Abstract
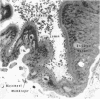
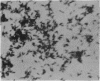
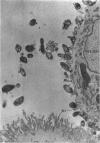
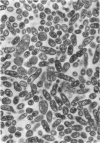
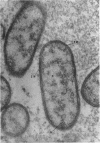
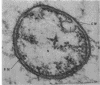
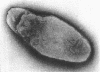
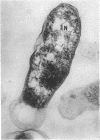
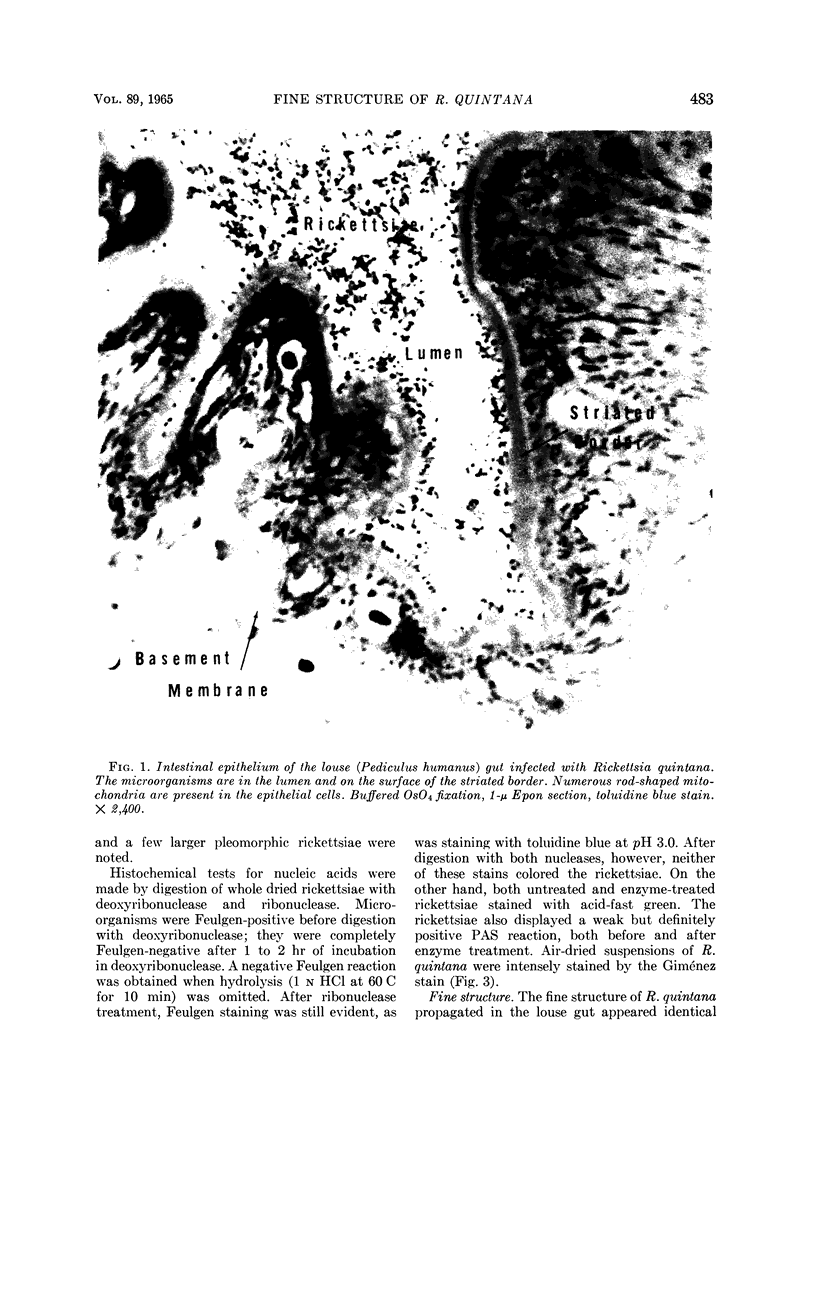
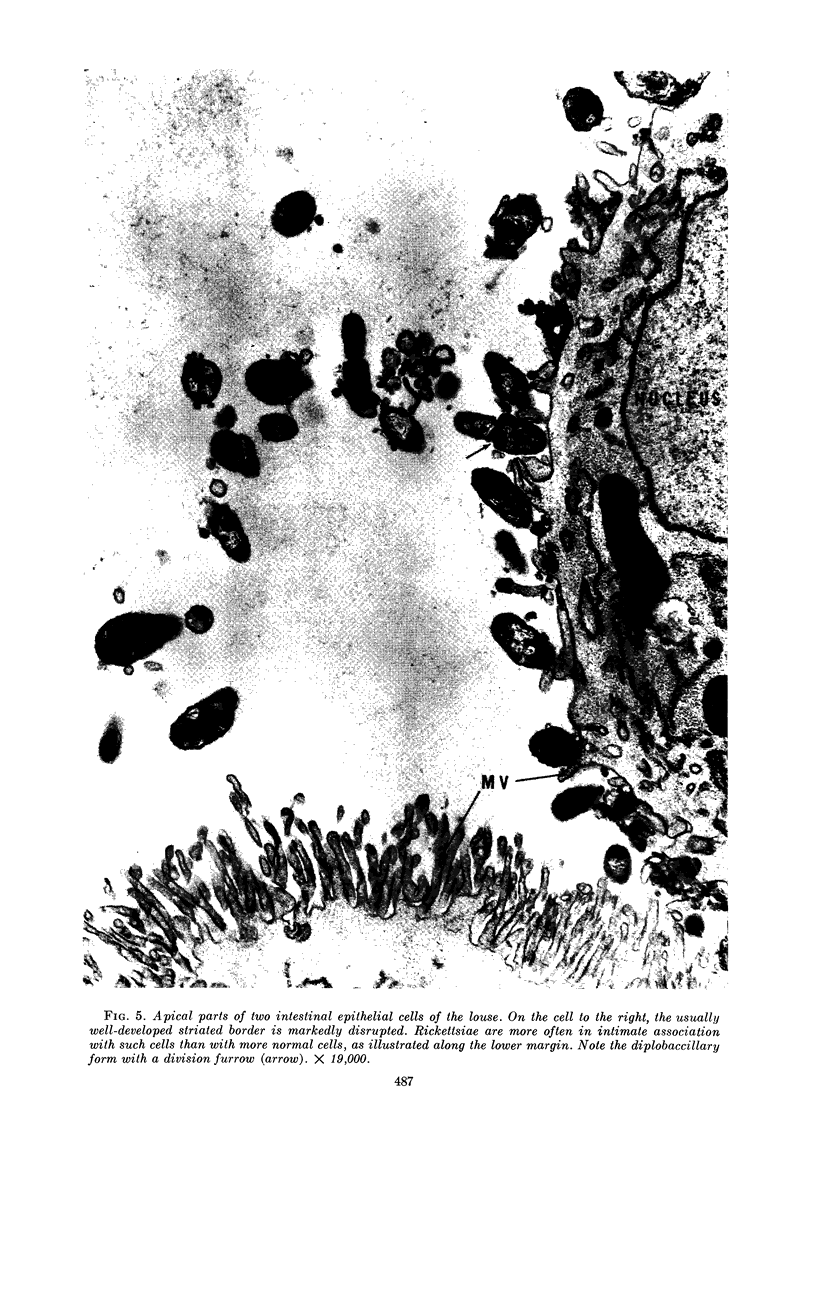
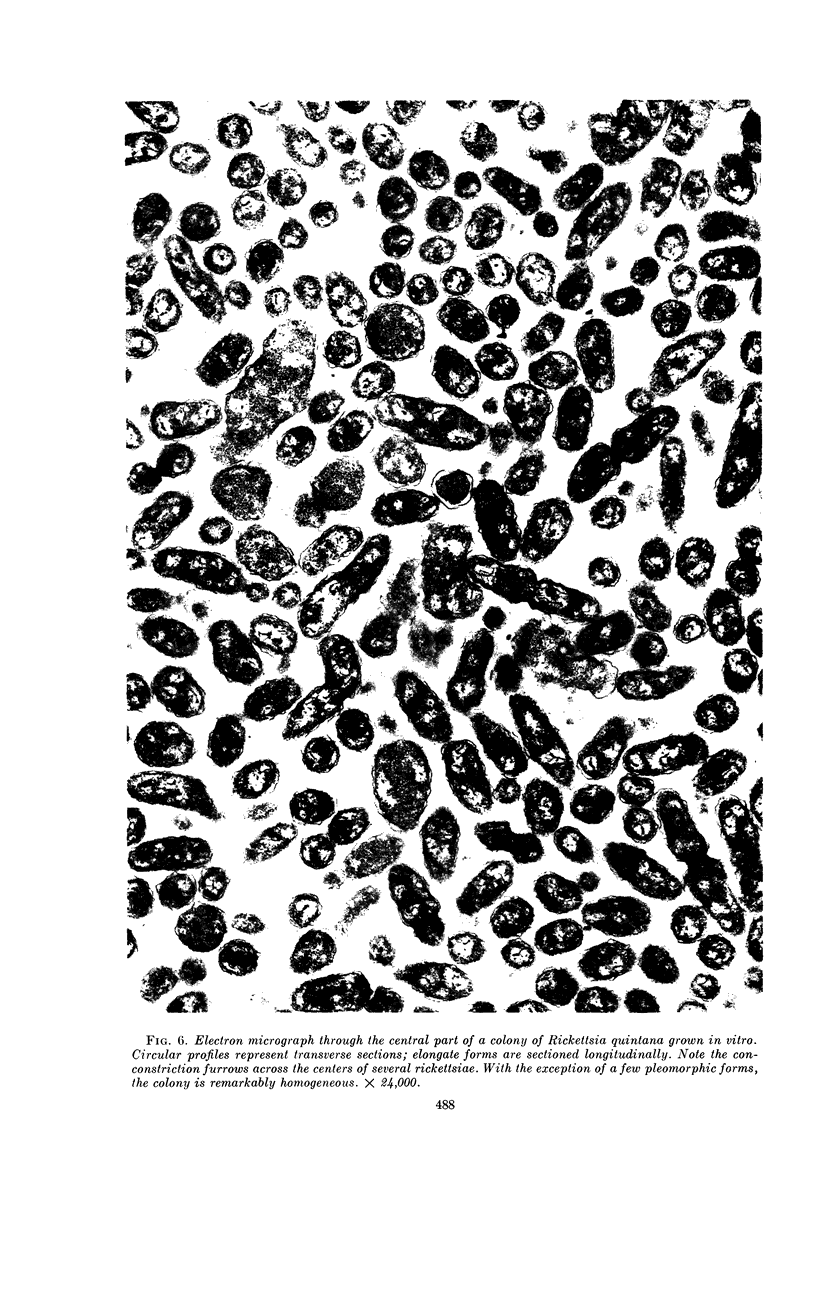
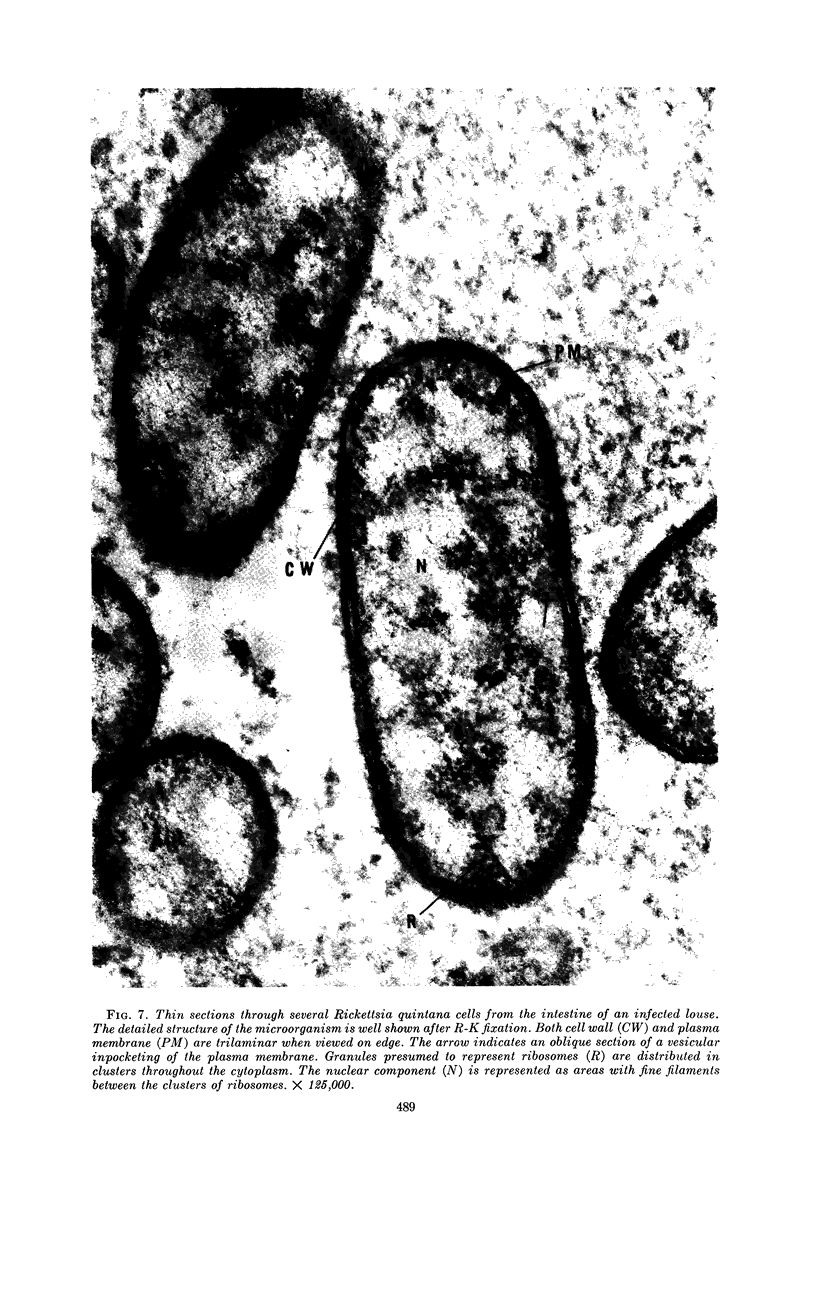
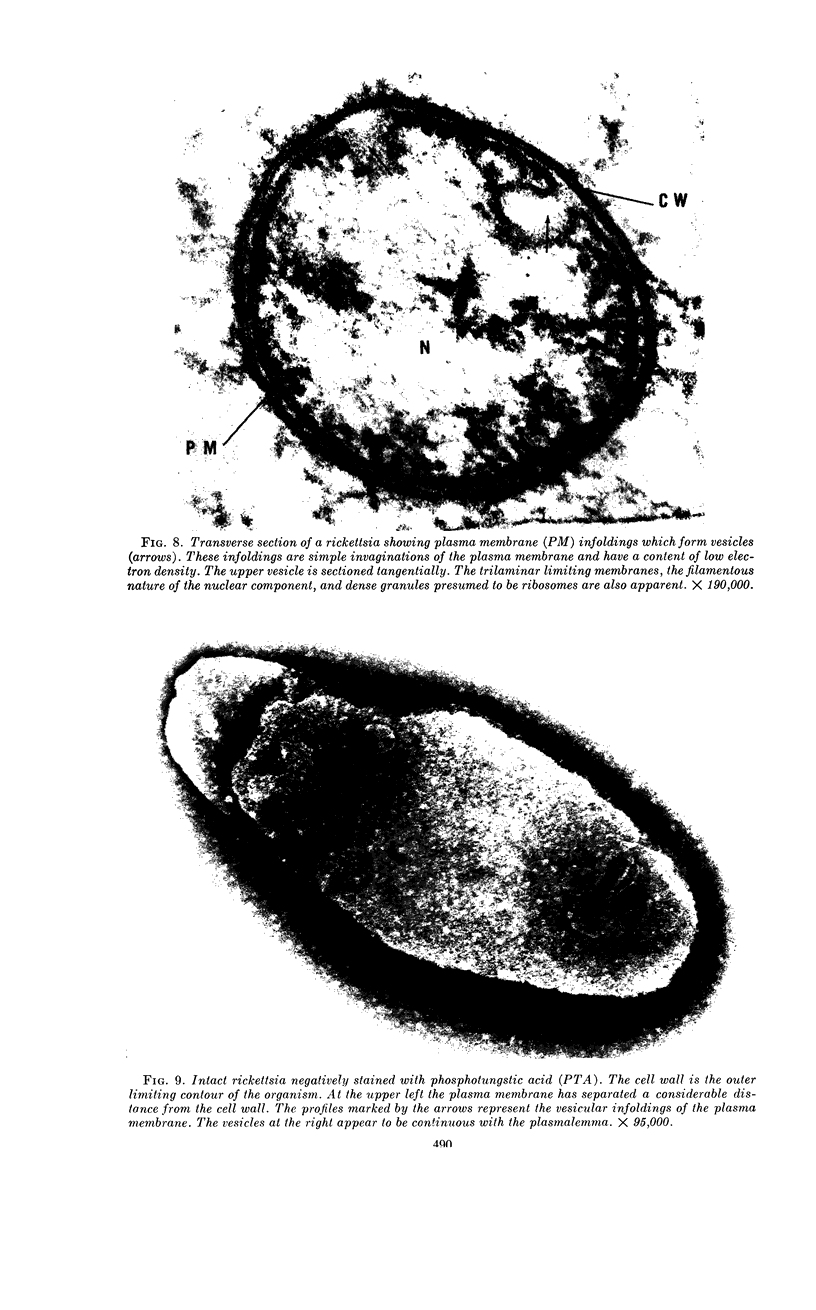
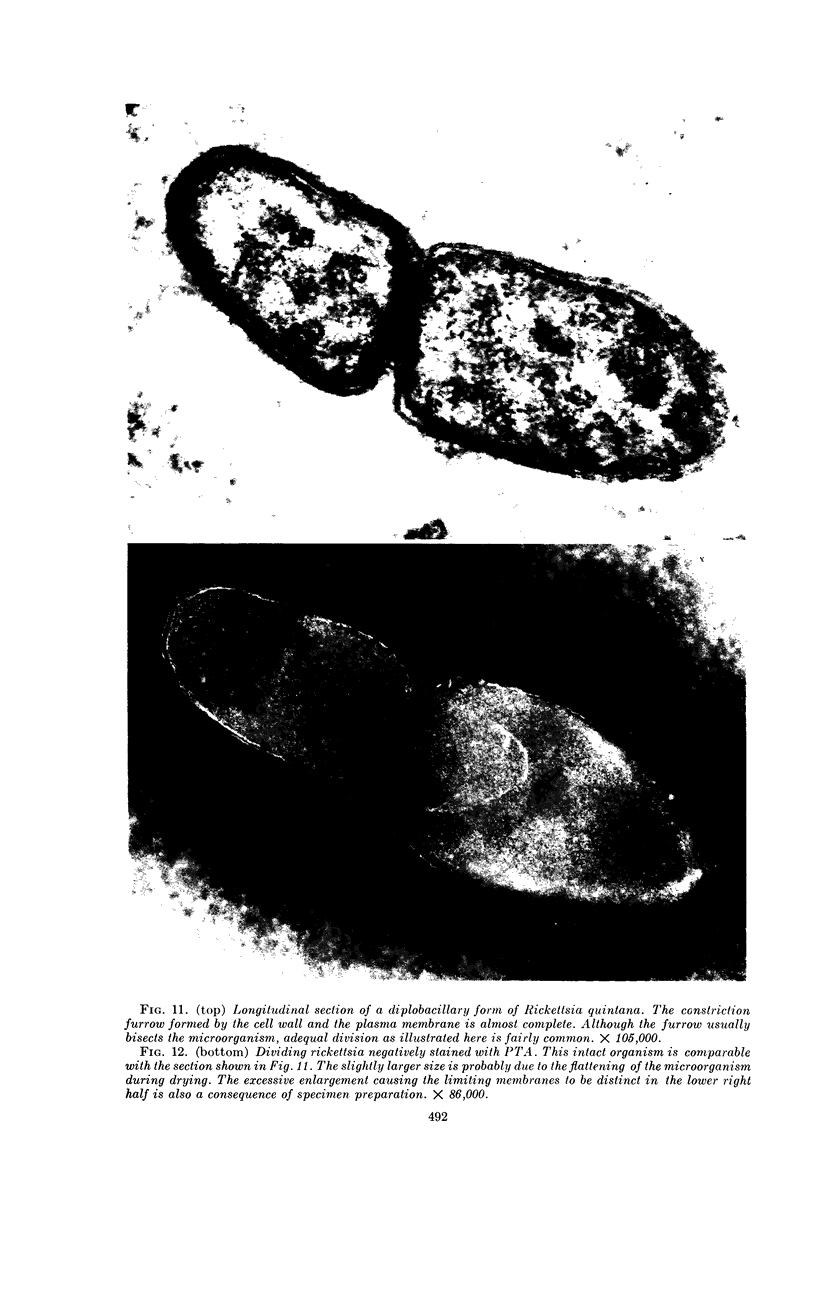
Ito, Susumu (Harvard Medical School, Boston, Mass.), and J. W. Vinson. Fine structure of Rickettsia quintana cultivated in vitro and in the louse. J. Bacteriol. 89:481–495. 1965.—Usually rod-shaped, Rickettsia quintana cells measure about 0.2 to 0.5 μ wide and up to 1.6 μ long. The rickettsiae have both an outer cell wall, about 80 A thick, and a plasma membrane, about 70 A thick, each of which is trilaminar. Occasional vesicular invaginations of the plasma membrane occur. The nuclear material, distributed in irregular zones throughout the cytoplasm, appears as a loose network of fine fibrils when postfixed with uranyl acetate and as thick strands or clumps after routine OsO4 fixation. The cytoplasm is densely packed with numerous granules, presumably ribosomes, about 150 A in diameter. Histochemical studies revealed the presence of both ribonucleic and deoxyribonucleic acids. During binary fission, a constricting furrow is formed by the cell wall and plasmalemma. No difference in fine structure was observed between R. quintana propagated on cell-free media and in the louse.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANACKER R. L., FUKUSHI K., PICKENS E. G., LACKMAN D. B. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF COXIELLA BURNETII IN THE CHICK YOLK SAC. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1130–1138. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1130-1138.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENNETT H. S., LUFT J. H. zeta-Collidine as a basis for buffering fixatives. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 Aug;6(1):113–114. doi: 10.1083/jcb.6.1.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLADEN H. A., WATERS J. F. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF SOME STRAINS OF BACTEROIDES. J Bacteriol. 1963 Dec;86:1339–1344. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.6.1339-1344.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARO L. G., JACKSON E. B., SMADEL J. E., WISSIG S. L. Electron microscopic observations on intracellular rickettsiae. Am J Pathol. 1956 Nov-Dec;32(6):1117–1133. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti S. F., Gettner M. E. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF CELLULAR DIVISION IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1962 Mar;83(3):544–550. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.3.544-550.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISET P., SMITH K. M., STOKER M. G. Internal structure of Rickettsia burnetii as shown by electron microscopy of thin sections. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Dec;15(3):632–635. doi: 10.1099/00221287-15-3-632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZ-JAMES P. THIN SECTIONS OF DIVIDING NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jun;87:1477–1482. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.6.1477-1482.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLAUERT A. M. The fine structure of bacteria. Br Med Bull. 1962 Sep;18:245–250. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE S. Fixation of E. coli spheroplasts for electron microscopy. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Oct;21:252–255. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90377-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGURA M. High resolution electron microscopy on the surface structure of Escherichia coli. J Ultrastruct Res. 1963 Apr;8:251–263. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(63)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J., ROSEN S. M., ROTHFIELD L., ZELEZNICK L. D., HORECKER B. L. LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. Science. 1964 Aug 21;145(3634):783–789. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3634.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON J. D. The ultrastructure of cell membranes and their derivatives. Biochem Soc Symp. 1959;16:3–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., KELLENBERGER E., BIRCHANDERSEN A., MAALOE O. Etude au microscope électronique de plasmas contenant de l'acide désoxyribonucliéique. I. Les nucléoides des bactéries en croissance active. Z Naturforsch B. 1958 Sep;13B(9):597–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAECHTER M., TOUSIMIS A. J., COHN Z. A., ROSEN H., CAMPBELL J., HAHN F. E. Morphological, chemical, and serological studies of the cell walls of Rickettsia mooseri. J Bacteriol. 1957 Dec;74(6):822–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.6.822-829.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH J. D., STOKER M. G. P. The nucleic acids of Rickettsia burneti. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Oct;32(5):433–441. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUMP B. F., SMUCKLER E. A., BENDITT E. P. A method for staining epoxy sections for light microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1961 Aug;5:343–348. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(61)80011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN ITERSON, LEENE W. A CYTOCHEMICAL LOCALIZATION OF REDUCTIVE SITES IN A GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIUM. TELLURITE REDUCTION IN PROTEUS VULGARIS. J Cell Biol. 1964 Mar;20:377–387. doi: 10.1083/jcb.20.3.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VINSON J. W., FULLER H. S. Studies on trench fever. I. Propagation of Rickettsia-like microorganisms from a patient's blood. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1961;24(Suppl):152–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]