Abstract
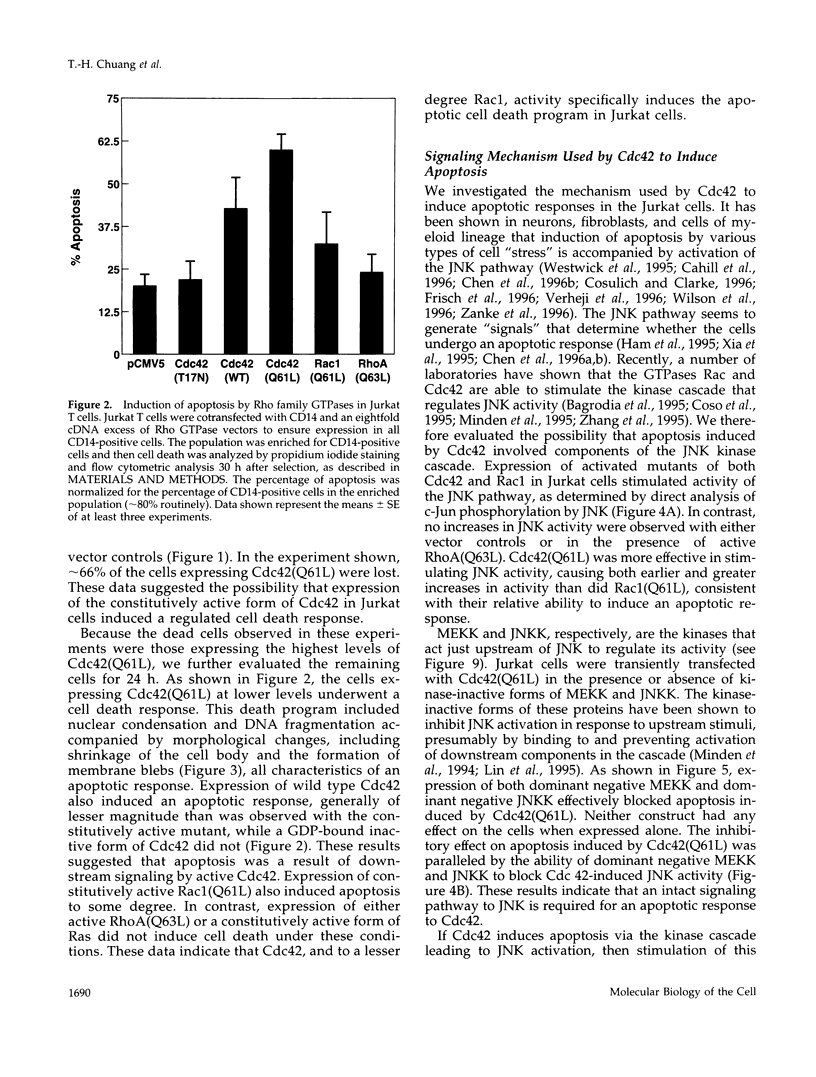
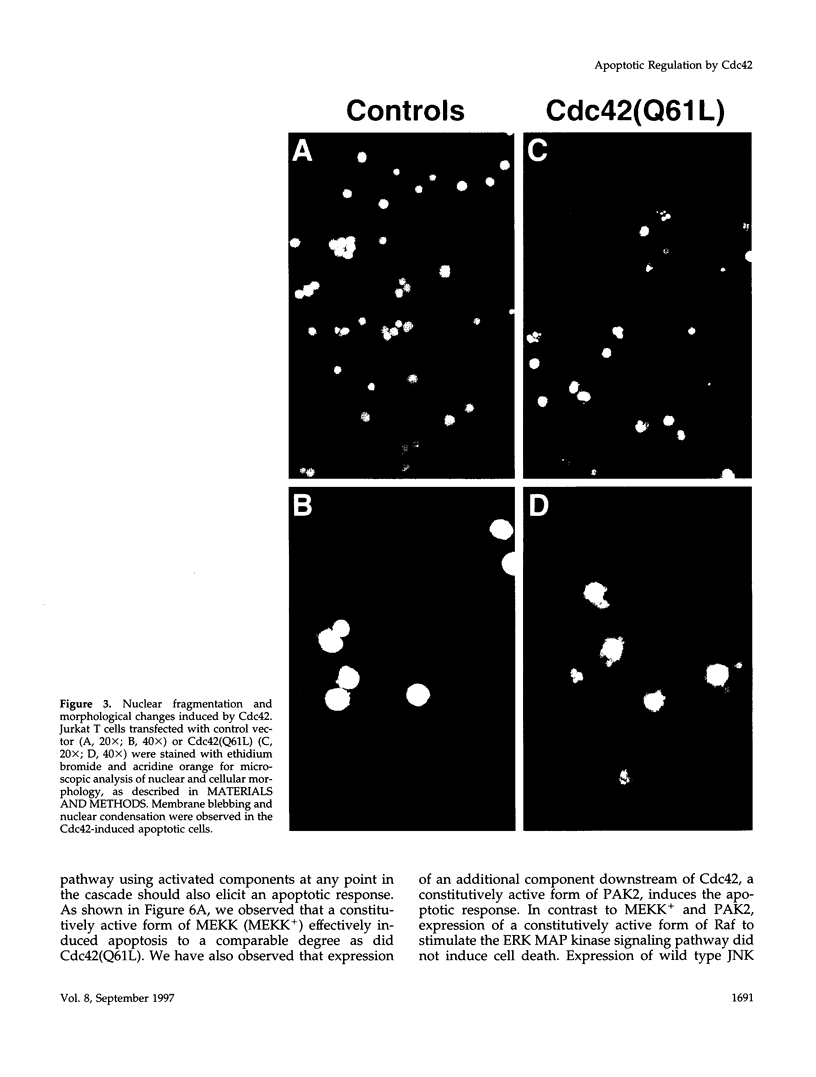
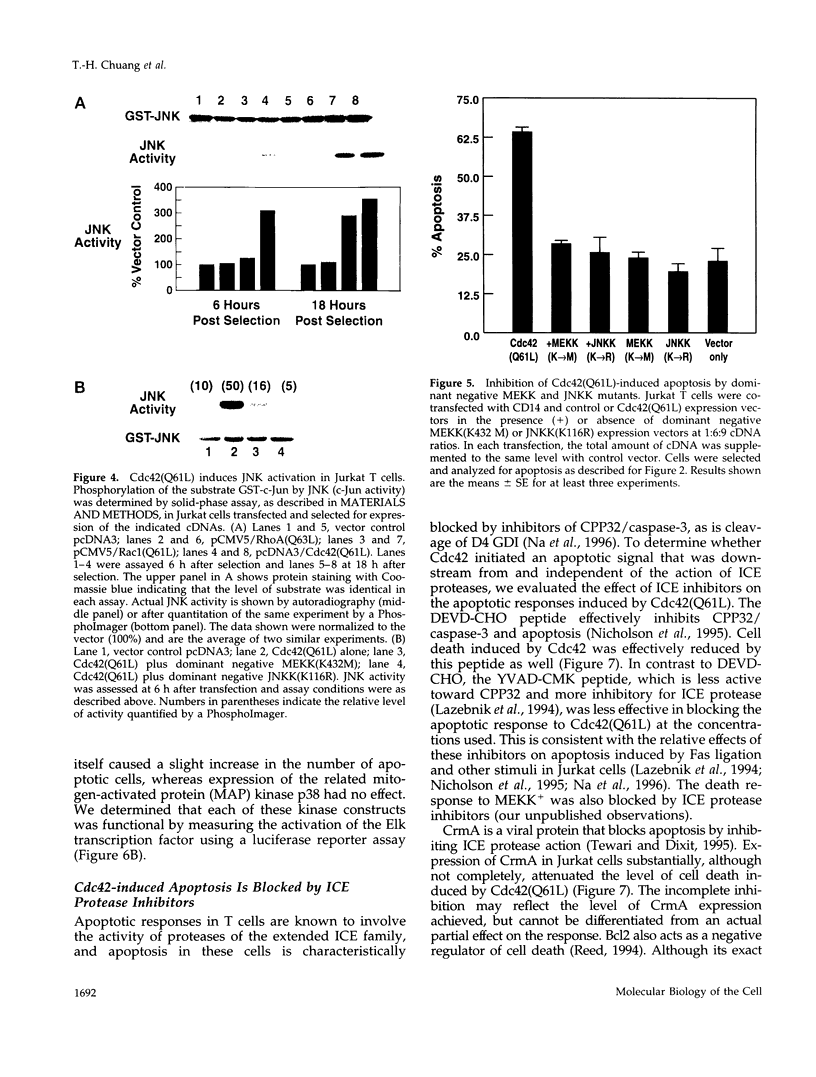
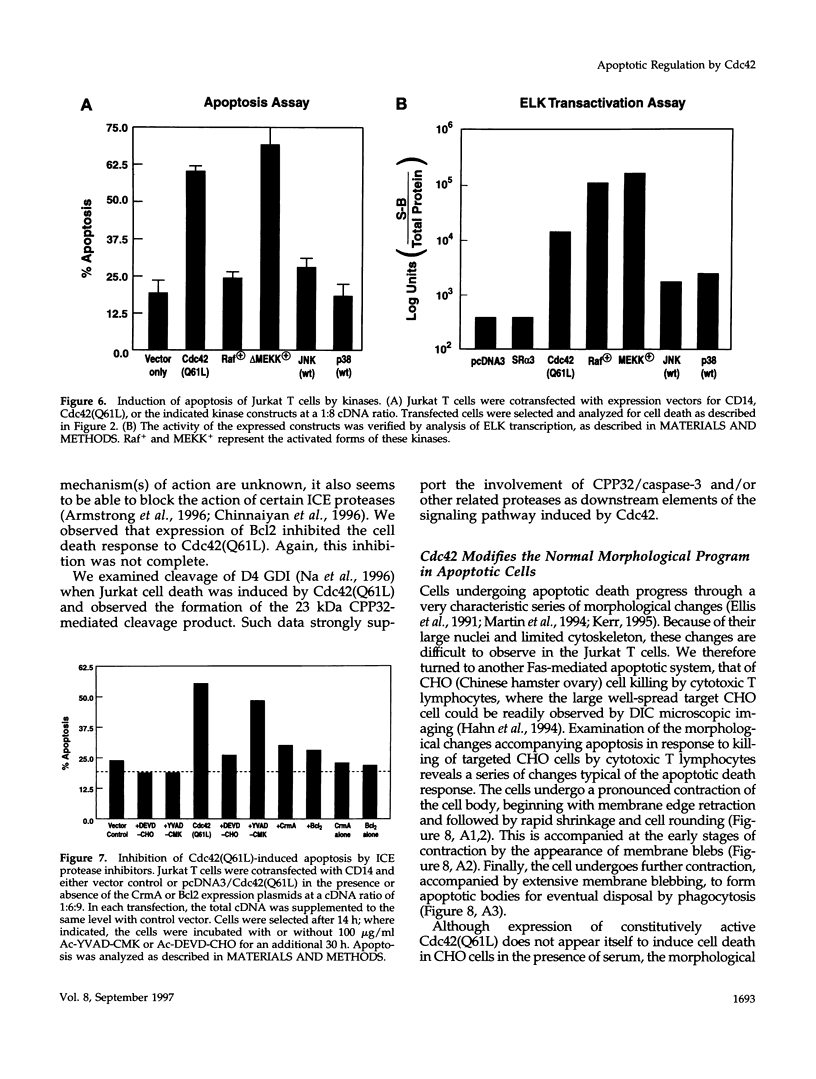
Apoptosis plays an important role in regulating development and homeostasis of the immune system, yet the elements of the signaling pathways that control cell death have not been well defined. When expressed in Jurkat T cells, an activated form of the small GTPase Cdc42 induces cell death exhibiting the characteristics of apoptosis. The death response induced by Cdc42 is mediated by activation of a protein kinase cascade leading to stimulation of c-Jun amino terminal kinase (JNK). Apoptosis initiated by Cdc42 is inhibited by dominant negative components of the JNK cascade and by reagents that block activity of the ICE protease (caspase) family, suggesting that stimulation of the JNK kinase cascade can lead to caspase activation. The sequence of morphological events observed typically in apoptotic cells is modified in the presence of activated Cdc42, suggesting that this GTPase may account for some aspects of cytoskeletal regulation during the apoptotic program. These data suggest a means through which the biochemical and morphological events occurring during apoptosis may be coordinately regulated.
Full text
PDF

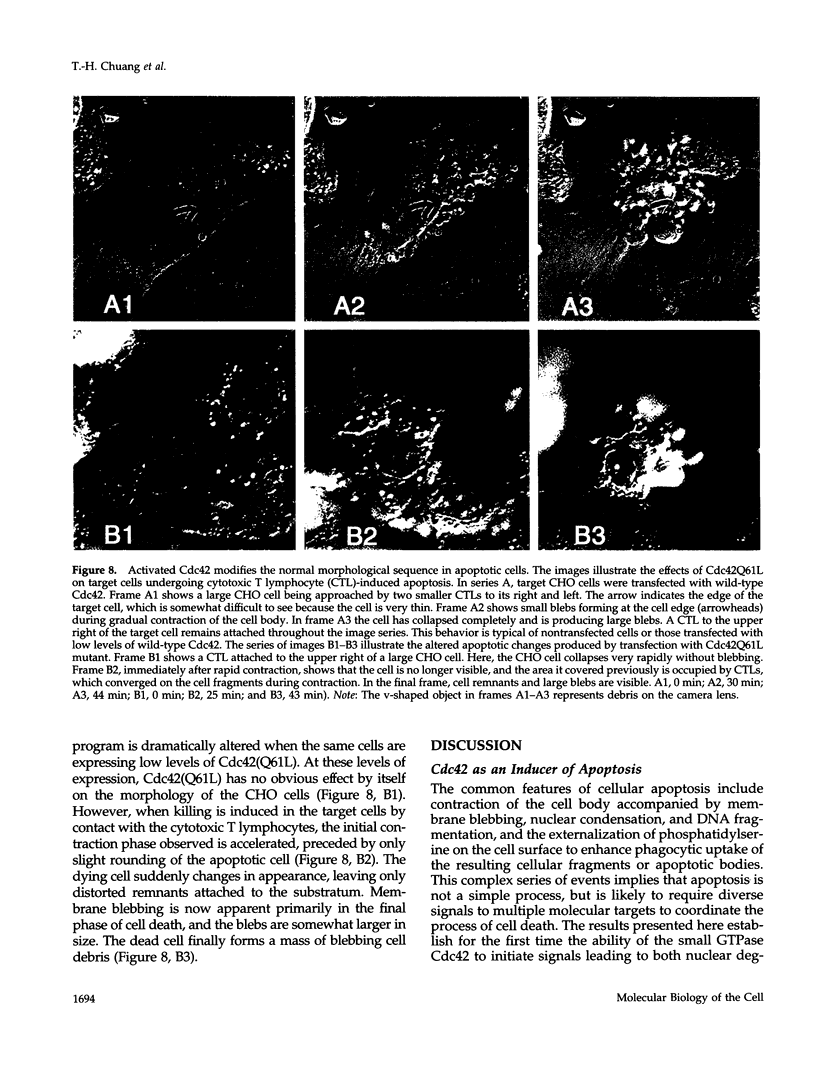
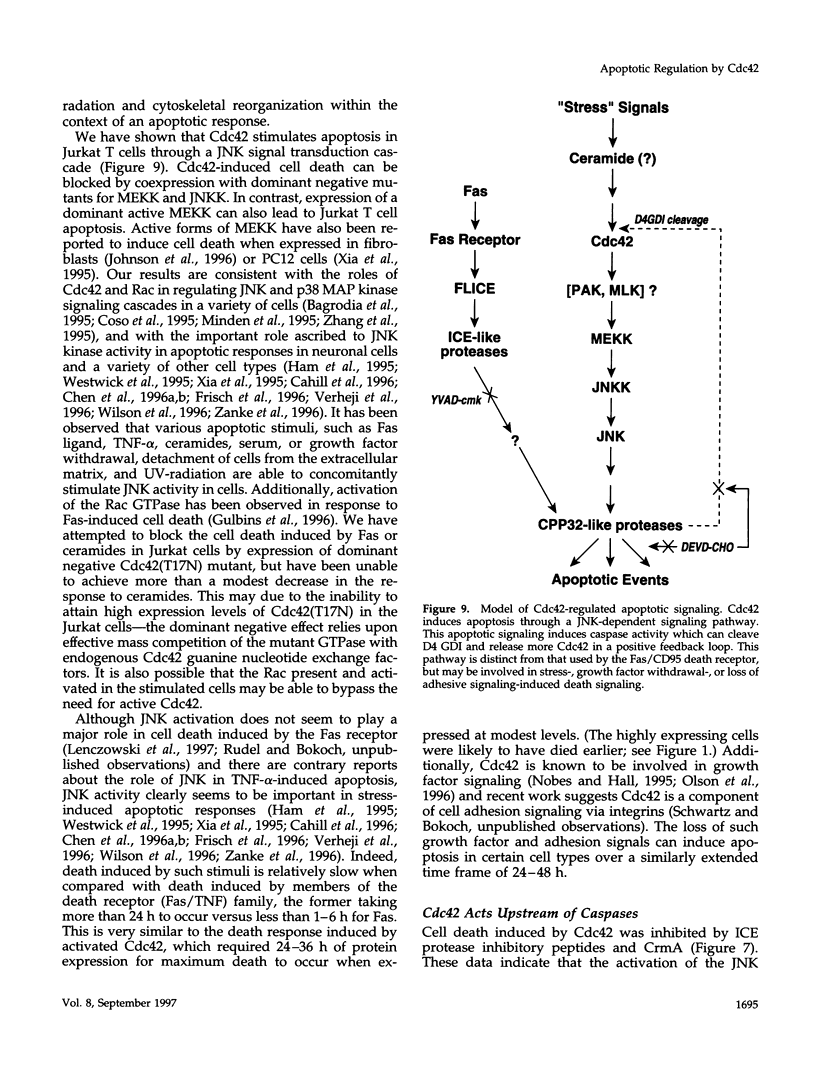



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbas A. K. Die and let live: eliminating dangerous lymphocytes. Cell. 1996 Mar 8;84(5):655–657. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81042-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alnemri E. S., Livingston D. J., Nicholson D. W., Salvesen G., Thornberry N. A., Wong W. W., Yuan J. Human ICE/CED-3 protease nomenclature. Cell. 1996 Oct 18;87(2):171–171. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81334-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong R. C., Aja T., Xiang J., Gaur S., Krebs J. F., Hoang K., Bai X., Korsmeyer S. J., Karanewsky D. S., Fritz L. C. Fas-induced activation of the cell death-related protease CPP32 Is inhibited by Bcl-2 and by ICE family protease inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jul 12;271(28):16850–16855. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.28.16850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagrodia S., Dérijard B., Davis R. J., Cerione R. A. Cdc42 and PAK-mediated signaling leads to Jun kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1995 Nov 24;270(47):27995–27998. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.47.27995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Der C. J. Emerging concepts in the Ras superfamily of GTP-binding proteins. FASEB J. 1993 Jun;7(9):750–759. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.9.8330683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boldin M. P., Goncharov T. M., Goltsev Y. V., Wallach D. Involvement of MACH, a novel MORT1/FADD-interacting protease, in Fas/APO-1- and TNF receptor-induced cell death. Cell. 1996 Jun 14;85(6):803–815. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81265-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill M. A., Peter M. E., Kischkel F. C., Chinnaiyan A. M., Dixit V. M., Krammer P. H., Nordheim A. CD95 (APO-1/Fas) induces activation of SAP kinases downstream of ICE-like proteases. Oncogene. 1996 Nov 21;13(10):2087–2096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. R., Meyer C. F., Tan T. H. Persistent activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) in gamma radiation-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 12;271(2):631–634. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.2.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. R., Wang X., Templeton D., Davis R. J., Tan T. H. The role of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) in apoptosis induced by ultraviolet C and gamma radiation. Duration of JNK activation may determine cell death and proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1996 Dec 13;271(50):31929–31936. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.50.31929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnaiyan A. M., Dixit V. M. The cell-death machine. Curr Biol. 1996 May 1;6(5):555–562. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00541-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnaiyan A. M., Orth K., O'Rourke K., Duan H., Poirier G. G., Dixit V. M. Molecular ordering of the cell death pathway. Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL function upstream of the CED-3-like apoptotic proteases. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 1;271(9):4573–4576. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.9.4573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coso O. A., Chiariello M., Yu J. C., Teramoto H., Crespo P., Xu N., Miki T., Gutkind J. S. The small GTP-binding proteins Rac1 and Cdc42 regulate the activity of the JNK/SAPK signaling pathway. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1137–1146. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosulich S., Clarke P. Apoptosis: does stress kill? Curr Biol. 1996 Dec 1;6(12):1586–1588. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)70779-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis H. M., Horvitz H. R. Genetic control of programmed cell death in the nematode C. elegans. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):817–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. E., Yuan J. Y., Horvitz H. R. Mechanisms and functions of cell death. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:663–698. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisch S. M., Vuori K., Kelaita D., Sicks S. A role for Jun-N-terminal kinase in anoikis; suppression by bcl-2 and crmA. J Cell Biol. 1996 Dec;135(5):1377–1382. doi: 10.1083/jcb.135.5.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulbins E., Coggeshall K. M., Brenner B., Schlottmann K., Linderkamp O., Lang F. Fas-induced apoptosis is mediated by activation of a Ras and Rac protein-regulated signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 1996 Oct 18;271(42):26389–26394. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.42.26389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
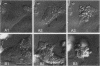
- Hahn K., DeBiasio R., Tishon A., Lewicki H., Gairin J. E., LaRocca G., Taylor D. L., Oldstone M. Antigen presentation and cytotoxic T lymphocyte killing studied in individual, living cells. Virology. 1994 Jun;201(2):330–340. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ham J., Babij C., Whitfield J., Pfarr C. M., Lallemand D., Yaniv M., Rubin L. L. A c-Jun dominant negative mutant protects sympathetic neurons against programmed cell death. Neuron. 1995 May;14(5):927–939. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90331-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A. Functions of ceramide in coordinating cellular responses to stress. Science. 1996 Dec 13;274(5294):1855–1859. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5294.1855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockenbery D. M., Oltvai Z. N., Yin X. M., Milliman C. L., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 functions in an antioxidant pathway to prevent apoptosis. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):241–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80066-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson N. L., Gardner A. M., Diener K. M., Lange-Carter C. A., Gleavy J., Jarpe M. B., Minden A., Karin M., Zon L. I., Johnson G. L. Signal transduction pathways regulated by mitogen-activated/extracellular response kinase kinase kinase induce cell death. J Biol Chem. 1996 Feb 9;271(6):3229–3237. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.6.3229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juo P., Kuo C. J., Reynolds S. E., Konz R. F., Raingeaud J., Davis R. J., Biemann H. P., Blenis J. Fas activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling pathway requires ICE/CED-3 family proteases. Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Jan;17(1):24–35. doi: 10.1128/mcb.17.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F. Neglected opportunities in apoptosis research. Trends Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;5(2):55–57. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)88940-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kägi D., Vignaux F., Ledermann B., Bürki K., Depraetere V., Nagata S., Hengartner H., Golstein P. Fas and perforin pathways as major mechanisms of T cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Science. 1994 Jul 22;265(5171):528–530. doi: 10.1126/science.7518614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazebnik Y. A., Kaufmann S. H., Desnoyers S., Poirier G. G., Earnshaw W. C. Cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase by a proteinase with properties like ICE. Nature. 1994 Sep 22;371(6495):346–347. doi: 10.1038/371346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. D., Kato K., Tobias P. S., Kirkland T. N., Ulevitch R. J. Transfection of CD14 into 70Z/3 cells dramatically enhances the sensitivity to complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. J Exp Med. 1992 Jun 1;175(6):1697–1705. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.6.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lelias J. M., Adra C. N., Wulf G. M., Guillemot J. C., Khagad M., Caput D., Lim B. cDNA cloning of a human mRNA preferentially expressed in hematopoietic cells and with homology to a GDP-dissociation inhibitor for the rho GTP-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1479–1483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenczowski J. M., Dominguez L., Eder A. M., King L. B., Zacharchuk C. M., Ashwell J. D. Lack of a role for Jun kinase and AP-1 in Fas-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Jan;17(1):170–181. doi: 10.1128/mcb.17.1.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A., Minden A., Martinetto H., Claret F. X., Lange-Carter C., Mercurio F., Johnson G. L., Karin M. Identification of a dual specificity kinase that activates the Jun kinases and p38-Mpk2. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):286–290. doi: 10.1126/science.7716521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linette G. P., Korsmeyer S. J. Differentiation and cell death: lessons from the immune system. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;6(6):809–815. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90049-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. J., Green D. R., Cotter T. G. Dicing with death: dissecting the components of the apoptosis machinery. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jan;19(1):26–30. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. J., Green D. R. Protease activation during apoptosis: death by a thousand cuts? Cell. 1995 Aug 11;82(3):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90422-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGahon A. J., Martin S. J., Bissonnette R. P., Mahboubi A., Shi Y., Mogil R. J., Nishioka W. K., Green D. R. The end of the (cell) line: methods for the study of apoptosis in vitro. Methods Cell Biol. 1995;46:153–185. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61929-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minden A., Lin A., Claret F. X., Abo A., Karin M. Selective activation of the JNK signaling cascade and c-Jun transcriptional activity by the small GTPases Rac and Cdc42Hs. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1147–1157. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minden A., Lin A., McMahon M., Lange-Carter C., Dérijard B., Davis R. J., Johnson G. L., Karin M. Differential activation of ERK and JNK mitogen-activated protein kinases by Raf-1 and MEKK. Science. 1994 Dec 9;266(5191):1719–1723. doi: 10.1126/science.7992057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzio M., Chinnaiyan A. M., Kischkel F. C., O'Rourke K., Shevchenko A., Ni J., Scaffidi C., Bretz J. D., Zhang M., Gentz R. FLICE, a novel FADD-homologous ICE/CED-3-like protease, is recruited to the CD95 (Fas/APO-1) death--inducing signaling complex. Cell. 1996 Jun 14;85(6):817–827. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81266-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
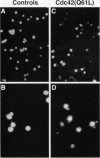
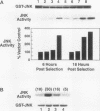
- Na S., Chuang T. H., Cunningham A., Turi T. G., Hanke J. H., Bokoch G. M., Danley D. E. D4-GDI, a substrate of CPP32, is proteolyzed during Fas-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1996 May 10;271(19):11209–11213. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.19.11209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S., Golstein P. The Fas death factor. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1449–1456. doi: 10.1126/science.7533326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson D. W., Ali A., Thornberry N. A., Vaillancourt J. P., Ding C. K., Gallant M., Gareau Y., Griffin P. R., Labelle M., Lazebnik Y. A. Identification and inhibition of the ICE/CED-3 protease necessary for mammalian apoptosis. Nature. 1995 Jul 6;376(6535):37–43. doi: 10.1038/376037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
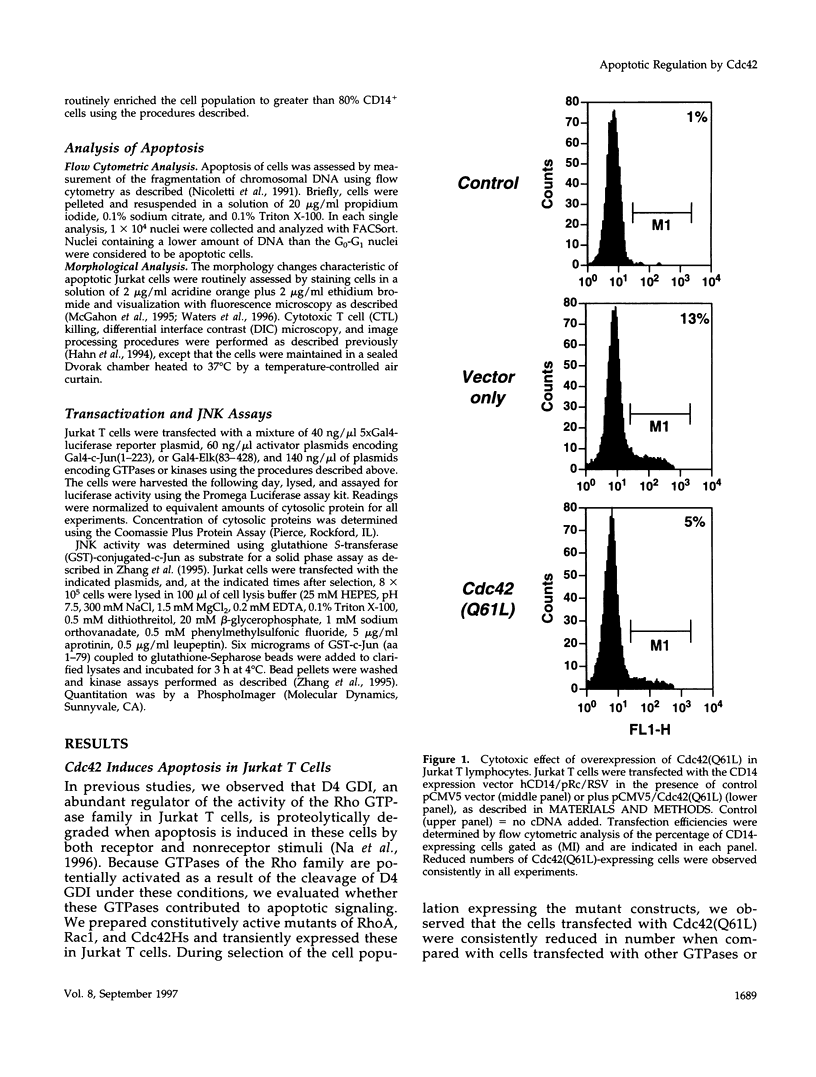
- Nicoletti I., Migliorati G., Pagliacci M. C., Grignani F., Riccardi C. A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Jun 3;139(2):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90198-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobes C. D., Hall A. Rho, rac, and cdc42 GTPases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia. Cell. 1995 Apr 7;81(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90370-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. F., Pasteris N. G., Gorski J. L., Hall A. Faciogenital dysplasia protein (FGD1) and Vav, two related proteins required for normal embryonic development, are upstream regulators of Rho GTPases. Curr Biol. 1996 Dec 1;6(12):1628–1633. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)70786-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathmell J. C., Cooke M. P., Ho W. Y., Grein J., Townsend S. E., Davis M. M., Goodnow C. C. CD95 (Fas)-dependent elimination of self-reactive B cells upon interaction with CD4+ T cells. Nature. 1995 Jul 13;376(6536):181–184. doi: 10.1038/376181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C. Bcl-2 and the regulation of programmed cell death. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):1–6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieux-Laucat F., Le Deist F., Hivroz C., Roberts I. A., Debatin K. M., Fischer A., de Villartay J. P. Mutations in Fas associated with human lymphoproliferative syndrome and autoimmunity. Science. 1995 Jun 2;268(5215):1347–1349. doi: 10.1126/science.7539157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherle P., Behrens T., Staudt L. M. Ly-GDI, a GDP-dissociation inhibitor of the RhoA GTP-binding protein, is expressed preferentially in lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7568–7572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seimiya H., Mashima T., Toho M., Tsuruo T. c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-mediated activation of interleukin-1beta converting enzyme/CED-3-like protease during anticancer drug-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1997 Feb 14;272(7):4631–4636. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.7.4631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi A., Earnshaw W. C. ICE-related proteases in apoptosis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1996 Feb;6(1):50–55. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(96)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Tanaka M., Brannan C. I., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Suda T., Nagata S. Generalized lymphoproliferative disease in mice, caused by a point mutation in the Fas ligand. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):969–976. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90375-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari M., Dixit V. M. Fas- and tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis is inhibited by the poxvirus crmA gene product. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 17;270(7):3255–3260. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.7.3255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheij M., Bose R., Lin X. H., Yao B., Jarvis W. D., Grant S., Birrer M. J., Szabo E., Zon L. I., Kyriakis J. M. Requirement for ceramide-initiated SAPK/JNK signalling in stress-induced apoptosis. Nature. 1996 Mar 7;380(6569):75–79. doi: 10.1038/380075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters J. B., Oldstone M. B., Hahn K. M. Changes in the cytoplasmic structure of CTLs during target cell recognition and killing. J Immunol. 1996 Oct 15;157(8):3396–3403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westwick J. K., Bielawska A. E., Dbaibo G., Hannun Y. A., Brenner D. A. Ceramide activates the stress-activated protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 29;270(39):22689–22692. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.39.22689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte M. ICE/CED-3 proteasesin apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 1996 Jul;6(7):245–248. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(96)20025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. J., Fortner K. A., Lynch D. H., Mattingly R. R., Macara I. G., Posada J. A., Budd R. C. JNK, but not MAPK, activation is associated with Fas-mediated apoptosis in human T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1996 May;26(5):989–994. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830260505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia Z., Dickens M., Raingeaud J., Davis R. J., Greenberg M. E. Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases on apoptosis. Science. 1995 Nov 24;270(5240):1326–1331. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5240.1326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J. Molecular control of life and death. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;7(2):211–214. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanke B. W., Boudreau K., Rubie E., Winnett E., Tibbles L. A., Zon L., Kyriakis J., Liu F. F., Woodgett J. R. The stress-activated protein kinase pathway mediates cell death following injury induced by cis-platinum, UV irradiation or heat. Curr Biol. 1996 May 1;6(5):606–613. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00547-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S., Han J., Sells M. A., Chernoff J., Knaus U. G., Ulevitch R. J., Bokoch G. M. Rho family GTPases regulate p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase through the downstream mediator Pak1. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 13;270(41):23934–23936. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.41.23934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Y., Fischer D. J., Santos M. F., Tigyi G., Pasteris N. G., Gorski J. L., Xu Y. The faciogenital dysplasia gene product FGD1 functions as a Cdc42Hs-specific guanine-nucleotide exchange factor. J Biol Chem. 1996 Dec 27;271(52):33169–33172. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.52.33169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]