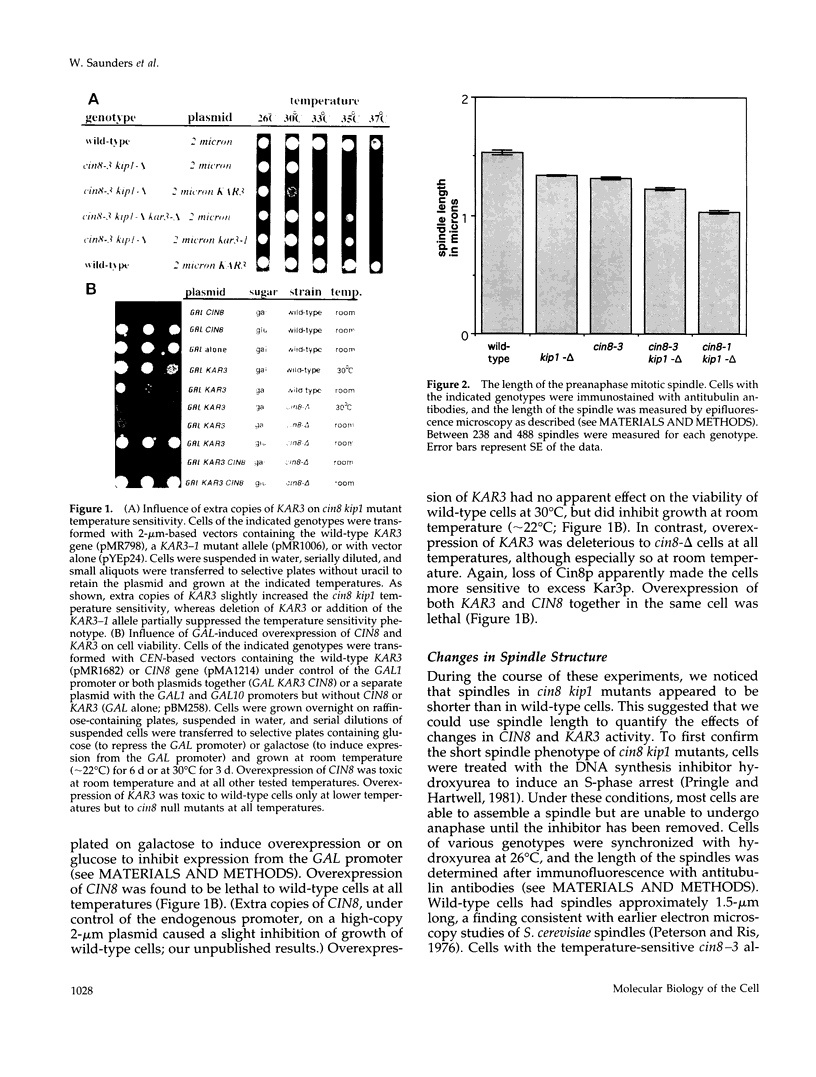
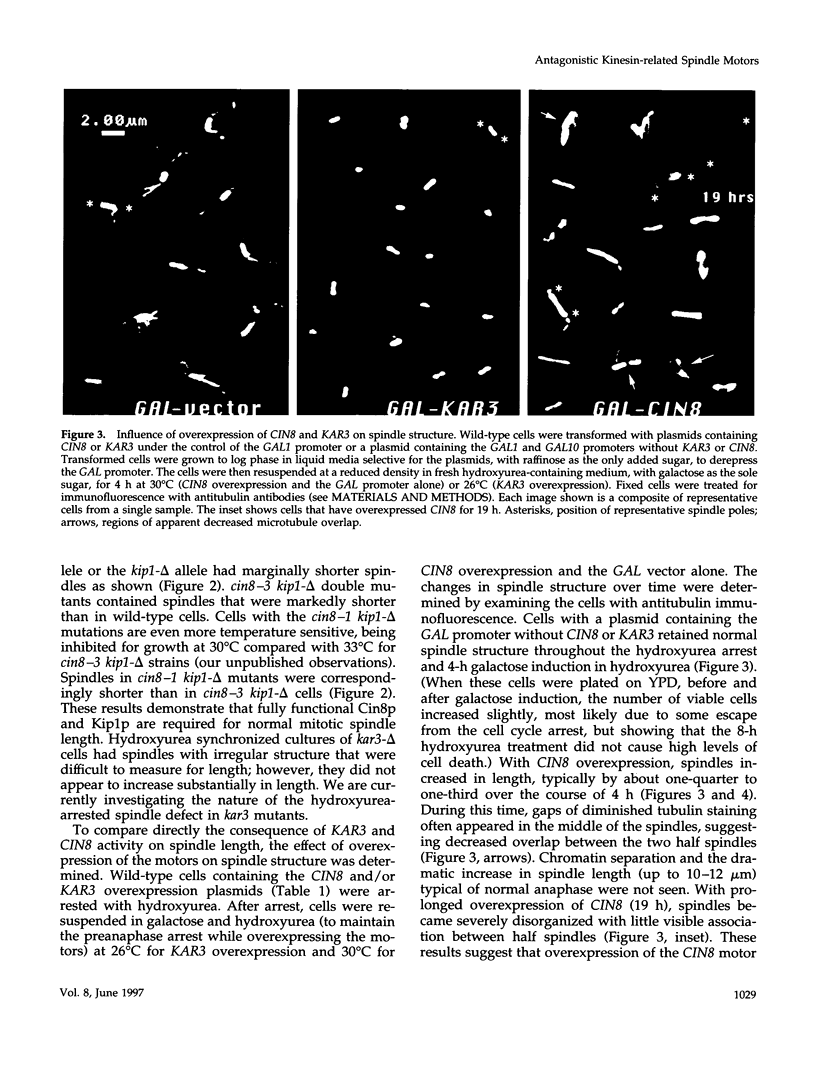
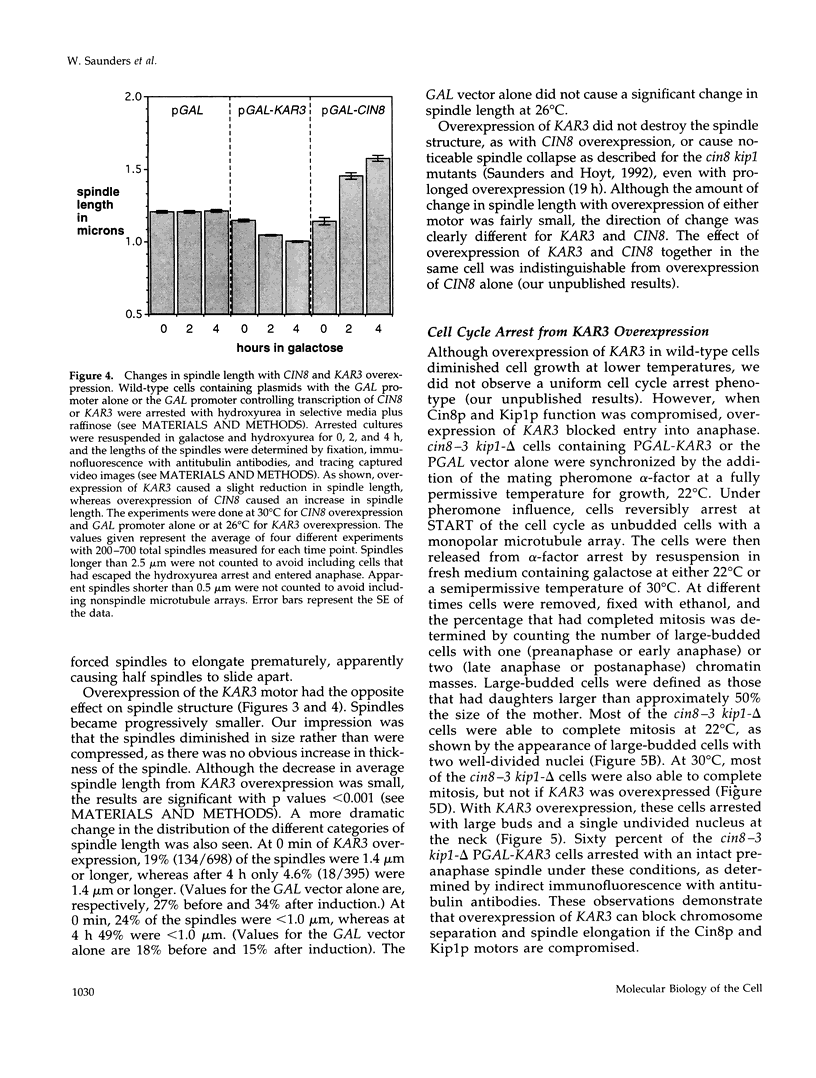
Abstract
Two Saccharomyces cerevisiae kinesin-related motors, Cin8p and Kip1p, perform an essential role in the separation of spindle poles during spindle assembly and a major role in spindle elongation. Cin8p and Kip1p are also required to prevent an inward spindle collapse prior to anaphase. A third kinesin-related motor, Kar3p, may act antagonistically to Cin8p and Kip1p since loss of Kar3p partially suppresses the spindle collapse in cin8 kip1 mutants. We have tested the relationship between Cin8p and Kar3p by overexpressing both motors using the inducible GAL1 promoter. Overexpression of KAR3 results in a shrinkage of spindle size and a temperature-dependent inhibition of the growth of wild-type cells. Excess Kar3p has a stronger inhibitory effect on the growth of cin8 kip1 mutants and can completely block anaphase spindle elongation in these cells. In contrast, overexpression of CIN8 leads to premature spindle elongation in all cells tested. This is the first direct demonstration of antagonistic motors acting on the intact spindle and suggests that spindle length is determined by the relative activity of Kar3p-like and Cin8p/Kip1p-like motors.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aist J. R., Berns M. W. Mechanics of chromosome separation during mitosis in Fusarium (Fungi imperfecti): new evidence from ultrastructural and laser microbeam experiments. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):446–458. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aist J. R., Liang H., Berns M. W. Astral and spindle forces in PtK2 cells during anaphase B: a laser microbeam study. J Cell Sci. 1993 Apr;104(Pt 4):1207–1216. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.4.1207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endow S. A., Kang S. J., Satterwhite L. L., Rose M. D., Skeen V. P., Salmon E. D. Yeast Kar3 is a minus-end microtubule motor protein that destabilizes microtubules preferentially at the minus ends. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 1;13(11):2708–2713. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06561.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enos A. P., Morris N. R. Mutation of a gene that encodes a kinesin-like protein blocks nuclear division in A. nidulans. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):1019–1027. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90350-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt M. A. Cellular roles of kinesin and related proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;6(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90117-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt M. A., He L., Loo K. K., Saunders W. S. Two Saccharomyces cerevisiae kinesin-related gene products required for mitotic spindle assembly. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(1):109–120. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda H., Cande W. Z. The role of tubulin polymerization during spindle elongation in vitro. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):193–202. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90560-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meluh P. B., Rose M. D. KAR3, a kinesin-related gene required for yeast nuclear fusion. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):1029–1041. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90351-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton K., Carbon J. KAR3-encoded kinesin is a minus-end-directed motor that functions with centromere binding proteins (CBF3) on an in vitro yeast kinetochore. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):7212–7216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell M. J., Meluh P. B., Rose M. D., Morris N. R. Suppression of the bimC4 mitotic spindle defect by deletion of klpA, a gene encoding a KAR3-related kinesin-like protein in Aspergillus nidulans. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(1):153–162. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. B., Ris H. Electron-microscopic study of the spindle and chromosome movement in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Sci. 1976 Nov;22(2):219–242. doi: 10.1242/jcs.22.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pidoux A. L., LeDizet M., Cande W. Z. Fission yeast pkl1 is a kinesin-related protein involved in mitotic spindle function. Mol Biol Cell. 1996 Oct;7(10):1639–1655. doi: 10.1091/mbc.7.10.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polaina J., Conde J. Genes involved in the control of nuclear fusion during the sexual cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(2):253–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00331858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. R., Adams A. E., Drubin D. G., Haarer B. K. Immunofluorescence methods for yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:565–602. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94043-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roof D. M., Meluh P. B., Rose M. D. Kinesin-related proteins required for assembly of the mitotic spindle. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(1):95–108. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roof D. M., Meluh P. B., Rose M. D. Multiple kinesin-related proteins in yeast mitosis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:693–703. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders W. S., Hoyt M. A. Kinesin-related proteins required for structural integrity of the mitotic spindle. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):451–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90169-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders W. S., Koshland D., Eshel D., Gibbons I. R., Hoyt M. A. Saccharomyces cerevisiae kinesin- and dynein-related proteins required for anaphase chromosome segregation. J Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;128(4):617–624. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.4.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders W., Hornack D., Lengyel V., Deng C. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae kinesin-related motor Kar3p acts at preanaphase spindle poles to limit the number and length of cytoplasmic microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1997 Apr 21;137(2):417–431. doi: 10.1083/jcb.137.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh E., Skibbens R. V., Cheng J. W., Salmon E. D., Bloom K. Spindle dynamics and cell cycle regulation of dynein in the budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1995 Aug;130(3):687–700. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.3.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang D., Nicklas R. B. 'Anaphase' and cytokinesis in the absence of chromosomes. Nature. 1996 Aug 1;382(6590):466–468. doi: 10.1038/382466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]