Abstract
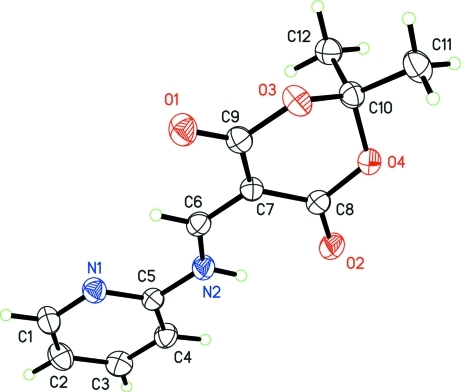
In the title compound, C12H12N2O4, the dihedral angle between the pyridine and enamine planes is 3.5 (3)°, while the angle between the dioxanedione (seven atoms) and enamine planes is 4.6 (3)°. The dioxane ring approximates an envelope conformation.
Related literature
The title compound is an intermediate in the synthesis of 4(1H)-quinolone-based drugs. For the synthesis and structures of related antitumor precursors, see: Cassis et al. (1985 ▶); Ruchelman et al. (2003 ▶); Shi et al. (2009 ▶).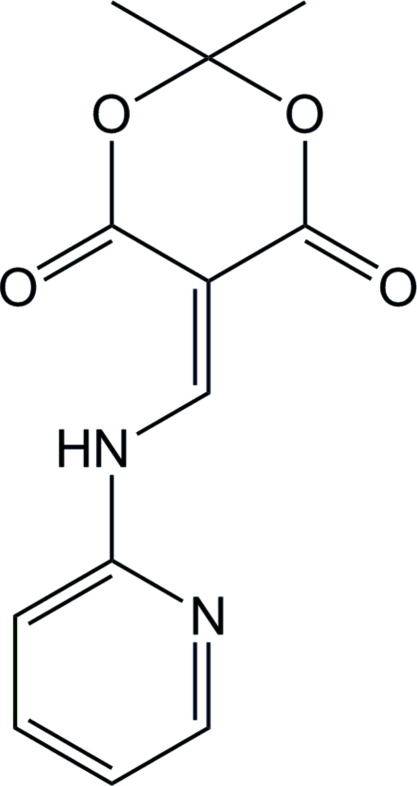
Experimental
Crystal data
C12H12N2O4
M r = 248.24
Monoclinic,
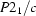
a = 8.7344 (10) Å
b = 13.9712 (15) Å
c = 9.4744 (11) Å
β = 94.601 (11)°
V = 1152.4 (2) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.11 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.22 × 0.18 × 0.16 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur diffractometer with an Eos CCD detector
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.997, T max = 1.0
4873 measured reflections
2334 independent reflections
1659 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.018
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.040
wR(F 2) = 0.096
S = 1.03
2334 reflections
166 parameters
1 restraint
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.14 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.14 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: OLEX2 (Dolomanov et al., 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810053250/bh2327sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810053250/bh2327Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
We thank Mr Zhihua Mao of the Analysis and Testing Center (Sichuan University) for the data collection.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound is a key intermediates, which can be used to synthesize 4(1H)-quinolone derivatives by thermolysis. These compounds can be used as precursors for anti-malarial and anticancer agents (Cassis et al., 1985; Ruchelman et al., 2003; Shi et al., 2009).
Experimental
A mixture of 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane-4,6-dione (1.44 g, 0.01 mol) and methylorthoformate (1.27 g, 0.012 mol) was refluxed for 2.5 h. Then pyridin-2-amine (0.94 g, 0.01 mol) was added and the mixture was refluxed for 4 h, then poured into cold water and filtered, to afford the title compound as a powder. Single crystals were obtained by slow evaporation of a CH2Cl2-methanol solution over 3 days.
Refinement
All H atoms were placed in calculated positions, with C—H bond lengths fixed to 0.93 (aromatic CH), 0.96 (methyl CH3) or 0.86 Å (NH group). Isotropic displacement parameters for H atoms were calculated as 1.5 (methyl) or 1.2 (other H atoms) times that of the equivalent displacement parameter of the carrier C atom.
Figures
Fig. 1.
ORTEP-like view of the title compound.
Crystal data
| C12H12N2O4 | F(000) = 520 |
| Mr = 248.24 | Dx = 1.431 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.7107 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 1780 reflections |
| a = 8.7344 (10) Å | θ = 3.1–29.2° |
| b = 13.9712 (15) Å | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| c = 9.4744 (11) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 94.601 (11)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 1152.4 (2) Å3 | 0.22 × 0.18 × 0.16 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur diffractometer with an Eos CCD detector | 2334 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1659 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.018 |
| Detector resolution: 16.0874 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.4°, θmin = 3.4° |
| ω scans | h = −10→9 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2009) | k = −17→16 |
| Tmin = 0.997, Tmax = 1.0 | l = −11→11 |
| 4873 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.096 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0383P)2 + 0.0655P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.03 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2334 reflections | Δρmax = 0.14 e Å−3 |
| 166 parameters | Δρmin = −0.14 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 0 constraints | Extinction coefficient: 0.0060 (9) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O3 | 0.21039 (13) | 0.15916 (7) | 0.50800 (11) | 0.0497 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.37760 (12) | 0.11610 (7) | 0.33485 (12) | 0.0504 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.22965 (17) | −0.10004 (11) | 0.49185 (16) | 0.0421 (4) | |
| H6 | 0.1613 | −0.1134 | 0.5596 | 0.050* | |
| O1 | 0.10857 (14) | 0.05240 (7) | 0.64457 (11) | 0.0556 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.44968 (12) | −0.03377 (8) | 0.30745 (12) | 0.0559 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.29233 (14) | −0.17386 (8) | 0.43038 (13) | 0.0455 (3) | |
| H2 | 0.3571 | −0.1614 | 0.3692 | 0.055* | |
| C7 | 0.25719 (16) | −0.00541 (10) | 0.46383 (15) | 0.0388 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.17056 (15) | −0.28950 (8) | 0.55799 (13) | 0.0474 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.1423 (2) | −0.38227 (11) | 0.58158 (18) | 0.0532 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.0776 | −0.3976 | 0.6515 | 0.064* | |
| C9 | 0.18429 (18) | 0.06634 (10) | 0.54492 (16) | 0.0428 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.36562 (17) | 0.02142 (11) | 0.36380 (16) | 0.0434 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.26224 (16) | −0.27096 (10) | 0.45637 (16) | 0.0400 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.2993 (2) | −0.43431 (11) | 0.40519 (18) | 0.0547 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.3432 | −0.4829 | 0.3548 | 0.066* | |
| C4 | 0.32929 (19) | −0.34013 (11) | 0.37743 (17) | 0.0487 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.3930 | −0.3233 | 0.3074 | 0.058* | |
| C12 | 0.11654 (19) | 0.16341 (11) | 0.26210 (16) | 0.0493 (4) | |
| H12B | 0.1452 | 0.1783 | 0.1689 | 0.074* | |
| H12C | 0.0343 | 0.2048 | 0.2851 | 0.074* | |
| H12A | 0.0833 | 0.0980 | 0.2649 | 0.074* | |
| C11 | 0.3145 (2) | 0.27839 (11) | 0.36841 (19) | 0.0606 (5) | |
| H11A | 0.3519 | 0.2923 | 0.2781 | 0.091* | |
| H11C | 0.3969 | 0.2843 | 0.4412 | 0.091* | |
| H11B | 0.2342 | 0.3226 | 0.3864 | 0.091* | |
| C2 | 0.2036 (2) | −0.45560 (11) | 0.50844 (18) | 0.0582 (5) | |
| H2A | 0.1806 | −0.5189 | 0.5286 | 0.070* | |
| C10 | 0.25227 (18) | 0.17780 (10) | 0.36764 (16) | 0.0439 (4) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O3 | 0.0704 (8) | 0.0405 (6) | 0.0386 (6) | −0.0001 (5) | 0.0061 (5) | −0.0014 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0432 (7) | 0.0437 (6) | 0.0656 (8) | −0.0011 (5) | 0.0137 (5) | 0.0085 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0384 (9) | 0.0485 (9) | 0.0395 (9) | 0.0012 (7) | 0.0042 (7) | −0.0004 (7) |
| O1 | 0.0669 (8) | 0.0573 (7) | 0.0448 (7) | 0.0015 (6) | 0.0178 (6) | 0.0005 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0470 (7) | 0.0543 (7) | 0.0692 (8) | 0.0047 (6) | 0.0208 (6) | 0.0026 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0452 (8) | 0.0426 (8) | 0.0502 (8) | 0.0012 (6) | 0.0140 (6) | 0.0015 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0374 (8) | 0.0399 (8) | 0.0390 (8) | −0.0006 (7) | 0.0034 (6) | 0.0022 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0516 (9) | 0.0447 (8) | 0.0471 (8) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0102 (6) | 0.0016 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0620 (11) | 0.0477 (10) | 0.0511 (10) | −0.0035 (9) | 0.0121 (8) | 0.0056 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0460 (9) | 0.0445 (9) | 0.0373 (9) | −0.0010 (7) | −0.0001 (7) | 0.0006 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0372 (9) | 0.0438 (9) | 0.0491 (9) | −0.0005 (7) | 0.0020 (7) | 0.0017 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0376 (8) | 0.0403 (9) | 0.0418 (9) | −0.0009 (7) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0015 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0624 (12) | 0.0465 (10) | 0.0557 (11) | 0.0058 (8) | 0.0072 (9) | −0.0100 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0478 (10) | 0.0521 (10) | 0.0477 (10) | 0.0015 (8) | 0.0123 (8) | −0.0025 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0534 (10) | 0.0523 (9) | 0.0422 (10) | 0.0029 (8) | 0.0047 (7) | 0.0012 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0704 (13) | 0.0451 (10) | 0.0651 (12) | −0.0087 (9) | −0.0009 (9) | 0.0058 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0728 (13) | 0.0414 (9) | 0.0606 (12) | −0.0031 (9) | 0.0069 (9) | 0.0017 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0495 (10) | 0.0411 (9) | 0.0419 (9) | −0.0002 (7) | 0.0078 (7) | 0.0016 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O3—C9 | 1.3671 (16) | C1—C2 | 1.370 (2) |
| O3—C10 | 1.4311 (18) | C5—C4 | 1.381 (2) |
| O4—C8 | 1.3567 (17) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| O4—C10 | 1.4465 (18) | C3—C4 | 1.371 (2) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C3—C2 | 1.370 (2) |
| C6—N2 | 1.3242 (18) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C7 | 1.374 (2) | C12—H12B | 0.9600 |
| O1—C9 | 1.2112 (17) | C12—H12C | 0.9600 |
| O2—C8 | 1.2172 (17) | C12—H12A | 0.9600 |
| N2—H2 | 0.8600 | C12—C10 | 1.502 (2) |
| N2—C5 | 1.4072 (18) | C11—H11A | 0.9600 |
| C7—C9 | 1.442 (2) | C11—H11C | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.442 (2) | C11—H11B | 0.9600 |
| N1—C1 | 1.3415 (19) | C11—C10 | 1.507 (2) |
| N1—C5 | 1.3263 (18) | C2—H2A | 0.9300 |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | ||
| O3—C9—C7 | 115.68 (13) | C5—N2—H2 | 117.1 |
| O3—C10—O4 | 110.21 (11) | C5—N1—C1 | 116.06 (13) |
| O3—C10—C12 | 110.33 (13) | C5—C4—H4 | 120.9 |
| O3—C10—C11 | 106.51 (12) | C3—C4—C5 | 118.16 (15) |
| O4—C8—C7 | 116.85 (13) | C3—C4—H4 | 120.9 |
| O4—C10—C12 | 110.35 (12) | C3—C2—C1 | 118.99 (15) |
| O4—C10—C11 | 106.15 (13) | C3—C2—H2A | 120.5 |
| C6—N2—H2 | 117.1 | C4—C5—N2 | 119.12 (13) |
| C6—N2—C5 | 125.74 (13) | C4—C3—H3 | 120.6 |
| C6—C7—C9 | 118.33 (13) | C12—C10—C11 | 113.15 (13) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 120.77 (14) | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| O1—C9—O3 | 117.68 (13) | H12B—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| O1—C9—C7 | 126.57 (14) | H12C—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| O2—C8—O4 | 118.03 (13) | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| O2—C8—C7 | 125.08 (14) | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| N2—C6—H6 | 117.3 | H11C—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| N2—C6—C7 | 125.42 (14) | C2—C1—H1 | 118.2 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 117.3 | C2—C3—H3 | 120.6 |
| N1—C1—H1 | 118.2 | C2—C3—C4 | 118.84 (15) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 123.64 (15) | C10—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| N1—C5—N2 | 116.58 (13) | C10—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 124.30 (14) | C10—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 120.5 | C10—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| C9—O3—C10 | 118.08 (11) | C10—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C9—C7—C8 | 120.72 (13) | C10—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C8—O4—C10 | 117.75 (11) | ||
| C6—N2—C5—N1 | −4.6 (2) | C9—O3—C10—C11 | −165.07 (13) |
| C6—N2—C5—C4 | 175.96 (15) | C9—C7—C8—O4 | −9.6 (2) |
| C6—C7—C9—O3 | −177.16 (12) | C9—C7—C8—O2 | 168.03 (15) |
| C6—C7—C9—O1 | 6.0 (2) | C8—O4—C10—O3 | 47.99 (17) |
| C6—C7—C8—O4 | 175.36 (13) | C8—O4—C10—C12 | −74.10 (16) |
| C6—C7—C8—O2 | −7.0 (2) | C8—O4—C10—C11 | 162.95 (12) |
| N2—C6—C7—C9 | −177.35 (14) | C8—C7—C9—O3 | 7.7 (2) |
| N2—C6—C7—C8 | −2.2 (2) | C8—C7—C9—O1 | −169.19 (15) |
| N2—C5—C4—C3 | 179.53 (14) | C5—N1—C1—C2 | 0.7 (2) |
| C7—C6—N2—C5 | −178.57 (14) | C4—C3—C2—C1 | −0.7 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 0.0 (3) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.6 (2) |
| N1—C5—C4—C3 | 0.2 (2) | C10—O3—C9—O1 | −159.37 (14) |
| C1—N1—C5—N2 | 179.83 (13) | C10—O3—C9—C7 | 23.48 (19) |
| C1—N1—C5—C4 | −0.8 (2) | C10—O4—C8—O2 | 162.84 (14) |
| C9—O3—C10—O4 | −50.35 (17) | C10—O4—C8—C7 | −19.38 (19) |
| C9—O3—C10—C12 | 71.76 (16) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BH2327).
References
- Cassis, R., Tapia, R. & Valderrama, J. A. (1985). Synth. Commun 15, 125–133.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Oxford Diffraction (2009). CrysAlis PRO Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Ruchelman, A. L., Singh, S. K., Ray, A., Wu, X. H., Yang, J.-M., Li, T.-K., Liu, A., Liu, L. F. & LaVoie, E. J. (2003). Bioorg. Med. Chem 11, 2061–2073. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.-Y., Yang, J.-C. & Yang, J.-L. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o2458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810053250/bh2327sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810053250/bh2327Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report