9300 |
| C2A—C3A | 1.390 (11) | C6A—H6A | 0.9300 |
| C2B—C3B | 1.391 (14) | C6B—H6B | 0.9300 |
| C3A—C4A | 1.390 (11) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| C3B—C4B | 1.391 (15) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C4A—C5A | 1.389 (10) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C4B—C5B | 1.390 (15) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C5A—C6A | 1.390 (11) | C13—H13B | 0.9600 |
| C5B—C6B | 1.390 (16) | C13—H13C | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.372 (6) | C13—H13A | 0.9600 |
| S1···H8 | 3.2000 | C9···H8viii | 3.0000 |
| O1···C3Ai | 3.366 (9) | C10···H11vi | 2.8200 |
| O2···C8 | 3.045 (5) | C11···H11vi | 2.9700 |
| O2···N1ii | 3.039 (4) | C13···H5Av | 2.9300 |
| O1···H4Aiii | 2.9200 | C13···H9 | 2.5100 |
| O1···H2B | 2.4800 | H1···O2vii | 2.22 (2) |
| O1···H3Aiv | 2.8400 | H1···H12 | 2.4500 |
| O1···H3Biv | 2.6400 | H2A···O1 | 2.6200 |
| O1···H2A | 2.6200 | H2B···O1 | 2.4800 |
| O2···H1ii | 2.22 (2) | H2B···H4Biv | 2.3300 |
| O2···H6A | 2.6600 | H2B···C4Biv | 2.9800 |
| O2···H8 | 2.6000 | H2B···H3Biv | 2.5800 |
| O2···H6B | 2.7000 | H3A···O1xi | 2.8400 |
| O3···H5Av | 2.8000 | H3B···O1xi | 2.6400 |
| O3···H6Av | 2.8200 | H3B···H2Bxi | 2.5800 |
| O3···H12vi | 2.9000 | H4A···O1xii | 2.9200 |
| N1···O2vii | 3.039 (4) | H4A···C2Aix | 3.0300 |
| N1···H9viii | 2.8000 | H4B···C2Bxi | 3.0300 |
| C2A···C4Ai | 3.547 (12) | H4B···H2Bxi | 2.3300 |
| C3A···O1ix | 3.366 (9) | H5A···O3vi | 2.8000 |
| C3B···C6Bvii | 3.594 (18) | H5A···C13vi | 2.9300 |
| C4A···C2Aix | 3.547 (12) | H6A···O3vi | 2.8200 |
| C5A···C13v | 3.266 (9) | H6A···O2 | 2.6600 |
| C6A···C7 | 3.540 (9) | H6B···H13Bvi | 2.4500 |
| C6B···C3Bii | 3.594 (18) | H6B···O2 | 2.7000 |
| C7···C9viii | 3.509 (6) | H8···S1 | 3.2000 |
| C7···C6A | 3.540 (9) | H8···O2 | 2.6000 |
| C8···C12ii | 3.597 (6) | H8···C8x | 3.0400 |
| C8···O2 | 3.045 (5) | H8···C9x | 3.0000 |
| C9···C7x | 3.509 (6) | H9···C13 | 2.5100 |
| C9···C11ii | 3.573 (6) | H9···H13A | 2.2000 |
| C10···C11vi | 3.544 (7) | H9···H13C | 2.4200 |
| C11···C10v | 3.544 (7) | H9···N1x | 2.8000 |
| C11···C9vii | 3.573 (6) | H9···C7x | 2.9200 |
| C12···C8vii | 3.597 (6) | H9···C8x | 3.0600 |
| C13···C5Avi | 3.266 (9) | H11···C11v | 2.9700 |
| C2A···H4Ai | 3.0300 | H11···C10v | 2.8200 |
| C2B···H4Biv | 3.0300 | H12···O3v | 2.9000 |
| C4A···H13Bv | 2.9900 | H12···H1 | 2.4500 |
| C4B···H13Bv | 2.9300 | H13A···C9 | 2.6500 |
| C4B···H2Bxi | 2.9800 | H13A···C5Avi | 3.0500 |
| C5A···H13Av | 3.0500 | H13A···H9 | 2.2000 |
| C5A···H13Bv | 2.7700 | H13B···C4Avi | 2.9900 |
| C5B···H13Bv | 3.0600 | H13B···C6Avi | 3.1000 |
| C6A···H13Bv | 3.1000 | H13B···C4Bvi | 2.9300 |
| C7···H9viii | 2.9200 | H13B···C5Bvi | 3.0600 |
| C8···H8viii | 3.0400 | H13B···H6Bv | 2.4500 |
| C8···H9viii | 3.0600 | H13B···C5Avi | 2.7700 |
| C9···H13C | 2.8500 | H13C···C9 | 2.8500 |
| C9···H13A | 2.6500 | H13C···H9 | 2.4200 |
| O1—S1—O2 | 120.1 (2) | C10—C11—C12 | 120.6 (4) |
| O1—S1—N1 | 106.2 (2) | C7—C12—C11 | 119.9 (4) |
| O1—S1—C1A | 107.5 (2) | C1A—C2A—H2A | 120.00 |
| O1—S1—C1B | 109.2 (3) | C3A—C2A—H2A | 120.00 |
| O2—S1—N1 | 106.85 (17) | C1B—C2B—H2B | 120.00 |
| O2—S1—C1A | 107.8 (3) | C3B—C2B—H2B | 120.00 |
| O2—S1—C1B | 107.0 (3) | C4A—C3A—H3A | 120.00 |
| N1—S1—C1A | 107.9 (3) | C2A—C3A—H3A | 120.00 |
| N1—S1—C1B | 106.9 (3) | C4B—C3B—H3B | 120.00 |
| C10—O3—C13 | 117.3 (4) | C2B—C3B—H3B | 120.00 |
| S1—N1—C7 | 124.2 (3) | C3A—C4A—H4A | 120.00 |
| S1—N1—H1 | 112 (2) | C5A—C4A—H4A | 120.00 |
| C7—N1—H1 | 115 (3) | C5B—C4B—H4B | 120.00 |
| S1—C1A—C2A | 122.6 (5) | C3B—C4B—H4B | 120.00 |
| S1—C1A—C6A | 117.4 (5) | C6A—C5A—H5A | 120.00 |
| C2A—C1A—C6A | 120.0 (6) | C4A—C5A—H5A | 120.00 |
| S1—C1B—C2B | 113.8 (7) | C4B—C5B—H5B | 120.00 |
| C2B—C1B—C6B | 120.0 (8) | C6B—C5B—H5B | 120.00 |
| S1—C1B—C6B | 126.3 (8) | C1A—C6A—H6A | 120.00 |
| C1A—C2A—C3A | 120.0 (7) | C5A—C6A—H6A | 120.00 |
| C1B—C2B—C3B | 120.2 (11) | C5B—C6B—H6B | 120.00 |
| C2A—C3A—C4A | 120.0 (7) | C1B—C6B—H6B | 120.00 |
| C2B—C3B—C4B | 119.8 (12) | C9—C8—H8 | 120.00 |
| C3A—C4A—C5A | 120.0 (6) | C7—C8—H8 | 120.00 |
| C3B—C4B—C5B | 120.1 (9) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.00 |
| C4A—C5A—C6A | 120.0 (7) | C10—C9—H9 | 120.00 |
| C4B—C5B—C6B | 120.0 (8) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.00 |
| C1A—C6A—C5A | 120.0 (7) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.00 |
| C1B—C6B—C5B | 120.0 (10) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.00 |
| N1—C7—C12 | 119.9 (4) | C7—C12—H12 | 120.00 |
| N1—C7—C8 | 120.6 (4) | O3—C13—H13C | 109.00 |
| C8—C7—C12 | 119.4 (4) | O3—C13—H13B | 109.00 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 120.5 (4) | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.00 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 120.4 (4) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.00 |
| O3—C10—C11 | 115.8 (4) | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.00 |
| O3—C10—C9 | 125.1 (4) | O3—C13—H13A | 109.00 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 119.1 (4) | ||
| O1—S1—N1—C7 | −173.2 (3) | C2A—C1A—C6A—C5A | 0.0 (12) |
| O2—S1—N1—C7 | −43.9 (4) | C1A—C2A—C3A—C4A | −0.1 (14) |
| C1A—S1—N1—C7 | 71.8 (4) | C2A—C3A—C4A—C5A | 0.0 (13) |
| O1—S1—C1A—C2A | −11.8 (7) | C3A—C4A—C5A—C6A | 0.0 (12) |
| O1—S1—C1A—C6A | 168.6 (6) | C4A—C5A—C6A—C1A | 0.0 (12) |
| O2—S1—C1A—C2A | −142.6 (7) | N1—C7—C8—C9 | 175.8 (4) |
| O2—S1—C1A—C6A | 37.8 (6) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | −0.7 (6) |
| N1—S1—C1A—C2A | 102.3 (7) | N1—C7—C12—C11 | −174.4 (4) |
| N1—S1—C1A—C6A | −77.3 (6) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | 2.2 (7) |
| C13—O3—C10—C9 | −3.3 (7) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −0.1 (7) |
| C13—O3—C10—C11 | 178.3 (4) | C8—C9—C10—O3 | −178.9 (4) |
| S1—N1—C7—C8 | 67.4 (5) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.6 (7) |
| S1—N1—C7—C12 | −116.2 (4) | O3—C10—C11—C12 | −179.4 (4) |
| S1—C1A—C2A—C3A | −179.6 (7) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 2.1 (7) |
| C6A—C1A—C2A—C3A | 0.0 (13) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | −2.9 (7) |
| S1—C1A—C6A—C5A | 179.6 (6) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) x−1, y, z; (iii) x, y+1, z; (iv) −x+2, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (v) x+1/2, −y+3/2, −z; (vi) x−1/2, −y+3/2, −z; (vii) x+1, y, z; (viii) x+1/2, −y+5/2, −z; (ix) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (x) x−1/2, −y+5/2, −z; (xi) −x+2, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (xii) x, y−1, z.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| Cg1, Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the C1A–C6A, C7–C12 and C1B–C6B rings, respectively. |
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O2vii | 0.83 (2) | 2.22 (2) | 3.039 (4) | 170 (4) |
| C8—H8···Cg2x | 0.93 | 2.93 | 3.613 (5) | 132 |
| C13—H13B···Cg1vi | 0.96 | 2.98 | 3.766 (6) | 140 |
| C13—H13B···Cg3vi | 0.96 | 2.96 | 3.763 (7) | 143 |
Symmetry codes: (vii) x+1, y, z; (x) x−1/2, −y+5/2, −z; (vi) x−1/2, −y+3/2, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BQ2272).
References
- Bruker (2005). SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2009). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Kato, T., Okamoto, I., Tanatani, A., Hatano, T., Uchiyama, M., Kagechika, H., Masu, H., Katagiri, K., Tominaga, M., Yamaguchi, K. & Azumaya, I. (2006). Org. Lett. 8, 5017–5020. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Perlovich, G. L., Tkachev, V. V., Strakhova, N. N., Kazachenko, V. P., Volkova, T. V., Surov, O. V., Schaper, K.-J. & Raevsky, O. A. (2009). J. Pharm. Sci. 98, 4738–4755. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811000365/bq2272sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811000365/bq2272Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report