Abstract
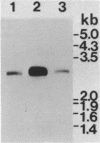
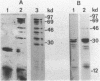
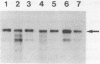
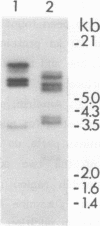
We have isolated a full length cDNA (cDNA) coding for the human poly(A) binding protein. The cDNA derived 73 kd basic translation product has the same Mr, isoelectric point and peptidic map as the poly(A) binding protein. DNA sequence analysis reveals a 70,244 dalton protein. The N terminal part, highly homologous to the yeast poly(A) binding protein, is sufficient for poly(A) binding activity. This domain consists of a four-fold repeated unit of approximately 80 amino acids present in other nucleic acid binding proteins. In the C terminal part there is, as in the yeast protein, a sequence of approximately 150 amino acids, rich in proline, alanine and glutamine which together account for 48% of the residues. A 2,9 kb mRNA corresponding to this cDNA has been detected in several vertebrate cell types and in Drosophila melanogaster at every developmental stage including oogenesis.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Nakagawa T., Swanson M. S., Woodruff T. K., Dreyfuss G. mRNA polyadenylate-binding protein: gene isolation and sequencing and identification of a ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2932–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bablanian R., Banerjee A. K. Poly(riboadenylic acid) preferentially inhibits in vitro translation of cellular mRNAs compared with vaccinia virus mRNAs: possible role in vaccinia virus cytopathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1290–1294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. A protein of molecular weight 78,000 bound to the polyadenylate region of eukaryotic messenger RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):924–928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. The Role of the poly(A) sequence in mammalian messenger RNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1981;10(1):1–38. doi: 10.3109/10409238109114634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke N. E., Coit D., Weiner R. I., Baxter J. D., Martial J. A. Structure of cloned DNA complementary to rat prolactin messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6502–6510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond D. R., Armstrong J., Colman A. The effect of capping and polyadenylation on the stability, movement and translation of synthetic messenger RNAs in Xenopus oocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7375–7394. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange T., Guénet C., Dietrich J. B., Chasserot S., Fromont M., Befort N., Jami J., Beck G., Pictet R. Complete complementary DNA of rat tyrosine aminotransferase messenger RNA. Deduction of the primary structure of the enzyme. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 20;184(2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Hunt T. Preparation and use of nuclease-treated rabbit reticulocyte lysates for the translation of eukaryotic messenger RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:50–74. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson A., Favreau M. Possible involvement of poly(A) in protein synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6353–6368. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffery W. R. Characterization of polypeptides associated with messenger RNA and its polyadenylate segment in Ehrlich ascites messenger ribonucleoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3525–3532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kish V. M., Pederson T. Poly (A)-rich ribonucleoprotein complexes from HeLa cell messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5888–5894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapeyre B., Bourbon H., Amalric F. Nucleolin, the major nucleolar protein of growing eukaryotic cells: an unusual protein structure revealed by the nucleotide sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1472–1476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littauer U. Z., Soreq H. The regulatory function of poly(A) and adjacent 3' sequences in translated RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1982;27:53–83. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60597-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maundrell K., Imaizumi-Scherrer M. T., Maxwell E. S., Civelli O., Scherrer K. Messenger RNA for the 73,000-dalton poly(A)-binding protein occurs as translationally repressed mRNP in duck reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1387–1390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Coussens L., Totty N., Rhee L., Young S., Chen E., Stabel S., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A. The complete primary structure of protein kinase C--the major phorbol ester receptor. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):853–859. doi: 10.1126/science.3755547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preobrazhensky A. A., Spirin A. S. Informosomes and their protein components: the present state of knowledge. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1978;21:1–38. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60265-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigaud G., Grange T., Pictet R. The use of NaOH as transfer solution of DNA onto nylon membrane decreases the hybridization efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):857–857. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Bond M. W., Kornberg R. D. A single gene from yeast for both nuclear and cytoplasmic polyadenylate-binding proteins: domain structure and expression. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90557-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Kornberg R. D. Nuclear polyadenylate-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1993–1996. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz H., Darnell J. E. The association of protein with the polyadenylic acid of HeLa cell messenger RNA: evidence for a "transport" role of a 75,000 molecular weight polypeptide. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 15;104(4):833–851. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90185-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönfelder M., Horsch A., Schmid H. P. Heat shock increases the synthesis of the poly(A)-binding protein in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6884–6888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setyono B., Greenberg J. R. Proteins associated with poly(A) and other regions of mRNA and hnRNA molecules as investigated by crosslinking. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):775–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2951–2961. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standart N., Vincent A., Scherrer K. The polyribosomal poly(A)-binding protein is highly conserved in vertebrate species. Comparison in duck, mouse and rabbit. FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 30;135(1):56–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80942-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theissen H., Etzerodt M., Reuter R., Schneider C., Lottspeich F., Argos P., Lührmann R., Philipson L. Cloning of the human cDNA for the U1 RNA-associated 70K protein. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3209–3217. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Thomas G. Translational control of mRNA expression during the early mitogenic response in Swiss mouse 3T3 cells: identification of specific proteins. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2137–2144. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. B., Tomkins G. M., Curran J. F. Induction of tyrosine alpha-ketoglutarate transaminase by steroid hormones in a newly established tissue culture cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):296–303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Goldenberg S., Scherrer K. Comparisons of proteins associated with duck-globin mRNA and its polyadenylated segment in polyribosomal and repressed free messenger ribonucleoprotein complexes. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Feb;114(2):179–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Venrooij W. J., van Eekelen C. A., Jansen R. T., Princen J. M. Specific poly-A-binding protein of 76,000 molecular weight in polyribosomes is not present on poly A of free cytoplasmic mRNP. Nature. 1977 Nov 10;270(5633):189–191. doi: 10.1038/270189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]