Abstract
The title compound, C2H10N2 2+·2C6H2N3O7 −·2H2O, crystallizes with a complete picrate anion and half an ethylenediammonium dication on a mirror plane, and two half-water molecules (both on a mirror plane) in the asymmetric unit. The N atoms from separate half ethylenediammonium dications are in near proximity to a phenolate O atom and two o-NO2 groups from the picrate anion, which, along with the water molecule form N—H⋯O, O—H⋯O and weak intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds that create cyclic patterns with graph-set descriptors R 2 4(8), R 4 4(12), and R 4 4(16). The crystal packing is strongly influenced by these intermolecular interactions between symmetry-related water molecules, the half ethylenediammonium dication and the picrate anion, forming a three-dimensional supermolecular structure.
Related literature
For related structures, see: Muthamizhchelvan et al. (2005a
▶,b
▶,c
▶); Subashini et al. (2006 ▶); Narayana et al. (2008 ▶). For standard bond lengths, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶). For picrates of biologically important molecules, see: Harrison et al. (2007 ▶); Swamy et al. (2007 ▶).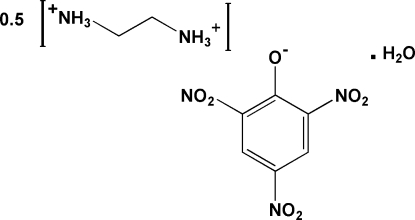
Experimental
Crystal data
C2H10N2 2+·2C6H2N3O7 −·2H2O
M r = 554.36
Orthorhombic,
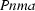
a = 13.4795 (4) Å
b = 20.4372 (7) Å
c = 8.0410 (3) Å
V = 2215.16 (13) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.15 mm−1
T = 295 K
0.52 × 0.42 × 0.27 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Gemini R diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2007 ▶) T min = 0.837, T max = 0.960
16775 measured reflections
3846 independent reflections
2322 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.026
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.063
wR(F 2) = 0.196
S = 1.03
3846 reflections
207 parameters
10 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Oxford Diffraction, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL, enCIFer (Allen et al., 2004 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811004855/om2399sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811004855/om2399Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N4—H41⋯O2Wi | 0.87 (1) | 2.06 (2) | 2.872 (4) | 156 (3) |
| N4—H42⋯O1 | 0.86 (1) | 1.98 (1) | 2.815 (2) | 164 (2) |
| N4—H42⋯O7 | 0.86 (1) | 2.41 (2) | 2.9166 (16) | 118 (2) |
| N5—H51⋯O1Wii | 0.87 (1) | 1.91 (1) | 2.778 (3) | 176 (3) |
| N5—H52⋯O1iii | 0.86 (1) | 2.18 (2) | 2.892 (2) | 140 (2) |
| N5—H52⋯O2iii | 0.86 (1) | 2.34 (2) | 3.018 (3) | 136 (2) |
| C3—H3⋯O6iv | 0.93 | 2.53 | 3.337 (3) | 145 |
| C7—H7⋯O2v | 0.96 | 2.39 | 3.128 (3) | 134 |
| C7—H7⋯O7vi | 0.96 | 2.56 | 3.1203 (19) | 117 |
| O1W—H1W2⋯O3 | 0.84 (1) | 2.21 (3) | 3.008 (2) | 159 (6) |
| O1W—H1W2⋯O2 | 0.84 (1) | 2.52 (4) | 3.243 (3) | 145 (5) |
| O2W—H2W2⋯O5 | 0.85 (1) | 2.26 (2) | 3.082 (2) | 163 (7) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 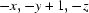 ; (ii)
; (ii) 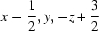 ; (iii)
; (iii) 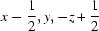 ; (iv)
; (iv) 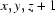 ; (v)
; (v) 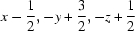 ; (vi)
; (vi) 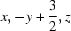 .
.
Acknowledgments
QNMHA thanks the University of Mysore for use of its research facilities. RJB acknowledges the NSF MRI program (grant No. CHE-0619278) for funds to purchase an X-ray diffractometer.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The crystal structures of compounds similar to ethylenediammonium picrate, 3-(dimethylammonio)propanaminium dipicrate and triethylaminium picrate (Muthamizhchelvan et al., 2005a, 2005b, 2005c), 2-amino-4,6-dimethylpyrimidinium picrate (Subashini et al., 2006) and 2-aminopyrimidinium picrate (Narayana et al., 2008) have been reported. In continuation of our work on picrates of biologically important molecules (Harrison et al., 2007; Swamy et al., 2007), we have prepared a new picrate of ethylenediammonium hydrate, [C7H8N4O8] and its crystal structure is reported.
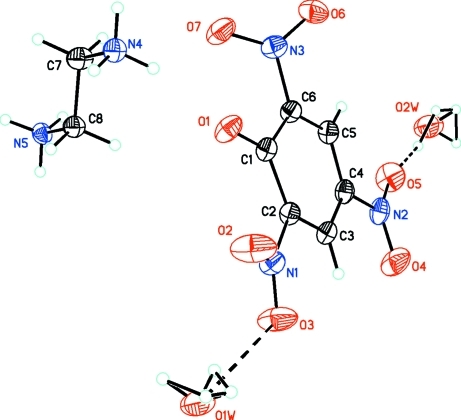
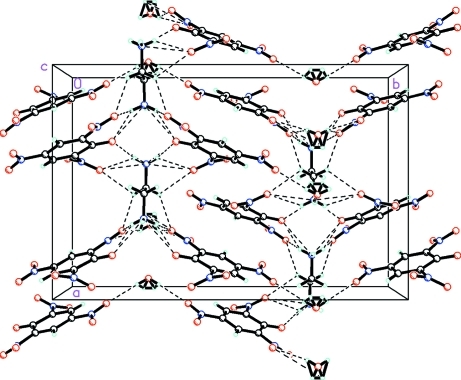
The title compound, 0.5(C2H10N22+), C6H2N3O7-, H2O, crystallizes with a complete picrate anion and a half-ethylenediammonium group on a mirror plane thus producing a 0.5 di-cation (i.e. protonated at both ends), and two half-water molecules (both on a mirror plane) in the asymmetric unit (Fig. 1). Bond distances and angles are in normal ranges (Allen et al., 1998). In the picrate anion the depronated phenolate oxygen atom is slightly deviated from the plane of the benzene ring (torsion angle O1/C1/C2/C3 = 177.84 (17) Å). The twist angles between the mean plane of the benzene ring and the two o-NO2 groups are 20.3 (0)° (N1) and 39.6 (7)° (N3). The p-NO2group is twisted by 3.3 (4)° and most likely influenced by a weak hydrogen bond interaction (O2W—H2W2···O5). The deviation of the p-NO2 groups from the plane of the benzene ring is due to a network of hydrogen bond interactions with the half-ethylenediammonium di-cation involving both nitrogen atoms (N4 and N5 lying across a morror plane). The position of N4 and N5 from separate half-ethylenediammonium di-cations, in near proximity to a phenolate oxygen atom and two o-NO2 groups from the picrate anion, along with the water molecule form N—H···O, O—H···O hydrogen bonds and weak C—H···O intermolecular interactions (Table 1) that create cyclic patterns with graph-set descriptors R24(8), R44(12) and R44(16). These intermolecular interactions of symmetry-related molecules link the cations and anions through a half-water molecule (on a mirror plane), the half-ethylenediammonium di-cation and the picrate anion forming a 3-D supermolecular structure (Fig. 2).
Experimental
Ethylenediamine dihydrochloride (1.33 g, 0.01 mol) was dissolved in 25 ml of water. Picric acid (2.29 g, 0.01 mol) was dissolved in 50 ml of water. Both the solutions were mixed and stirred for few minutes. The formed complex was filtered and dried. Good quality crystals were grown from ethanol solution by slow evaporation (m. p.: 476–478 K). Composition: Found (Calculated): C: 30.44 (30.40); H: 2.92 (2.96); N: 20.29% (20.36%).
Refinement
The H atoms on the water O atoms and N atoms were located by difference Fourier maps, fixed at 0.84Å (O-H) and 1.36° (O···O), or 0.86Å (N-H) and refined isotropically. All of the remaining H atoms were placed in their calculated positions and then refined using the riding model with Atom—H lengths of 0.93 or 0.95Å (CH). Isotropic displacement parameters for these atoms were set to 1.19–1.20 (CH) times Ueq of the parent atom.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound, 0.5(C2H10N22+), C6H2N3O7-, H2O, showing the atom labeling scheme and 30% probability displacement ellipsoids. The asymmetric unit consists of a complete picrate anion, a half-ethylenediammonium group on a mirror plane thus producing a 0.5 di-cation (i.e. protonated at both ends), and two half-water molecules (both on a mirror plane). Dashed lines indicate O—H···O hydrogen bond interactions with a disordered water molecule..
Fig. 2.
Packing diagram of the title compound viewed down the c axis. Dashed lines indicate intermolecular N—H···O and O—H···O hydrogen bonds and weak C—H···O intermolecular interactions which produces a 3-D superstructure. Disordered water molecules are displayed.
Crystal data
| C2H10N22+·2C6H2N3O7−·2H2O | F(000) = 1144 |
| Mr = 554.36 | Dx = 1.662 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pnma | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ac 2n | Cell parameters from 5241 reflections |
| a = 13.4795 (4) Å | θ = 4.6–32.5° |
| b = 20.4372 (7) Å | µ = 0.15 mm−1 |
| c = 8.0410 (3) Å | T = 295 K |
| V = 2215.16 (13) Å3 | Chunk, pale orange |
| Z = 4 | 0.52 × 0.42 × 0.27 mm |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Gemini R diffractometer | 3846 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2322 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.026 |
| Detector resolution: 10.50 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 32.5°, θmin = 5.0° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −19→14 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2007) | k = −29→23 |
| Tmin = 0.837, Tmax = 0.960 | l = −11→9 |
| 16775 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.063 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.196 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.110P)2 + 0.1282P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3846 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 207 parameters | Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3 |
| 10 restraints | Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| O1 | 0.17845 (10) | 0.65746 (6) | 0.24678 (18) | 0.0483 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.27913 (16) | 0.67547 (9) | 0.5303 (2) | 0.0816 (6) | |
| O3 | 0.22821 (17) | 0.62252 (9) | 0.7372 (2) | 0.0797 (6) | |
| O4 | 0.11929 (14) | 0.40318 (8) | 0.6662 (2) | 0.0745 (5) | |
| O5 | 0.05313 (14) | 0.37346 (7) | 0.4353 (3) | 0.0707 (5) | |
| O6 | 0.10573 (12) | 0.51165 (8) | −0.0500 (2) | 0.0590 (4) | |
| O7 | 0.05455 (14) | 0.60949 (7) | 0.0004 (2) | 0.0663 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.23259 (12) | 0.63071 (7) | 0.5874 (2) | 0.0435 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.09604 (12) | 0.41363 (7) | 0.5211 (3) | 0.0472 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.09158 (12) | 0.55764 (8) | 0.0443 (2) | 0.0452 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.16145 (11) | 0.60249 (8) | 0.3089 (2) | 0.0350 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.18375 (12) | 0.58407 (8) | 0.4784 (2) | 0.0343 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.16198 (12) | 0.52426 (8) | 0.5472 (2) | 0.0374 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.1760 | 0.5160 | 0.6584 | 0.045* | |
| C4 | 0.11908 (12) | 0.47672 (8) | 0.4495 (2) | 0.0373 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.09762 (12) | 0.48793 (8) | 0.2839 (3) | 0.0378 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.0705 | 0.4550 | 0.2182 | 0.045* | |
| C6 | 0.11716 (12) | 0.54860 (8) | 0.2185 (2) | 0.0365 (4) | |
| N4 | 0.08177 (14) | 0.7500 | 0.0444 (3) | 0.0373 (5) | |
| H41 | 0.092 (2) | 0.7500 | −0.0622 (14) | 0.049 (9)* | |
| H42 | 0.1081 (14) | 0.7162 (8) | 0.092 (3) | 0.052 (6)* | |
| N5 | −0.15992 (16) | 0.7500 | 0.2772 (3) | 0.0368 (5) | |
| H51 | −0.171 (2) | 0.7500 | 0.3843 (14) | 0.039 (7)* | |
| H52 | −0.1861 (13) | 0.7149 (7) | 0.237 (2) | 0.041 (5)* | |
| C7 | −0.02674 (18) | 0.7500 | 0.0673 (3) | 0.0439 (6) | |
| H7 | −0.0549 | 0.7881 | 0.0158 | 0.053* | |
| C8 | −0.05052 (18) | 0.7500 | 0.2490 (3) | 0.0383 (6) | |
| H8 | −0.0219 | 0.7880 | 0.3001 | 0.046* | |
| O1W | 0.2964 (2) | 0.7500 | 0.8852 (3) | 0.0739 (7) | |
| H1W1 | 0.349 (3) | 0.764 (3) | 0.845 (7) | 0.111* | 0.50 |
| H1W2 | 0.274 (4) | 0.721 (2) | 0.821 (6) | 0.111* | 0.50 |
| O2W | −0.0548 (2) | 0.2500 | 0.3099 (4) | 0.0840 (8) | |
| H2W1 | −0.007 (3) | 0.234 (3) | 0.254 (8) | 0.126* | 0.50 |
| H2W2 | −0.031 (4) | 0.282 (3) | 0.364 (8) | 0.126* | 0.50 |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0535 (8) | 0.0364 (7) | 0.0551 (9) | −0.0132 (6) | −0.0188 (6) | 0.0128 (6) |
| O2 | 0.1095 (14) | 0.0797 (11) | 0.0556 (11) | −0.0613 (11) | −0.0105 (10) | 0.0031 (9) |
| O3 | 0.1239 (16) | 0.0683 (11) | 0.0470 (10) | −0.0350 (11) | −0.0241 (10) | 0.0044 (9) |
| O4 | 0.1063 (13) | 0.0433 (9) | 0.0739 (13) | −0.0095 (8) | −0.0225 (10) | 0.0227 (8) |
| O5 | 0.0867 (12) | 0.0409 (8) | 0.0846 (14) | −0.0227 (8) | −0.0085 (10) | 0.0033 (8) |
| O6 | 0.0713 (10) | 0.0602 (9) | 0.0454 (9) | −0.0108 (7) | −0.0001 (7) | −0.0100 (7) |
| O7 | 0.0900 (13) | 0.0520 (9) | 0.0568 (10) | −0.0035 (8) | −0.0298 (8) | 0.0076 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0470 (8) | 0.0382 (8) | 0.0453 (10) | −0.0081 (6) | −0.0098 (7) | 0.0002 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0442 (8) | 0.0300 (7) | 0.0674 (13) | −0.0006 (6) | −0.0024 (8) | 0.0078 (8) |
| N3 | 0.0483 (9) | 0.0453 (9) | 0.0419 (9) | −0.0102 (7) | −0.0065 (7) | 0.0009 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0308 (7) | 0.0314 (8) | 0.0430 (10) | −0.0024 (6) | −0.0051 (7) | 0.0021 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0321 (7) | 0.0297 (7) | 0.0411 (10) | −0.0021 (6) | −0.0050 (7) | −0.0012 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0358 (8) | 0.0339 (8) | 0.0427 (10) | 0.0013 (6) | −0.0045 (7) | 0.0054 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0343 (8) | 0.0274 (7) | 0.0501 (11) | −0.0014 (6) | −0.0004 (7) | 0.0038 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0340 (8) | 0.0320 (8) | 0.0475 (10) | −0.0034 (6) | −0.0041 (7) | −0.0033 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0366 (8) | 0.0337 (8) | 0.0392 (10) | −0.0020 (6) | −0.0047 (7) | 0.0008 (7) |
| N4 | 0.0278 (9) | 0.0434 (12) | 0.0407 (13) | 0.000 | −0.0018 (9) | 0.000 |
| N5 | 0.0405 (11) | 0.0317 (10) | 0.0383 (12) | 0.000 | 0.0094 (9) | 0.000 |
| C7 | 0.0315 (11) | 0.0627 (17) | 0.0377 (14) | 0.000 | −0.0010 (10) | 0.000 |
| C8 | 0.0399 (12) | 0.0387 (12) | 0.0363 (14) | 0.000 | 0.0001 (10) | 0.000 |
| O1W | 0.110 (2) | 0.0650 (16) | 0.0466 (14) | 0.000 | −0.0253 (14) | 0.000 |
| O2W | 0.099 (2) | 0.094 (2) | 0.0583 (18) | 0.000 | −0.0144 (15) | 0.000 |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C1 | 1.251 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.373 (2) |
| O2—N1 | 1.201 (2) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| O3—N1 | 1.218 (2) | N4—C7 | 1.474 (3) |
| O4—N2 | 1.227 (3) | N4—H41 | 0.869 (10) |
| O5—N2 | 1.218 (2) | N4—H42 | 0.864 (9) |
| O6—N3 | 1.222 (2) | N5—C8 | 1.492 (3) |
| O7—N3 | 1.223 (2) | N5—H51 | 0.874 (10) |
| N1—C2 | 1.452 (2) | N5—H52 | 0.863 (9) |
| N2—C4 | 1.446 (2) | C7—C8 | 1.496 (4) |
| N3—C6 | 1.454 (2) | C7—H7 | 0.9599 |
| C1—C2 | 1.445 (2) | C8—H8 | 0.9598 |
| C1—C6 | 1.449 (2) | O1W—H1W1 | 0.833 (10) |
| C2—C3 | 1.373 (2) | O1W—H1W2 | 0.842 (10) |
| C3—C4 | 1.377 (3) | O2W—H2W1 | 0.847 (10) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | O2W—H2W2 | 0.846 (10) |
| C4—C5 | 1.382 (3) | ||
| O2—N1—O3 | 120.56 (17) | C6—C5—C4 | 118.62 (16) |
| O2—N1—C2 | 120.41 (17) | C6—C5—H5 | 120.7 |
| O3—N1—C2 | 118.99 (15) | C4—C5—H5 | 120.7 |
| O5—N2—O4 | 122.85 (18) | C5—C6—C1 | 124.98 (17) |
| O5—N2—C4 | 118.51 (19) | C5—C6—N3 | 116.01 (16) |
| O4—N2—C4 | 118.63 (17) | C1—C6—N3 | 119.00 (15) |
| O6—N3—O7 | 123.42 (18) | C7—N4—H41 | 107 (2) |
| O6—N3—C6 | 117.55 (16) | C7—N4—H42 | 110.7 (14) |
| O7—N3—C6 | 118.99 (17) | H41—N4—H42 | 111 (2) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 124.93 (16) | C8—N5—H51 | 108.3 (19) |
| O1—C1—C6 | 123.89 (17) | C8—N5—H52 | 110.3 (13) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 111.18 (14) | H51—N5—H52 | 107.7 (17) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 124.54 (15) | N4—C7—C8 | 109.5 (2) |
| C3—C2—N1 | 115.98 (16) | N4—C7—H7 | 109.8 |
| C1—C2—N1 | 119.48 (14) | C8—C7—H7 | 109.7 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.21 (17) | N5—C8—C7 | 111.1 (2) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.4 | N5—C8—H8 | 109.4 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.4 | C7—C8—H8 | 109.4 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.40 (15) | H1W1—O1W—H1W2 | 108.3 (18) |
| C3—C4—N2 | 119.49 (18) | H2W1—O2W—H2W2 | 106.5 (17) |
| C5—C4—N2 | 119.12 (16) | ||
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | 177.84 (17) | O4—N2—C4—C5 | 176.88 (18) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −2.6 (2) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −2.0 (3) |
| O1—C1—C2—N1 | −2.2 (3) | N2—C4—C5—C6 | 178.14 (15) |
| C6—C1—C2—N1 | 177.34 (15) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | 1.6 (3) |
| O2—N1—C2—C3 | 158.7 (2) | C4—C5—C6—N3 | −179.11 (16) |
| O3—N1—C2—C3 | −19.0 (3) | O1—C1—C6—C5 | −179.87 (17) |
| O2—N1—C2—C1 | −21.3 (3) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.6 (2) |
| O3—N1—C2—C1 | 161.01 (18) | O1—C1—C6—N3 | 0.9 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 2.4 (3) | C2—C1—C6—N3 | −178.70 (15) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | −177.56 (15) | O6—N3—C6—C5 | −37.8 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.1 (3) | O7—N3—C6—C5 | 140.02 (18) |
| C2—C3—C4—N2 | 179.96 (16) | O6—N3—C6—C1 | 141.56 (16) |
| O5—N2—C4—C3 | 175.99 (18) | O7—N3—C6—C1 | −40.6 (2) |
| O4—N2—C4—C3 | −3.0 (3) | N4—C7—C8—N5 | 180.0 |
| O5—N2—C4—C5 | −4.1 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N4—H41···O2Wi | 0.87 (1) | 2.06 (2) | 2.872 (4) | 156 (3) |
| N4—H42···O1 | 0.86 (1) | 1.98 (1) | 2.815 (2) | 164 (2) |
| N4—H42···O7 | 0.86 (1) | 2.41 (2) | 2.9166 (16) | 118.(2) |
| N5—H51···O1Wii | 0.87 (1) | 1.91 (1) | 2.778 (3) | 176 (3) |
| N5—H52···O1iii | 0.86 (1) | 2.18 (2) | 2.892 (2) | 140.(2) |
| N5—H52···O2iii | 0.86 (1) | 2.34 (2) | 3.018 (3) | 136.(2) |
| C3—H3···O6iv | 0.93 | 2.53 | 3.337 (3) | 145 |
| C7—H7···O2v | 0.96 | 2.39 | 3.128 (3) | 134 |
| C7—H7···O7vi | 0.96 | 2.56 | 3.1203 (19) | 117 |
| O1W—H1W2···O3 | 0.84 (1) | 2.21 (3) | 3.008 (2) | 159 (6) |
| O1W—H1W2···O2 | 0.84 (1) | 2.52 (4) | 3.243 (3) | 145 (5) |
| O2W—H2W2···O5 | 0.85 (1) | 2.26 (2) | 3.082 (2) | 163 (7) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z; (ii) x−1/2, y, −z+3/2; (iii) x−1/2, y, −z+1/2; (iv) x, y, z+1; (v) x−1/2, −y+3/2, −z+1/2; (vi) x, −y+3/2, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: OM2399).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Allen, F. H., Johnson, O., Shields, G. P., Smith, B. R. & Towler, M. (2004). J. Appl. Cryst. 37, 335–338.
- Harrison, W. T. A., Bindya, S., Ashok, M. A., Yathirajan, H. S. & Narayana, B. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o3143.
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 453–457.
- Muthamizhchelvan, C., Saminathan, K., SethuSankar, K., Fraanje, J., Peschar, R. & Sivakumar, K. (2005a). Acta Cryst. E61, o1546–o1548.
- Muthamizhchelvan, C., Saminathan, K., SethuSankar, K., Fraanje, J., Peschar, R. & Sivakumar, K. (2005b). Acta Cryst. E61, o2887–o2890.
- Muthamizhchelvan, C., Saminathan, K., SethuSankar, K., Fraanje, J., Peschar, R. & Sivakumar, K. (2005c). Acta Cryst. E61, o2987–o2989.
- Narayana, B., Sarojini, B. K., Prakash Kamath, K., Yathirajan, H. S. & Bolte, M. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o117–o118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Oxford Diffraction (2007). CrysAlis PRO and CrysAlis RED Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Abingdon, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Subashini, A., Muthiah, P. T., Bocelli, G. & Cantoni, A. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o3847–o3849.
- Swamy, M. T., Ashok, M. A., Yathirajan, H. S., Narayana, B. & Bolte, M. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o4919.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811004855/om2399sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811004855/om2399Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report