Abstract
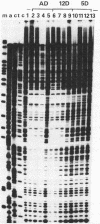
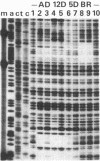
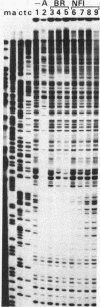
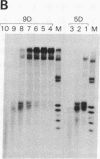
In an earlier paper we identified a tissue-specific enhancer in the 3' flanking region of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. In this paper we analyze the properties of this enhancer. Deletion analysis and transient expression assays show that the domain responsible for activation of transcription is at most 136 base pairs long. Specific factors that bind to discrete sequences within the enhancer DNA are found in extracts of embryonic and adult erythrocytes and in brain. These factors are specific for the tissue or the erythrocyte developmental stage and protect at least five discrete regions in or near the enhancer against DNase I digestion in "footprinting" experiments. Four of these regions reside wholly within the 136-base-pair functional enhancer domain, which also comprises a site in chromatin that is hypersensitive to nucleases. The nature of the binding sites and the program of appearance of the factors during development suggest that a subset of these interactions may be responsible for the developmental specificity of the enhancer.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caplan A., Kimura T., Gould H., Allan J. Perturbation of chromatin structure in the region of the adult beta-globin gene in chicken erythrocyte chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 5;193(1):57–70. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90626-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi O. R., Engel J. D. A 3' enhancer is required for temporal and tissue-specific transcriptional activation of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):731–734. doi: 10.1038/323731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Lewis C. D., Felsenfeld G. Interaction of specific nuclear factors with the nuclease-hypersensitive region of the chicken adult beta-globin gene: nature of the binding domain. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse J. E., Nickol J. M., Lieber M. R., Felsenfeld G. Regulated gene expression in transfected primary chicken erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4312–4316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P. Enhancer elements. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):313–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Wood W. I., Dolan M., Engel J. D., Felsenfeld G. A 200 base pair region at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene is accessible to nuclease digestion. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead D. A., Szczesna-Skorupa E., Kemper B. Single-stranded DNA 'blue' T7 promoter plasmids: a versatile tandem promoter system for cloning and protein engineering. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):67–74. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills F. C., Fisher L. M., Kuroda R., Ford A. M., Gould H. J. DNase I hypersensitive sites in the chromatin of human mu immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):809–812. doi: 10.1038/306809a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Hurwitz J. Specific binding of a cellular DNA replication protein to the origin of replication of adenovirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6177–6181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Granner D. K. Chromatin changes accompany immunoglobulin kappa gene activation: a potential control region within the gene. Nature. 1982 Sep 30;299(5882):449–451. doi: 10.1038/299449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins D. R., Rosenfeld P. J., Wides R. J., Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J., Jr Structure and function of the adenovirus origin of replication. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90327-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Hennighausen L., Battey J., Leder P. Chromatin structure and protein binding in the putative regulatory region of the c-myc gene in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theisen M., Stief A., Sippel A. E. The lysozyme enhancer: cell-specific activation of the chicken lysozyme gene by a far-upstream DNA element. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):719–724. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04273.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theisen M., Stief A., Sippel A. E. The lysozyme enhancer: cell-specific activation of the chicken lysozyme gene by a far-upstream DNA element. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):719–724. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04273.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaniv M. Regulation of eukaryotic gene expression by transactivating proteins and cis acting DNA elements. Biol Cell. 1984;50(3):203–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1984.tb00268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Yamamoto K. R. Reversible and persistent changes in chromatin structure accompany activation of a glucocorticoid-dependent enhancer element. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90523-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Schatz C., Wildeman A., Chambon P. Multiple sequence motifs are involved in SV40 enhancer function. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):387–397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]