Abstract
In the title compound, C23H22ClN3O, the benzene ring of the 4-chorobenzyl group makes a dihedral angle of 78.56 (6)° with the best plane of the indole ring. The double bond connecting the azabicyclic and indole groups adopts a Z geometry. The geometry adopted by the C=N bond with respect to the N—OH bond is trans. The absolute configuration of the compound was determined from refinement of the Flack parameter.
Related literature
For 2-indol-3-yl-methylenequinuclidin-3-ols and NADPH oxidase activity, see: Sekhar et al. (2003 ▶) and for novel substituted (Z)-2-(N-benzylindol-3-ylmethylene)quinuclidin-3-one and (Z)-(±)-2-(N-benzylindol-3-ylmethylene)quinuclidin-3-ol derivatives as potent thermal sensitizing agents, see: Sonar et al. (2007 ▶). For di- and triindolylmethanes: molecular structures, see: Mason et al. (2003 ▶) and for structures of 1H-indole-3-ethylene-3′-methoxysalicylaldimine and 3-[3′-azapentyl-3′-en-4′-(2′′-hydroxyphenyl)]indole, see: Zarza et al. (1988 ▶). For the radio-sensitization activity associated with N-benzylindolyl-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-ones, see: Sonar et al. (2003 ▶).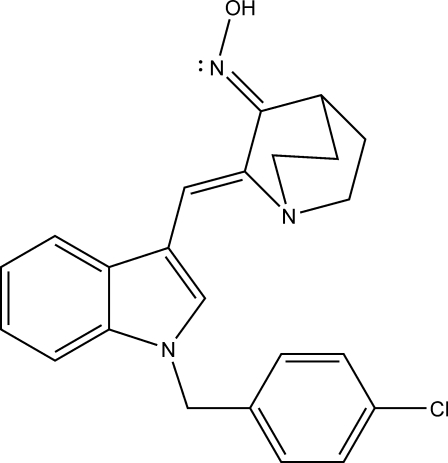
Experimental
Crystal data
C23H22ClN3O
M r = 391.89
Orthorhombic,
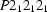
a = 5.8382 (1) Å
b = 10.7005 (2) Å
c = 30.9451 (6) Å
V = 1933.19 (6) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.22 mm−1
T = 90 K
0.40 × 0.12 × 0.08 mm
Data collection
Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SCALEPACK; Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶) T min = 0.918, T max = 0.983
37270 measured reflections
4433 independent reflections
3150 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.103
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.049
wR(F 2) = 0.137
S = 1.06
4433 reflections
254 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.40 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.24 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 1853 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: −0.03 (4)
Data collection: COLLECT (Nonius, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: SCALEPACK (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); data reduction: DENZO-SMN (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: XP in SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and local procedures.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681100612X/fj2375sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681100612X/fj2375Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the NCI/NIH for their financial support under grant No. CA 140409.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
In view of the radio-sensitization activity associated with N-benzylindolyl-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-ones (Sonar et al., 2007), we have undertaken the synthesis and structural analysis of a series of (2Z,3E)-2-((1-benzyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methylene) quinuclidin-3-one oximes. Systematic structural modification of the active molecule (Z)-2-(1-benzyl-1H-indol-3-ylmethylene)1- azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-ol, was carried out, and the title compound was synthesized as its structural analogue. The X-ray analysis of the title compound was carried out to confirm the double-bond geometry of the molecule, and to determine the molecular conformation in the crystal structure.
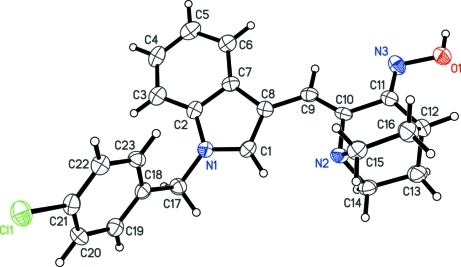
X-ray crystallography confirmed the molecular structure and atom connectivity for title compound, as illustrated in Fig. 1. The indole ring is planar, with bond distances and angles comparable with those previously reported for other indole derivatives (Mason et al.., 2003; Zarza et al.., 1988). The benzene ring of the benzyl group linked to the N1 position of the indole ring is slightly twisted, making a dihedral angle of 78.56 (6)° with the plane of the indole ring system.
The title compound is the Z isomer, with the C10—C11 bond in a trans disposition with respect to the C8—C9 bond. The double bond has a nearly planar arrangement, since the r.m.s. deviation from the best plane passing through atoms N2/C10/ C11/C9/C8 is 0.0143 (15) Å. The azabicyclic system presents very small distortions around atoms N2, C14, C13, C12, C16 and C11. The value of the C1=C8—C9=C10 torsion angle -13.87° indicates the deviation of the indole ring from the plane of the double bond connected to the azabicyclic ring.
Experimental
Compound 2-((1-(4-chlorobenzyl)-1H-indol-3-yl)methylene) quinuclidin-3-one was prepared by aldol condensation of 1-(4-chlorobenzyl-indole-3-carboxaldehyde with 1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan- 3-one to afford (Z)-2-(1-(4-chlorobenzyl-1H-indol-3-yl methylene)-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-one, as a single geometric isomer, according to the previously reported procedure of Sonar et al. (2003). A mixture (Z)-2-(1-(4-chlorobenzyl-1H-indol-3-yl methylene)1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-one (0.5 g, 1.32 mmol), hydroxylamine hydrocloride (0.18 g, 2.65 mmol) and sodium acetate trihydrate (0.36 g, 2.65 mmol) was stirred in methanol (25 ml) under reflux for 8 hrs. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, diluted with water (15 ml), and the light yellow solid that separated was collected by filtration, washed with water and dried, to afford the the crude product. Crystallization from methanol gave a colorless crystalline product of (2Z,3E)-2- ((1-(4-chlorobenzyl)-1H-indol-3-yl)methylene) quinuclidin-3-one oxime that was suitable for X-ray analysis. 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ 1.76–1.79 (m, 4H), 2.91–3.09 (m, 4H), 3.67–3.69 (m, 1H), 5.34 (s, 2H), 7.01–7.04 (d, 2H), 7.10 (s, 1H), 7.14–7.25 (m, 5H), 7.30 (bs, 1H), 7.79–7.83 (d, 1H), 8.21 (s, 1H) p.p.m.; 13C NMR (DMSO d6): δ 24.46, 25.87, 47.77, 50.06, 109.92, 110.45, 111.47, 119.34, 120.34, 122.39, 128.05, 128.63, 129.09, 131.27, 133.54, 135.80, 135.98, 138.23, 161.31 p.p.m..
Refinement
H atoms were found in difference Fourier maps and subsequently placed in idealized positions with constrained distances of 0.99 Å (R2CH2), 1.00 Å (R3CH), 0.95 Å (CArH), 0.84 Å (O—H), and with Uiso(H) values set to either 1.2Ueq or 1.5Ueq (OH) of the attached atom.
Figures
Fig. 1.
A view of the molecule with the atom numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Crystal data
| C23H22ClN3O | F(000) = 824 |
| Mr = 391.89 | Dx = 1.346 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 2610 reflections |
| a = 5.8382 (1) Å | θ = 1.0–27.5° |
| b = 10.7005 (2) Å | µ = 0.22 mm−1 |
| c = 30.9451 (6) Å | T = 90 K |
| V = 1933.19 (6) Å3 | Plate, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.40 × 0.12 × 0.08 mm |
Data collection
| Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer | 4433 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3150 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.103 |
| Detector resolution: 9.1 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 1.3° |
| ω scans at fixed χ = 55° | h = −7→7 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SCALEPACK; Otwinowski & Minor, 1997) | k = −13→13 |
| Tmin = 0.918, Tmax = 0.983 | l = −39→40 |
| 37270 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.049 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.137 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0788P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.06 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 4433 reflections | Δρmax = 0.40 e Å−3 |
| 254 parameters | Δρmin = −0.24 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 1853 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: −0.03 (4) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.1498 (4) | 0.0866 (2) | 0.89083 (7) | 0.0245 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.0660 (4) | 0.1260 (2) | 0.75130 (7) | 0.0265 (5) | |
| N3 | 0.3789 (4) | 0.4000 (2) | 0.71465 (7) | 0.0311 (6) | |
| O1 | 0.3831 (4) | 0.45515 (18) | 0.67293 (6) | 0.0327 (5) | |
| H1O | 0.4731 | 0.5164 | 0.6730 | 0.049* | |
| Cl1 | 0.28052 (15) | −0.51575 (6) | 0.95786 (2) | 0.0408 (2) | |
| C1 | 0.1254 (5) | 0.1143 (3) | 0.84757 (8) | 0.0263 (6) | |
| H1 | 0.0091 | 0.0816 | 0.8293 | 0.032* | |
| C2 | 0.3379 (5) | 0.1501 (2) | 0.90706 (9) | 0.0257 (6) | |
| C3 | 0.4304 (5) | 0.1521 (2) | 0.94836 (9) | 0.0313 (7) | |
| H3 | 0.3656 | 0.1040 | 0.9711 | 0.038* | |
| C4 | 0.6191 (5) | 0.2263 (3) | 0.95518 (10) | 0.0338 (7) | |
| H4 | 0.6823 | 0.2314 | 0.9834 | 0.041* | |
| C5 | 0.7198 (5) | 0.2941 (2) | 0.92199 (9) | 0.0357 (7) | |
| H5 | 0.8529 | 0.3425 | 0.9276 | 0.043* | |
| C6 | 0.6283 (5) | 0.2917 (2) | 0.88076 (9) | 0.0303 (7) | |
| H6 | 0.6975 | 0.3385 | 0.8582 | 0.036* | |
| C7 | 0.4340 (5) | 0.2203 (2) | 0.87271 (9) | 0.0252 (6) | |
| C8 | 0.2938 (5) | 0.1964 (2) | 0.83457 (8) | 0.0241 (6) | |
| C9 | 0.3253 (5) | 0.2570 (2) | 0.79299 (9) | 0.0249 (6) | |
| H9 | 0.4310 | 0.3245 | 0.7925 | 0.030* | |
| C10 | 0.2250 (5) | 0.2300 (2) | 0.75544 (8) | 0.0232 (6) | |
| C11 | 0.2554 (5) | 0.2987 (2) | 0.71447 (8) | 0.0254 (6) | |
| C12 | 0.1228 (5) | 0.2401 (3) | 0.67821 (9) | 0.0307 (7) | |
| H12 | 0.1483 | 0.2857 | 0.6504 | 0.037* | |
| C13 | −0.1316 (5) | 0.2419 (3) | 0.69126 (10) | 0.0371 (7) | |
| H13A | −0.2244 | 0.1972 | 0.6694 | 0.044* | |
| H13B | −0.1872 | 0.3292 | 0.6931 | 0.044* | |
| C14 | −0.1551 (5) | 0.1767 (3) | 0.73590 (9) | 0.0306 (7) | |
| H14A | −0.2140 | 0.2376 | 0.7573 | 0.037* | |
| H14B | −0.2677 | 0.1078 | 0.7336 | 0.037* | |
| C15 | 0.1538 (5) | 0.0380 (2) | 0.71842 (8) | 0.0297 (7) | |
| H15A | 0.0415 | −0.0303 | 0.7143 | 0.036* | |
| H15B | 0.2984 | 0.0004 | 0.7289 | 0.036* | |
| C16 | 0.1976 (6) | 0.1027 (3) | 0.67474 (9) | 0.0355 (7) | |
| H16A | 0.3624 | 0.0980 | 0.6674 | 0.043* | |
| H16B | 0.1096 | 0.0603 | 0.6517 | 0.043* | |
| C17 | −0.0065 (5) | 0.0109 (2) | 0.91598 (9) | 0.0283 (6) | |
| H17A | −0.1531 | 0.0046 | 0.9001 | 0.034* | |
| H17B | −0.0380 | 0.0546 | 0.9435 | 0.034* | |
| C18 | 0.0755 (5) | −0.1200 (3) | 0.92624 (8) | 0.0256 (6) | |
| C19 | −0.0692 (5) | −0.1968 (3) | 0.95003 (8) | 0.0289 (6) | |
| H19 | −0.2120 | −0.1649 | 0.9597 | 0.035* | |
| C20 | −0.0099 (5) | −0.3190 (2) | 0.95994 (9) | 0.0295 (6) | |
| H20 | −0.1105 | −0.3710 | 0.9760 | 0.035* | |
| C21 | 0.1993 (5) | −0.3631 (2) | 0.94579 (9) | 0.0291 (7) | |
| C22 | 0.3478 (5) | −0.2890 (2) | 0.92239 (8) | 0.0292 (7) | |
| H22 | 0.4916 | −0.3209 | 0.9131 | 0.035* | |
| C23 | 0.2838 (5) | −0.1665 (2) | 0.91249 (8) | 0.0263 (6) | |
| H23 | 0.3841 | −0.1148 | 0.8962 | 0.032* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0254 (13) | 0.0248 (12) | 0.0232 (12) | 0.0017 (10) | 0.0011 (10) | −0.0014 (9) |
| N2 | 0.0248 (13) | 0.0252 (12) | 0.0297 (13) | −0.0052 (11) | 0.0008 (11) | 0.0003 (10) |
| N3 | 0.0348 (15) | 0.0266 (12) | 0.0321 (13) | 0.0075 (11) | 0.0085 (12) | 0.0067 (10) |
| O1 | 0.0341 (13) | 0.0300 (11) | 0.0340 (11) | −0.0025 (9) | 0.0030 (9) | 0.0037 (8) |
| Cl1 | 0.0491 (5) | 0.0268 (4) | 0.0464 (4) | 0.0042 (4) | 0.0006 (4) | 0.0036 (3) |
| C1 | 0.0252 (15) | 0.0261 (13) | 0.0277 (15) | 0.0036 (12) | −0.0044 (12) | −0.0025 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0287 (17) | 0.0232 (14) | 0.0252 (14) | 0.0076 (12) | −0.0020 (12) | −0.0046 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0337 (17) | 0.0270 (15) | 0.0332 (17) | 0.0081 (13) | −0.0022 (14) | −0.0056 (12) |
| C4 | 0.0417 (19) | 0.0278 (14) | 0.0318 (16) | 0.0108 (14) | −0.0103 (15) | −0.0074 (13) |
| C5 | 0.0348 (18) | 0.0264 (14) | 0.0460 (18) | 0.0022 (14) | −0.0096 (15) | −0.0120 (13) |
| C6 | 0.0320 (17) | 0.0222 (14) | 0.0367 (17) | 0.0010 (13) | −0.0031 (14) | −0.0031 (12) |
| C7 | 0.0217 (15) | 0.0228 (14) | 0.0311 (15) | 0.0027 (12) | 0.0008 (12) | −0.0048 (12) |
| C8 | 0.0264 (15) | 0.0173 (12) | 0.0287 (14) | 0.0014 (12) | 0.0010 (12) | −0.0016 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0198 (14) | 0.0208 (12) | 0.0342 (15) | 0.0015 (12) | 0.0011 (12) | 0.0005 (11) |
| C10 | 0.0175 (14) | 0.0199 (12) | 0.0323 (15) | −0.0013 (12) | 0.0050 (12) | 0.0021 (11) |
| C11 | 0.0221 (15) | 0.0217 (13) | 0.0325 (15) | 0.0015 (12) | 0.0029 (13) | 0.0031 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0309 (17) | 0.0337 (16) | 0.0275 (16) | −0.0038 (14) | 0.0004 (13) | 0.0065 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0264 (17) | 0.0386 (17) | 0.0462 (18) | −0.0001 (14) | −0.0041 (15) | 0.0116 (14) |
| C14 | 0.0216 (16) | 0.0336 (15) | 0.0368 (17) | −0.0003 (13) | −0.0009 (13) | 0.0009 (13) |
| C15 | 0.0326 (17) | 0.0222 (13) | 0.0342 (16) | −0.0013 (13) | −0.0030 (13) | −0.0045 (12) |
| C16 | 0.0412 (19) | 0.0346 (16) | 0.0306 (16) | −0.0054 (15) | 0.0029 (14) | −0.0057 (13) |
| C17 | 0.0265 (16) | 0.0286 (15) | 0.0298 (15) | 0.0020 (13) | 0.0035 (12) | 0.0011 (12) |
| C18 | 0.0261 (15) | 0.0285 (14) | 0.0224 (14) | 0.0010 (13) | −0.0023 (12) | −0.0018 (11) |
| C19 | 0.0289 (16) | 0.0324 (15) | 0.0254 (15) | 0.0032 (13) | 0.0012 (13) | −0.0002 (12) |
| C20 | 0.0311 (17) | 0.0284 (14) | 0.0288 (15) | −0.0034 (13) | 0.0066 (13) | 0.0033 (13) |
| C21 | 0.0377 (18) | 0.0229 (13) | 0.0268 (14) | 0.0035 (13) | −0.0051 (13) | −0.0020 (11) |
| C22 | 0.0308 (17) | 0.0297 (15) | 0.0270 (15) | 0.0041 (13) | −0.0003 (13) | −0.0038 (12) |
| C23 | 0.0255 (16) | 0.0289 (14) | 0.0247 (14) | −0.0023 (13) | 0.0022 (13) | −0.0009 (11) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| N1—C1 | 1.379 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.500 (4) |
| N1—C2 | 1.385 (4) | C12—C16 | 1.538 (4) |
| N1—C17 | 1.448 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.539 (4) |
| N2—C10 | 1.455 (3) | C12—H12 | 1.0000 |
| N2—C15 | 1.479 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.554 (4) |
| N2—C14 | 1.479 (4) | C13—H13A | 0.9900 |
| N3—C11 | 1.302 (4) | C13—H13B | 0.9900 |
| N3—O1 | 1.420 (3) | C14—H14A | 0.9900 |
| O1—H1O | 0.8400 | C14—H14B | 0.9900 |
| Cl1—C21 | 1.741 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.540 (4) |
| C1—C8 | 1.378 (4) | C15—H15A | 0.9900 |
| C1—H1 | 0.9500 | C15—H15B | 0.9900 |
| C2—C3 | 1.387 (4) | C16—H16A | 0.9900 |
| C2—C7 | 1.418 (4) | C16—H16B | 0.9900 |
| C3—C4 | 1.374 (4) | C17—C18 | 1.514 (4) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C17—H17A | 0.9900 |
| C4—C5 | 1.388 (4) | C17—H17B | 0.9900 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C18—C23 | 1.381 (4) |
| C5—C6 | 1.383 (4) | C18—C19 | 1.389 (4) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C19—C20 | 1.387 (4) |
| C6—C7 | 1.390 (4) | C19—H19 | 0.9500 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C20—C21 | 1.380 (4) |
| C7—C8 | 1.459 (4) | C20—H20 | 0.9500 |
| C8—C9 | 1.453 (4) | C21—C22 | 1.381 (4) |
| C9—C10 | 1.333 (3) | C22—C23 | 1.397 (4) |
| C9—H9 | 0.9500 | C22—H22 | 0.9500 |
| C10—C11 | 1.476 (3) | C23—H23 | 0.9500 |
| C1—N1—C2 | 109.2 (2) | C12—C13—H13A | 110.1 |
| C1—N1—C17 | 125.3 (2) | C14—C13—H13A | 110.1 |
| C2—N1—C17 | 125.4 (2) | C12—C13—H13B | 110.1 |
| C10—N2—C15 | 109.1 (2) | C14—C13—H13B | 110.1 |
| C10—N2—C14 | 107.7 (2) | H13A—C13—H13B | 108.4 |
| C15—N2—C14 | 108.3 (2) | N2—C14—C13 | 112.0 (2) |
| C11—N3—O1 | 110.6 (2) | N2—C14—H14A | 109.2 |
| N3—O1—H1O | 109.5 | C13—C14—H14A | 109.2 |
| C8—C1—N1 | 110.3 (2) | N2—C14—H14B | 109.2 |
| C8—C1—H1 | 124.9 | C13—C14—H14B | 109.2 |
| N1—C1—H1 | 124.9 | H14A—C14—H14B | 107.9 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 130.6 (3) | N2—C15—C16 | 112.0 (2) |
| N1—C2—C7 | 107.6 (2) | N2—C15—H15A | 109.2 |
| C3—C2—C7 | 121.9 (3) | C16—C15—H15A | 109.2 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 117.6 (3) | N2—C15—H15B | 109.2 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 121.2 | C16—C15—H15B | 109.2 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 121.2 | H15A—C15—H15B | 107.9 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.8 (3) | C12—C16—C15 | 108.8 (2) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.1 | C12—C16—H16A | 109.9 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.1 | C15—C16—H16A | 109.9 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.6 (3) | C12—C16—H16B | 109.9 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.7 | C15—C16—H16B | 109.9 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.7 | H16A—C16—H16B | 108.3 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 119.4 (3) | N1—C17—C18 | 115.6 (2) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.3 | N1—C17—H17A | 108.4 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 120.3 | C18—C17—H17A | 108.4 |
| C6—C7—C2 | 118.7 (3) | N1—C17—H17B | 108.4 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 134.4 (3) | C18—C17—H17B | 108.4 |
| C2—C7—C8 | 106.9 (2) | H17A—C17—H17B | 107.4 |
| C1—C8—C9 | 129.3 (3) | C23—C18—C19 | 119.0 (3) |
| C1—C8—C7 | 106.0 (2) | C23—C18—C17 | 123.2 (3) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 124.5 (2) | C19—C18—C17 | 117.8 (3) |
| C10—C9—C8 | 128.3 (3) | C20—C19—C18 | 121.5 (3) |
| C10—C9—H9 | 115.9 | C20—C19—H19 | 119.2 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 115.9 | C18—C19—H19 | 119.2 |
| C9—C10—N2 | 121.5 (2) | C21—C20—C19 | 118.2 (3) |
| C9—C10—C11 | 126.0 (2) | C21—C20—H20 | 120.9 |
| N2—C10—C11 | 112.5 (2) | C19—C20—H20 | 120.9 |
| N3—C11—C10 | 118.5 (2) | C20—C21—C22 | 121.7 (3) |
| N3—C11—C12 | 129.5 (2) | C20—C21—Cl1 | 119.6 (2) |
| C10—C11—C12 | 111.9 (2) | C22—C21—Cl1 | 118.7 (2) |
| C11—C12—C16 | 107.8 (2) | C21—C22—C23 | 119.0 (3) |
| C11—C12—C13 | 107.3 (2) | C21—C22—H22 | 120.5 |
| C16—C12—C13 | 107.7 (3) | C23—C22—H22 | 120.5 |
| C11—C12—H12 | 111.3 | C18—C23—C22 | 120.4 (3) |
| C16—C12—H12 | 111.3 | C18—C23—H23 | 119.8 |
| C13—C12—H12 | 111.3 | C22—C23—H23 | 119.8 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 108.2 (2) | ||
| C2—N1—C1—C8 | −0.5 (3) | C9—C10—C11—N3 | −4.8 (4) |
| C17—N1—C1—C8 | 175.3 (2) | N2—C10—C11—N3 | 174.5 (2) |
| C1—N1—C2—C3 | −180.0 (3) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 178.1 (3) |
| C17—N1—C2—C3 | 4.3 (4) | N2—C10—C11—C12 | −2.7 (3) |
| C1—N1—C2—C7 | 0.2 (3) | N3—C11—C12—C16 | 127.3 (3) |
| C17—N1—C2—C7 | −175.5 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C16 | −55.9 (3) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | −179.1 (3) | N3—C11—C12—C13 | −117.0 (3) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | 0.7 (4) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 59.8 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −2.1 (4) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −54.6 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.9 (4) | C16—C12—C13—C14 | 61.1 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −0.2 (4) | C10—N2—C14—C13 | 60.5 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—C2 | −1.1 (4) | C15—N2—C14—C13 | −57.4 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 179.7 (3) | C12—C13—C14—N2 | −3.5 (4) |
| N1—C2—C7—C6 | −179.3 (2) | C10—N2—C15—C16 | −55.6 (3) |
| C3—C2—C7—C6 | 0.9 (4) | C14—N2—C15—C16 | 61.4 (3) |
| N1—C2—C7—C8 | 0.1 (3) | C11—C12—C16—C15 | 57.8 (3) |
| C3—C2—C7—C8 | −179.7 (2) | C13—C12—C16—C15 | −57.6 (3) |
| N1—C1—C8—C9 | −175.4 (2) | N2—C15—C16—C12 | −3.0 (3) |
| N1—C1—C8—C7 | 0.5 (3) | C1—N1—C17—C18 | 104.6 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—C1 | 178.9 (3) | C2—N1—C17—C18 | −80.3 (3) |
| C2—C7—C8—C1 | −0.4 (3) | N1—C17—C18—C23 | −0.6 (4) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −5.0 (5) | N1—C17—C18—C19 | −179.5 (2) |
| C2—C7—C8—C9 | 175.8 (2) | C23—C18—C19—C20 | −0.5 (4) |
| C1—C8—C9—C10 | −13.9 (5) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | 178.4 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 170.9 (3) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | 0.5 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—N2 | −2.2 (4) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | 0.0 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 176.9 (3) | C19—C20—C21—Cl1 | 179.6 (2) |
| C15—N2—C10—C9 | −121.0 (3) | C20—C21—C22—C23 | −0.5 (4) |
| C14—N2—C10—C9 | 121.6 (3) | Cl1—C21—C22—C23 | 179.9 (2) |
| C15—N2—C10—C11 | 59.7 (3) | C19—C18—C23—C22 | 0.0 (4) |
| C14—N2—C10—C11 | −57.7 (3) | C17—C18—C23—C22 | −178.9 (3) |
| O1—N3—C11—C10 | −178.2 (2) | C21—C22—C23—C18 | 0.5 (4) |
| O1—N3—C11—C12 | −1.6 (4) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: FJ2375).
References
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Mason, M. R., Barnard, T. S., Segla, M. F., Xie, B. & Kirschbaum, K. (2003). J. Chem. Crystallogr. 33, 531–540.
- Nonius (1998). COLLECT Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Sekhar, K. R., Crooks, P. A., Sonar, V. N., Friedman, D. B., Chan, J. Y., Meredith, M. J., Stames, J. H., Kelton, K. R., Summar, S. R., Sasi, S. & Freeman, M. L. (2003). Cancer Res. 63, 5636–5645. [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sonar, V. N., Parkin, S. & Crooks, P. A. (2003). Acta Cryst. E59, o1478–o1480. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sonar, V. N., Reddy, Y. T., Sekhar, K. R., Sowmya, S., Freeman, M. L. & Crooks, P. A. (2007). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 17, 6821–6824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zarza, P. M., Gill, P., Díaz González, M. C., Martin Reyes, M. G., Arrieta, J. M., Nastopoulos, V., Germain, G. & Debaerdemaeker, T. (1988). Acta Cryst. C44, 678–681.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681100612X/fj2375sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681100612X/fj2375Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report