Abstract
In the crystal structure of the title compound [systematic name: 1-methylpiperazine-1,4-diium bis(2,4,6-trinitrophenolate)], C5H14N2 2+·2C6H2N3O7 −, the ionic components are connected by relatively strong N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds into centrosymmetric six-membered conglomerates, which comprise two dications and four anions. Besides Coulombic interactions, only weak C—H⋯O interactions and some stacking between picrates (separation between the planes of ca. 3.4 Å but only a small overlapping) can be identified between these ‘building blocks’ of the crystal structure. The piperazine ring adopts a chair conformation with the methyl substituent in the equatorial position. In the picrate anions, the twist angles of the nitro groups depend on their positions relative to the phenolate O atom: it is much smaller for the NO2 groups para to the C—O− group [15.23 (9)and 3.92 (14)°] than for the groups in the ortho positions [28.76 (13)–39.84 (11)°].
Related literature
For examples of the biological activity of piperazines: Brockunier et al. (2004 ▶); Bogatcheva et al. (2006 ▶). For the crystal structures of simple piperidinium picrates, see: Fun et al. (2010 ▶); Li et al. (2009 ▶); Verdonk et al. (1997 ▶); Wang & Jia (2008 ▶). For a description of the Cambridge Structural Database, see: Allen (2002 ▶). For asymmetry parameters, see: Duax & Norton (1975 ▶). 
Experimental
Crystal data
C5H14N2 2+·2C6H2N3O7 −
M r = 558.39
Triclinic,

a = 8.2001 (12) Å
b = 10.1780 (15) Å
c = 13.7399 (18) Å
α = 89.798 (12)°
β = 78.130 (11)°
γ = 81.558 (12)°
V = 1109.6 (3) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.15 mm−1
T = 295 K
0.4 × 0.15 × 0.07 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Eos diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.936, T max = 1.000
21056 measured reflections
4891 independent reflections
3624 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.021
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.044
wR(F 2) = 0.123
S = 0.95
4891 reflections
424 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.24 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.30 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR92 (Altomare et al., 1993 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: Stereochemical Workstation Operation Manual (Siemens, 1989 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811001024/fl2330sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811001024/fl2330Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N11—H11⋯O1A | 0.892 (18) | 1.831 (18) | 2.6305 (17) | 148.1 (16) |
| N11—H11⋯O22A | 0.892 (18) | 2.356 (18) | 2.996 (2) | 128.8 (14) |
| N14—H14B⋯O1Bi | 0.88 (2) | 1.98 (2) | 2.8181 (19) | 157.3 (17) |
| N14—H14A⋯O1B | 0.92 (2) | 1.99 (2) | 2.7962 (18) | 146.4 (18) |
| N14—H14A⋯O22B | 0.92 (2) | 2.28 (2) | 2.992 (2) | 133.9 (16) |
| C5A—H5A⋯O21Aii | 0.917 (19) | 2.476 (19) | 3.383 (2) | 170.3 (16) |
| C5B—H5B⋯O21Biii | 0.913 (18) | 2.487 (18) | 3.394 (2) | 172.3 (15) |
| C11A—H11C⋯O41Aiv | 0.93 (3) | 2.48 (3) | 3.345 (2) | 155 (2) |
| C11A—H11A⋯O62Aiii | 0.94 (3) | 2.57 (3) | 3.496 (3) | 168 (2) |
| C13—H13A⋯O62Bv | 0.96 (2) | 2.46 (2) | 3.386 (2) | 162.9 (17) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v)  .
.
Acknowledgments
SS thanks Mangalore University for the research facilities.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Piperazines are among the most important building blocks in today's drug discovery. They are found in biologically active compounds across a number of different therapeutic areas such as antifungal, antibacterial, antimalarial, antipsychotic, antidepressant and antitumour activity against colon, prostate, breast, lung and leukemia tumors (for instance, Brockunier et al., 2004, Bogatcheva et al., 2006). A small number of piperazinium picrates or piperazinediium dipicrates have been structurally characterized, however generally the cations were heavily substituted. On the other hand, picric acid (pKa=0.38) has been studied for its ability to form salts which display wide spectrum of intermolecular interactions, for instance hydrogen bonds of different strengths and/or π···π stacking interactions. In the course of our studies of picrates of simple organic cations we have determined the crystal and molecular structure of the title compound (I: 1-methylpiprazinediium di(2,4,6-trinitrophenolate), Scheme 1).
In the CSD (Allen, 2002; Version 5.31 of Nov. 2009, updated August 2010) there are only a few picrates of simple piperazinium derivatives, for instance 4-(4-carboxybenzyl)-1-methylpiperazin-1-ium picrate (Li et al., 2009), 1-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazinium picrate (Verdonk et al., 1997) or piperazine-1,4-diium–dipicrate piperazine complex (Wang & Jia, 2008). Also some more complicated structures were reported, for instance 4-(3-Carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4- dihydro-7-quinolyl)-1-methylpiperazinium picrate (Fun et al., 2010).
In the crystal structure I there are two picrate anions and 1-methylpiperidinediium dication (Fig. 1); the presence of ionic species is supported by the successful location and refinement of the hydrogen atoms at both nitrogen atoms in the piperidine ring as well as by inspection of the pattern of bond distances and angles. The piperazine ring adopts an almost ideal chair conformation; the values of asymmetry parameters (Duax & Norton, 1975), which measure the deviations from the ideal symmetry (in the case D3d), are very small, less than 1.6°. The methyl substituent is in the equatorial position as can be seen from the torsion angles C13—C12—C11—C11A: 176.60 (15)° and C15—C16—C11—C11A: -176.72 (14)°. Both aromatic rings are in a good approximation planar, maximum deviation from the least-squares plane calculated by the six ring atoms is 0.0248 (11)Å in the anion A and 0.0297 (10)Å in anion B. The nitro groups are twisted with respect to the ring planes, for the groups ortho with respect to the C—O- group (at C2 and C6) this twist is of course significantly larger (ranging from 28.76 (13)° to 39.84 (11)°) than for the groups in para positions, at C4 (15.23 (9)° in anion A, only 3.92 (14)° in B).
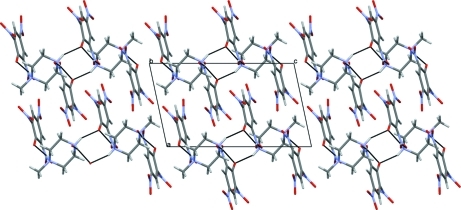
In the crystal structure the building block is made up of a centrosymetric pair of hydrogen bonded ionic components: two dications and four anions (Table 1, Fig. 2). Using graph set notation one can identify - taking into account the primary interactions only - the centrosymmetric ring R24(8) and dimeric D motifs. Interestingly no strong hydrogen bonds are observed between these structures; besides the coulombic interactions only weak C—H···O and some stacking between picrates (Fig. 3) organize the crystal packing.
Experimental
1-Methyl piperazine (1.00 g, 0.01 mol) was dissolved in 20 ml of alcohol. Picric acid (4.58 g, 0.02 mol) was dissolved in 50 ml of water. Both the solutions were mixed and to this, 5 ml of 3M HCl was added and stirred for few minutes. The formed complex was filtered and dried, crystals appropriate for X-ray data collection were found without further recrystallization (m. p. >523 K). Composition: Found (Calculated): C: 36.48 (36.57); H: 3.20 (3.25); N:19.98 (20.07).
Refinement
Hydrogen atoms were located in difference Fourier maps and isotropically refined.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Anisotropic ellipsoid representation of the ionic components of I together with atom labelling scheme. The ellipsoids are drawn at 50% probability level, hydrogen atoms are depicted as spheres with arbitrary radii; hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Fig. 2.
The centrosymmetric dimer of salt I; hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. Symmetry codes: (i) -x,1 - y,1 - z.
Fig. 3.
The crystal packing as seen approximately along y-direction. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C5H14N22+·2C6H2N3O7− | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 558.39 | F(000) = 576 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.671 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.2001 (12) Å | Cell parameters from 12041 reflections |
| b = 10.1780 (15) Å | θ = 3.0–28.0° |
| c = 13.7399 (18) Å | µ = 0.15 mm−1 |
| α = 89.798 (12)° | T = 295 K |
| β = 78.130 (11)° | Block, yellow |
| γ = 81.558 (12)° | 0.4 × 0.15 × 0.07 mm |
| V = 1109.6 (3) Å3 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Eos diffractometer | 4891 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 3624 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.021 |
| Detector resolution: 16.1544 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 28.0°, θmin = 3.0° |
| ω scans | h = −10→10 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2009) | k = −13→12 |
| Tmin = 0.936, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −18→18 |
| 21056 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.044 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.123 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 0.95 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0725P)2 + 0.3607P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4891 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 424 parameters | Δρmax = 0.24 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.30 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1A | −0.10838 (19) | 0.86643 (15) | 0.10686 (11) | 0.0303 (3) | |
| O1A | −0.02003 (16) | 0.75573 (12) | 0.08429 (10) | 0.0469 (3) | |
| C2A | −0.04660 (18) | 0.98367 (16) | 0.13439 (12) | 0.0309 (3) | |
| N2A | 0.12392 (16) | 0.97199 (15) | 0.15030 (11) | 0.0394 (3) | |
| O21A | 0.19522 (16) | 1.07010 (15) | 0.13867 (13) | 0.0601 (4) | |
| O22A | 0.18805 (16) | 0.86647 (14) | 0.17951 (12) | 0.0568 (4) | |
| C3A | −0.1404 (2) | 1.10787 (16) | 0.14843 (12) | 0.0314 (3) | |
| H3A | −0.091 (3) | 1.179 (2) | 0.1651 (16) | 0.052 (6)* | |
| C4A | −0.30793 (18) | 1.12289 (14) | 0.14285 (11) | 0.0284 (3) | |
| N4A | −0.40990 (18) | 1.25160 (13) | 0.16554 (10) | 0.0350 (3) | |
| O41A | −0.56396 (15) | 1.25745 (13) | 0.18252 (10) | 0.0474 (3) | |
| O42A | −0.33873 (18) | 1.34906 (12) | 0.16819 (12) | 0.0566 (4) | |
| C5A | −0.38244 (19) | 1.01553 (15) | 0.12063 (11) | 0.0288 (3) | |
| H5A | −0.495 (2) | 1.0237 (18) | 0.1186 (13) | 0.036 (5)* | |
| C6A | −0.28521 (19) | 0.89319 (14) | 0.10388 (11) | 0.0294 (3) | |
| N6A | −0.36772 (18) | 0.78285 (13) | 0.08081 (11) | 0.0370 (3) | |
| O61A | −0.3268 (2) | 0.67315 (13) | 0.11180 (13) | 0.0662 (5) | |
| O62A | −0.47823 (18) | 0.80553 (14) | 0.03359 (11) | 0.0557 (4) | |
| C1B | 0.29112 (18) | 0.24867 (15) | 0.41703 (11) | 0.0270 (3) | |
| O1B | 0.19899 (13) | 0.35763 (11) | 0.44572 (8) | 0.0353 (3) | |
| C2B | 0.23173 (18) | 0.13264 (16) | 0.38650 (12) | 0.0299 (3) | |
| N2B | 0.05928 (16) | 0.14283 (15) | 0.37308 (12) | 0.0404 (3) | |
| O21B | −0.00902 (16) | 0.04406 (15) | 0.38274 (15) | 0.0690 (5) | |
| O22B | −0.00859 (16) | 0.24821 (14) | 0.34659 (12) | 0.0576 (4) | |
| C3B | 0.32794 (19) | 0.00995 (16) | 0.36639 (12) | 0.0315 (3) | |
| H3B | 0.279 (2) | −0.0637 (19) | 0.3481 (14) | 0.040 (5)* | |
| C4B | 0.49633 (19) | −0.00422 (15) | 0.37139 (11) | 0.0301 (3) | |
| N4B | 0.59846 (18) | −0.13327 (14) | 0.34997 (11) | 0.0389 (3) | |
| O41B | 0.74541 (16) | −0.14586 (14) | 0.35957 (12) | 0.0558 (4) | |
| O42B | 0.53534 (19) | −0.22459 (14) | 0.32327 (14) | 0.0652 (4) | |
| C5B | 0.56874 (19) | 0.10308 (16) | 0.39575 (11) | 0.0303 (3) | |
| H5B | 0.681 (2) | 0.0949 (17) | 0.3956 (13) | 0.033 (4)* | |
| C6B | 0.46974 (18) | 0.22393 (16) | 0.41531 (11) | 0.0295 (3) | |
| N6B | 0.55497 (17) | 0.33587 (15) | 0.43280 (12) | 0.0414 (4) | |
| O61B | 0.5170 (2) | 0.44149 (14) | 0.39533 (12) | 0.0590 (4) | |
| O62B | 0.66595 (18) | 0.31520 (16) | 0.47993 (14) | 0.0699 (5) | |
| N11 | 0.16733 (15) | 0.57565 (13) | 0.16779 (10) | 0.0291 (3) | |
| H11 | 0.114 (2) | 0.6554 (18) | 0.1567 (13) | 0.030 (4)* | |
| C11A | 0.2986 (3) | 0.5363 (2) | 0.07575 (15) | 0.0456 (5) | |
| H11C | 0.346 (3) | 0.450 (3) | 0.0848 (19) | 0.071 (7)* | |
| H11B | 0.243 (3) | 0.539 (2) | 0.024 (2) | 0.068 (7)* | |
| H11A | 0.372 (3) | 0.600 (3) | 0.068 (2) | 0.079 (8)* | |
| C12 | 0.2433 (2) | 0.58588 (17) | 0.25660 (13) | 0.0348 (4) | |
| H12B | 0.300 (2) | 0.498 (2) | 0.2664 (14) | 0.041 (5)* | |
| H12A | 0.322 (3) | 0.647 (2) | 0.2416 (16) | 0.053 (6)* | |
| C13 | 0.1088 (2) | 0.63356 (18) | 0.34660 (13) | 0.0387 (4) | |
| H13B | 0.054 (2) | 0.7194 (19) | 0.3366 (13) | 0.035 (5)* | |
| H13A | 0.157 (2) | 0.636 (2) | 0.4042 (16) | 0.049 (5)* | |
| N14 | −0.02066 (18) | 0.54247 (15) | 0.36518 (11) | 0.0361 (3) | |
| H14B | −0.100 (3) | 0.576 (2) | 0.4161 (16) | 0.044 (5)* | |
| H14A | 0.031 (3) | 0.460 (2) | 0.3783 (15) | 0.048 (5)* | |
| C15 | −0.0961 (2) | 0.52998 (19) | 0.27659 (13) | 0.0364 (4) | |
| H15B | −0.153 (2) | 0.616 (2) | 0.2644 (15) | 0.042 (5)* | |
| H15A | −0.171 (3) | 0.471 (2) | 0.2906 (15) | 0.047 (5)* | |
| C16 | 0.0398 (2) | 0.48330 (17) | 0.18685 (13) | 0.0338 (3) | |
| H16B | 0.098 (2) | 0.3954 (19) | 0.1948 (14) | 0.036 (5)* | |
| H16A | −0.012 (3) | 0.481 (2) | 0.1283 (17) | 0.056 (6)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1A | 0.0339 (8) | 0.0278 (8) | 0.0286 (8) | 0.0045 (6) | −0.0116 (6) | 0.0010 (6) |
| O1A | 0.0507 (7) | 0.0349 (6) | 0.0543 (8) | 0.0144 (5) | −0.0239 (6) | −0.0092 (6) |
| C2A | 0.0257 (7) | 0.0361 (8) | 0.0310 (8) | −0.0019 (6) | −0.0081 (6) | 0.0030 (6) |
| N2A | 0.0275 (7) | 0.0450 (8) | 0.0462 (9) | −0.0034 (6) | −0.0097 (6) | −0.0010 (7) |
| O21A | 0.0355 (7) | 0.0566 (9) | 0.0925 (12) | −0.0161 (6) | −0.0166 (7) | 0.0067 (8) |
| O22A | 0.0422 (7) | 0.0511 (8) | 0.0820 (11) | 0.0035 (6) | −0.0320 (7) | 0.0070 (7) |
| C3A | 0.0342 (8) | 0.0290 (8) | 0.0324 (8) | −0.0068 (6) | −0.0088 (6) | 0.0024 (6) |
| C4A | 0.0311 (7) | 0.0244 (7) | 0.0284 (8) | 0.0010 (6) | −0.0072 (6) | 0.0014 (6) |
| N4A | 0.0435 (8) | 0.0274 (7) | 0.0324 (7) | 0.0029 (6) | −0.0099 (6) | −0.0003 (5) |
| O41A | 0.0381 (7) | 0.0415 (7) | 0.0571 (8) | 0.0112 (5) | −0.0094 (6) | −0.0042 (6) |
| O42A | 0.0646 (9) | 0.0267 (6) | 0.0792 (11) | −0.0052 (6) | −0.0174 (8) | −0.0055 (6) |
| C5A | 0.0280 (7) | 0.0307 (8) | 0.0287 (8) | −0.0012 (6) | −0.0102 (6) | 0.0027 (6) |
| C6A | 0.0357 (8) | 0.0260 (7) | 0.0289 (8) | −0.0037 (6) | −0.0130 (6) | 0.0011 (6) |
| N6A | 0.0453 (8) | 0.0307 (7) | 0.0387 (8) | −0.0068 (6) | −0.0163 (6) | −0.0020 (6) |
| O61A | 0.0923 (11) | 0.0293 (7) | 0.0920 (12) | −0.0132 (7) | −0.0508 (10) | 0.0087 (7) |
| O62A | 0.0606 (8) | 0.0531 (8) | 0.0682 (9) | −0.0181 (7) | −0.0407 (8) | 0.0056 (7) |
| C1B | 0.0256 (7) | 0.0315 (8) | 0.0221 (7) | 0.0001 (6) | −0.0036 (5) | −0.0009 (6) |
| O1B | 0.0338 (6) | 0.0350 (6) | 0.0336 (6) | 0.0054 (5) | −0.0061 (5) | −0.0059 (5) |
| C2B | 0.0227 (7) | 0.0359 (8) | 0.0308 (8) | −0.0032 (6) | −0.0055 (6) | 0.0006 (6) |
| N2B | 0.0265 (7) | 0.0434 (8) | 0.0523 (9) | −0.0043 (6) | −0.0108 (6) | −0.0032 (7) |
| O21B | 0.0357 (7) | 0.0529 (9) | 0.1243 (15) | −0.0158 (6) | −0.0236 (8) | 0.0045 (9) |
| O22B | 0.0400 (7) | 0.0510 (8) | 0.0875 (11) | 0.0010 (6) | −0.0315 (7) | 0.0076 (7) |
| C3B | 0.0312 (8) | 0.0310 (8) | 0.0331 (8) | −0.0061 (6) | −0.0070 (6) | −0.0003 (6) |
| C4B | 0.0288 (7) | 0.0312 (8) | 0.0278 (8) | 0.0027 (6) | −0.0050 (6) | −0.0014 (6) |
| N4B | 0.0388 (8) | 0.0355 (8) | 0.0370 (8) | 0.0050 (6) | −0.0031 (6) | −0.0023 (6) |
| O41B | 0.0365 (7) | 0.0511 (8) | 0.0751 (10) | 0.0147 (6) | −0.0155 (6) | −0.0074 (7) |
| O42B | 0.0597 (9) | 0.0352 (7) | 0.0992 (13) | 0.0017 (6) | −0.0186 (8) | −0.0210 (8) |
| C5B | 0.0227 (7) | 0.0402 (9) | 0.0264 (8) | 0.0003 (6) | −0.0053 (6) | −0.0026 (6) |
| C6B | 0.0273 (7) | 0.0349 (8) | 0.0264 (7) | −0.0051 (6) | −0.0056 (6) | −0.0037 (6) |
| N6B | 0.0318 (7) | 0.0453 (9) | 0.0462 (9) | −0.0065 (6) | −0.0052 (6) | −0.0166 (7) |
| O61B | 0.0718 (9) | 0.0448 (8) | 0.0644 (9) | −0.0235 (7) | −0.0133 (8) | 0.0015 (7) |
| O62B | 0.0495 (8) | 0.0688 (10) | 0.0995 (13) | 0.0001 (7) | −0.0399 (9) | −0.0343 (9) |
| N11 | 0.0286 (6) | 0.0248 (6) | 0.0310 (7) | 0.0034 (5) | −0.0047 (5) | −0.0002 (5) |
| C11A | 0.0464 (10) | 0.0415 (11) | 0.0383 (10) | 0.0077 (9) | 0.0055 (8) | 0.0011 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0280 (8) | 0.0350 (9) | 0.0423 (9) | −0.0012 (7) | −0.0122 (7) | −0.0009 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0431 (9) | 0.0357 (9) | 0.0386 (9) | 0.0020 (7) | −0.0169 (8) | −0.0092 (7) |
| N14 | 0.0343 (7) | 0.0384 (8) | 0.0289 (7) | 0.0082 (6) | −0.0010 (6) | −0.0024 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0271 (8) | 0.0411 (9) | 0.0403 (9) | −0.0024 (7) | −0.0073 (7) | 0.0020 (7) |
| C16 | 0.0376 (8) | 0.0309 (8) | 0.0342 (9) | −0.0054 (7) | −0.0104 (7) | −0.0033 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1A—O1A | 1.2494 (18) | N4B—O42B | 1.220 (2) |
| C1A—C2A | 1.443 (2) | N4B—O41B | 1.2271 (19) |
| C1A—C6A | 1.445 (2) | C5B—C6B | 1.365 (2) |
| C2A—C3A | 1.372 (2) | C5B—H5B | 0.913 (18) |
| C2A—N2A | 1.4470 (19) | C6B—N6B | 1.466 (2) |
| N2A—O21A | 1.2233 (19) | N6B—O62B | 1.215 (2) |
| N2A—O22A | 1.2283 (19) | N6B—O61B | 1.217 (2) |
| C3A—C4A | 1.378 (2) | N11—C16 | 1.490 (2) |
| C3A—H3A | 0.93 (2) | N11—C12 | 1.490 (2) |
| C4A—C5A | 1.391 (2) | N11—C11A | 1.495 (2) |
| C4A—N4A | 1.4445 (19) | N11—H11 | 0.892 (18) |
| N4A—O42A | 1.2267 (19) | C11A—H11C | 0.93 (3) |
| N4A—O41A | 1.2291 (18) | C11A—H11B | 0.92 (3) |
| C5A—C6A | 1.369 (2) | C11A—H11A | 0.94 (3) |
| C5A—H5A | 0.917 (19) | C12—C13 | 1.505 (2) |
| C6A—N6A | 1.4605 (19) | C12—H12B | 0.97 (2) |
| N6A—O62A | 1.2144 (18) | C12—H12A | 0.96 (2) |
| N6A—O61A | 1.2190 (19) | C13—N14 | 1.493 (2) |
| C1B—O1B | 1.2612 (18) | C13—H13B | 0.946 (19) |
| C1B—C2B | 1.437 (2) | C13—H13A | 0.96 (2) |
| C1B—C6B | 1.445 (2) | N14—C15 | 1.488 (2) |
| C2B—C3B | 1.372 (2) | N14—H14B | 0.88 (2) |
| C2B—N2B | 1.4521 (19) | N14—H14A | 0.92 (2) |
| N2B—O21B | 1.215 (2) | C15—C16 | 1.507 (2) |
| N2B—O22B | 1.2238 (19) | C15—H15B | 0.96 (2) |
| C3B—C4B | 1.383 (2) | C15—H15A | 0.92 (2) |
| C3B—H3B | 0.959 (19) | C16—H16B | 0.965 (18) |
| C4B—C5B | 1.390 (2) | C16—H16A | 0.99 (2) |
| C4B—N4B | 1.446 (2) | ||
| O1A—C1A—C2A | 124.85 (14) | C5B—C6B—C1B | 124.82 (14) |
| O1A—C1A—C6A | 123.25 (15) | C5B—C6B—N6B | 116.40 (13) |
| C2A—C1A—C6A | 111.84 (13) | C1B—C6B—N6B | 118.76 (13) |
| C3A—C2A—C1A | 124.24 (13) | O62B—N6B—O61B | 123.87 (16) |
| C3A—C2A—N2A | 116.59 (14) | O62B—N6B—C6B | 117.52 (16) |
| C1A—C2A—N2A | 119.16 (13) | O61B—N6B—C6B | 118.50 (14) |
| O21A—N2A—O22A | 122.68 (14) | C16—N11—C12 | 110.14 (13) |
| O21A—N2A—C2A | 118.32 (14) | C16—N11—C11A | 111.97 (14) |
| O22A—N2A—C2A | 118.91 (14) | C12—N11—C11A | 111.84 (14) |
| C2A—C3A—C4A | 119.12 (15) | C16—N11—H11 | 107.5 (11) |
| C2A—C3A—H3A | 118.9 (13) | C12—N11—H11 | 109.0 (11) |
| C4A—C3A—H3A | 121.8 (13) | C11A—N11—H11 | 106.2 (11) |
| C3A—C4A—C5A | 121.40 (14) | N11—C11A—H11C | 106.1 (16) |
| C3A—C4A—N4A | 119.07 (14) | N11—C11A—H11B | 106.3 (15) |
| C5A—C4A—N4A | 119.46 (13) | H11C—C11A—H11B | 110 (2) |
| O42A—N4A—O41A | 123.36 (14) | N11—C11A—H11A | 106.9 (17) |
| O42A—N4A—C4A | 118.51 (14) | H11C—C11A—H11A | 116 (2) |
| O41A—N4A—C4A | 118.12 (14) | H11B—C11A—H11A | 111 (2) |
| C6A—C5A—C4A | 118.49 (14) | N11—C12—C13 | 110.48 (13) |
| C6A—C5A—H5A | 119.2 (11) | N11—C12—H12B | 106.7 (11) |
| C4A—C5A—H5A | 122.3 (11) | C13—C12—H12B | 110.9 (11) |
| C5A—C6A—C1A | 124.74 (14) | N11—C12—H12A | 107.2 (13) |
| C5A—C6A—N6A | 116.96 (13) | C13—C12—H12A | 110.5 (13) |
| C1A—C6A—N6A | 118.30 (13) | H12B—C12—H12A | 110.9 (16) |
| O62A—N6A—O61A | 122.69 (14) | N14—C13—C12 | 110.29 (14) |
| O62A—N6A—C6A | 118.18 (13) | N14—C13—H13B | 107.8 (11) |
| O61A—N6A—C6A | 119.09 (13) | C12—C13—H13B | 110.5 (11) |
| O1B—C1B—C2B | 124.76 (13) | N14—C13—H13A | 108.6 (12) |
| O1B—C1B—C6B | 123.54 (14) | C12—C13—H13A | 110.3 (12) |
| C2B—C1B—C6B | 111.65 (13) | H13B—C13—H13A | 109.3 (16) |
| C3B—C2B—C1B | 124.68 (13) | C15—N14—C13 | 111.26 (14) |
| C3B—C2B—N2B | 115.96 (14) | C15—N14—H14B | 109.5 (13) |
| C1B—C2B—N2B | 119.34 (13) | C13—N14—H14B | 107.5 (13) |
| O21B—N2B—O22B | 122.20 (14) | C15—N14—H14A | 108.4 (13) |
| O21B—N2B—C2B | 118.69 (14) | C13—N14—H14A | 108.3 (12) |
| O22B—N2B—C2B | 118.96 (14) | H14B—N14—H14A | 111.8 (18) |
| C2B—C3B—C4B | 118.77 (15) | N14—C15—C16 | 110.20 (13) |
| C2B—C3B—H3B | 120.1 (11) | N14—C15—H15B | 108.1 (12) |
| C4B—C3B—H3B | 121.1 (11) | C16—C15—H15B | 109.3 (12) |
| C3B—C4B—C5B | 121.27 (14) | N14—C15—H15A | 108.0 (13) |
| C3B—C4B—N4B | 119.00 (14) | C16—C15—H15A | 110.7 (13) |
| C5B—C4B—N4B | 119.73 (13) | H15B—C15—H15A | 110.4 (16) |
| O42B—N4B—O41B | 122.89 (14) | N11—C16—C15 | 110.70 (13) |
| O42B—N4B—C4B | 118.86 (14) | N11—C16—H16B | 108.1 (10) |
| O41B—N4B—C4B | 118.24 (14) | C15—C16—H16B | 112.1 (11) |
| C6B—C5B—C4B | 118.58 (14) | N11—C16—H16A | 108.9 (13) |
| C6B—C5B—H5B | 120.0 (11) | C15—C16—H16A | 108.8 (13) |
| C4B—C5B—H5B | 121.3 (11) | H16B—C16—H16A | 108.2 (16) |
| O1A—C1A—C2A—C3A | 172.55 (16) | C3B—C2B—N2B—O21B | 27.4 (2) |
| C6A—C1A—C2A—C3A | −4.8 (2) | C1B—C2B—N2B—O21B | −153.91 (17) |
| O1A—C1A—C2A—N2A | −8.5 (2) | C3B—C2B—N2B—O22B | −148.21 (17) |
| C6A—C1A—C2A—N2A | 174.11 (14) | C1B—C2B—N2B—O22B | 30.5 (2) |
| C3A—C2A—N2A—O21A | −26.5 (2) | C1B—C2B—C3B—C4B | −2.8 (2) |
| C1A—C2A—N2A—O21A | 154.53 (16) | N2B—C2B—C3B—C4B | 175.80 (14) |
| C3A—C2A—N2A—O22A | 150.03 (16) | C2B—C3B—C4B—C5B | −0.3 (2) |
| C1A—C2A—N2A—O22A | −29.0 (2) | C2B—C3B—C4B—N4B | −179.82 (14) |
| C1A—C2A—C3A—C4A | 4.6 (2) | C3B—C4B—N4B—O42B | 3.6 (2) |
| N2A—C2A—C3A—C4A | −174.39 (14) | C5B—C4B—N4B—O42B | −175.90 (16) |
| C2A—C3A—C4A—C5A | −1.8 (2) | C3B—C4B—N4B—O41B | −176.40 (15) |
| C2A—C3A—C4A—N4A | 175.04 (14) | C5B—C4B—N4B—O41B | 4.1 (2) |
| C3A—C4A—N4A—O42A | 15.4 (2) | C3B—C4B—C5B—C6B | 0.3 (2) |
| C5A—C4A—N4A—O42A | −167.73 (15) | N4B—C4B—C5B—C6B | 179.78 (14) |
| C3A—C4A—N4A—O41A | −163.68 (14) | C4B—C5B—C6B—C1B | 2.9 (2) |
| C5A—C4A—N4A—O41A | 13.2 (2) | C4B—C5B—C6B—N6B | −175.30 (14) |
| C3A—C4A—C5A—C6A | −0.2 (2) | O1B—C1B—C6B—C5B | 172.05 (15) |
| N4A—C4A—C5A—C6A | −177.01 (14) | C2B—C1B—C6B—C5B | −5.4 (2) |
| C4A—C5A—C6A—C1A | −0.4 (2) | O1B—C1B—C6B—N6B | −9.8 (2) |
| C4A—C5A—C6A—N6A | 179.97 (13) | C2B—C1B—C6B—N6B | 172.77 (14) |
| O1A—C1A—C6A—C5A | −174.70 (15) | C5B—C6B—N6B—O62B | −38.6 (2) |
| C2A—C1A—C6A—C5A | 2.7 (2) | C1B—C6B—N6B—O62B | 143.11 (16) |
| O1A—C1A—C6A—N6A | 4.9 (2) | C5B—C6B—N6B—O61B | 137.68 (16) |
| C2A—C1A—C6A—N6A | −177.70 (13) | C1B—C6B—N6B—O61B | −40.6 (2) |
| C5A—C6A—N6A—O62A | 33.9 (2) | C16—N11—C12—C13 | −58.20 (17) |
| C1A—C6A—N6A—O62A | −145.77 (16) | C11A—N11—C12—C13 | 176.60 (15) |
| C5A—C6A—N6A—O61A | −144.12 (17) | N11—C12—C13—N14 | 57.33 (18) |
| C1A—C6A—N6A—O61A | 36.3 (2) | C12—C13—N14—C15 | −56.74 (18) |
| O1B—C1B—C2B—C3B | −172.05 (15) | C13—N14—C15—C16 | 56.51 (19) |
| C6B—C1B—C2B—C3B | 5.3 (2) | C12—N11—C16—C15 | 58.16 (17) |
| O1B—C1B—C2B—N2B | 9.4 (2) | C11A—N11—C16—C15 | −176.72 (14) |
| C6B—C1B—C2B—N2B | −173.25 (14) | N14—C15—C16—N11 | −57.15 (19) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N11—H11···O1A | 0.892 (18) | 1.831 (18) | 2.6305 (17) | 148.1 (16) |
| N11—H11···O22A | 0.892 (18) | 2.356 (18) | 2.996 (2) | 128.8 (14) |
| N14—H14B···O1Bi | 0.88 (2) | 1.98 (2) | 2.8181 (19) | 157.3 (17) |
| N14—H14A···O1B | 0.92 (2) | 1.99 (2) | 2.7962 (18) | 146.4 (18) |
| N14—H14A···O22B | 0.92 (2) | 2.28 (2) | 2.992 (2) | 133.9 (16) |
| C5A—H5A···O21Aii | 0.917 (19) | 2.476 (19) | 3.383 (2) | 170.3 (16) |
| C5B—H5B···O21Biii | 0.913 (18) | 2.487 (18) | 3.394 (2) | 172.3 (15) |
| C11A—H11C···O41Aiv | 0.93 (3) | 2.48 (3) | 3.345 (2) | 155 (2) |
| C11A—H11A···O62Aiii | 0.94 (3) | 2.57 (3) | 3.496 (3) | 168 (2) |
| C12—H12A···O22A | 0.96 (2) | 2.56 (2) | 3.046 (2) | 111.6 (15) |
| C13—H13A···O62Bv | 0.96 (2) | 2.46 (2) | 3.386 (2) | 162.9 (17) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) x−1, y, z; (iii) x+1, y, z; (iv) x+1, y−1, z; (v) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: FL2330).
References
- Allen, F. H. (2002). Acta Cryst. B58, 380–388. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Altomare, A., Cascarano, G., Giacovazzo, C. & Guagliardi, A. (1993). J. Appl. Cryst. 26, 343–350.
- Bogatcheva, E., Hanrahan, C., Nikonenko, B., Samala, R., Chen, P., Gearhart, J., Barbosa, F., Einck, L., Nacy, C. A. & Protopopova, M. (2006). J. Med. Chem. 49, 3045–3048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Brockunier, L. L., He, J., Colwell, L. F. Jr, Habulihaz, B., He, H., Leiting, B., Lyons, K. A., Marsilio, F., Patel, R. A., Teffera, Y., Wu, J. K., Thornberry, N. A., Weber, A. E. & Parmee, E. R. (2004). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 14, 4763–4766. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Duax, W. L. & Norton, D. A. (1975). Atlas of Steroid Structures, pp. 16–22. New York: Plenum.
- Fun, H.-K., Hemamalini, M., Shetty, D. N., Narayana, B. & Yathirajan, H. S. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o714–o715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Li, H., Hakim Al-arique, Q. N. M., Yathirajan, H. S., Narayana, B. & Ramesha, A. R. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Oxford Diffraction (2009). CrysAlis PRO Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Siemens (1989). Stereochemical Workstation Operation Manual Siemens Analytical X-ray Instruments Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Verdonk, M. L., Voogd, J. W., Kanters, J. A., Kroon, J., den Besten, R., Brandsma, L., Leysen, D. & Kelder, J. (1997). Acta Cryst. B53, 976–983. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-L. & Jia, L.-H. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o665–o666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811001024/fl2330sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811001024/fl2330Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report