Abstract
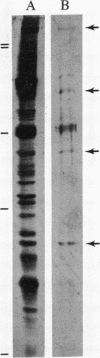
In skeletal muscle, dihydropyridine receptors and dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channels are preferentially localized in the transverse tubular membranes. Starting with an antigenic membrane fraction enriched in rabbit muscle transverse tubules (T-tubules), several monoclonal antibodies were produced by a fusion of spleen cells from an immunized BALB/c mouse with P3 X 63Ag.8.6.5.3 mouse myeloma cells. Antibodies were screened according to a scheme designed to select IgG immunoglobins that recognized a determinant specifically associated with the T-tubule membrane. Antibodies that fulfilled the screening criteria were used in in vitro planar bilayer recording of the activity of the dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channel present in T-tubules. Cells producing one antibody (Ab 21) survived cloning dilution and stably produced a monoclonal antibody (mAb21-4) that increased the rate of single channel opening when interacting with the internal side of the channel protein. mAb21-4 immobilized by covalent crosslinking on beads (Affi-Gel 10) consistently immunoprecipitated polypeptide bands with the following electrophoretic mobility: Mr values of greater than or equal to 175,000; 90,000; 55,000; and 34,000.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affolter H., Coronado R. Agonists Bay-K8644 and CGP-28392 open calcium channels reconstituted from skeletal muscle transverse tubules. Biophys J. 1985 Aug;48(2):341–347. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83789-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Affolter H., Coronado R. Sidedness of reconstituted calcium channels from muscle transverse tubules as determined by D600 and D890 blockade. Biophys J. 1986 Mar;49(3):767–771. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83703-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Fink R., Palade P. T. Calcium depletion in frog muscle tubules: the decline of calcium current under maintained depolarization. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:177–207. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsotto M., Barhanin J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. The 1,4-dihydropyridine receptor associated with the skeletal muscle voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel. Purification and subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14255–14263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. P., Lipshutz G. M., Denney G. H. Direct photoaffinity labeling of the high affinity nitrendipine-binding site in subcellular membrane fractions isolated from canine myocardium. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5384–5387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coronado R., Affolter H. Insulation of the conduction pathway of muscle transverse tubule calcium channels from the surface charge of bilayer phospholipid. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Jun;87(6):933–953. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.6.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Catterall W. A. Phosphorylation of the calcium antagonist receptor of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2528–2532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Catterall W. A. Purification of the calcium antagonist receptor of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel from skeletal muscle transverse tubules. Biochemistry. 1984 May 8;23(10):2113–2118. doi: 10.1021/bi00305a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Catterall W. A. Reconstitution of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel purified from skeletal muscle transverse tubules. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3077–3083. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flockerzi V., Oeken H. J., Hofmann F., Pelzer D., Cavalié A., Trautwein W. Purified dihydropyridine-binding site from skeletal muscle t-tubules is a functional calcium channel. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):66–68. doi: 10.1038/323066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosset M., Jaimovich E., Delpont E., Lazdunski M. [3H]nitrendipine receptors in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6086–6092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. R., Meissner G. Na+, K+, H+ and Cl- permeability properties of rabbit skeletal muscle sarcolemmal vesicles. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 May;223(1):9–23. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90566-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glossmann H., Ferry D. R., Boschek C. B. Purification of the putative calcium channel from skeletal muscle with the aid of [3H]-nimodipine binding. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;323(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00498821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne W. A., Weiland G. A., Oswald R. E. Solubilization and hydrodynamic characterization of the dihydropyridine receptor from rat ventricular muscle. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3588–3594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Tsien R. W. Mechanism of calcium channel blockade by verapamil, D600, diltiazem and nitrendipine in single dialysed heart cells. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):790–794. doi: 10.1038/302790a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malouf N. N., Meissner G. Localization of a Mg2+- or Ca2+-activated ("basic") ATPase in skeletal muscle. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Sep;122(2):233–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90301-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malouf N. N., Taylor S., Gillespie G. Y., Bynum J. M., Wilson P. E., Meissner G. Monoclonal antibody specific for the T-tubule of skeletal muscle. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986 Mar;34(3):347–355. doi: 10.1177/34.3.3950385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. W., Williams A. F. The kinetics of antibody binding to membrane antigens in solution and at the cell surface. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 1;187(1):1–20. doi: 10.1042/bj1870001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G. Adenine nucleotide stimulation of Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release in sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2365–2374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. L., Hess P., Reeves J. P., Smilowitz H., Tsien R. W. Calcium channels in planar lipid bilayers: insights into mechanisms of ion permeation and gating. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1564–1566. doi: 10.1126/science.2420007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez J. A., Stefani E. Inward calcium current in twitch muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:197–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid A., Barhanin J., Coppola T., Borsotto M., Lazdunski M. Immunochemical analysis of subunit structures of 1,4-dihydropyridine receptors associated with voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscles. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 17;25(12):3492–3495. doi: 10.1021/bi00360a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. M., McCleskey E. W., Almers W. Dihydropyridine receptors in muscle are voltage-dependent but most are not functional calcium channels. 1985 Apr 25-May 1Nature. 314(6013):747–751. doi: 10.1038/314747a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W. Calcium channels in excitable cell membranes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:341–358. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watters D., Maelicke A. Organization of ligand binding sites at the acetylcholine receptor: a study with monoclonal antibodies. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 12;22(8):1811–1819. doi: 10.1021/bi00277a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]