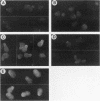
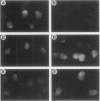
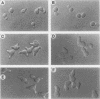
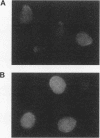
Abstract
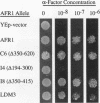
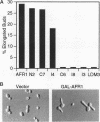
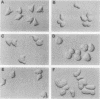
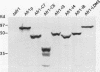
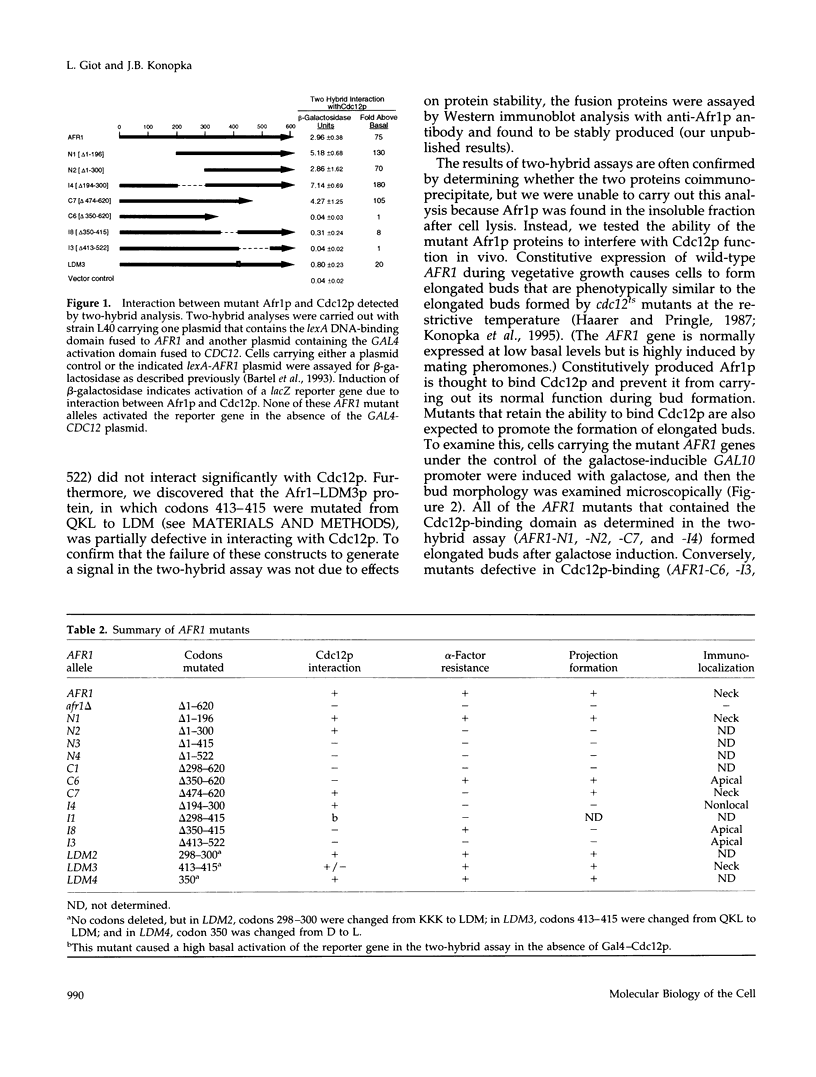
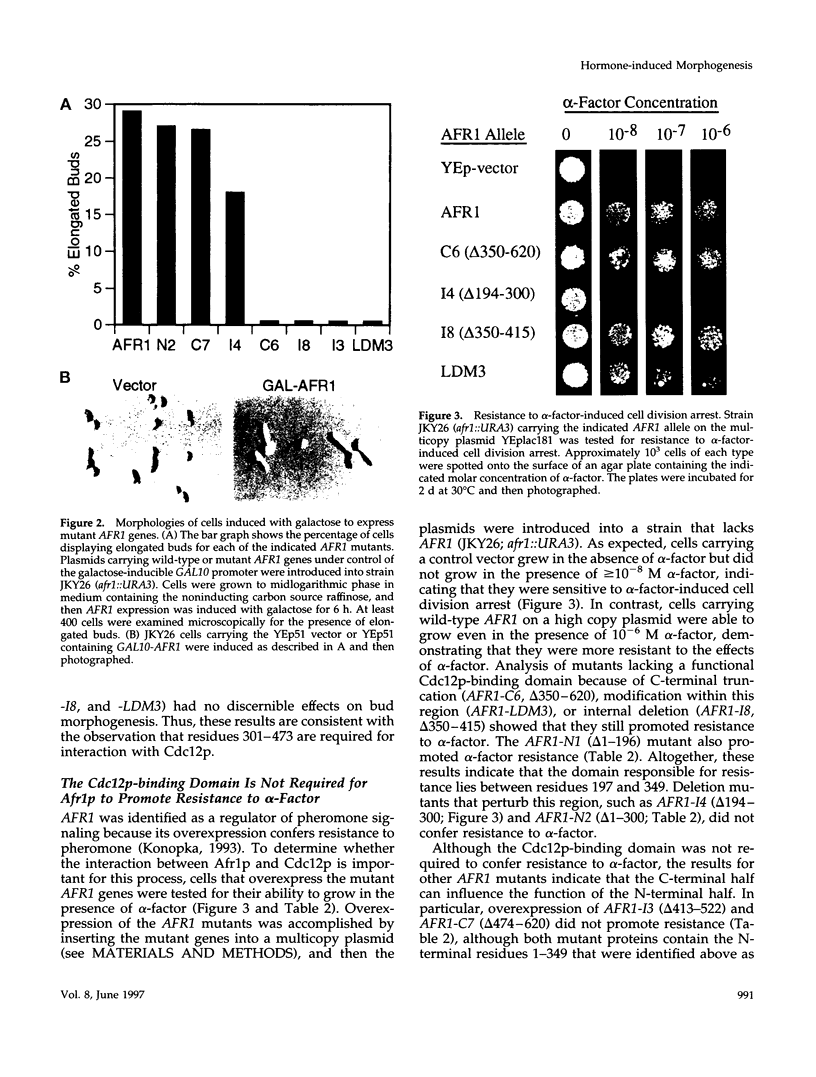
Saccharomyces cerevisiae mating pheromones induce production of Afr1p, a protein that negatively regulates pheromone receptor signaling and is required for normal formation of the projection of cell growth that becomes the site of cell fusion during conjugation. Afr1p interacts with Cdc12p, which belongs to a family of filament-forming proteins termed septins that have been studied primarily for their role in bud morphogenesis and cytokinesis. The significance of the interaction between Afr1p and Cdc12p was tested in this study by examining the effects of AFR1 mutations that destroy the Cdc12p-binding domain. The results demonstrate that sequences in the C-terminal half of Afr1p are required for interaction with Cdc12p and for proper localization of Afr1p to the base of the mating projection. However, the Cdc12p-binding domain was not required for regulation of receptor signaling or for mating projection formation. This result was surprising because cells carrying a temperature-sensitive cdc12-6 mutation were defective in projection formation, indicating a role for Cdc12p in this process. Although the Cdc12p-binding domain was no essential for Afr1p function, this domain did improve the ability of Afr1p to promote morphogenesis, suggesting that the proper localization of Afr1p is important for its function.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A. E., Johnson D. I., Longnecker R. M., Sloat B. F., Pringle J. R. CDC42 and CDC43, two additional genes involved in budding and the establishment of cell polarity in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;111(1):131–142. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams A. E., Pringle J. R. Relationship of actin and tubulin distribution to bud growth in wild-type and morphogenetic-mutant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):934–945. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blacketer M. J., Madaule P., Myers A. M. Mutational analysis of morphologic differentiation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1995 Aug;140(4):1259–1275. doi: 10.1093/genetics/140.4.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers B., Goetsch L. A highly ordered ring of membrane-associated filaments in budding yeast. J Cell Biol. 1976 Jun;69(3):717–721. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.3.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chant J., Mischke M., Mitchell E., Herskowitz I., Pringle J. R. Role of Bud3p in producing the axial budding pattern of yeast. J Cell Biol. 1995 May;129(3):767–778. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chant J. Septin scaffolds and cleavage planes in Saccharomyces. Cell. 1996 Jan 26;84(2):187–190. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80972-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Q., Konopka J. B. Regulation of the G-protein-coupled alpha-factor pheromone receptor by phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Jan;16(1):247–257. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenevert J. Cell polarization directed by extracellular cues in yeast. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Nov;5(11):1169–1175. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.11.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cvrcková F., De Virgilio C., Manser E., Pringle J. R., Nasmyth K. Ste20-like protein kinases are required for normal localization of cell growth and for cytokinesis in budding yeast. Genes Dev. 1995 Aug 1;9(15):1817–1830. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.15.1817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman H. G., Thorner J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Model systems for the study of seven-transmembrane-segment receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:653–688. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorer R., Pryciak P. M., Hartwell L. H. Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells execute a default pathway to select a mate in the absence of pheromone gradients. J Cell Biol. 1995 Nov;131(4):845–861. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.4.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G., Nelson W. J. Origins of cell polarity. Cell. 1996 Feb 9;84(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81278-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fares H., Goetsch L., Pringle J. R. Identification of a developmentally regulated septin and involvement of the septins in spore formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1996 Feb;132(3):399–411. doi: 10.1083/jcb.132.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fares H., Peifer M., Pringle J. R. Localization and possible functions of Drosophila septins. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Dec;6(12):1843–1859. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.12.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field C. M., al-Awar O., Rosenblatt J., Wong M. L., Alberts B., Mitchison T. J. A purified Drosophila septin complex forms filaments and exhibits GTPase activity. J Cell Biol. 1996 May;133(3):605–616. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.3.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):245–246. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flescher E. G., Madden K., Snyder M. Components required for cytokinesis are important for bud site selection in yeast. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(2):373–386. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford S. K., Pringle J. R. Cellular morphogenesis in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell cycle: localization of the CDC11 gene product and the timing of events at the budding site. Dev Genet. 1991;12(4):281–292. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020120405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz R. D., Sugino A. New yeast-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors constructed with in vitro mutagenized yeast genes lacking six-base pair restriction sites. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):527–534. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90185-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haarer B. K., Pringle J. R. Immunofluorescence localization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CDC12 gene product to the vicinity of the 10-nm filaments in the mother-bud neck. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3678–3687. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Genetic control of the cell division cycle in yeast. IV. Genes controlling bud emergence and cytokinesis. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Dec;69(2):265–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90223-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler J. R., Gilman A. G. G proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):383–387. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90005-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. MAP kinase pathways in yeast: for mating and more. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):187–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90402-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. L., Konopka J. B., Hartwell L. H. S. cerevisiae alpha pheromone receptors activate a novel signal transduction pathway for mating partner discrimination. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):389–402. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90190-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. B., Haarer B. K., Pringle J. R. Cellular morphogenesis in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell cycle: localization of the CDC3 gene product and the timing of events at the budding site. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):535–544. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka J. B. AFR1 acts in conjunction with the alpha-factor receptor to promote morphogenesis and adaptation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):6876–6888. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.6876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka J. B., DeMattei C., Davis C. AFR1 promotes polarized apical morphogenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;15(2):723–730. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.2.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka J. B., Jenness D. D., Hartwell L. H. The C-terminus of the S. cerevisiae alpha-pheromone receptor mediates an adaptive response to pheromone. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):609–620. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J. Pheromone response in yeast. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1097–1129. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leberer E., Dignard D., Harcus D., Thomas D. Y., Whiteway M. The protein kinase homologue Ste20p is required to link the yeast pheromone response G-protein beta gamma subunits to downstream signalling components. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4815–4824. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05587.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longtine M. S., DeMarini D. J., Valencik M. L., Al-Awar O. S., Fares H., De Virgilio C., Pringle J. R. The septins: roles in cytokinesis and other processes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996 Feb;8(1):106–119. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(96)80054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden K., Snyder M. Specification of sites for polarized growth in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the influence of external factors on site selection. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Sep;3(9):1025–1035. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.9.1025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh L., Neiman A. M., Herskowitz I. Signal transduction during pheromone response in yeast. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:699–728. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. A. Comparison of dose-response curves for alpha factor-induced cell division arrest, agglutination, and projection formation of yeast cells. Implication for the mechanism of alpha factor action. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13849–13856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulholland J., Preuss D., Moon A., Wong A., Drubin D., Botstein D. Ultrastructure of the yeast actin cytoskeleton and its association with the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(2):381–391. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P. M. The molecular biology of leukocyte chemoattractant receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:593–633. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld T. P., Rubin G. M. The Drosophila peanut gene is required for cytokinesis and encodes a protein similar to yeast putative bud neck filament proteins. Cell. 1994 May 6;77(3):371–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. R., Adams A. E., Drubin D. G., Haarer B. K. Immunofluorescence methods for yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:565–602. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94043-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read E. B., Okamura H. H., Drubin D. G. Actin- and tubulin-dependent functions during Saccharomyces cerevisiae mating projection formation. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Apr;3(4):429–444. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.4.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roemer T., Madden K., Chang J., Snyder M. Selection of axial growth sites in yeast requires Axl2p, a novel plasma membrane glycoprotein. Genes Dev. 1996 Apr 1;10(7):777–793. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.7.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Broach J. R. Cloning genes by complementation in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:195–230. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders S. L., Field C. M. Cell division. Septins in common? Curr Biol. 1994 Oct 1;4(10):907–910. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00201-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders S. L., Herskowitz I. The BUD4 protein of yeast, required for axial budding, is localized to the mother/BUD neck in a cell cycle-dependent manner. J Cell Biol. 1996 Jul;134(2):413–427. doi: 10.1083/jcb.134.2.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiestl R. H., Gietz R. D. High efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells using single stranded nucleic acids as a carrier. Curr Genet. 1989 Dec;16(5-6):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00340712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J. E. Polarization of yeast cells in spatial gradients of alpha mating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8332–8336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman F. Getting started with yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:3–21. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94004-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. N., De Virgilio C., Souza B., Pringle J. R., Abo A., Reed S. I. Role for the Rho-family GTPase Cdc42 in yeast mating-pheromone signal pathway. Nature. 1995 Aug 24;376(6542):702–705. doi: 10.1038/376702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtz N., Peter M., Herskowitz I. FAR1 is required for oriented polarization of yeast cells in response to mating pheromones. J Cell Biol. 1995 Nov;131(4):863–873. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.4.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Z. S., Leung T., Manser E., Lim L. Pheromone signalling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires the small GTP-binding protein Cdc42p and its activator CDC24. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;15(10):5246–5257. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.10.5246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziman M., Preuss D., Mulholland J., O'Brien J. M., Botstein D., Johnson D. I. Subcellular localization of Cdc42p, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae GTP-binding protein involved in the control of cell polarity. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Dec;4(12):1307–1316. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.12.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]