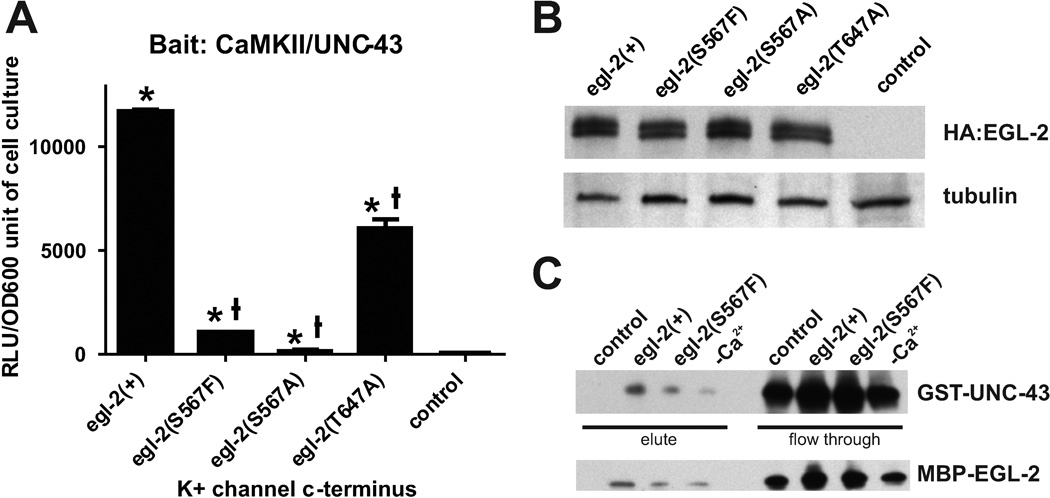
Figure 3.
Direct interaction between CaMKII/UNC-43 and the EAG K+ channel EGL-2. (A) Protein interaction in a yeast two-hybrid assay. The x axis lists the EGL-2 constructs with amino acid substitutions at the c-terminus and the y axis depicts the amount of real light units (RLU) given off per unit of cell culture. The control column depicts the amount of RLU released from wild-type yeast cells that do not contain either EGL-2 or UNC-43 sequences. An * above the column indicates a p value < 0.005 compared to the control, while a † above the column indicates a p value < 0.005 compared to egl-2(+). p values were determined by the unpaired t test. (B) Western blot assaying for the presence of HA-tagged EGL-2 in yeast cells. α-tubulin was used as a loading control. (C) Western blots assaying for the presence of UNC-43-GST bound to amylose resin-associated EGL-2 –MBP (top panel) and for the presence of EGL-2-MBP bound to glutathione-associated UNC-43-GST (bottom panel).