Abstract
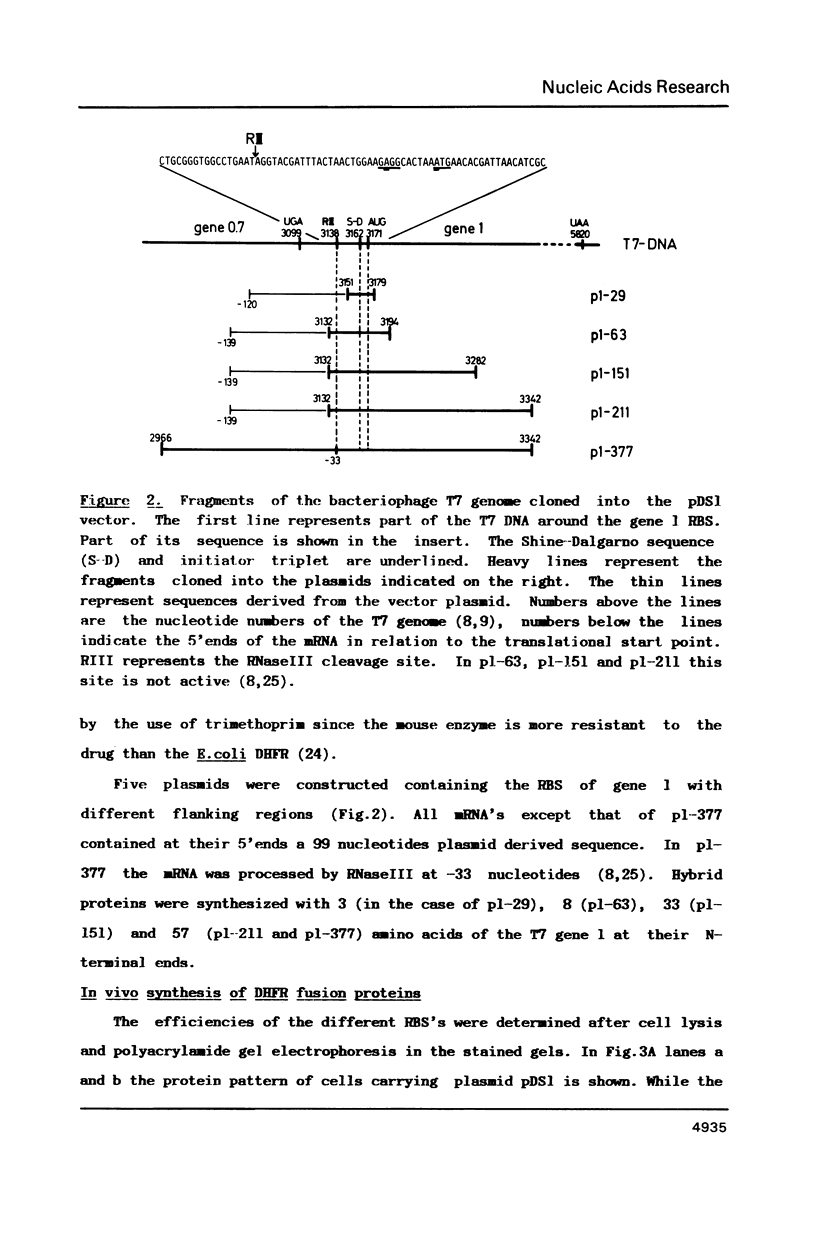
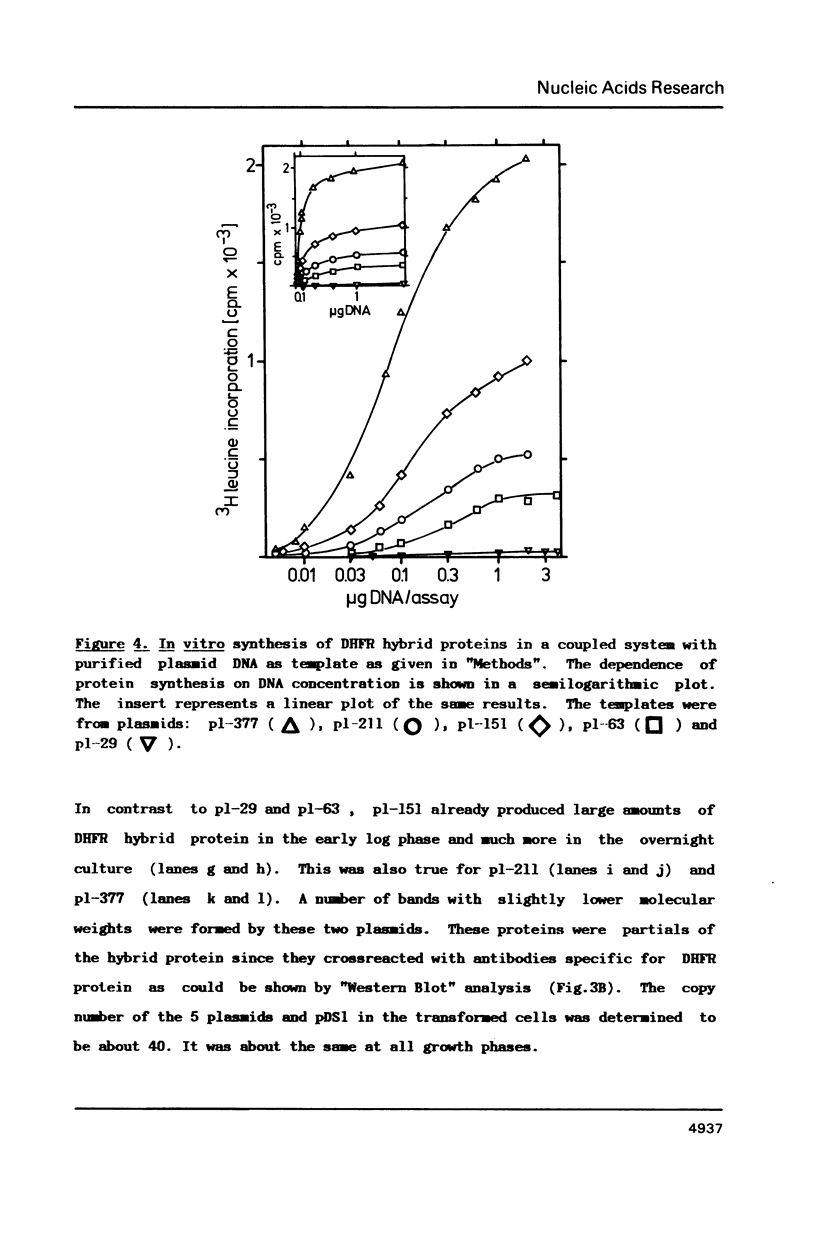
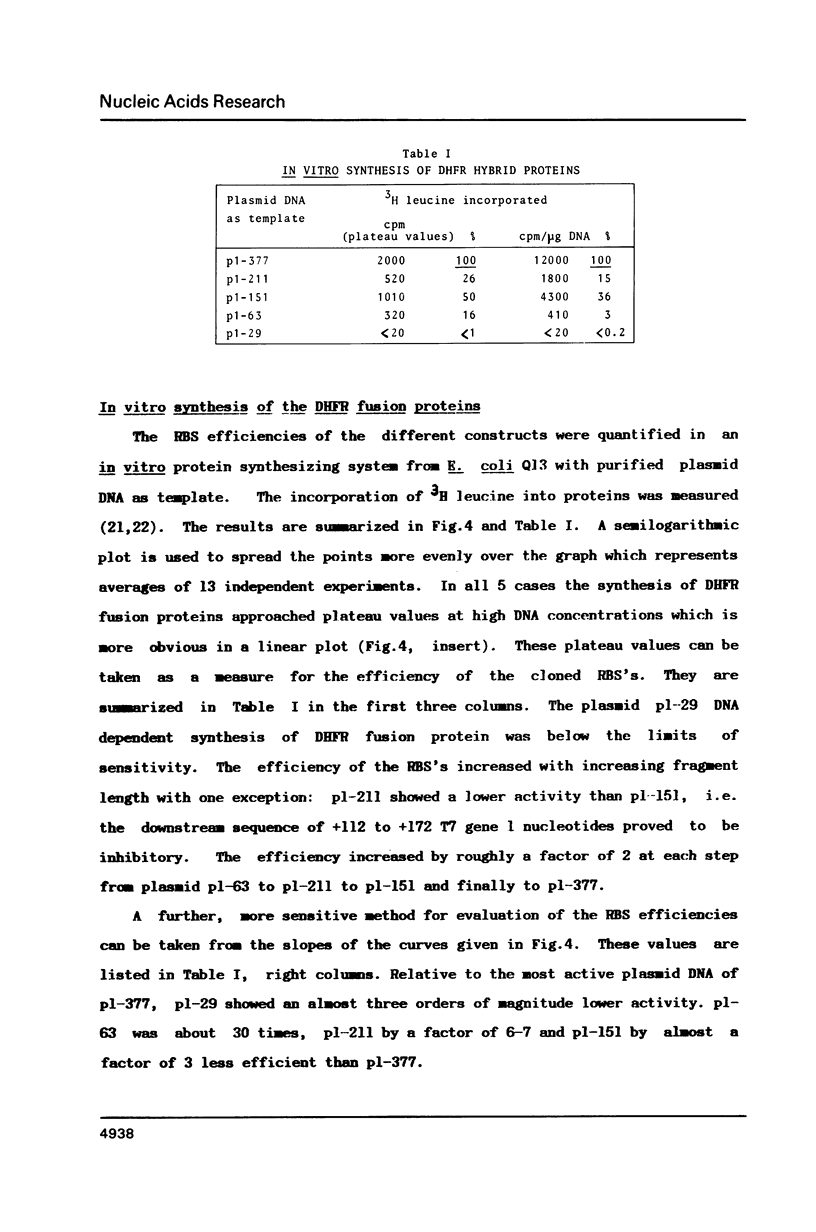
The ribosomal binding site (RBS) from gene 1 of bacteriophage T7 was isolated on fragments of differing length and cloned upstream of the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene to control the translation of its sequence. A 29 base pair sequence containing all elements generally believed to be essential for the RBS's showed extremely low activity. Additional upstream and downstream sequences were required to obtain a several orders of magnitude higher efficiency. By contrast, areas further downstream than +112 nucleotides from the initiator proved to be inhibitory, whereas the presence of an upstream RNaseIII cleavage site showed a strong stimulatory effect. This suggests that tertiary structures are involved in the function of the RBS studied. The efficient RBS's were complexed by ribosomes at much lower concentrations of the mRNA than the weak ones.
Full text
PDF




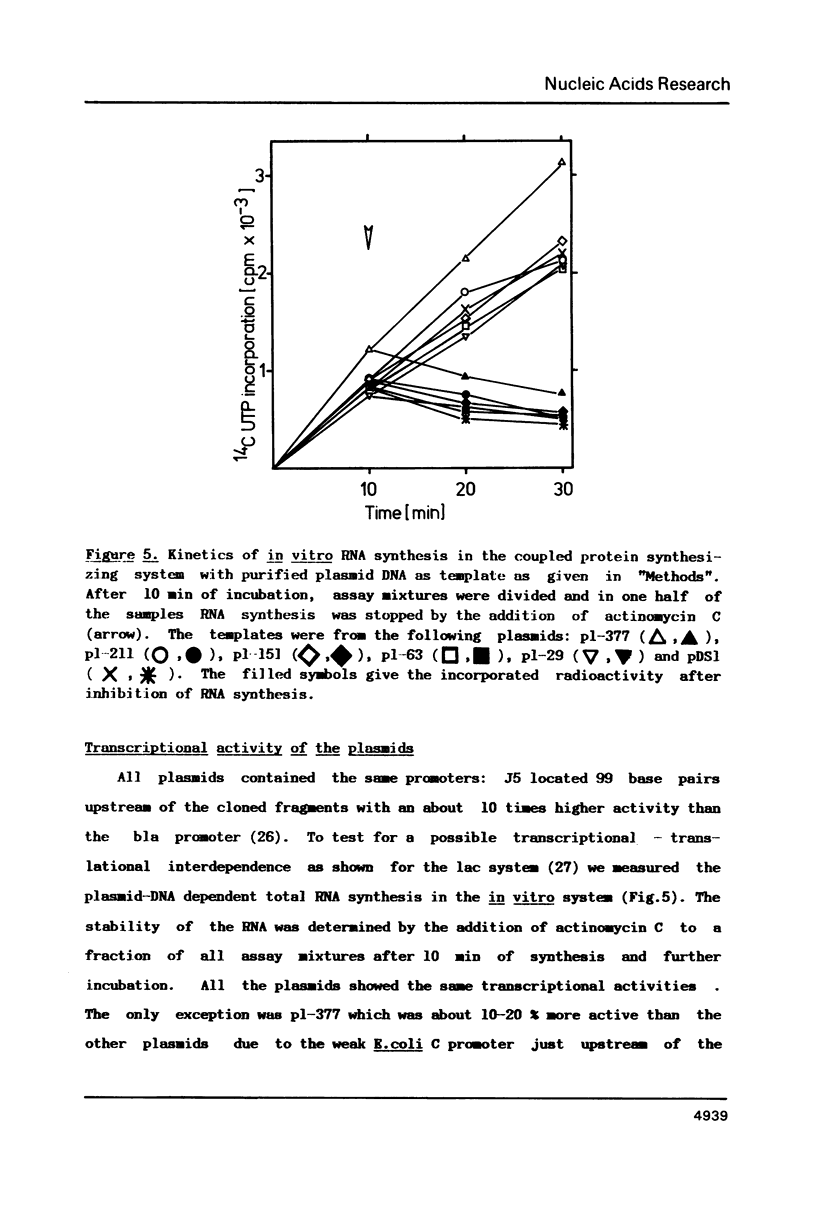

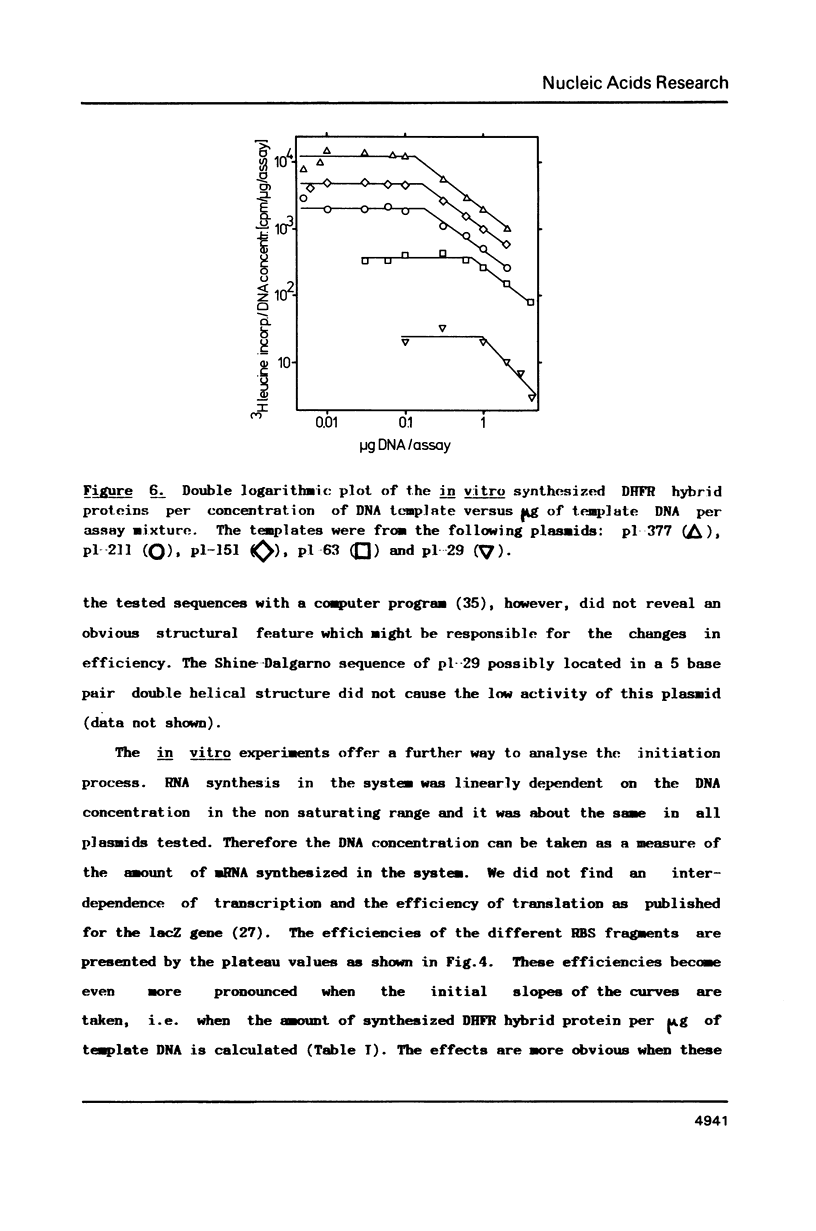


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bannwarth W., Iaiza P. A system for the simultaneous chemical synthesis of different DNA fragments on solid support. DNA. 1986 Oct;5(5):413–419. doi: 10.1089/dna.1986.5.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Erlich H. A., Schimke R. T., Cohen S. N. Phenotypic expression in E. coli of a DNA sequence coding for mouse dihydrofolate reductase. Nature. 1978 Oct 19;275(5681):617–624. doi: 10.1038/275617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuschle U., Kammerer W., Gentz R., Bujard H. Promoters of Escherichia coli: a hierarchy of in vivo strength indicates alternate structures. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2987–2994. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04596.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus M., Kotlarz D., Busby S. Point mutations that affect translation initiation in the Escherichia coli gal E gene. J Mol Biol. 1985 Apr 5;182(3):411–417. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90200-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Buzash-Pollert E., Studier F. W. Mutations of bacteriophage T7 that affect initiation of synthesis of the gene 0.3 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2741–2745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage T7 DNA and the locations of T7 genetic elements. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):477–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. T7 early RNAs are generated by site-specific cleavages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1559–1563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Hirth K. P., Henrich B., Kälberer G. Demonstration of the early--late switch in vitro with bacteriophage T7 DNA as template. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Dec;113(1):61–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E. The interdependence of magnesium with spermidine and phosphoenolpyruvate in an enzyme-synthesizing system in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Mar 16;63(1):15–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganoza M. C., Marliere P., Kofoid E. C., Louis B. G. Initiator tRNA may recognize more than the initiation codon in mRNA: a model for translational initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4587–4591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Bujard H. Promoters recognized by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase selected by function: highly efficient promoters from bacteriophage T5. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):70–77. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.70-77.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L., Pribnow D., Schneider T., Shinedling S., Singer B. S., Stormo G. Translational initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:365–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastelein R. A., Berkhout B., Overbeek G. P., van Duin J. Effect of the sequences upstream from the ribosome-binding site on the yield of protein from the cloned gene for phage MS2 coat protein. Gene. 1983 Sep;23(3):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolaskar A. S., Reddy B. V. A method to locate protein coding sequences in DNA of prokaryotic systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 11;13(1):185–194. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffatt B. A., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 25;173(2):265–269. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90194-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Truong K. Cleavage within an RNase III site can control mRNA stability and protein synthesis in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2227–2240. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Determinant of cistron specificity in bacterial ribosomes. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):34–38. doi: 10.1038/254034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl S. J., Chamberlin M. J. An expanded transcriptional map of T7 bacteriophage. Reading of minor T7 promoter sites in vitro by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 5;112(4):577–601. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanssens P., Remaut E., Fiers W. Inefficient translation initiation causes premature transcription termination in the lacZ gene. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):711–718. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90837-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L. M. Characterization of translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2971–2996. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L., Ehrenfeucht A. Use of the 'Perceptron' algorithm to distinguish translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2997–3011. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stueber D., Bujard H. Transcription from efficient promoters can interfere with plasmid replication and diminish expression of plasmid specified genes. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1399–1404. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessier L. H., Sondermeyer P., Faure T., Dreyer D., Benavente A., Villeval D., Courtney M., Lecocq J. P. The influence of mRNA primary and secondary structure on human IFN-gamma gene expression in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7663–7675. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Suyama A., Mori N., Yokota T., Wada A. Gene expression in the polycistronic operons of Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin and cholera toxin: a new model of translational control. FEBS Lett. 1985 Feb 25;181(2):377–380. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]