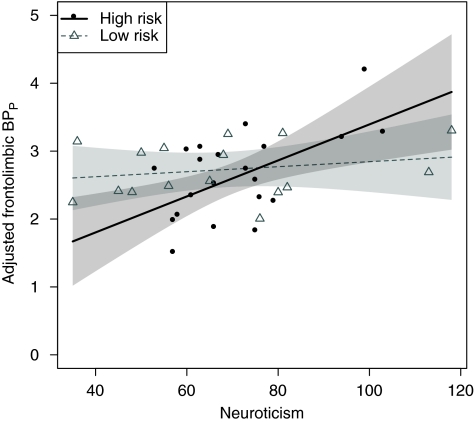
Figure 1.
Effect of familial risk on the association between frontolimbic 5-HT2A receptor BPP and neuroticism, adjusted for BMI and age. In the high end of the neuroticism scale, the high-risk group showed an elevated BPP, whereas in the low end, they showed a decreased BPP as compared with the low-risk group. This reflects the stronger association between neuroticism and frontolimbic 5-HT2A receptor binding in individuals at high familial risk of developing mood disorders (p=0.026). The high-risk group showed a significant positive association between neuroticism and frontolimbic 5-HT2A receptor binding, whereas the low-risk group did not. Please see text for estimates. Point-wise 95% symmetric confidence bands of the regression lines are displayed. The regression lines represent the associations given a mean BMI and mean age.