Abstract
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer associated deaths among men in the western countries. Here, we report that human RecQL4 helicase, which is implicated in the pathogenesis of a subset of cancer prone Rothmund-Thomson syndrome, is highly elevated in metastatic prostate cancer cell lines. Increased RecQL4 expression was also detected in human prostate tumor tissues as a function of tumor grade with the highest expression level in metastatic tumor samples suggesting that RecQL4 may be a potential prognostic factor for advanced stage of prostate cancer. Transient and stable suppression of RecQL4 by siRNA and shRNA vectors drastically reduced the growth and survival of metastatic prostate cancer cells indicating that RecQL4 is a pro-survival factor for prostate cancer cells. RecQL4 suppression led to increased poly (ADP) ribose polymer (PAR) synthesis and RecQL4 suppressed prostate cancer cells underwent an extensive apoptotic death in a PARP-1 dependent manner. Most notably, RecQL4 knockdown in metastatic prostate cancer cells drastically reduced their cell invasiveness in vitro and tumorigenicity in vivo demonstrating that RecQL4 is essential for prostate cancer promotion. Observation of a direct interaction of Rb and E2F1 proteins with RecQL4 promoter suggests that Rb-E2F1 pathway may regulate RecQL4 expression. Collectively, our study demonstrates that RecQL4 is an essential factor for prostate carcinogenesis.
Keywords: Human RecQ helicases, prostate cancer, DNA replication, premature aging and genomic instability
Introduction
The prototypical E.coli RecQ protein acts as a suppressor of illegitimate recombination and RecQ mutants exhibit genomic instability due to improper resolution of DNA secondary and tertiary structures arising during replication and recombination (1). Human cells express five distinct RecQ homologues, three of which are associated with autosomal recessive diseases characterized by cancer susceptibility (2, 3): Bloom syndrome (BS), Werner syndrome (WS) and Rothmund-Thomson syndrome (RTS). Mutations in RecQL4 are linked to three autosomal recessive disorders: RTS, RAPADILINO and Baller-Gerold syndrome (4) and the RecQL4 protein shares 40.8% homology with the E.coli RecQ protein [See (5) and references therein].
Human RecQ helicases play diverse roles in DNA metabolism (3, 6). RecQL1 promotes chromosome stability and integrity (7), WRN and BLM participate in organizing the DNA replication complex (8) and WRN helicase plays a role in RNA polymerase II mediated basal transcription in human cells (9). Although the precise biological role of RecQL4 awaits further investigations, some studies implicate RecQL4 in DNA replication and DNA repair (10, 11). Interaction of RecQL4 with proteins involved in genome surveillance was recently reported (12). Xu and Liu (13) provided initial evidence for the DNA unwinding activity of RecQL4 in vitro in the presence of ssDNA and the activity has been subsequently demonstrated for both ssDNA and dsDNA (14). It is currently unclear whether or not cancer cells exhibit deregulation of RecQ helicases and if so whether deregulated RecQ helicase activities initiate and promote cancer development processes.
Prostate cancer incidence is increasing at an alarming rate, now representing 33% of new cases of male cancers. Gene deletion and amplification events involving chromosome 8 are intimately associated with prostate carcinogenesis (15–19), although the critical genes in this region have not been extensively characterized. Chromosome 8q amplification was reported in metastatic and recurrent prostate cancers (20–22). Chromosome 8q (11–24) gain is not only observed in prostate cancers but also in cervical cancer (23, 24), breast cancer (25) and colorectal cancer (26) indicating its intimate association with tumorigenesis. RecQL4 imbalance in expression has recently been reported in 18 sporadic osteoblastoma samples (27). Here, we report that human RecQL4 helicase localized at 8q24.3, is highly expressed in metastatic human prostate cancer cells and tumor tissues. RecQL4 suppressed PC3 cells displayed drastically reduced cell invasion potential in vitro and tumorigenic potential in vivo. These findings suggest that RecQL4 may play a critical role in prostate carcinogenesis. Further, the high level of RecQL4 expression in metastatic prostate cancer samples suggests that RecQL4 may be a novel biomarker for advanced stage of prostate cancer.
Materials and Methods
Cell lines and prostate tumor tissues
Human primary prostate epithelial cells (PrEC) were procured from Lonza Inc., USA. Immortalized (RWPE1) and metastatic prostate cancer cells lines (CRW22, DU145, LNCaP and PC3 and RWPE2) were procured from ATCC. All the cell lines were authenticated based on viability, recovery, growth and morphology by the suppliers. Human prostate tissue panel array slides (PR951 and PR751) were procured from US Biomax Inc., MD, USA.
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and Immunohistochemistry
Procedures for metaphase chromosome preparation, FISH and multicolor FISH were essentially the same as described before (28). FISH was performed using multicolor band probe specific for chromosome 8 and a spectrum orange labeled BAC (Bacterial Artificial Chromosome) probe (RP11-374B7, Open Biosystems, Huntsville, AL) corresponding to the proximal region of chromosome 8q24.3 locus. Human M-band and M-FISH probes were obtained from MetaSystems, MA, USA.
Rabbit polyclonal antibodies specific for N-terminal and C-terminal regions of RecQL4 were generously provided by Dr. Igor Stagljar, University of Toronto, Canada. RecQL4 expression in the prostate tumor tissue arrays was analyzed by immunohistochemistry using a C-terminal antibody. Detailed procedures for immunostaining, image acquisition and quantification are given in the supplemental section.
Suppression of RecQL4 in prostate cancer cells
Immortalized normal prostate epithelial cells (RWPE1) and metastatic prostate cancer cell lines (DU145, LNCaP and PC3) in exponential growth phase were transfected with 25–100 nM of either control scrambled siRNA (sc-37007: Santa Cruz Biotechnology, CA) or RecQL4 specific siRNA (sc-38219; Santa Cruz Biotechnology). Cells were transfected using Lipofectamine RNAi Max (Invitrogen). RecQL4 expression in the total cellular proteins isolated 72 hr after transfection was monitored by western blot using either C-terminal or N-terminal antibody. Empty (TR20002), scrambled (TR30003) and 4 different RecQL4 specific shRNA vectors (TI339521, TI339522, TI339523 and TI339524) were procured from Origene, USA (Cat. No#TR309882). Transfection of PC3 cells with different shRNA vectors (2–4μg) were performed using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) essentially following the manufacturer’s protocol.
Cell proliferation, survival, cell invasion and tumorigenicity of RecQL4 suppressed prostate cancer cells
Proliferation of prostate cancer cells transfected with control and RecQL4 specific siRNA was analyzed by fluorescence based CyQuant assay (Invitrogen) essentially as described before (29). To measure cellular invasion, InnoCyte™ cell invasion kit (EMD Biosciences Inc.) was used following the manufacturer’s instructions. To determine whether RecQL4 suppression also leads to reduced tumorigenicity in vivo, 6×106 cells from each of the four cell lines [non-transfected PC3, empty vector transfected clone C5 and two RecQL4 shRNA vector transfected clones (C6 and C4)] were injected into nude mice. At least 5 mice were used for each treatment. The entire experimental animal protocol and procedure were in compliance with the guidelines of IACUC, Columbia University Medical Center, NY. Tumor growth and size (mm3) were monitored for up to 4 weeks.
Effect of histone deacetylase inhibitor TSA on RecQL4 expression
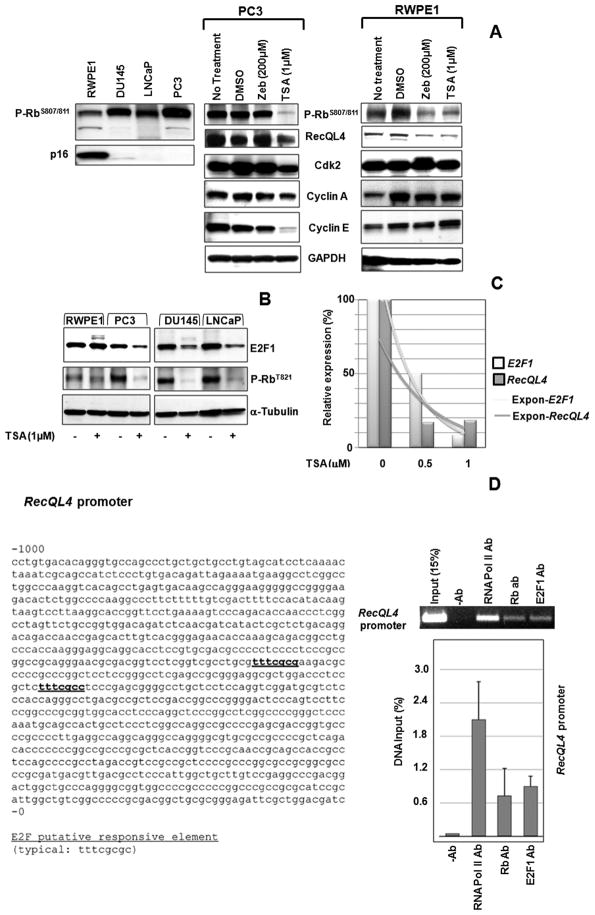
Immortalized prostate epithelial cells (RWPE1) and the three metastatic prostate cancer cell lines (DU145, LNCaP and PC3) in exponential growth phase were treated with 0.5μM and 1 μM of Trichostatin A (Sigma-Aldrich) for 48 hr. RecQL4 expression was monitored at the mRNA and protein levels by RT-PCR, quantitative real time PCR and western blot analyses. Forward and reverse primer sequences for RecQL4 are given in the supplemental section. Antibodies were procured from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Cyclin A, Cyclin E, Cdk2, GAPDH, β-actin and α-Tubulin), Millipore (γ-H2AX), Cell Signaling Technology (Phospho-Rb ser807/811) and Invitrogen (Phospho-Rb T821).
Chip Assay
The ChIP assay was performed in HeLa cells using a standard protocol essentially as described before (30). Antibodies for Rb and E2F1 were procured from Santa Cruz Biotechnology and Novus Biologicals respectively.
Results
Human RecQL4 helicase expression is elevated in human prostate cancer cell lines
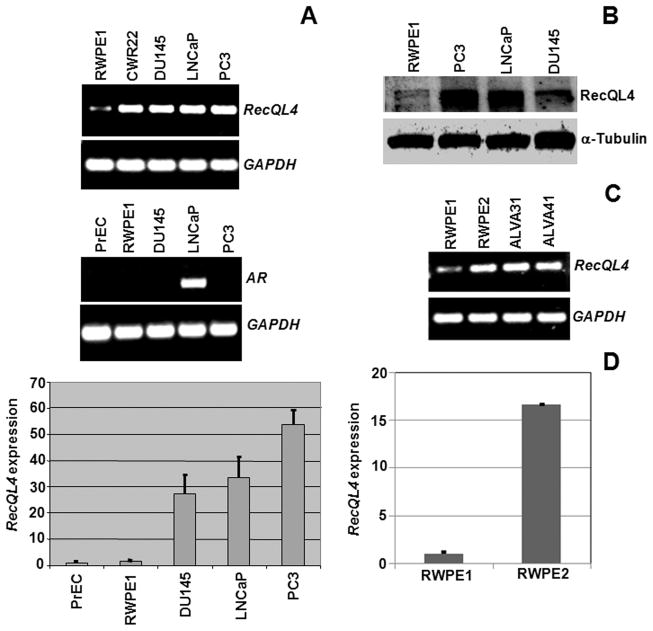
RecQL4 expression was assessed by RT-PCR and quantitative real time PCR in primary (PrEC) and immortalized (RWPE1) human prostate epithelial cell lines as well as in four human prostate cancer cell lines (CRW22, DU145, LNCaP and PC3). RecQL4 expression was markedly increased in all the metastatic prostate cancer cell lines in comparison to primary (PrEC) and immortalized human prostate epithelial cells (RWPE1; Fig. 1A) in an androgen independent manner (Fig. 1A). RecQL4 transcript detected by real-time PCR (Fig. 1A) correlated well with RecQL4 protein in the prostate cancer cells (Fig. 1B). To examine whether or not elevated RecQL4 expression is linked with malignant transformation process, RecQL4 expression was analyzed in the moderately tumorigenic RWPE2 cells that were derived from the parental non-tumorigenic RWPE1 cells by transformation with Ki-ras using the Kirsten murine sarcoma virus [Ki-MuSV; (31)]. Strikingly, RecQL4 expression was approximately 15 fold higher in tumorigenic RWPE2 cells than RWPE1 cells (Fig. 1C & D). RecQL4 expression was found elevated in all the 6 human prostate cancer cell lines: CRW22, DU145, LNCaP, PC3, ALVA31 and ALVA41 (Fig. 1A & C). Consistent with elevated RecQL4 expression, spectrum orange labeled BAC (Bacterial Artificial Chromosome) probe proximal to RecQL4 locus (8q24.3) revealed 3, 4 and 6 hybridization spots in DU145, LNCaP and PC3 cell lines respectively (Suppl. Fig 1).
Fig. 1.
RecQL4 expression analyses at the mRNA and protein levels in normal and prostate cancer cell lines of human origin. (A) RT-PCR analysis of RecQL4 and androgen receptor (AR) expression in normal immortalized human prostate epithelial cells (RWPE1) and four metastatic prostate cancer cell lines. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of RecQL4 expression in primary (PrEC), SV-40 immortalized (RWPE1) and metastatic prostate cancer cell lines (DU145, LNCaP and PC3). RecQL4 expression in normal and cancer cell lines was normalized to β-Actin. Bars indicate SEM. (B) Western blot analysis of RecQL4 expression in normal and prostate cancer cell lines. α-Tubulin was used as a loading control. (C) RT-PCR analysis of RecQL4 expression in non-tumorigenic (RWPE1), tumorigenic (RWPE2) and prostate cancer cell lines (ALVA31 and ALVA41). (D) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of RecQL4 in non-tumorigenic (RWPE1) and tumorigenic (RWPE2) cells. Error bars indicate SEM.
RecQL4 expression is enhanced in human prostate tumor tissues
RecQL4 expression was next investigated in human prostate panel arrays PR951 and PR751. PR951 array included 8 normal prostate, 36 prostate adenocarcinoma with different Gleason scores and 4 metastatic adenocarcinoma. PR751 array included 7 benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), 4 prostatic intraepithelial neoplasias (PIN) and 64 prostate adenocarcinoma with Gleason scores from 2–10. In general, intense RecQL4 protein staining was mainly detected in the nucleoplasmic regions. The integrated optical density (IOD) was used to categorize the staining intensity for RecQL4 as low, medium and high. Representative images of normal and prostate tumor tissue sections are shown in Fig. 2A&B and quantitative results are summarized in Table 1 and Fig. 2C. The highest level of RecQL4 expression was detected in all the metastatic prostate adenocarcinoma samples (Fig. 2A; IV–VI) and RecQL4 immunoreactivity somewhat correlated with increasing Gleason scores in the prostate tumor samples. Thirty prostate tumor tissue samples out of 48 in the PR951 array had PSA values ranging from 0.5 ng/ml to 161 ng/ml but the PSA value was unavailable for the samples in the PR751 array. In general, PSA values of the samples did not seem to correlate with Gleason scores (2–10). However, PSA value and RecQL4 staining intensity correlated for 12 out of 30 samples. Two of four PIN samples and two of seven BPH samples showed a medium level of RecQL4 staining intensity in prostatic ducts, ductules and acini (Fig. 2B). The cumulative average IOD values obtained for normal, malignant and metastatic tumor tissue samples are presented in Fig. 2C. Importantly, the aggregate data show that higher RecQL4 expression correlates with higher prostate cancer grade/severity in this set of 123 tissue samples.
Fig. 2.
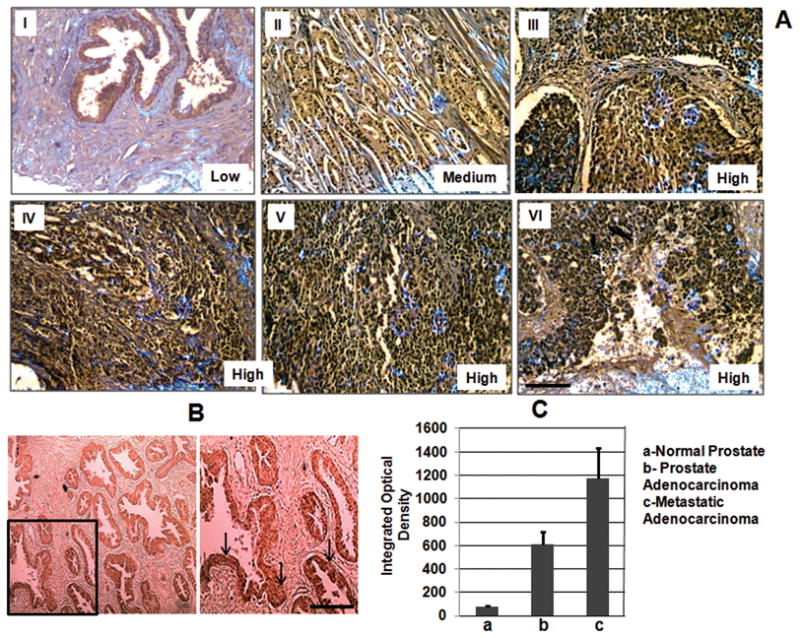
(A) Immunohistochemical analysis of RecQL4 expression in normal (I), malignant (II & III) and metastatic prostate tumor tissues (IV–VI). Prostate tissue panel arrays (PR951 and PR751) purchased from US Biomax Inc., MD, USA were utilized. Malignant tumor samples shown in II (67 year old, Gleason score 7, PSA 37.3 ng/ml) and III (63 year old, Gleason score 10, PSA not determined) illustrate that the RecQL4 expression increases with increasing tumor grade. Samples: IV (61 year old male; metastatic adenocarcinoma to bone), V and VI (65 year old, metastatic adenocarcinoma to bone and abdominal wall respectively). (B) Staining pattern of a PIN sample (50 year old, Gleason grade III) is shown in the lower left bottom panel. Arrows indicate the regions of positive RecQL4 staining. (C) The cumulative average value of integrated optical density obtained for all the normal, malignant and metastatic samples are given. Bars indicate SEM. Scale bar = 50μM.
Table 1.
Summary of immunological staining analysis of RecQL4 in prostate tumor tissues
| Samples | Gleason score | RecQL4 staining intensity |
Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Medium | High | |||
| Normal | 7 | 1 | 0 | 8 | |
| BPH | 5 | 2 | 0 | 7 | |
| PIN | 2 | 2 | 0 | 4 | |
| Adenocarcinoma | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Adenocarcinoma | 3 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 7 |
| Adenocarcinoma | 4 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 8 |
| Adenocarcinoma | 5 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 10 |
| Adenocarcinoma | 6 | 0 | 6 | 4 | 10 |
| Adenocarcinoma | 7 | 3 | 13 | 7 | 23 |
| Adenocarcinoma | 8 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 8 |
| Adenocarcinoma | 9 | 0 | 7 | 12 | 19 |
| Adenocarcinoma | 10 | 0 | 3 | 7 | 10 |
| Metastatic | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 | |
| 28 | 49 | 42 | 119 | ||
| (23.5%) | (41.2%) | (35.3%) | |||
The data obtained from two prostate tumor tissue arrays (PR951 with 48 core samples and PR751 with 75 core samples) were pooled together. 4 tumor samples in the arrays without any Gleason score were omitted from the analysis. Out of 4 PIN samples, 3 had Gleason grades I, II and III respectively while the 4th sample has Gleason grade between I-II. BPH-Benign prostatic hyperplasia, PIN- Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasias
RecQL4 gene silencing inhibits proliferation potential of prostate cancer cells
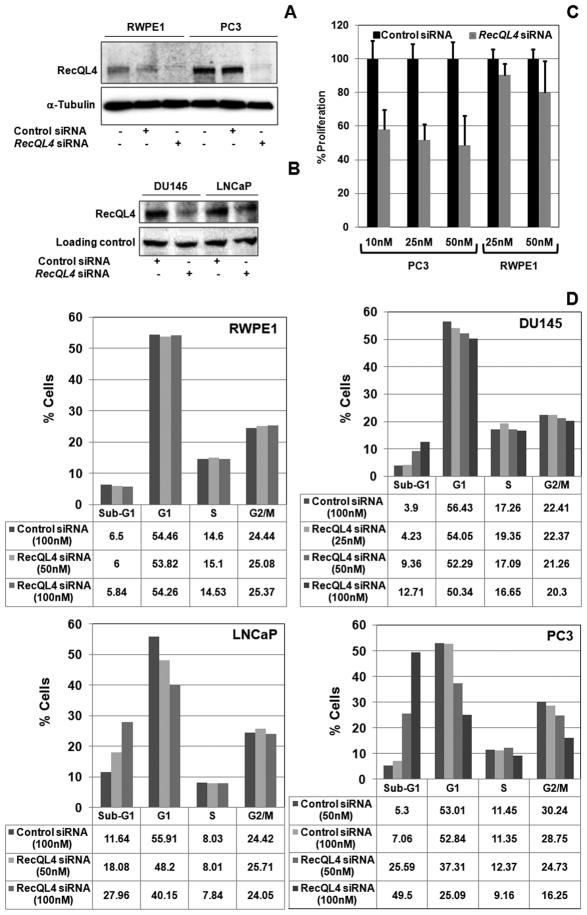
To verify the importance of RecQL4 in prostate cancer cell proliferation and survival, siRNA mediated RecQL4 gene silencing studies were performed in normal immortalized (RWPE1) and metastatic prostate cancer cell lines. Transfection of RecQL4 specific siRNA reduced the expression of RecQL4 by 70–90% in all the cell lines. Representative pictures of RecQL4 knockdown in prostate cancer cell lines after transfection with 50nM of control and RecQL4 specific siRNA are shown in Fig. 3A & B. Proliferation measured using the CyQuant assay kit (Invitrogen, USA; Meador et al., 2008) showed a modest inhibition in proliferation in RWPE1 cells transfected with 10 nm (9.8%) 25 nM (20.2%) of RecQL4 specific siRNA. In contrast, PC3 cells transfected with 10 nM, 25 nM and 50 nM of RecQL4 specific siRNA showed 42.1%, 48.3% and 51.4% inhibition in proliferation respectively (Fig. 3C). These findings suggest that RecQL4 depletion affected the proliferation more profoundly in metastatic prostate cancer cells than in normal prostate epithelial cells.
Fig. 3.
RecQL4 suppression leads to proliferation failure and apoptosis in metastatic prostate cancer cells. (A & B) Analysis of RecQL4 expression in RWPE1 and prostate cancer cell lines 72 hr after transfection with control and RecQL4 specific siRNA. (C) Effect of RecQL4 silencing on proliferation by CyQuant assay 48 hr after transfection with indicated concentrations of scrambled and RecQL4 specific siRNA in RWPE1 and PC3 cell lines. Error bars indicate SD. (D) Cell cycle analysis of immortalized RWPE1 and three metastatic prostate cancer cell lines (DU145, LNCaP and PC3) transfected with 25–100 nM of either scrambled control or RecQL4 specific siRNA. Cell cycle analysis was performed 72 hr after siRNA transfection.
RecQL4 gene silencing reduces prostate cancer cell viability
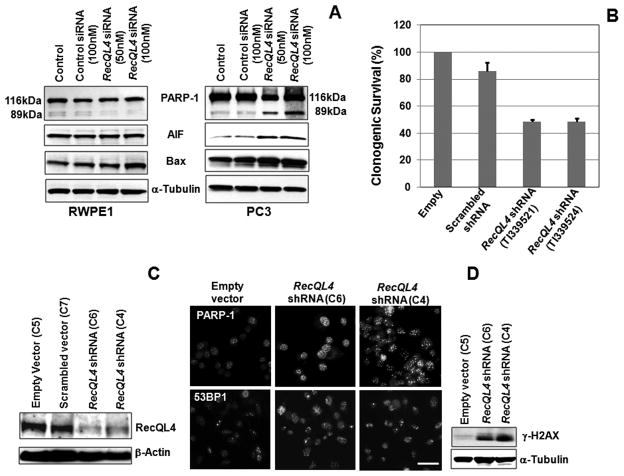
The reduced proliferation potential in RecQL4 silenced PC3 cells prompted us to examine the effects of RecQL4 ablation on cell cycle progression and cell death in the three prostate cancer cell lines. For this purpose, cells in exponential growth phase (RWPE1, DU145, LNCaP and PC3) were transfected with 25–100 nM of either control siRNA or RecQL4 specific siRNA and subjected to cell cycle analysis 72 hr after transfection. While cell cycle progression was hardly affected by RecQL4 knockdown in RWPE1 cells, all the prostate cancer cell lines transfected with RecQL4 specific siRNA showed a dose dependent increase in the sub-G1 fraction (Fig. 3D). The proportion of G1 cells also decreased as a function of increasing RecQL4 siRNA concentration in all the prostate cancer cell lines but most notably in LNCaP and PC3 cell lines (Fig. 3D). The fraction of G2/M phase cells was also reduced in PC3 cells at the highest dose of RecQL4 siRNA (Fig. 3D). Induction of apoptotic markers [Poly (ADP) ribose polymerase I, Bax and apoptosis inducing factor (AIF)] was next analyzed in RecQL4 suppressed PC3 cells. Consistent with the cell cycle data, cleaved PARP-1, Bax and AIF proteins showed a dose dependent enrichment in RecQL4 siRNA transfected PC3 cells but not in RWPE1 cells (Fig. 4A). Collectively, these results point out that RecQL4 is critical not only for maintaining cell cycle progression but also for survival in prostate cancer cells.
Fig. 4.
RecQL4 suppression leads to PARP-1 mediated apoptotic death in prostate cancer cells. (A) Analysis of cleaved PARP-1, Bax and AIF proteins in RWPE1 and PC3 cells after 72 hr of transfection with control and RecQL4 siRNA. (B) PC3 cells transfected with RecQL4 shRNA targeting vectors (TI339521 and TI339524) showed reduced survival. (C) Analysis of RecQL4 expression in empty vector (clone 5), scrambled vector (clone7) and RecQL4 shRNA (clones 6 and 4) transfected clonal cell lines of PC3.β-Actin was used as a loading control. (D) RecQL4 suppressed clonal cell lines (C6 and C4) showed increased focalization of PARP-1 and 53BP1. Western blot analysis showed increased γ-H2AX level in RecQL4 suppressed cells. Scale bar =10μM.
Stable RecQL4 knockdown increases spontaneous DNA strand break accumulation in metastatic prostate cancer cells
Effects of RecQL4 suppression on clonogenic survival was subsequently analyzed in PC3 cells through the use of RecQL4 targeting shRNA vectors (TI339521 and TI339524) together with empty (TR20003) and scrambled shRNA (TR30003) control vectors (Origene Technology, USA). Transient RecQL4 suppression by both shRNA vectors reduced the clonogenic survival of PC3 cells (Fig. 4B). To extend these studies, several stably transfected (empty, scrambled and RecQL4 specific) puromycin resistant clones were selected. Since complete RecQL4 silencing dramatically increased the apoptotic cell death, two stable clones (TI339521 vector transfected clone 6 and TI339524 vector transfected clone 4; hereafter designated as clone 6 and clone 4) with RecQL4 expression level similar to non-tumorigenic RWPE1 cells were selected. These clones showed 80–90% suppression in RecQL4 protein expression (Fig. 4C). For comparison, clonal cell lines stably expressing empty (Clone 5) and scrambled (Clone 7) vectors were also established.
The increased apoptotic death of RecQL4 suppressed cells is presumably due to a high level of spontaneous DNA damage accumulation. To test this possibility, intra-nuclear distribution of PARP-1, a marker for DNA single strand breaks and nicks, was monitored in PC3 cells. In comparison to empty vector transfected cells, RecQL4 suppressed clonal cell lines showed increased focalization of PARP-1 protein indicating the spontaneous accumulation of DNA single strand breaks (Fig. 4D). Additionally, increased focalization of a DNA double strand break (DSB) marker, 53BP1 as well as specific enrichment of yet another DSB marker, phosphorylated histone H2AX (γ-H2AX) was also detected in RecQL4 suppressed clonal cell lines (Fig. 4D). Consistent with DNA strand break accumulation, elevation of structural and numerical chromosomal aberrations were observed in RecQL4 suppressed clonal cell lines (Suppl. Fig. 2A). Also, RecQL4 suppressed PC3 cells showed elevated apoptotic death after treatment with UV-C (Suppl. Fig. 2B) and γ-rays radiation. These findings illustrate that RecQL4 is critical for protecting the prostate cancer cells from exogenous DNA damage.
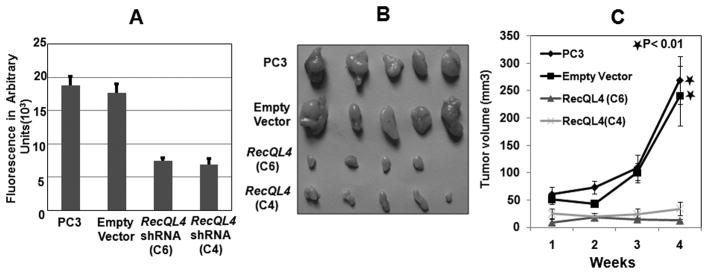
RecQL4 suppression reduces invasiveness and tumorigenicity of prostate cancer cells
To verify whether RecQL4 silencing affects the tumorigenic potential of PC3 cells, an in vitro cell invasion assay was performed. The results showed that cell invasion was greatly reduced in C4 and C6 cell lines (Fig. 5A). In vivo tumorigenicity of RecQL4 suppressed cell lines was subsequently evaluated in a xenograft mouse model. For this purpose, empty vector (C5) and RecQL4 shRNA transfected clonal cell lines (C6 and C4) were injected into athymic nude mice. Representative images of the tumor dissected after 4 weeks from the injected nude mice are shown in Fig. 5B. Tumor size (mm3) measured over four weeks of post-injection is given in Fig. 5C. Tumors grew rapidly in mice injected with PC3 or C5 (empty vector transfected) cells. In contrast, tumor growth was much slower in mice injected with C6 or C4 cells. In fact, one mouse injected with clone 6 remained tumor free for 4 weeks. These in vivo data strongly support the conclusion that RecQL4 is essential for tumorigenic potential of prostate cancer cells.
Fig. 5.
RecQL4 suppression drastically reduces cell invasiveness in vitro and tumorigenic growth in vivo. (A) RecQL4 suppressed clonal cell lines (C4 and C6) showed reduced cell invasion capacity. (B&C) Suppression of RecQL4 expression in prostate cancer cells reduces tumorigenicity in nude mice. Images of tumors dissected out from the sacrificed mice are shown in B. The tumor size (mm3) versus days of post-injection is shown in C. Difference in relative tumor volume observed at 4 weeks between empty vector and RecQL4 ShRNA transfected cells were found to be statistically significant. *p < 0.01.
Histone deacetylase inhibitor Trichostatin A reduces RecQL4 expression in prostate cancer cells
As p16 methylation and Rb hyperphosphorylation are frequent molecular events during tumorigenesis, expression levels of p16 and phosphorylated Rb (serine 807/811) were monitored in RWPE1 and the three prostate cancer cell lines. While p16 was hardly detectable in DU145, LNCaP and PC3 cell lines (Fig. 6A), a high level of hyperphosphorylated Rb was observed in the three prostate cancer cell lines. Immunohistochemical studies also demonstrated a positive correlation between Rb hyperphosphorylation and RecQL4 expression in 64 prostate tumor tissues from the PR751 array (Suppl. Fig. 3A).
Fig. 6.
Expression of RecQL4 expression is modulated by Rb-E2F1 pathway in prostate cancer cells. (A) Prostate cancer cells showed an inverse correlation between p16 level and Rb hyperphosphorylation (Ser807/811). TSA treatment abolished Rb hyperphosphorylation and reduced the expression of RecQL4 in both PC3 and RWPE1 cells. TSA treatment also reduced the levels of Cyclin A, Cyclin E and Cdk2 in PC3 cells but not in RWPE1 cells. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (B) TSA reduced the levels of E2F1 and phosphorylated Rb (T821) proteins in metastatic prostate cancer cell lines. (C) Quantitative real time PCR analysis showing the reduced expression levels of both E2F1 and RecQL4 in DU145 after TSA treatment. (D) Nucleotide sequence of RecQL4 promoter highlighting the putative responsive element for E2F1 binding is shown. The ChIP assay was performed in HeLa cells using antibodies specific for Rb and E2F1. Rb and E2F1 associated RecQL4 promoter DNA was amplified by PCR using appropriate primers. RNA polymerase II antibody was used as a positive control. Enrichment of the RecQL4 promoter in the immunoprecipitated DNA was quantified by real time PCR using the primers specific for RecQL4 promoter. Expon- Exponential curve.
To reverse p16 methylation and Rb hyperphosphorylation, PC3 cells were treated separately with either a DNA demethylating agent Zebularine (200μM) or a histone deacetylase inhibitor Trichostatin A (TSA, 1μM) for 48 hr. In both RWPE1 and PC3 cell lines, TSA treatment (1μM) reduced the proportion of G1 phase cells with a concomitant increase in G2/M phase cells but the enrichment of G2/M phase cells was higher at a lower TSA concentration (0.5μM). TSA at 1μM concentration reduced the proportion of S-phase cells only by 2–3% relative to mock control in both cell lines (Suppl. Fig. 3B). Strikingly, the apoptotic sub-G1 cells were more in PC3 cells (23.28%) than in RWPE1 cells (6.42%) after treatment with 1μM of TSA. Although p16 status remained unaffected, Rb hyperphosphorylation was abolished to a great extent in TSA treated PC3 cells with a concomitant decline in RecQL4 expression (Fig. 6A). However, RecQL4 expression was reduced by either of the treatments (Zebularine and TSA) in RWPE1 cells (Fig. 6A). As Cyclin A, Cyclin E and Cdk2 mediate Rb phosphorylation, their expression levels were monitored in PC3 and RWPE1 cells (Fig. 6A). The results showed that Cyclin A, Cyclin E and Cdk2 levels were noticeably reduced in PC3 cells (Fig. 6A), but were essentially unchanged by TSA treatment in RWPE1 cells. These results suggest that Rb hyperphosphorylation may be regulated by different mechanisms in non-tumorigenic and tumorigenic cells. In addition to phospho-Rb ser807/811, expression of phospho-Rb (T821) was also monitored in RWPE1 and the three prostate cancer cell lines. Similar to phospho-Rb (Ser807/811), phospho-Rb (T821) expression was also reduced in all the cell lines examined (Fig. 6B).
RT-PCR analysis showed that TSA treatment for 48 hr caused a dose dependent reduction in RecQL4 mRNA in DU145, LNCaP and PC3 cell lines (Suppl. Fig. 3C). We next verified whether the reduced RecQL4 expression after TSA treatment is due to reduced E2F1 expression. We found that E2F1 protein expression was considerably reduced only in TSA treated prostate cancer cell lines but not in RWPE1 cells (Fig. 6B). Also, TSA reduced the expression of both RecQL4 and E2F1 mRNAs in a dose dependent manner in DU145 cells (Fig. 6C) as well as in LNCaP and PC3 cell lines (Data not shown). Collectively, these studies suggest that elevation of RecQL4 expression in prostate cancer cells and prostate tumor tissues is likely due to deregulation of Rb-E2F1 pathway.
Rb and E2F1 proteins physically interact with RecQL4 promoter in vivo
The nucleotide sequence of the RecQL4 promoter with potential target sequence for E2F1 binding is shown in Fig. 6D. To test whether Rb and E2F1 proteins directly regulate transcription of RecQL4 via these sites, ChIP assay was performed to detect E2F1 and Rb binding to the RecQL4 promoter in HeLa cells (Fig. 6D). RT-PCR analysis of immunoprecipitated HeLa chromatin DNA detected the RecQL4 promoter bound to Rb and E2F1 proteins (Fig. 6D). The RecQL4 promoter was undetectable in the negative control without any antibody while a positive control using RNA polymerase II antibody detected a specific enrichment of the RecQL4 promoter. Quantification of the RecQL4 promoter bound to Rb and E2F1 proteins was analyzed by real time PCR (Fig. 6D). These results suggest the possibility that Rb and E2F1 regulate RecQL4 expression in prostate cancer cells.
Discussion
Here, we report the novel finding that RecQL4 helicase which maps to 8q24.3 is up regulated in prostate cancer cells and tissues. The salient findings of this study are: (I) RecQL4 expression is elevated in metastatic prostate cancer cells and tumor tissues, (II) RecQL4 depletion causes proliferation failure and apoptosis in prostate cancer cells lines, (II) RecQL4 protects the genomic integrity of prostate cancer cells from endogenous and exogenous DNA damage and (IV) RecQL4 suppression in metastatic PC3 cells drastically reduced their tumorigenic potential both in vitro and in vivo. These data support our hypothesis that RecQL4 is a critical factor for prostate carcinogenesis. Based on our study, we propose that elevated RecQL4 expression confers survival advantage to prostate cancer cells by protecting their genomic integrity from endogenous and exogenous DNA damage. In support, several earlier studies have demonstrated a direct or indirect participation of RecQL4 in diverse DNA repair pathways (10, 32–36). Collectively our findings demonstrate that RecQL4 is a critical factor for prostate cancer cell growth and viability.
Unlimited replicative potential is a hallmark of immortalized and metastatic prostate cancer cells. Recent evidences indicate an essential role for RecQL4 in DNA replication initiation (11, 13, 40–42). Further, the N-terminal domain of RecQL4 shares extensive homology to an essential DNA replication protein, Sld2 (40). Recent studies have established a direct interaction of RecQL4 with factors involved in replisome assembly (43, 44). A direct interaction of RecQL4 with minimal chromosome maintenance complex (MCM 10, and MCM 2-7 helicase), CDC45 and GINS was recently documented (44). A more direct role of RecQL1 and RecQL4 in DNA replication initiation was also recently established (45). Therefore, reduced proliferation observed in RecQL4 suppressed prostate cancer cells is probably due to deficiencies in DNA replication initiation.
Liu et al. (37) showed that disruption of the retinoblastoma (Rb) and E2F pathway leads to the enhanced expression of RecQ helicases using the mouse model systems deficient in these pathways. The present study shows that Rb hyperphosphorylation and RecQL4 expression correlated with each other in both prostate cancer cells and tissues. Consistent with this, TSA treatment resulted in the abolition of Rb hyperphosphorylation and reduced expression of both E2F1 and RecQL4. Loss of Rb hyperphosphorylation was accompanied by the reduction in the levels of Cdk2, Cyclin A and Cyclin E in PC3 cells. Collectively, these data suggest that RecQL4 expression may be regulated by the Rb-E2F1 pathway in prostate cancer cells. Other mechanisms may also regulate RecQL4 expression in prostate cancer cells. For example, p53 mediated transcriptional repression of RecQL4 has been documented in the literature (38) in immortalized human fibroblasts by wild type p53 but not by tumor derived mutant p53 forms. However, in this study, elevated RecQL4 expression was found both in p53 mutated (DU145 and PC3) and p53 wild type (LNCaP) prostate cancer cell lines (39). Thus, different mechanisms may regulate RecQL4 expression in immortalized fibroblasts and metastatic prostate cancer cells.
Among the 5 RecQ helicases, RecQL4 alone showed an elevated expression consistently in all the 6 prostate cancer cells lines examined by us. In contrast, BLM helicase was highly expressed only in DU145 cells while the expression levels of other human RecQ helicases (RecQL1, RecQL5 and WRN) were grossly similar in immortalized prostate epithelial and prostate cancer cell lines (Suppl. Fig. 4). On this basis, we propose that elevated RecQL4 expression has two well defined biological functions in prostate carcinogenesis: (I) To confer infinite proliferation potential to prostate cancer cells through its direct participation in DNA replication and (II) to protect the genomic integrity of prostate cancer cells from endogenous and exogenous DNA damage by regulating the efficiency of diverse DNA repair pathways. Observations of the reduced proliferation, clonogenic survival, cell invasion and in vivo tumorigenicity of RecQL4 suppressed metastatic prostate cancer cells convincingly favor the aforementioned functions of RecQL4 in prostate cancer cells. Specific elevation of RecQL4 expression in the metastatic prostate cancer cells and tumor tissues indicate that RecQL4 may be a novel biomarker for the advanced stage of prostate cancer. Additionally, RecQL4 suppression by TSA raises a potential possibility for development of new therapeutic strategies for RecQL4 targeting in prostate cancer cells.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Igor Stagljar, University of Toronto, Canada for the generous gift RecQL4 antibodies. We appreciate the generous gift of fluorescence labeled BAC and centromeric DNA probes from Dr. V.V. Murty, CUMC, NY. We thank Dr. David J. Brenner, Center for Radiological Research, CUMC, NY for allowing us to use ISIS MetaSystems software for the image analysis. We thank Dr. Howard Lieberman for critical comments and suggestions.
Grant support
U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Sciences (BER; DE-FG02-05ER64055) and National Institutes of Health (NCI/NIH: CA127120).
Footnotes
Conflict of research interest
None
References
- 1.Heyer WD. Damage signaling: RecQ sends an SOS to you. Curr Biol. 2004;14:R895–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.09.073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hanada K, Hickson ID. Molecular genetics of RecQ helicase disorders. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007;64:2306–22. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-7121-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vindigni A, Hickson ID. RecQ helicases: multiple structures for multiple functions? HFSP J. 2009;3:153–64. doi: 10.2976/1.3079540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lindor NM, Furuichi Y, Kitao S, Shimamoto A, Arndt C, Jalal S. Rothmund-Thomson syndrome due to RECQ4 helicase mutations: report and clinical and molecular comparisons with Bloom syndrome and Werner syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 2000;90:223–8. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-8628(20000131)90:3<223::aid-ajmg7>3.0.co;2-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kellermayer R. The versatile RECQL4. Genet Med. 2006;8:213–6. doi: 10.1097/01.gim.0000214457.58378.1a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bohr VA. Rising from the RecQ-age: the role of human RecQ helicases in genome maintenance. Trends Biochem Sci. 2008;33:609–20. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2008.09.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sharma S, Stumpo DJ, Balajee AS, et al. RECQL, a member of the RecQ family of DNA helicases, suppresses chromosomal instability. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27:1784–94. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01620-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Enomoto T. Function of RecQ family helicases and Bloom’s syndrome. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2001;46:1082–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Balajee AS, Machwe A, May A, et al. The Werner syndrome protein is involved in RNA polymerase II transcription. Mol Biol Cell. 1999;10:2655–68. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.8.2655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kumata Y, Tada S, Yamanada Y, et al. Possible involvement of RecQL4 in the repair of double-strand DNA breaks in Xenopus egg extracts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1773:556–64. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2007.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sangrithi MN, Bernal JA, Madine M, et al. Initiation of DNA replication requires the RECQL4 protein mutated in Rothmund-Thomson syndrome. Cell. 2005;121:887–98. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.05.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Petkovic M, Dietschy T, Freire R, Jiao R, Stagljar I. The human Rothmund-Thomson syndrome gene product, RECQL4, localizes to distinct nuclear foci that coincide with proteins involved in the maintenance of genome stability. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:4261–9. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Xu X, Liu Y. Dual DNA unwinding activities of the Rothmund-Thomson syndrome protein, RECQ4. EMBO J. 2009;28:568–77. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rossi ML, Ghosh AK, Kulikowicz T, Croteau DL, Bohr VA. Conserved helicase domain of human RecQ4 is required for strand annealing-independent DNA unwinding. DNA Repair (Amst) 9:796–804. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2010.04.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Begley L, Keeney D, Beheshti B, et al. Concordant copy number and transcriptional activity of genes mapping to derivative chromosomes 8 during cellular immortalization in vitro. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2006;45:136–46. doi: 10.1002/gcc.20274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Laitinen S, Karhu R, Sawyers CL, Vessella RL, Visakorpi T. Chromosomal aberrations in prostate cancer xenografts detected by comparative genomic hybridization. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2002;35:66–73. doi: 10.1002/gcc.10097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rubin MA, Varambally S, Beroukhim R, et al. Overexpression, amplification, and androgen regulation of TPD52 in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2004;64:3814–22. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-3881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Schulz WA, Elo JP, Florl AR, et al. Genomewide DNA hypomethylation is associated with alterations on chromosome 8 in prostate carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2002;35:58–65. doi: 10.1002/gcc.10092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Torring N, Borre M, Sorensen KD, Andersen CL, Wiuf C, Orntoft TF. Genome-wide analysis of allelic imbalance in prostate cancer using the Affymetrix 50K SNP mapping array. Br J Cancer. 2007;96:499–506. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bubendorf L, Kononen J, Koivisto P, et al. Survey of gene amplifications during prostate cancer progression by high-throughout fluorescence in situ hybridization on tissue microarrays. Cancer Res. 1999;59:803–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cher ML, Bova GS, Moore DH, et al. Genetic alterations in untreated metastases and androgen-independent prostate cancer detected by comparative genomic hybridization and allelotyping. Cancer Res. 1996;56:3091–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Van Den Berg C, Guan XY, Von Hoff D, et al. DNA sequence amplification in human prostate cancer identified by chromosome microdissection: potential prognostic implications. Clin Cancer Res. 1995;1:11–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Choi YW, Bae SM, Kim YW, et al. Gene expression profiles in squamous cell cervical carcinoma using array-based comparative genomic hybridization analysis. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2007;17:687–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1438.2007.00834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Narayan G, Bourdon V, Chaganti S, et al. Gene dosage alterations revealed by cDNA microarray analysis in cervical cancer: identification of candidate amplified and overexpressed genes. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2007;46:373–84. doi: 10.1002/gcc.20418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Thomassen M, Tan Q, Kruse TA. Gene expression meta-analysis identifies chromosomal regions and candidate genes involved in breast cancer metastasis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009;113:239–49. doi: 10.1007/s10549-008-9927-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Buffart TE, Coffa J, Hermsen MA, et al. DNA copy number changes at 8q11-24 in metastasized colorectal cancer. Cell Oncol. 2005;27:57–65. doi: 10.1155/2005/401607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Maire G, Yoshimoto M, Chilton-MacNeill S, Thorner PS, Zielenska M, Squire JA. Recurrent RECQL4 imbalance and increased gene expression levels are associated with structural chromosomal instability in sporadic osteosarcoma. Neoplasia. 2009;11:260–8. doi: 10.1593/neo.81384. 3p following 8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Shen WH, Balajee AS, Wang J, et al. Essential role for nuclear PTEN in maintaining chromosomal integrity. Cell. 2007;128:157–70. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Meador JA, Zhao M, Su Y, Narayan G, Geard CR, Balajee AS. Histone H2AX is a critical factor for cellular protection against DNA alkylating agents. Oncogene. 2008;27:5662–71. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Filippi S, Latini P, Frontini M, Palitti F, Egly JM, Proietti-De-Santis L. CSB protein is (a direct target of HIF-1 and) a critical mediator of the hypoxic response. EMBO J. 2008;27:2545–56. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bello D, Webber MM, Kleinman HK, Wartinger DD, Rhim JS. Androgen responsive adult human prostatic epithelial cell lines immortalized by human papillomavirus 18. Carcinogenesis. 1997;18:1215–23. doi: 10.1093/carcin/18.6.1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Fan W, Luo J. RecQ4 facilitates UV light-induced DNA damage repair through interaction with nucleotide excision repair factor xeroderma pigmentosum group A (XPA) J Biol Chem. 2008;283:29037–44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801928200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Park SJ, Lee YJ, Beck BD, Lee SH. A positive involvement of RecQL4 in UV-induced S-phase arrest. DNA Cell Biol. 2006;25:696–703. doi: 10.1089/dna.2006.25.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Woo LL, Futami K, Shimamoto A, Furuichi Y, Frank KM. The Rothmund-Thomson gene product RECQL4 localizes to the nucleolus in response to oxidative stress. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312:3443–57. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.07.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Schurman SH, Hedayati M, Wang Z, et al. Direct and indirect roles of RECQL4 in modulating base excision repair capacity. Hum Mol Genet. 2009;18:3470–83. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Singh DK, Karmakar P, Aamann M, et al. The involvement of human RECQL4 in DNA double-strand break repair. Aging Cell. 9:358–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2010.00562.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Liu Y, El-Naggar S, Clem B, Chesney J, Dean DC. The Rb/E2F pathway and Ras activation regulate RecQ helicase gene expression. Biochem J. 2008;412:299–306. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sengupta S, Shimamoto A, Koshiji M, et al. Tumor suppressor p53 represses transcription of RECQ4 helicase. Oncogene. 2005;24:1738–48. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Carroll AG, Voeller HJ, Sugars L, Gelmann EP. p53 oncogene mutations in three human prostate cancer cell lines. Prostate. 1993;23:123–34. doi: 10.1002/pros.2990230206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Matsuno K, Kumano M, Kubota Y, Hashimoto Y, Takisawa H. The N-terminal noncatalytic region of Xenopus RecQ4 is required for chromatin binding of DNA polymerase alpha in the initiation of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:4843–52. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02267-05. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wu J, Capp C, Feng L, Hsieh TS. Drosophila homologue of the Rothmund-Thomson syndrome gene: essential function in DNA replication during development. Dev Biol. 2008;323:130–42. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.08.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Xu Y, Lei Z, Huang H, et al. dRecQ4 is required for DNA synthesis and essential for cell proliferation in Drosophila. PLoS One. 2009;4:e6107. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Im JS, Ki SH, Farina A, Jung DS, Hurwitz J, Lee JK. Assembly of the Cdc45-Mcm2-7-GINS complex in human cells requires the Ctf4/And-1, RecQL4, and Mcm10 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:15628–32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0908039106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Xu X, Rochette PJ, Feyissa EA, Su TV, Liu Y. MCM10 mediates RECQ4 association with MCM2-7 helicase complex during DNA replication. EMBO J. 2009;28:3005–14. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Thangavel S, Mendoza-Maldonado R, Tissino E, et al. Human RECQ1 and RECQ4 Helicases Play Distinct Roles in DNA Replication Initiation. Molecular and cellular biology. 30:1382–96. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01290-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.