Abstract
Carbonylated (oxidized) proteins are known to accumulate in the cerebral white matter (WM) and gray matter (GM) of patients with multiple sclerosis (MS). While oxidative stress is necessary for carbonyl generation, it is the failure of the degradation systems that ultimately leads to the build-up of carbonylated proteins within tissues. In this study, we measured the activity of the 20S proteasome and other proteolytic systems in the cerebral WM and GM of 13 MS patients and 13 controls. We report that the activities of the three peptidases of the 20S proteasome (i.e. chymotrypsin-like, caspase-like and trypsin-like) in both MS-WM and MS-GM are greatly reduced. Interestingly, neither the amount of proteasome nor the levels of the catalytic subunits (β1, β2, and β5) are diminished in this disease. Proteins containing Lys-48 poly-ubiquitin also accumulate in MS tissues, indicating failure of the 26S proteasome as well. Levels of the regulatory caps PA28α and PA700 are also lower in MS than in controls, suggesting that the activity of the more complex proteasomes may be reduced further. Finally, the activities of other proteases that might also remove oxidized proteins (calpain, cathepsin B, mitochondrial LonP) are not lessened in MS. Together, these studies suggest that direct inactivation of proteolytic centers in the 20S particle and/or the presence of specific inhibitors is the underlying cause of proteasomal dysfunction in MS.
Keywords: Multiple sclerosis, proteases, 20S proteasome, protein carbonylation, white matter, gray matter
Introduction
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the human CNS, which is characterized by perivascular inflammation, demyelination, oligodendrocyte death and axonal degeneration (Kornek & Lassmann 1999). Pathologically, the CNS in MS patients contains well-demarcated regions of myelin loss and increased astrogliosis called plaques that are surrounded by normal-appearing white matter (Lucchinetti et al 1996). While most of the pathology in chronic MS is observed in the plaque, cellular and chemical abnormalities are also found in both the normal-appearing white matter and gray matter as demonstrated in recent imaging (Sharma et al 2001; Husted et al 1994) and biochemical studies (Bizzozero et al 2005a; Bizzozero et al 2005b).
Like many other chronic neurological disorders, MS is accompanied by a substantial amount of oxidative damage, which seems to play a role in disease pathogenesis (Smith 1999). We have previously shown that protein carbonyls, the major oxidative modification in chronic disorders, accumulate in the white matter (WM) and gray matter (GM) of MS patients (Bizzozero et al 2005b) with GFAP, β-tubulin, β-actin and the neurofilaments as the major oxidized species (Hilgart & Bizzozero 2008). More recent studies from our laboratory have discovered that protein carbonyls are also elevated in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, a widely used animal model of MS (Smerjac & Bizzozero 2008; Zheng & Bizzozero 2010a). Carbonylation can lead to loss of protein function, the formation of insoluble aggregates and/or metabolic instability, all processes that likely result in cell damage (Bizzozero 2009). Because of their toxic nature, the concentration of carbonylated proteins within cells is normally kept very low, which is achieved through the action of efficient proteolytic systems that preferentially digest oxidized proteins (Bizzozero 2009). This has led to the idea that while oxidative stress is clearly necessary for the induction of protein carbonyls, it is the failure of the proteolytic activities that ultimately leads to the build up of oxidized proteins within tissues.
Mammalian cells contain several major proteolytic systems including the lysosomal cathepsins, the calcium-activated calpains and the 20S/26S proteasomes, all of which could potentially remove oxidized proteins (Grune et al 2001). However, various cell-culture studies that utilized protease inhibitors have identified the 20S proteasome as the system responsible for removal of most oxidized protein species (Shringarpure et al 2003; Divald & Powell 2006; Zheng & Bizzozero, 2010b). The 20S proteasome is a barrel-shaped structure that is made of two outer heptameric rings of α subunits and two inner heptameric rings of β subunits (Murata et al 2009). Three of the β subunits carry the proteolytic activity, classified as caspase-like or peptidyl glutamyl-peptide hydrolytic (β1), trypsin-like (β2), and chymotrypsin-like (β5), which cleave after acidic, basic and hydrophobic amino acids, respectively (Coux et al 1996). Of these, the β5 subunit is believed to be responsible for the degradation of oxidized (carbonylated) proteins (Ferrington et al 2005). The peptidase activity of the 20S proteasome can be increased by two different types of regulatory complexes that bind to the terminal rings of this particle. These are the 11S regulator (PA28) and the 19S (PA700) regulatory complex, which form the 11S-20S proteasome and the 26S proteasome, respectively (DeMartino & Slaughter 1999). A number of proteasome inhibitors, including the hsp90, PI31 and PR39, have been also described although their precise physiological role is currently unknown (Rechsteimer & Hill 2005).
The objective of the present study was to determine whether the various proteolytic activities of the 20S proteasome are altered in MS. The results clearly show that the enzymatic activities of the three peptidases of the 20S proteasome in both the WM and GM of MS patients are greatly reduced without significant decrease in the total amount of proteasome. Furthermore, the levels of the 20S proteasome β subunits where the peptidolytic activities reside are not affected in the diseased specimens. We also found that the amount of the regulatory caps PA28α and PA700 are lower in MS than in control samples, indicating that the activity of the larger proteasomes (i.e. 26S, 11S-20S and hybrid 19S-20S-11S) may be reduced to an even larger extent. Collectively, these studies suggest that the direct inactivation of proteolytic centers in the 20S particle and/or the presence of specific inhibitors are the most likely cause for impaired proteasome function in MS and the ensuing build-up of carbonylated proteins. This notion was strengthen by the finding that the other enzymatic system that might also aid in the removal of oxidized proteins, including calpain, lysosomal proteinases and the mitochondrial Lon protease, are not decreased in MS.
Materials and Methods
Tissue Specimens
Tissue specimens were obtained from the Rocky Mountain MS Center (Englewood, CO) and from the Human Brain and Spinal Fluid Resource Center (Los Angeles, CA) and were stored at −80°C until use. A total of 26 brain specimens including 13 control and 13 MS tissues were analyzed. In all cases the diagnosis of MS was based on clinical history, neurological examination and pathological analysis. Frozen tissue from control and pathological samples was thawed and a small piece (~50 mg) of WM was carefully dissected so that it did not include visible plaques. Normal-looking GM pieces were selected from cortical areas based also on gross examination. Immediately after dissection tissues were homogenized in PEN buffer (20 mM sodium phosphate, pH 7.5, 1 mM EDTA, and 0.1 mM neocuproine) containing 2 mM 4,5 dihydroxy-1, 3-benzene disulfonic acid and 1 mM dithiothreitol as antioxidants. Protein homogenates were stored at −20°C until use. Protein concentration was assessed with the Bio-Rad protein assay (Bio-Rad Laboratories; Hercules, CA) using bovine serum albumin as standard.
Protease activity assays
The various proteolytic activities of the 20S proteasome were determined in cerebral homogenates from control and MS patients using fluorescence assays (Rodgers & Dean 2003). Briefly, 50µg of protein were incubated for 2h at 25°C with 50µM of the 7-aminomethyl-4-coumarin (AMC)-labeled peptide Suc-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr-AMC (for chymotrypsin-like activity), Boc-Leu-Arg-Arg-AMC (for trypsin-like activity) or z-Leu-Leu-Glu-AMC (for caspase-like activity) in the absence or presence of 10µM clasto-lactacystin-β-lactone (Enzo Life Sciences, Plymouth Meeting, PA) or 50µM epoxomicin (for the trypsin-like activity). The different activities of the 20S proteasome were calculated as the difference in fluorescence intensity at 460nm between the samples without and with inhibitor using an excitation wavelength of 380nm.
Total calpain activity was determined by a similar procedure using the substrate Suc-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr-AMC in 100mM KCl, 10mM CaCl2, 25mM Hepes buffer pH 7.5, and carrying out the incubation in the absence or presence of 0.4 µg/µl calpeptin (Hassen et al 2006). To measure soluble (active) calpain activity, membrane-bound calpain was removed prior to the assay by centrifugation at 10,000 g for 25 min.
Lysosomal proteolytic activity was also measured fluorometrically by incubating cerebral homogenates with 50µM z-Phe-Arg-AMC (Enzo) in 100 mM sodium acetate (pH 5.5) for 2h at 37°C (Sitte et al 2000).
Western blot analysis
Proteins (5 µg) from tissue homogenates were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on 10% or 12% gels and were blotted to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. Blots were then incubated overnight at 4°C with antibodies against Lys-48 poly-ubiquitin chain (1:2,000; Millipore Corp., Billerica, MA), 20S proteasome α-subunits (α1–3/α5–7; 1:2,000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA), β1, β2 and β5 subunits (1:1,000; Enzo), PA28α (1:1,000, Enzo), 19S proteasome Rpt4 (1:1,000, Enzo); µ-calpain (1:1,000; Cell Signaling Technology, Boston, MA), cathepsin B (1:1,000; EMD Biosciences, San Diego, CA) and LonP1 protease (1:2,000; Proteintech Group Inc, Chicago, IL). Membranes were rinsed three times in phosphate-buffered saline solution containing 0.05% Tween-20 and were incubated for 2 h with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse antibody (1:2,000; Sigma) or anti-rabbit antibody (1:2,000; Sigma). Blots were developed by enhanced chemiluminescence using the Western Lightning ECL™ kit from Perkin-Elmer (Boston, MA). Films were scanned in a Hewlett Packard Scanjet 4890 and the images were quantified using the NIH Image 1.63 imaging analysis program. Band intensities were normalized by the amount of coomassie blue stain in the respective lanes. Normalization based on the amount of β-actin is not possible since the levels of this protein are increased in MS.
Statistical Analysis
Results were analyzed for statistical significance by t-test utilizing the GraphPad Prism® program (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA).
Results
Proteasomal peptidase activities are decreased in MS-WM and MS-GM
The age of the patients at the time of death, gender, post-mortem interval (PMI) and the pathological diagnosis are shown in Table 1. Age of controls and MS patients ranges from 34 to 80 years and from 33 to 83 years, respectively. The control group has 7 men/6 women and the MS group 4 men/9 women. PMI intervals are variable, 4h-20h for controls and 2h-25h for MS patients. Within each group (i.e. MS and controls) there was no discernible correlation between the biochemical parameters measured and either age, sex or PMI. Thus, the average values in the MS and control specimens were directly compared without segregation in subcategories. Tissues from patients with other chronic neurological disorders (e.g. Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease) were not included in the present study since proteasome failure in these illnesses has been already described (see Discussion).
Table 1.
Brain samples from control and MS patients
| Sample |
Age (years) |
Gender |
PMI (hours) |
Diagnosis / Brain pathology |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Controls | ||||
| 1 | 34 | M | uk | Acute pancreatitis / NB |
| 2 | 55 | M | 4 | Metastatic lung cancer / NB† |
| 3 | 58 | M | 9 | Colon cancer / NB† |
| 4 | 59 | F | 19 | Lymphoma / NB¥ |
| 5 | 68 | M | 10 | Lung cancer / NB† |
| 6 | 71 | M | 14 | Lymphoma / NB¥ |
| 7 | 72 | F | 20 | Congestive heart failure / NB |
| 8 | 73 | F | 12 | COPD / NB |
| 9 | 74 | F | 12 | Pancreatic cancer / NB† |
| 10 | 74 | F | 5 | Pneumonia / NB |
| 11 | 74 | M | 14 | Metastatic lung cancer /NB† |
| 12 | 75 | F | 15 | Liver cancer / NB† |
| 13 | 80 | M | 11 | Renal cancer / NB† |
| Multiple Sclerosis | ||||
| 1 | 33 | F | 3 | MS / chronic and active plaques |
| 2 | 36 | F | 4 | MS / chronic shadow plaques |
| 3 | 37 | M | 5 | MS / diffuse periventricular demyelination |
| 4 | 39 | F | 2 | MS / chronic and active plaques |
| 5 | 40 | F | 3 | MS / active plaques |
| 6 | 47 | F | 16 | MS / chronic and active plaques |
| 7 | 54 | M | 24 | MS / chronic and active plaques |
| 8 | 57 | F | 25 | MS / chronic plaques |
| 9 | 58 | F | 3 | MS / chronic plaques and optic neuritis |
| 10 | 61 | M | 3 | MS / chronic and active plaques |
| 11 | 65 | M | 6 | MS / chronic plaques |
| 12 | 70 | F | 16 | MS / chronic and active plaques |
| 13 | 83 | F | 3 | MS / chronic plaques |
No evidence of cerebral metastatic disease;
No evidence of intracranial lymphoma;
NB, normal brain; M, male; F, female; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; uk, unknown.
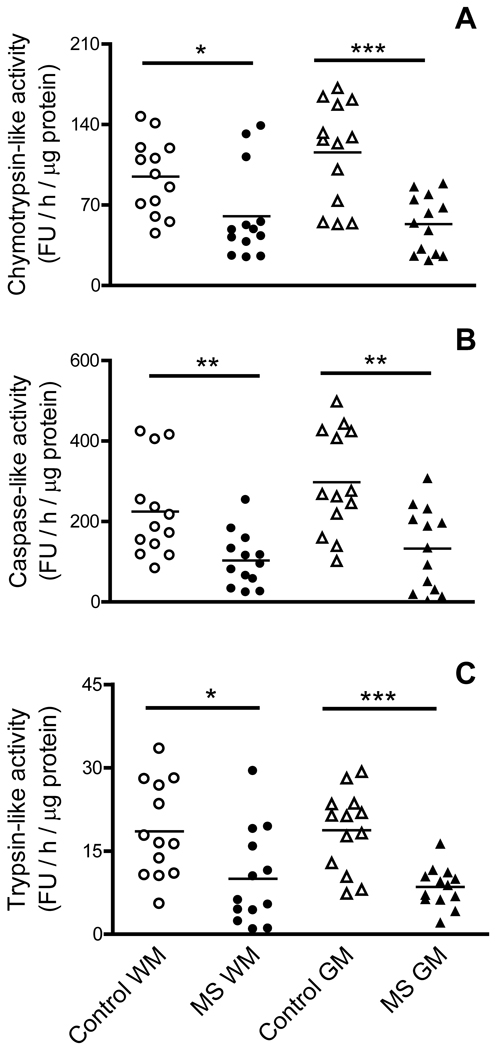
Aliquots of cerebral homogenates from MS-GM, MS-WM and their respective controls were used to determine the various proteolytic activities of the 20S proteasome (Fig. 1). The chymotrypsin-like activity is greatly reduced in both WM and GM of MS patients representing 56% and 38% of control values, respectively (panel A). A similar pattern exists for the caspase-like activity in MS-WM and MS-GM, which decreases by 61% and 60% of their respective controls (panel B). Values for the trypsin-like activity are generally more disperse but a significant reduction in both the WM and GM of diseased patients is nonetheless observed (panel C).
Fig. 1.
Proteasome peptidase activities are greatly reduced in MS. Aliquots of the cerebral homogenates from control and MS patients were used to determine the chymotrypsin-like (A), caspase-like (B) and trypsin-like activity (C) of the 20S proteasome using specific fluorescent peptides as described in “Materials and Methods”. Enzyme activity values are expressed as fluorescence units (FU) / hour / µg protein. Each point represents a patient and the horizontal bar is the average. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.005. Open circles, control WM; closed circles, MS WM; open triangles, control GM; closed triangles, MS GM.
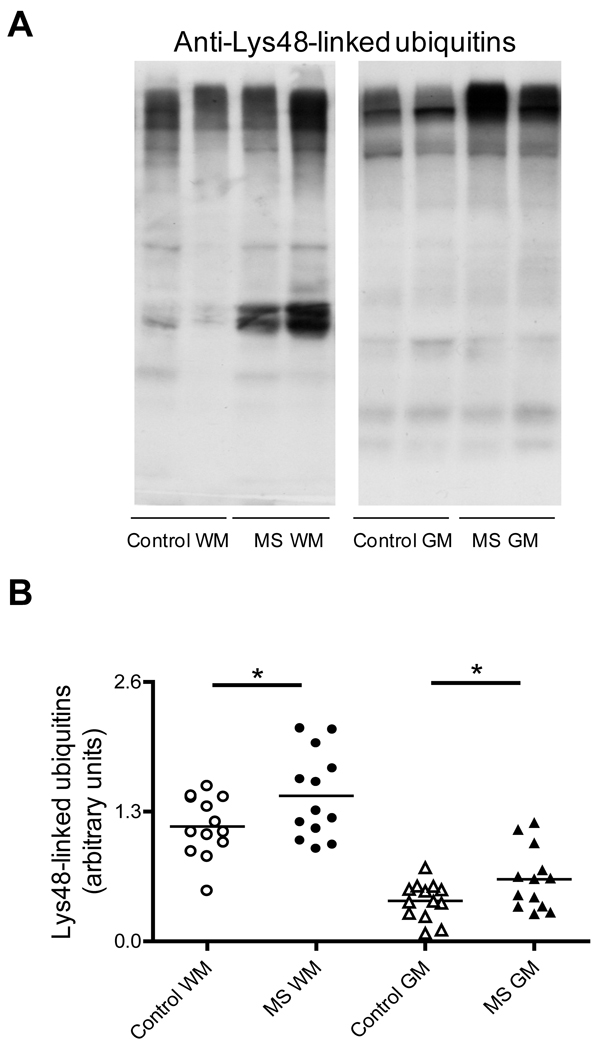
Since a significant proportion of the 20S catalytic particle is part of the 26S ubiquitin-dependent proteasome, we reasoned that the proteolytic activity of the latter, and thus the ability to remove ubiquitinated proteins, might be also compromised in MS. This possibility was explored by western blot analysis using an antibody that binds only poly-ubiquitin chains linked through the Lys-48 residue in ubiquitin. Lys-48 linked poly-ubiquitin chains are most commonly associated with proteins targeted for proteasomal degradation (Glickman & Ciechanover 2002). As shown in Fig. 2, several proteins containing Lys-48 poly-ubiquitin chains accumulate in the WM and GM of MS patients relative to controls. These data indicate that impairment of the 26S proteasome is also taking place in MS.
Fig. 2.
Proteins containing Lys-48-linked poly-ubiquitin accumulate in MS-WM and MS-GM. (A) Representative immunoblots from homogenates of the brain WM and GM areas of control and MS patients developed with antibodies against Lys-48 poly-ubiquitin. (B) The relative levels of proteins containing Lys-48 ubiquitin were calculated by dividing the whole lane intensity on the immunoblots by that of the corresponding coomassie blue stained lane. Each point represents a patient and the horizontal bar is the average. *p<0.05. Other symbols are as in Fig. 1.
Levels of 20S proteasome α, β1, β2 and β5 subunits are not reduced in MS tissue
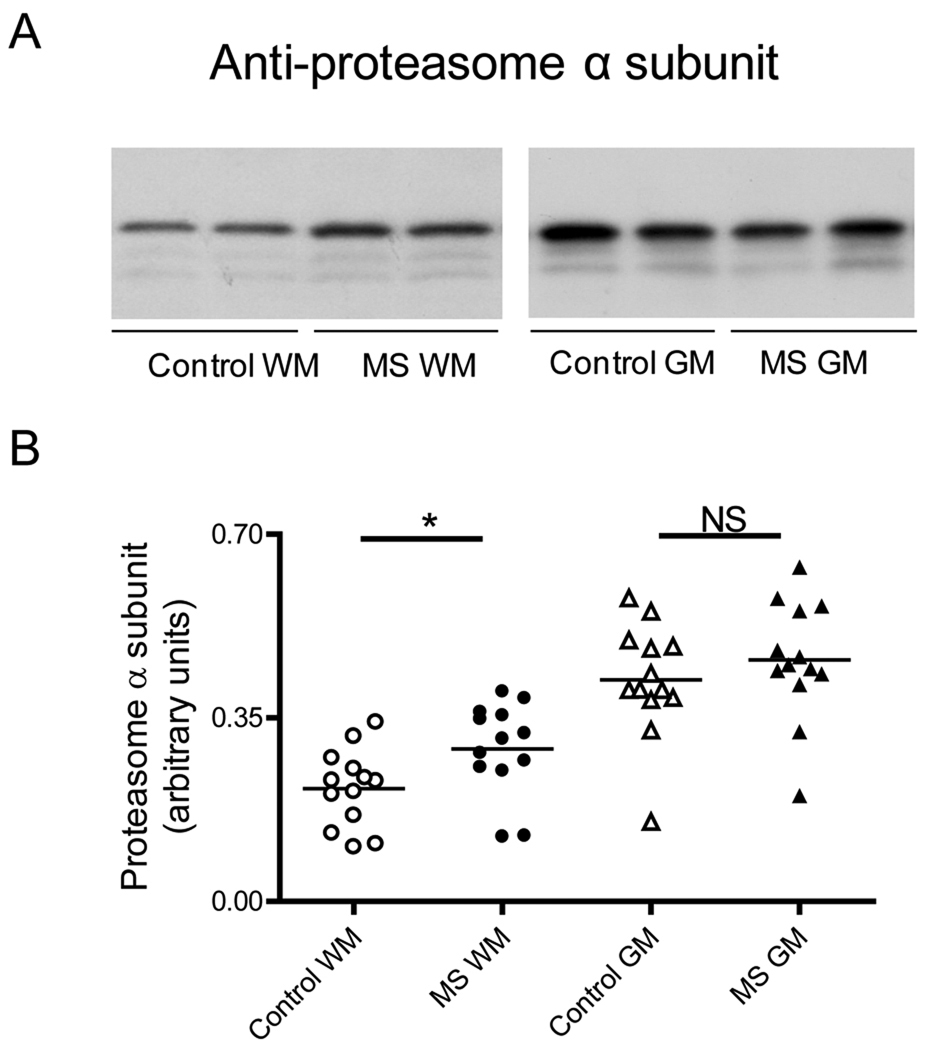
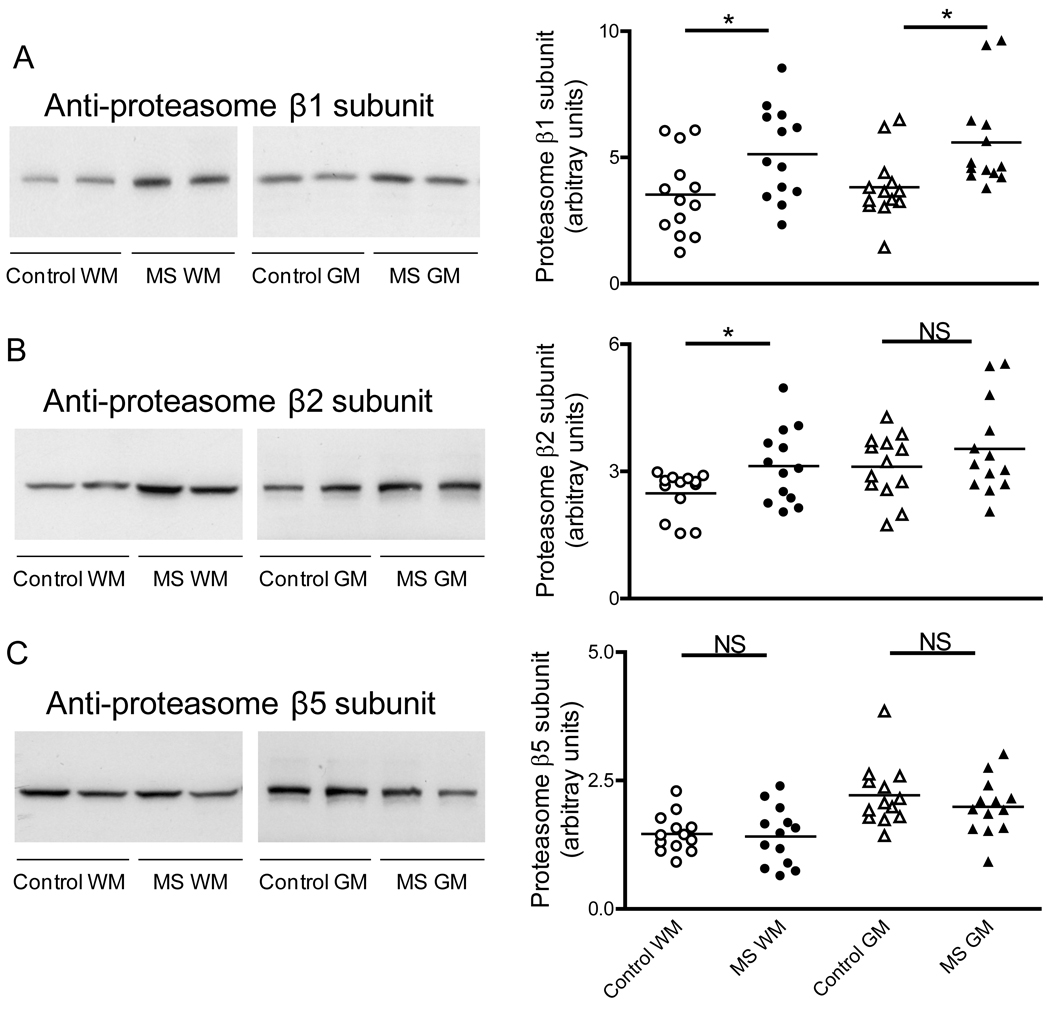
To establish if the decreased proteasomal activity observed in MS patients is due to reduction in proteasome concentration or to a change in the proportion of the catalytic subunits, we measured the relative levels of the constitutive 20S proteasome α subunit and those of each of the three protease-containing subunits (i.e. β1, β2 and β5) by western blot analysis. As depicted in Fig. 3, the amount of 20S proteasome α subunit in MS-GM is the same as those in the control group while there is a small increase in the WM of MS patients relative to the control. Furthermore, the relative amounts of β1, β2, and β5 subunits in the MS-WM and MS-GM are either increased or unchanged when compared to their respective controls (Fig. 4). These data indicate that diminished proteasome peptidase activity in MS is likely due to enzyme inactivation rather than to down-regulation of enzyme proteins or reduced proteasome levels.
Fig. 3.
The amount of 20S proteasome α subunits is not diminished in MS. (A) Representative immunoblots from homogenates of brain WM and GM areas of control and MS patients developed with antibodies against the constitutive α subunits of the 20S proteasome. (B) The relative levels of α subunits were calculated by dividing α subunits band intensity on the western blot by that of the corresponding coomassie blue stained lane. Each point represents a patient and the horizontal bar is the average. *p<0.05. Other symbols are as in Fig. 1.
Fig. 4.
Levels of 20S proteasome β1, β2 and β5 subunits are not decreased in MS. Left three panels show representative immunoblots from homogenates of brain WM and GM areas of control and MS patients developed with antibodies against the β1 subunit (A), β2 subunit (B) and β5 subunit (C) of the 20S proteasome. Right panels depict the corresponding levels of each of the β subunits, which were calculated by dividing band intensity on the western blot by that of the corresponding coomassie blue stained lane. Each point represents a patient and the horizontal bar is the average. *p<0.05. Other symbols are as in Fig. 1.
PA28α and PA700 levels are also diminished in MS
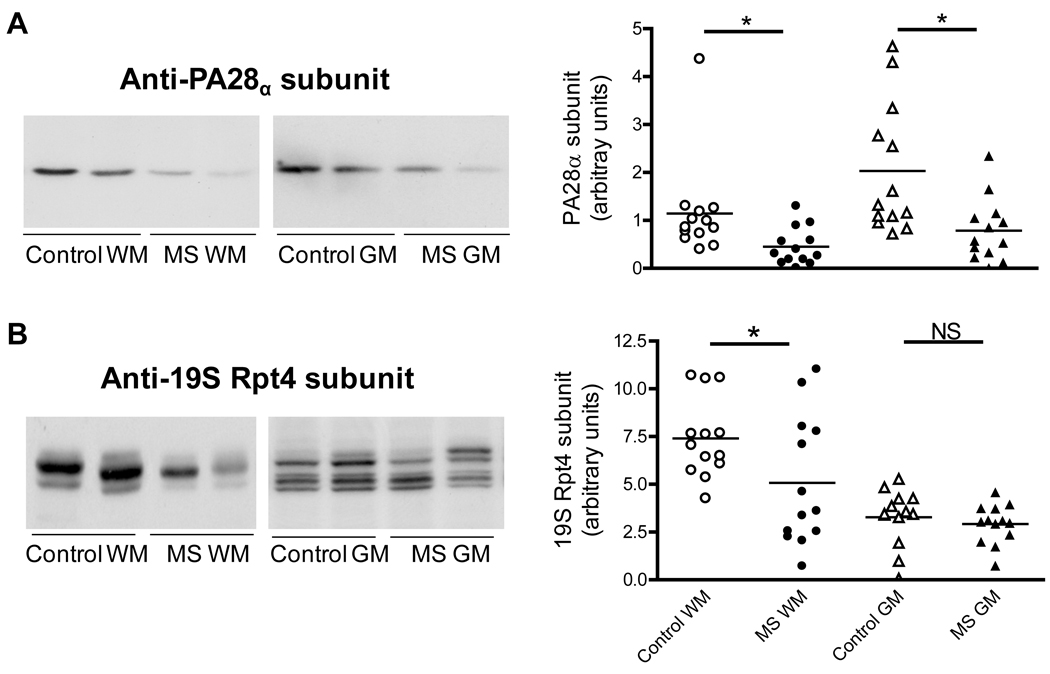
The 20S proteasome may associate with the PA28 and PA700 regulators, which are known to increase the proteolytic activity of the core particle (DeMartino & Slaughter 1999). There are three PA28 (11S) homologues, named α, β and γ. The α and β subunits form a heteroheptamer while the γ subunit forms a homoheptamer that is confined to the cell nucleus. The PA28β subunit is virtually absent from the brain (Rechsteimer & Hill 2005) but the α subunit is present and can assemble to form a PA28α homoheptamer that has also the capacity to activate the 20S proteasome (Realini et al 1997). For this reason we decided to assess the levels of PA28α in MS and controls samples. The results show a decrease of ~50% in the amount of PA28α in the MS-WM and MS-GM with respect to their controls (Fig. 5A). The relative levels of PA700 (19S) in MS and control homogenates were determined also by western blot analysis employing an antibody that recognizes the Rpt4/S10b subunit (ATPase subunit) in this activator. The results clearly show a reduction in PA700 (19S) levels only in the MS-WM (Fig. 5B). It is important to note that the reduced peptidolytic activities of the 20S proteasome in MS are not a consequence of decreased levels of the activators PA28α and PA700, since under the incubation conditions used in this study (i.e. without ATP or magnesium ions and in the presence of 0.03% sodium dodecyl sulfate) these caps are not attached to the catalytic particle (Rivett et al 2002). In vivo, however, these regulators may be largely bound to the 20S proteasome, suggesting that the activity of larger proteasomes (i.e. 26S, 11S-20S and hybrid 19S-20S-11S) in MS may be reduced more than that of the free 20S particle.
Fig. 5.
Changes in the levels of the proteasomal regulators 11S and 19S in MS. Left two panels show representative immunoblots from homogenates of brain WM and GM areas of control and MS patients developed with antibodies against the PA28α subunit of the 11S particle (A) and the Rpt4 subunit of the 19S particle (B). Right panels depict the corresponding levels of each of these subunits, which were calculated by dividing the band intensity on the western blot by that of the corresponding coomassie blue stained lane. Each point represents a patient and the horizontal bar is the average. *p<0.05. Other symbols are as in Fig. 1. Removal of the potential outlier in the scattered plot (panel A, control WM) does not alter the statistically significant difference between control and MS WM. The presence of multiple bands observed in the immunoblot of GM samples (panel B) is noteworthy and likely due to the various phosphorylation states of Rpt4 (Ferrell et al 2000).
Calpain activity and expression are significantly upregulated in MS brains
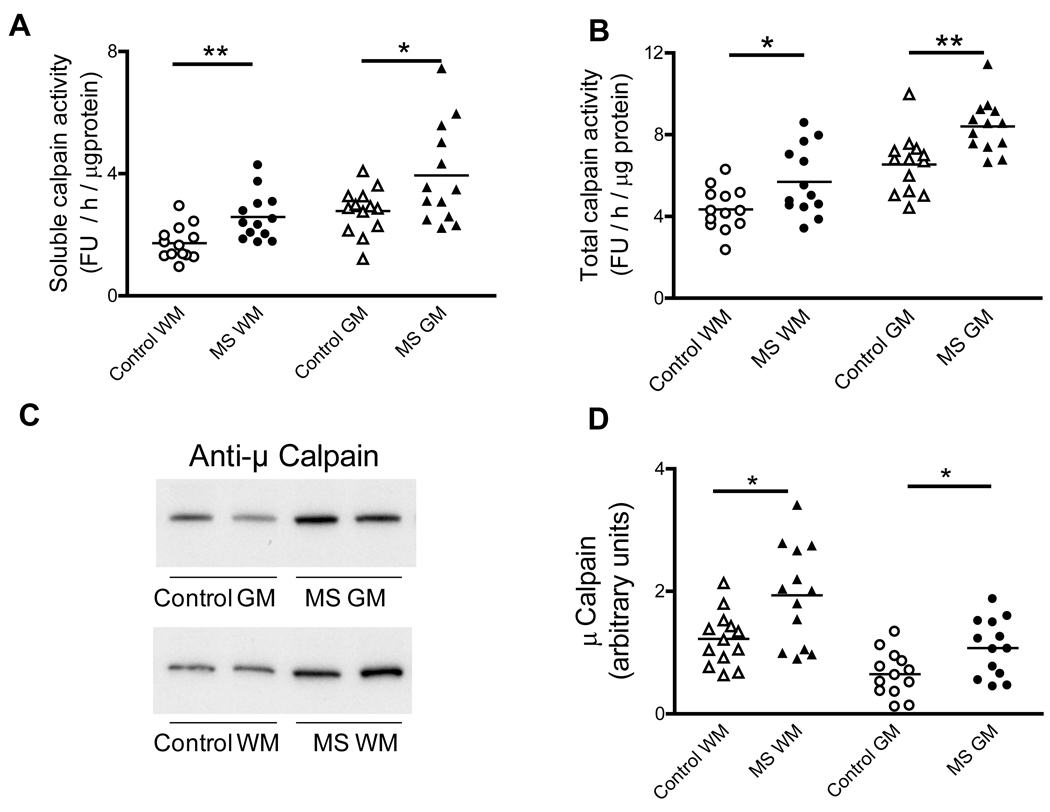
The activities/levels of the three other proteolytic systems that might potentially remove oxidized proteins (calpain, lysosomal cathepsins, mitochondrial LON protease) were also determined in control and MS tissues. Calpain is normally present as a membrane-bound pro-enzyme containing an 80kDa catalytic subunit that undergoes auto-proteolytic cleavage upon calcium activation, thus releasing the 75-kDa active calpain into the cytosol (Shield et al 1999). As shown in Fig. 6A–B, the total and the soluble (active) calpain activity are elevated in both the WM and GM of MS patients relative to their controls. Levels of total calpain-1 (µ-calpain) were determined in the brain homogenates from MS and control patients by western blotting. As depicted in Fig. 6C–D, total calpain levels in the MS-WM and MS-GM are increased by 54% and 67%, respectively. These data indicate that the enhancement in calpain activity in MS tissues is mostly due to an increase in the amount of enzyme.
Fig. 6.
Calpain activity and levels are increased in MS. Aliquots of the cerebral homogenates from control and MS patients were used to determine the soluble (active) (A) and total calpain activity (B) using a fluorescent peptide substrate as described in “Materials and Methods”. Enzyme activity values are expressed as fluorescence units (FU) / hour / µg protein. (C) Representative immunoblots from homogenates of brain WM and GM areas of control and MS patients developed with antibodies against µ-calpain. (D) The relative levels of µ-calpain were calculated by dividing the band intensity on the western blot by that of the corresponding coomassie blue stained lane. Each point represents a patient and the horizontal bar is the average. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. Other symbols are as in Fig. 1.
Lysosomal proteolytic activity is increased in MS
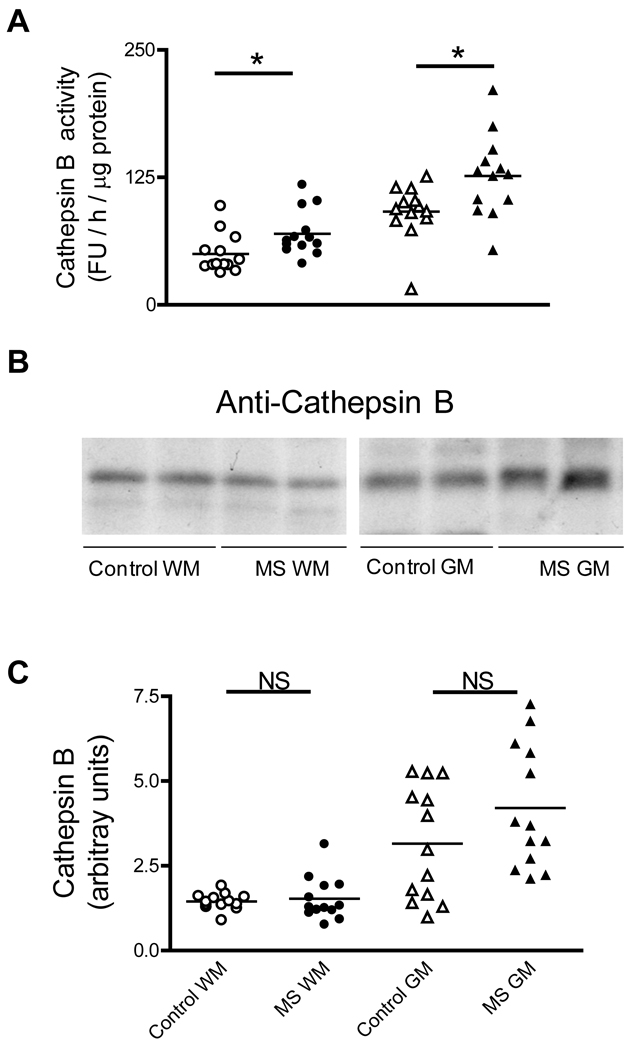
The proteolytic activity of the lysosome was also tested in MS patients. The activity of cathepsin B, one of the major lysosomal proteases, was assayed with the z-Phe-Arg-AMC peptide at acid pH. Measured under these conditions, the lysosomal proteolytic activity in MS-WM and MS-GM increases by 40% and 38% (Fig. 7A). Levels of the 31kDa form of cathepsin B, as determined by western blot analysis, are mostly unchanged in MS-WM and MS-GM relative to their controls (Fig. 7 B–C).
Fig. 7.
Cathepsin B activity is increased in MS-WM and MS-GM. (A) Aliquots of the cerebral homogenates from control and MS patients were used to determine cathepsin B activity with a specific fluorescent peptide substrate at acid pH as described in “Materials and Methods”. Enzyme activity values are expressed as fluorescence units (FU) / hour / µg protein. (B) Representative immunoblots from homogenates of brain WM and GM areas of control and MS patients developed with an anti-cathepsin B antibody. (C) The relative levels of 31kDa form of cathepsin B were calculated by dividing the band intensity on the western blot by that of the corresponding coomassie blue stained lane. Each point represents a patient and the horizontal bar is the average. *p<0.05. Other symbols are as in Fig. 1.
Levels of Lon protease are unaltered in MS
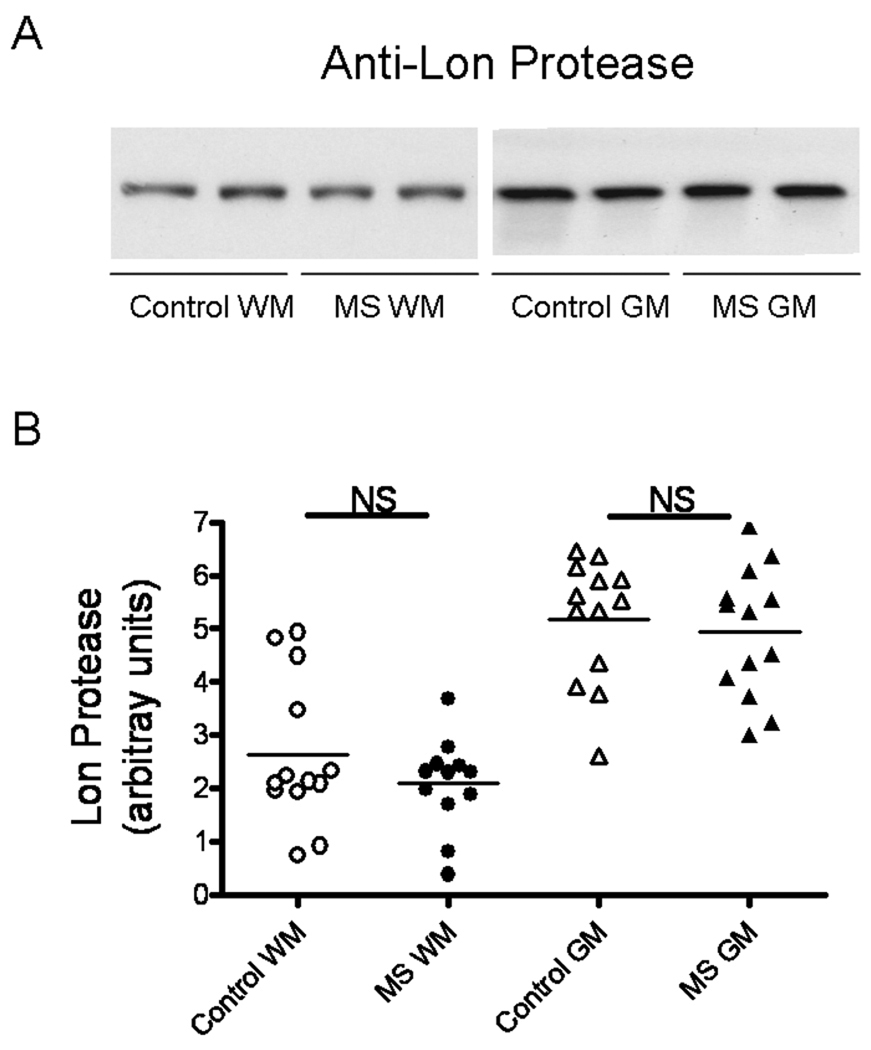
Lon is a proteasome-like protease localized in mitochondrial matrix and responsible for the removal of oxidized proteins within this organelle (Bota & Davies 2002). Therefore, it is unlikely that a deficiency in the activity of the Lon protease in MS would result in the accumulation of carbonylated cytoskeletal proteins that we have observed (Hilgart and Bizzozero 2008). Nonetheless, since Lon protease levels are known to decrease during aging and in several CNS disorders (Ugarte et al 2010), we sough to investigate its potential role in MS. As shown in Fig. 8, western blot analysis clearly shows that the amount of this protease in both MS-WM and MS-GM are the same as that in control specimens.
Fig. 8.
Levels of the mitochondrial LON protease are unchanged in MS. (A) Representative immunoblots from homogenates of brain WM and GM areas of control and MS patients developed with an antibody against LONp1. (B) The relative levels of Lon protease were calculated by dividing the band intensity on the western blot by that of the corresponding coomassie blue stained lane. Each point represents a patient and the horizontal bar is the average. Other symbols are as in Fig. 1.
Discussion
In this study we report that the peptidase activities present in the β1, β2 and β5 subunits of the 20S proteasome are greatly reduced in both the WM and GM of MS patients as compared to controls. Based on the quantification of the constitutive 20S proteasome α subunit by western blotting, we conclude that changes in proteasomal activity are not due to a decline in the number of 20S proteasome particles. More importantly, altered activities are not the result of decreased levels of the three catalytic subunits (Fig. 4). Indeed, the amount of the β1 and β2 subunits is increased in both MS-WM and MS-GM, perhaps as a result of compensatory mechanisms. Altogether these findings suggest that the activity of these proteases in MS are inhibited, a phenomenon that we have recently also observed in the chronic phase of MOG35–55 peptide-induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (Zheng & Bizzozero 2010b). Levels of the activators PA28α and PA700 are also lessened in the CNS of MS patients, indicating that the catalytic efficiency of larger proteasome particles are also affected in this disorder.
Several posttranslational modifications of the 20S subunits that are capable of reducing proteasomal activities have been discovered in oxidative stress paradigms. For example, proteasomal activity can be impaired by direct carbonylation (Kessova & Cederbaum 2005) or by modification with 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (Farout et al 2006), acrolein (Shamoto-Nagai et al 2003), glyoxal (Bulteau et al 2001), γ-ketoaldehydes (isoketals) (Davies et al 2002) and nitric oxide (Glockzin et al 1999). Direct inactivation of the proteasome by 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal cross-linked proteins (Friguet et al 1994) and lipofuscin/ceroid fluorescent pigments (Sitte et al 2000) have been also implicated in the inhibition of the 20S proteasome. An additional and still unexplored possibility might be proteasome inactivation by specific autoantibodies. Interestingly, antibodies against several proteasome subunits have been detected in serum and CSF from MS patients (Mayo et al 2002). It will be important to know if proteasome autoantibodies are also present in the diseased brain and are indeed capable of causing enzyme inhibition. Finally, the presence of endogenous negative regulators such as hsp90, PI31 and PR39 (Rechsteimer & Hill 2005) cannot be ruled out as the underlying cause for proteasomal impairment in MS. Studies are underway in this laboratory to identify potential inhibitors and the role of other regulators (e.g. PA200) using both cell extracts and purified proteasome particles from MS brain samples.
While impaired proteasomal activity has been reported in several neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease (Keller et al 2000), Parkinson’s disease (McNaught et al 2003) and Huntington’s disease (Seo et al 2004), this is the first study to demonstrate proteasome dysfunction in a human demyelinating disorder. Whether an identical mechanism causes proteasome dysfunction in chronic MS and the other neurodegenerative disorders is presently unclear. Yet, it is noteworthy that in all of these diseases the failure of the peptidase activities is not related to low levels of proteasome particles or their catalytic subunits. The pathophysiological consequences of decreased proteasomal activity in chronic MS as well as in classical neurodegenerative disorders are unknown. The structural and functional impact resulting from the accumulation of a number of ubiquitinated, misfolded, aggregated and oxidized proteins, along with reduced degradation of various signaling and pro-apoptotic molecules, are likely widespread and difficult to predict. However, decreased proteasomal activity is likely to be pathogenic and a contributor to neurodegeneration in MS. This notion is based mostly on experiments linking pharmacological inhibition of the proteasome catalytic core to axonal damage (Korhonen & Lindholm 2004), the development of pro-inflammatory responses via up-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E2 (Rockwell et al 2000) and apoptosis of neurons and oligodendrocytes via mitochondrial dysfunction (Goldbaum et al 2006), all of which are characteristics of chronic MS.
There is general agreement that oxidized proteins are degraded by the 20S proteasome via an ATP-independent mechanism (Rivett 1985; Pacifici et al 1993; Grune et al 1995; Shringarpure et al 2003; Divald & Powell 2006). However, there have been some reports suggesting that other proteases may be also involved in the degradation of carbonylated polypeptides. For example, the calcium-dependent cysteine protease calpain has been found to preferentially degrade oxidized neurofilaments over the non-oxidized protein forms in cell-free systems (Troncoso et al 1995) and there is some evidence that heavily oxidized proteins can be taken up by lysosomes, where in some cases are incompletely degraded and accumulate in the form of lipofuscin-like, autofluorescent aggregates (Dunlop et al 2009). Furthermore, in epithelial cells some of the 4-hydroxynonenal-modified proteins are degraded in the lysosome via an ubiquitin-dependent mechanism (Marques et al 2004). Due to these observations, we felt compelled to determine the enzymatic activities of these proteolytic systems in MS. In our study, we found that both the total and soluble calpain activities are increased in MS patients. Elevation of calpain activity seems to be due to an increase in its translational expression. Interestingly, calpain activity and expression is not only increased MS-WM, as reported earlier (Shields et al 1999), but also in the MS-GM, suggesting that extensive calcium dysregulation also occurs in this CNS area. We also found that the activity of cathepsin B, the major lysosomal protease, is elevated in MS. As suggested by Pandley et al (2007), an increase in the lysosomal degradation machinery when the proteasome system is not functioning may represent a compensatory mechanism for intracellular protein degradation. Finally, the relative amount of the Lon protease, an enzyme that specifically degrades oxidized mitochondrial proteins by an ATP-stimulated mechanism (Bota & Davies 2002; Ugarte et al 2010), was unaltered in MS. Thus, of the several proteolytic systems studied in post-mortem MS brains only the proteasome was found to be impaired. Proteasome failure explains the accumulation of both carbonylated proteins (Bizzozero et al 2005b) and ubiquitin-conjugates (Giordana et al 2002; this study) in chronic MS tissue.
Finally, it is important to emphasize that the pathological specimens analyzed in this study are mainly from patients with chronic MS and that a different pattern of proteasomal proteolytic activity may exist early in the disease, where inflammation rather than neurodegeneration is the main feature. Indeed, a substantial increase in proteasomal activity has been found in the acute, inflammatory phase of EAE, which seems to be due to over-expression of the IFN-γ-inducible forms of β subunits (a.k.a. iβ subunits) (Fissolo et al 2008). More recently, our laboratory reported that the proteasome trypsin-like and chymotrypsin-like activities augment in acute EAE (Zheng & Bizzozero 2010b), a change that likely arises from the replacement of the classical catalytic subunits by iβ1, iβ2 and iβ5. However, we also found that in the late stages of EAE, like in chronic MS, the activity of peptidases of the 20S proteasome decline. In the future, it will be important to determine the precise time during the course of EAE at which reversal of proteasome activity takes place as well as its underlying mechanism(s).
Acknowledgements
Post-mortem brain samples from control and MS patients were kindly provided by the Rocky Mountain MS Center (Englewood, CO) and by the Human Brain and Spinal Fluid Resource Center (Los Angeles, CA), which is sponsored by NINDS/NIMH, the National Multiple Sclerosis Society and the Department of Veteran Affairs. This work was supported by PHHS grant NS057755 from the National Institutes of Health.
Abbreviations
- AMC
7-aminomethyl-4-coumarin
- GM
cerebral gray matter without any visible lesion
- PA28
11S regulatory particle
- PA700
19S regulatory particle
- PMI
post-mortem interval
- MS
multiple sclerosis
- WM
cerebral white matter without any visible lesion
Footnotes
Disclosure/conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
References
- Bizzozero OA, DeJesus G, Bixler HA, Pastuszyn A. Evidence of nitrosative damage in the brain white matter of patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurochem. Res. 2005a;30:139–149. doi: 10.1007/s11064-004-9695-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bizzozero OA, DeJesus G, Callahan K, Pastuszyn A. Elevated protein carbonylation in the brain white matter and gray matter of patients with multiple sclerosis. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005b;81:687–695. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bizzozero OA. Protein carbonylation in neurodegenerative and demyelinating CNS diseases. In: Lajtha A, Banik N, Ray S, editors. Handbook of Neurochemistry and Molecular Neurobiology. New York, NY: Springer; 2009. pp. 543–562. [Google Scholar]
- Bota DA, Davies KJ. Lon protease preferentially degrades oxidized mitochondrial aconitase by an ATP-stimulated mechanism. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002;4:674–680. doi: 10.1038/ncb836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulteau AL, Verbeke P, Petropoulos I, Chaffotte AF, Friguet B. Proteasome inhibition in glyoxal-treated fibroblasts and resistance of glycated glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase to 20S proteasome degradation in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:45662–45668. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M105374200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coux O, Tanaka K, Goldberg AL. Structure and functions of the 20S and 26S proteasomes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1996;65:801–847. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.65.070196.004101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies SS, Amarnath V, Montine KS, Bernoud-Hubac N, Boutaud O, Montine TJ, Roberts LJ. Effects of reactive γ-ketoaldehydes formed by the isoprostane pathway (isoketals) and cyclooxygenase pathway (levuglandins) on proteasome function. FASEB J. 2002;16:715–717. doi: 10.1096/fj.01-0696fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMartino GN, Slaughter CA. The proteasome, a novel protease regulated by multiple mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:22123–22136. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.32.22123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divald A, Powell SR. Proteasome mediates removal of proteins oxidized during myocardial ischemia. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006;40:156–164. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.09.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop RA, Brunk UT, Rodgers KJ. Oxidized proteins: mechanisms of removal and consequences of accumulation. IUBMB Life. 2009;61:522–527. doi: 10.1002/iub.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farout L, Mary J, Vinh J, Szweda LI, Friguet B. Inactivation of the proteasome by 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal is site specific and dependent on 20S proteasome subtypes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2006;453:135–142. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2006.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell K, Wilkinson CR, Dubiel W, Gordon C. Regulatory subunit interactions of the 26S proteasome, a complex problem. TIBS. 2000;25:83–88. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(99)01529-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrington DA, Husom AD, Thompson LV. Altered proteasome structure, function and oxidation in aged muscle. FASEB J. 2005;19:644–646. doi: 10.1096/fj.04-2578fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fissolo N, Kraus M, Reich M, Ayturan M, Overkleeft H, Driessen C, Weissert R. Dual inhibition of proteasomal and lysosomal proteolysis ameliorates autoimmune central nervous system inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008;38:2401–2411. doi: 10.1002/eji.200838413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friguet B, Stadman ER, Szweda LI. Modification of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase by 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal: Formation of cross-linked protein that inhibits the multicatalytic protease. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:21639–21643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordana MT, Richiardi P, Trevisan E, Boghi A, Palmucci L. Abnormal ubiquitination of axons in normally myelinated white matter in multiple sclerosis brain. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2002;28:35–41. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2990.2002.00372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman MH, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway: destruction for the sake of construction. Physiol. Rev. 2002;82:373–428. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00027.2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glockzin S, von Knethen A, Scheffner M, Brune B. Activation of the cell death program by nitric oxide involves inhibition of the proteasome. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:19581–19586. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.28.19581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldbaum O, Vollmer G, Richter-Landsberg C. Proteasome inhibition by MG-132 induces apoptotic cell death and mitochondrial dysfunction in cultured rat brain oligodendrocytes but not in astrocytes. Glia. 2006;53:891–901. doi: 10.1002/glia.20348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grune T, Reinheckel T, Joshi M, Davies KJ. Proteolysis in cultured liver epithelial cells during oxidative stress. Role of the multicatalytic proteinase complex, proteasome. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:2344–2351. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.5.2344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grune T, Shringarpure R, Sitte N, Davies KJ. Age-related changes in protein oxidation and proteolysis in mammalian cells. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2001;56:459–467. doi: 10.1093/gerona/56.11.b459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassen GW, Feliberti J, Kesner L, Stracher A, Mokhtarian F. A novel calpain inhibitor for the treatment of acute experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2006;180:135–146. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2006.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilgart AA, Bizzozero OA. Carbonylation of major cytoskeletal proteins in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurochem. 2008;104 Suppl. 1 PTW06-03. [Google Scholar]
- Husted CA, Goodin DS, Hugg JW, Maudsley AA, Tsuruda JS, de Bie SH, Fein G, Matson GB, Weiner MW. Biochemical alterations in multiple sclerosis lesions and normal-appearing white matter detected by in vivo 31P and 1H spectroscopic imaging. Ann. Neurol. 1994;36:157–165. doi: 10.1002/ana.410360207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller JN, Hanni KB, Marksberry WR. Impaired proteasome function in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2000;75:436–439. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0750436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessova IG, Cederbaum AI. The effect of CYP2E1-dependent oxidant stress on activity of proteasomes in HepG2 cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005;315:304–312. doi: 10.1124/jpet.105.088047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen L, Lindholm D. The ubiquitin proteasome system in synaptic and axonal degeneration. J. Cell Biol. 2004;165:27–30. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200311091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornek B, Lassmann H. Axonal pathology in multiple sclerosis: a historical note. Brain Pathol. 1999;9:651–656. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1999.tb00547.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchinetti CF, Bruck W, Rodriguez M, Lassmann H. Distinct patterns of multiple sclerosis pathology indicate heterogeneity in pathogenesis. Brain Pathol. 1996;6:259–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1996.tb00854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marques C, Pereira P, Taylor A, Liang JN, Reddy VN, Szweda LI, Shang F. Ubiquitin-dependent lysosomal degradation of the HNE-modified proteins in lens epithelial cells. FASEB J. 2004;18:1424–1426. doi: 10.1096/fj.04-1743fje. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo I, Arribas J, Villoslada P, Alvarez DoForno R, Rodríguez-Vilariño S, Montalban X, De Sagarra MR, Castaño JG. The proteasome is a major autoantigen in multiple sclerosis. Brain. 2002;125:2658–2667. doi: 10.1093/brain/awf274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNaught KS, Belizaire R, Isacson O, Jenner P, Olanow CW. Altered proteasomal function in sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2003;179:38–46. doi: 10.1006/exnr.2002.8050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata S, Yashiroda H, Tanaka K. Molecular mechanism of proteasome assembly. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009;10:104–115. doi: 10.1038/nrm2630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacifici RE, Kono Y, Davies KJ. Hydrophobicity as the signal for selective degradation of hydroxyl radical-modified hemoglobin by the multicatalytic proteinase complex, proteasome. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:15405–15411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey UB, Nie Z, Batlevi Y, McCray B, Ritson GP, Nedelsky NB, Schwartz SL, DiProspero N, Knight MA, Schuldiner O, Padmanabhan R, Hild M, Berry DL, Garza D, Hubbert CC, Yao T, Baehrecke EH, Taylor JP. HDAC6 rescues neurodegeneration and provides an essential link between autophagy and the UPS. Nature. 2007;447:860–864. doi: 10.1038/nature05853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Realini C, Jensen CC, Zhang Z, Johnston SC, Knowlton JR, Hill CP, Rechsteiner M. Characterization of recombinant REGalpha, REGbeta, and REGgamma proteasome activators. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:25483–25492. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.41.25483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechsteimer M, Hill CP. Mobilizing the proteolytic machine: cell biological roles of proteasome activators and inhibitors. Trends Cell Biol. 2005;15:27–33. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2004.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivett AJ. Preferential degradation of the oxidatively modified form of glutamine synthetase by intracellular mammalian proteases. J. Biol. Chem. 1985;260:300–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivett AJ, Bose S, Pemberton AJ, Brooks P, Onion D, Shirley D, Stratford FL, Forti K. Assays of proteasome activity in relation to aging. Exp. Gerontol. 2002;37:1217–1222. doi: 10.1016/s0531-5565(02)00127-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockwell P, Yuan H, Magnusson R, Figueiredo-Pereira ME. Proteasome inhibition in neuronal cells induces a proinflammatory response manifested by upregulation of cyclooxygenase-2, its accumulation as ubiquitin conjugates, and production of the prostaglandin PGE(2) Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000;374:325–333. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1999.1646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers KJ, Dean RT. Assessment of proteasome activity in cell lysates and tissue homogenates using peptide substrates. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2003;35:716–727. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(02)00391-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seo H, Sonntag KC, Isacson O. Generalized brain and skin proteasome inhibition in Huntington’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2004;56:319–328. doi: 10.1002/ana.20207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamoto-Nagai M, Maruyama W, Kato Y, Isobe K, Tanaka M, Naoi M, Osawa T. An inhibitor of mitochondrial complex I, rotenone, inactivates proteasome by oxidative modification and induces aggregation of oxidized proteins in SH-SY5Y cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 2003;74:589–597. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma R, Narayama PA, Wolinsky JS. Gray matter abnormalities in multiple sclerosis: proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. Mult. Scler. 2001;7:221–226. doi: 10.1177/135245850100700402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields DC, Schaecher KE, Saido TC, Banik NL. A putative mechanism of demyelination in multiple sclerosis by a proteolytic enzyme, calpain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1999;96:11486–11491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.20.11486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shringarpure R, Grune T, Mehlhase J, Davies KJ. Ubiquitin conjugation is not required for the degradation of oxidized proteins by proteasome. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:311–318. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M206279200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitte N, Huber M, Grune T, Ladhoff A, Doecke W, Von Zglinicki T, Davies JA. Proteasome inhibition by lipofuscin/ceroid during postmitotic aging of fibroblasts. FASEB J. 2003;14:1490–1498. doi: 10.1096/fj.14.11.1490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smerjac SM, Bizzozero OA. Cytoskeletal protein carbonylation and degradation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neurochem. 2008;105:763–772. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05178.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. Demyelination: the role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Brain Pathol. 1999;9:69–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1999.tb00212.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troncoso JC, Costello AC, Kim JH, Johnson GV. Metal-catalyzed oxidation of bovine neurofilaments in vitro. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1995;18:891–899. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(94)00224-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugarte N, Petropoulos I, Friguet B. Oxidized mitochondrial protein degradation and repair in aging and oxidative stress. Antiox. Redox. Signal. 2010;13:539–549. doi: 10.1089/ars.2009.2998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng J, Bizzozero OA. Accumulation of protein carbonyls within cerebellar astrocytes in murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010a;88:3376–3385. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng J, Bizzozero OA. Reduced proteasomal activity contributes to accumulation of carbonylated proteins within cerebellar astrocytes in chronic EAE. J. Neurochem. 2010b;115:1556–1567. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07062.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]