Abstract
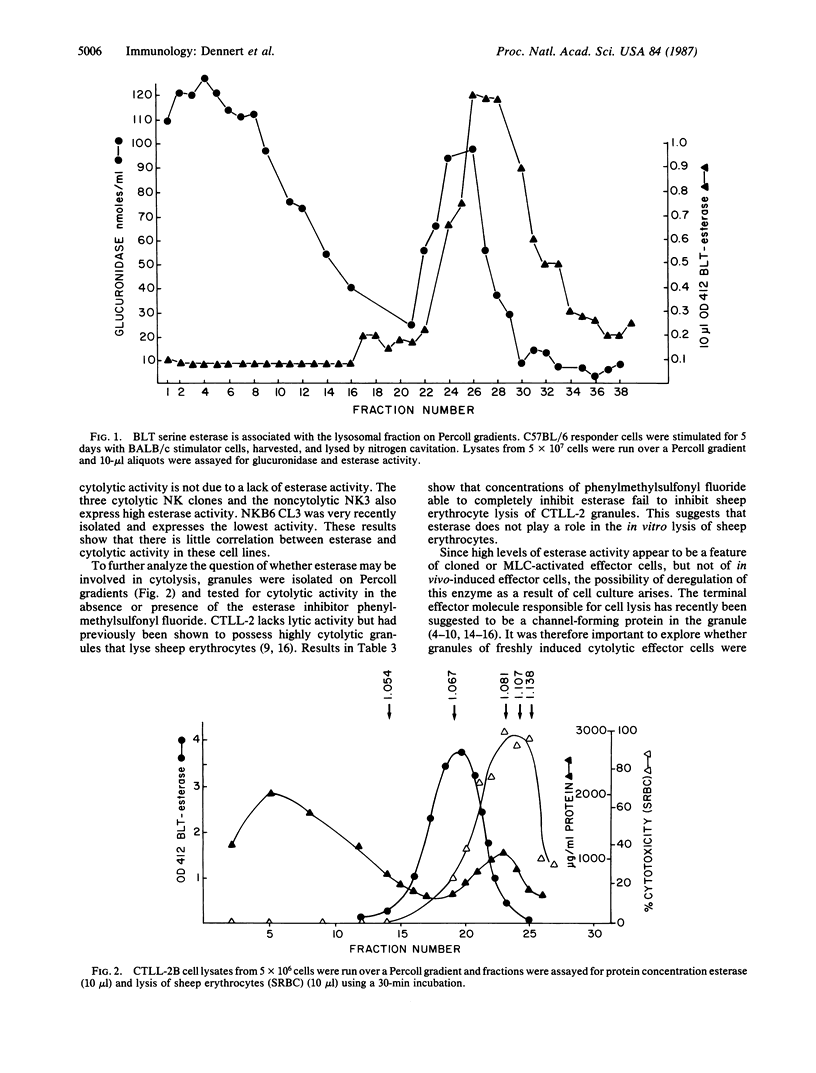
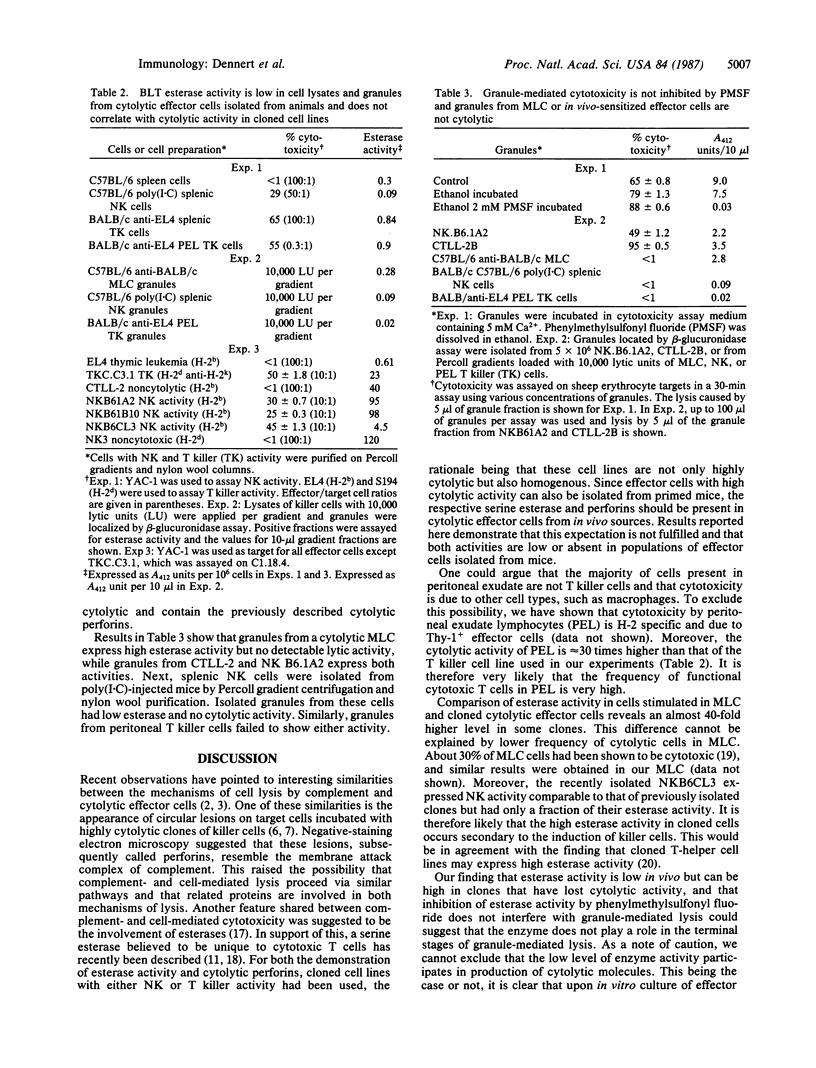
Recent observations have suggested striking similarities between complement-mediated and cell-mediated lysis. Both pathways share the terminal insertion of channels into target membranes, and unique esterases have been postulated to participate in the activation of cytolytic effector molecules. Since killer-specific esterases and channel-forming proteins can be demonstrated in in vitro cell lines, it is important to ascertain that the described esterase and channel-forming proteins are also present in killer cells from in vivo sources. Results presented here show that killer-cell-specific N alpha-benzyloxycarbonyl-L-lysine thiobenzyl ester serine esterase is induced in vitro concomitant with the sensitization of cytotoxic effector cells. In contrast, in-vivo-primed cytotoxic T cells or natural killer (NK) cells fail to express high levels of this enzyme. Assay of different cytotoxic effector cells reveals the presence of N alpha-benzyloxycarbonyl-L-lysine thiobenzyl ester serine esterase in clones with T killer and NK activity, but enzyme levels do not correlate with cytolytic activity nor does inhibition of esterase activity interfere with granule-mediated cell lysis. A similar result is seen with granule-mediated cytolytic activity. Cloned NK and T killer cell lines possess granules that are able to lyse erythrocyte targets. However, T killer cells sensitized in mixed lymphocyte culture or in vivo have no detectable cytotoxic granules. Cytotoxic granules are also not detected in NK cells isolated from animals.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumenthal R., Millard P. J., Henkart M. P., Reynolds C. W., Henkart P. A. Liposomes as targets for granule cytolysin from cytotoxic large granular lymphocyte tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5551–5555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criado M., Lindstrom J. M., Anderson C. G., Dennert G. Cytotoxic granules from killer cells: specificity of granules and insertion of channels of defined size into target membranes. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4245–4251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennert G. Cloned lines of natural killer cells. Nature. 1980 Sep 4;287(5777):47–49. doi: 10.1038/287047a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennert G., Podack E. R. Cytolysis by H-2-specific T killer cells. Assembly of tubular complexes on target membranes. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1483–1495. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennert G., Yogeeswaran G., Yamagata S. Cloned cell lines with natural killer activity. Specificity, function, and cell surface markers. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):545–556. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dourmashkin R. R., Deteix P., Simone C. B., Henkart P. Electron microscopic demonstration of lesions in target cell membranes associated with antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Dec;42(3):554–560. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E., Bonavida B. Mechanism of cell-mediated cytotoxicity at the single cell level. I. Estimation of cytotoxic T lymphocyte frequency and relative lytic efficiency. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2861–2869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A., Millard P. J., Reynolds C. W., Henkart M. P. Cytolytic activity of purified cytoplasmic granules from cytotoxic rat large granular lymphocyte tumors. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):75–93. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Mayer M. M. Specific cytolytic activity of lymphocytes: effect of antibodies against complement components C2, C3, and C5. Cell Immunol. 1971 Dec;2(6):702–705. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(71)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann Y., Berke G. Monoclonal cytotoxic T lymphocyte hybridomas capable of specific killing activity, antigenic responsiveness, and inducible interleukin secretion. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):50–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer M. D., Binninger L., Schirrmacher V., Moll H., Prester M., Nerz G., Simon M. M. Characterization and isolation of a trypsin-like serine protease from a long-term culture cytolytic T cell line and its expression by functionally distinct T cells. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4644–4651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupfer A., Singer S. J., Dennert G. On the mechanism of unidirectional killing in mixtures of two cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Unidirectional polarization of cytoplasmic organelles and the membrane-associated cytoskeleton in the effector cell. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):489–498. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Nabholz M., Estrade C., Tschopp J. Granules of cytolytic T-lymphocytes contain two serine esterases. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1595–1600. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04401.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Tschopp J. Isolation of a lytic, pore-forming protein (perforin) from cytolytic T-lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9069–9072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millard P. J., Henkart M. P., Reynolds C. W., Henkart P. A. Purification and properties of cytoplasmic granules from cytotoxic rat LGL tumors. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3197–3204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Eisen H. N. A novel serine esterase expressed by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. 1985 Apr 25-May 1Nature. 314(6013):743–745. doi: 10.1038/314743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Dennert G. Assembly of two types of tubules with putative cytolytic function by cloned natural killer cells. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):442–445. doi: 10.1038/302442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Konigsberg P. J. Cytolytic T cell granules. Isolation, structural, biochemical, and functional characterization. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):695–710. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid D. S., Tite J. P., Ruddle N. H. DNA fragmentation: manifestation of target cell destruction mediated by cytotoxic T-cell lines, lymphotoxin-secreting helper T-cell clones, and cell-free lymphotoxin-containing supernatant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1881–1885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundsmo J. S., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Neoantigen of the complement membrane attack complex of cytotoxic human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2371–2378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. C., Bonavida B. Selective lysis of NK-sensitive target cells by a soluble mediator released from murine spleen cells and human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1516–1521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



