Abstract
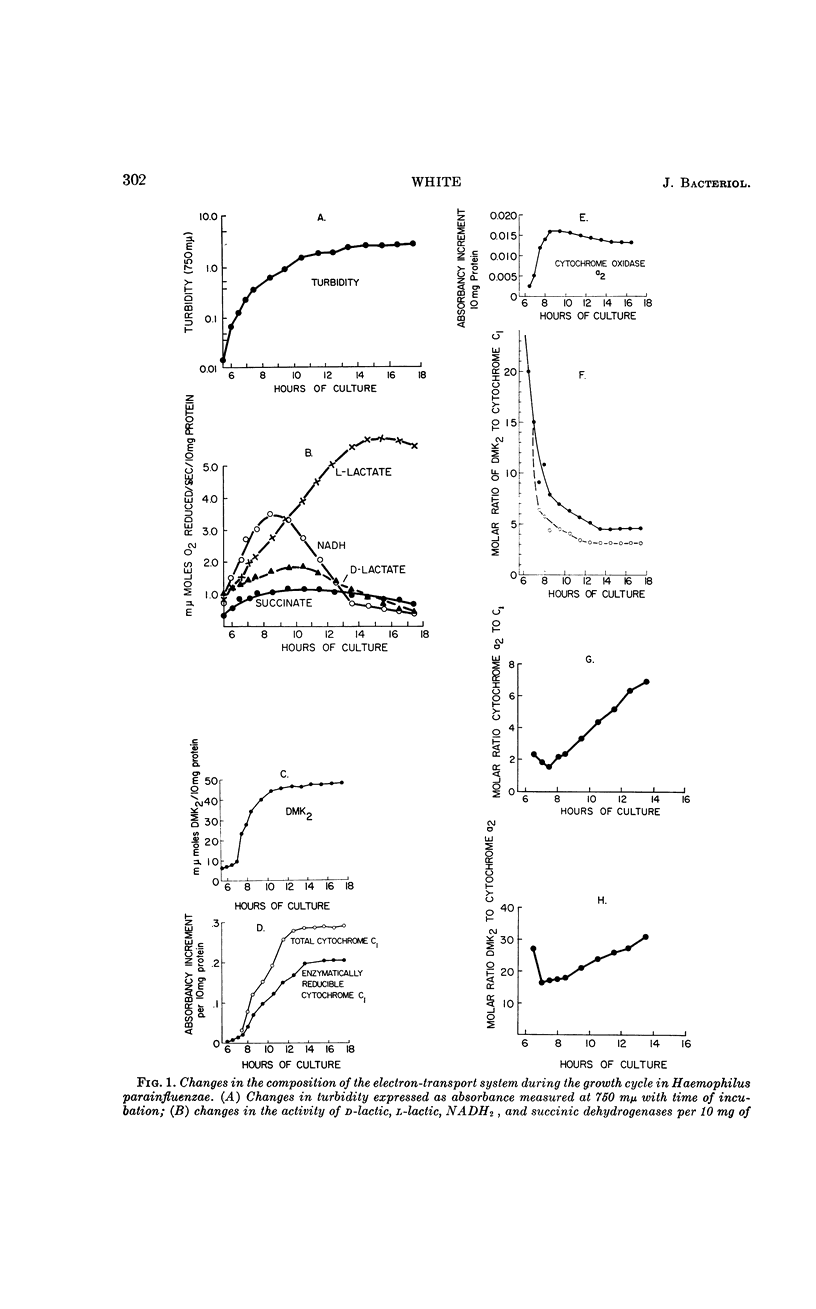
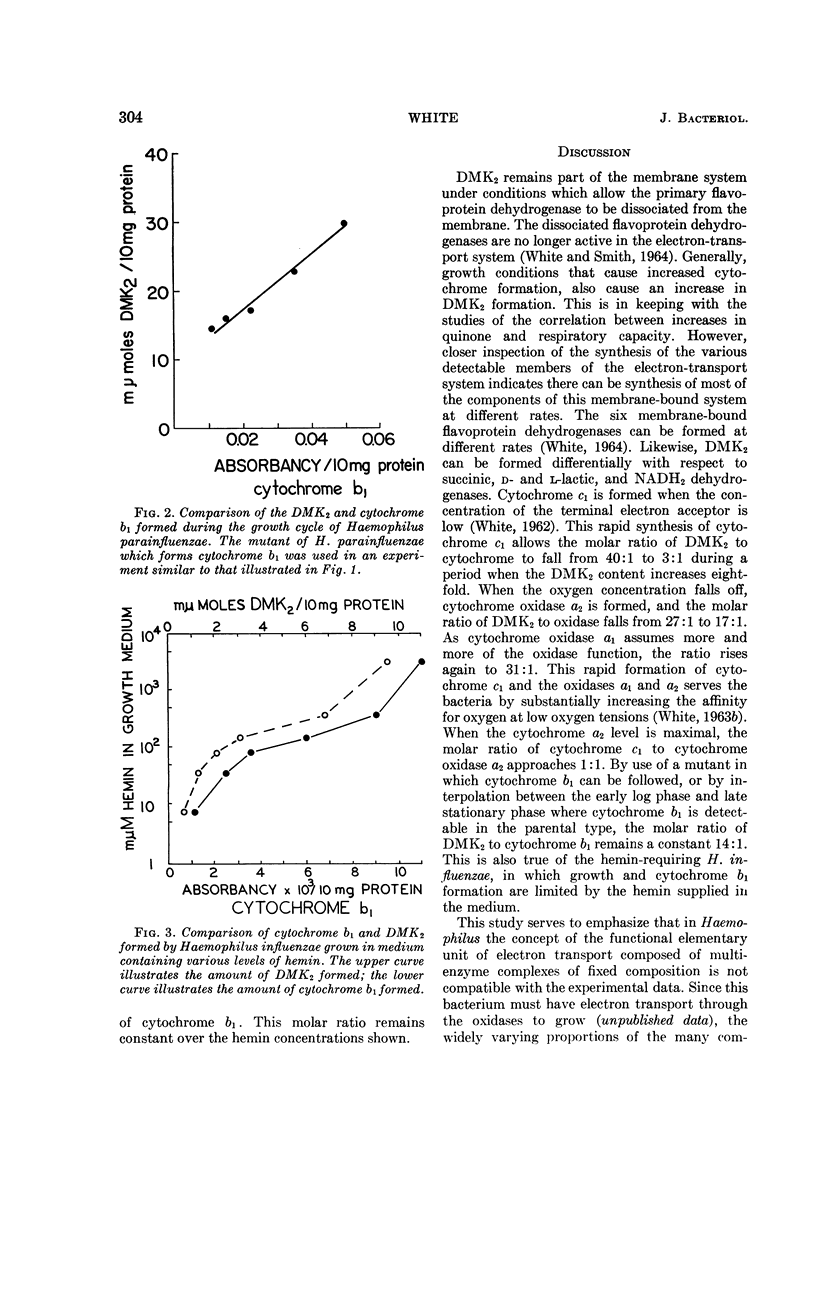
White, David C. (University of Kentucky College of Medicine, Lexington). Synthesis of 2-demethyl vitamin K2 and the cytochrome system in Haemophilus. J. Bacteriol. 89:299–305. 1965.—The synthesis of the respiratory quinone, 2-demethyl vitamin K2, is stimulated in Haemophilus parainfluenzae under conditions which provoke the synthesis of the cytochrome system. However, the various components of the electron-transport system can be formed in different proportions. The primary flavoprotein dehydrogenases are readily dissociated from the membrane without affecting the content of membrane-bound quinone, cytochrome b1, or the cytochrome oxidases. These dehydrogenases must be membrane-bound to function, and each can be formed at a different rate. Molar ratios of various constituents of the electron-transport chain were calculated by use of reasonable extinction coefficients for the cytochromes. The molar ratio of quinone to cytochrome c1 goes from 40 to 3 as the quinone content increases eightfold during the growth cycle. Similarly, the molar ratio of quinone to cytochrome oxidase a2 varies from 27 to 17, and then increases to 31 as cytochrome oxidase a1 assumes the oxidase function. The molar ratio of quinone to cytochrome b1 remains 14 to 1 over a sixfold increase in both components measured in a mutant where cytochrome c1 does not obscure cytochrome b1. A similar consistency was noted between the quinone and cytochrome b1 formation in the hemin-requiring H. influenzae.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BISHOP D. H., PANDYA K. P., KING H. K. Ubiquinone and vitamin K in bacteria. Biochem J. 1962 Jun;83:606–614. doi: 10.1042/bj0830606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B. Spectrophotometry of intracellular respiratory pigments. Science. 1954 Nov 12;120(3124):767–775. doi: 10.1126/science.120.3124.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B., WILLIAMS G. R. The respiratory chain and oxidative phosphorylation. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1956;17:65–134. doi: 10.1002/9780470122624.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORIO T., HIGASHI T., YAMANAKA T., MATSUBARA H., OKUNUKI K. Purification and properties of cytochrome oxidase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem. 1961 Mar;236:944–951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KASHKET E. R., BRODIE A. F. Subcellular distribution of a biologically active naphthoquinone Mycobacterium phlei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jun 3;40:550–552. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91404-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESTER R. L., CRANE F. L. The natural occurrence of coenzyme Q and related compounds. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):2169–2175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESTER R. L., WHITE D. C., SMITH S. L. THE 2-DESMETHYL VITAMIN K2'S. A NEW GROUP OF NAPHTHOQUINONES ISOLATED FROM HEMOPHILUS PARAINFLUENZAE. Biochemistry. 1964 Jul;3:949–954. doi: 10.1021/bi00895a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH L., WHITE D. C. Structure of the respiratory chain system as indicated by studies with Hemophilus parainfluenzae. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1337–1341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUGIMURA T., OKABE K., RUDNEY H. UBIQUINONE IN RESPIRATION-DEFICIENT MUTANTS OF SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Feb 10;82:350–354. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUGIMURA T., RUDNEY H. The adaptive formation of ubiquinone 30 (coenzyme Q6) in yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jan 29;37:560–561. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90527-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUGIMURA T. The effect of aerobiosis and diphenylamine on the content of ubiquinone in Rhodospirillum rubrum. Biochim Biophys. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 30;62:167–170. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE D. C. Cytochrome and catalase patterns during growth of Haemophilus parainfluenzae. J Bacteriol. 1962 Apr;83:851–859. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.4.851-859.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE D. C. DIFFERENTIAL SYNTHESIS OF FIVE PRIMARY ELECTRON TRANSPORT DEHYDROGENASES IN HEMOPHILUS PARAINFLUENZAE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jun;239:2055–2060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE D. C. FACTORS AFFECTING THE AFFINITY FOR OXYGEN OF CYTOCHROME OXIDASES IN HEMOPHILUS PARAINFLUENZAE. J Biol Chem. 1963 Nov;238:3757–3761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE D. C. Respiratory systems in the hemin-requiring Haemophilus species. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85:84–96. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.1.84-96.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE D. C., SMITH L. Hematin enzymes of Hemophilus parainfluenzae. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1332–1336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE D. C., SMITH L. LOCALIZATION OF THE ENZYMES THAT CATALYZE HYDROGEN AND ELECTRON TRANSPORT IN HEMOPHILUS PARAINFLUENZAE AND THE NATURE OF THE RESPIRATORY CHAIN SYSTEM. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3956–3963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



