Abstract
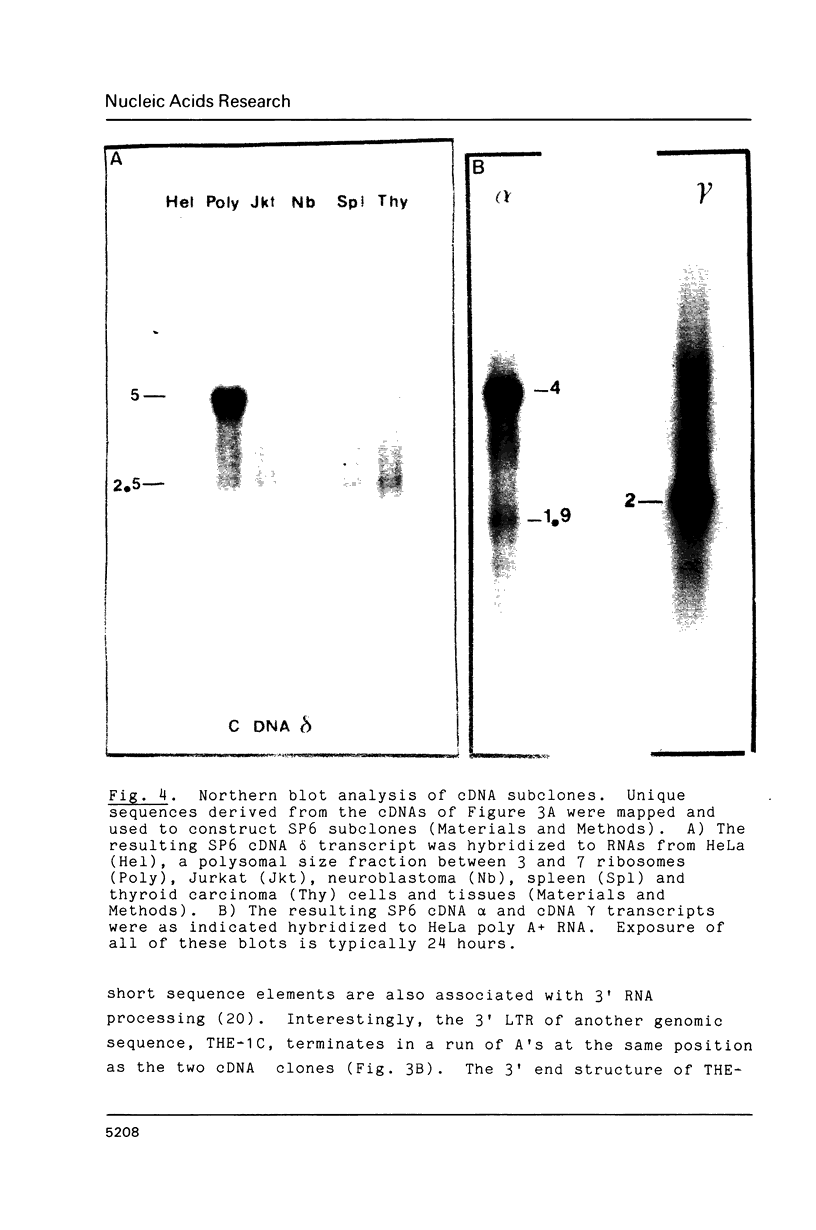
The transcriptional activity of a human transposon-like family of repeats, called the THE-1 family, has been studied in cell culture and in human tissue. Both strands of THE-1 are present in several discrete length poly A plus RNAs. Primer extension studies and the structures of cDNA clones show that these THE-1 transcripts are usually the product of other transcription units. The THE-1 LTR provides the polyadenylation processing site for two transcripts, which result from upstream non THE-1 promoters. Yet another transcript, containing an internal THE-1 element in the probable sense orientation, is greatly enriched in a polysomal size fraction.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arkhipova I. R., Mazo A. M., Cherkasova V. A., Gorelova T. V., Schuppe N. G., Llyin Y. V. The steps of reverse transcription of Drosophila mobile dispersed genetic elements and U3-R-U5 structure of their LTRs. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):555–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90265-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Retroviruses and retrotransposons: the role of reverse transcription in shaping the eukaryotic genome. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):481–482. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clare J., Farabaugh P. Nucleotide sequence of a yeast Ty element: evidence for an unusual mechanism of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2829–2833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev G. P., Ilyin Y. V., Chmeliauskaite V. G., Ryskov A. P., Kramerov D. A., Skryabin K. G., Krayev A. S., Lukanidin E. M., Grigoryan M. S. Mobile dispersed genetic elements and other middle repetitive DNA sequences in the genomes of Drosophila and mouse: transcription and biological significance. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):641–654. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Bifunctional messenger RNAs in eukaryotes. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):481–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90609-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress M., Barra Y., Seidman J. G., Khoury G., Jay G. Functional insertion of an Alu type 2 (B2 SINE) repetitive sequence in murine class I genes. Science. 1984 Nov 23;226(4677):974–977. doi: 10.1126/science.6095445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Rubin G. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Drosophila transposable element copia: homology between copia and retroviral proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1630–1638. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson K. E., Deka N., Schmid C. W., Misra R., Schindler C. W., Rush M. G., Kadyk L., Leinwand L. A transposon-like element in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):359–361. doi: 10.1038/316359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J., Sherman F. Dependence on mating type for the overproduction of iso-2-cytochrome c in the yeast mutant CYC7-H2. Genetics. 1980 Apr;94(4):891–898. doi: 10.1093/genetics/94.4.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saigo K., Kugimiya W., Matsuo Y., Inouye S., Yoshioka K., Yuki S. Identification of the coding sequence for a reverse transcriptase-like enzyme in a transposable genetic element in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):659–661. doi: 10.1038/312659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Conversion of RNA to DNA in mammals: Alu-like elements and pseudogenes. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):471–472. doi: 10.1038/301471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiba T., Saigo K. Retrovirus-like particles containing RNA homologous to the transposable element copia in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):119–124. doi: 10.1038/302119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Function of the retrovirus long terminal repeat. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90367-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M. An abundant cytoplasmic 7S RNA is complementary to the dominant interspersed middle repetitive DNA sequence family in the human genome. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):209–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]