Abstract
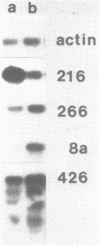
In an approach to study effects of UV light on gene expression in human epidermal keratinocytes, a cDNA library was constructed from poly(A)RNA isolated after UV irradiation from cultured keratinocytes. The cDNA library was differentially screened with labelled cDNA probes synthesized on poly(A)RNA isolated from UV irradiated or nonirradiated keratinocytes. Forty clones were selected and subjected to further analysis, 31 of them are described in this report. Whereas total mRNA synthesis is reduced after UV irradiation or treatment with 4-NQO Northern blot analysis revealed that there is an at least relative increase in the level of mRNAs corresponding to the majority of the isolated cDNA clones. Among these 15 were identified as corresponding to mRNAs for 50K and 56K keratins and for 50K- and 46K-related keratin. In addition, clones were found corresponding to the proteinase inhibitor cystatin A and to the glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). Treatment of keratinocytes with the tumor promoter TPA had no effect on the mRNA level for most of the clones except those corresponding to keratins. Our results indicate that in keratinocytes UV irradiation leads to a relative increase in the level of some mRNAs.
Full text
PDF
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C., Magnus I. A., Young M. R. Role of lysosomes and of cell membranes in photosensitization. Nature. 1966 Feb 26;209(5026):874–878. doi: 10.1038/209874a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Pöting A., Mallick U., Rahmsdorf H. J., Schorpp M., Herrlich P. Induction of metallothionein and other mRNA species by carcinogens and tumor promoters in primary human skin fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1760–1766. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M. Are U4 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins involved in polyadenylation? Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):179–182. doi: 10.1038/309179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Rosbash M. Polynucleotide sequences in eukaryotic DNA and RNA that form ribonuclease-resistant complexes with polyuridylic acid. J Mol Biol. 1974 May 5;85(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohr V. A., Smith C. A., Okumoto D. S., Hanawalt P. C. DNA repair in an active gene: removal of pyrimidine dimers from the DHFR gene of CHO cells is much more efficient than in the genome overall. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):359–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brands J. H., Maassen J. A., van Hemert F. J., Amons R., Möller W. The primary structure of the alpha subunit of human elongation factor 1. Structural aspects of guanine-nucleotide-binding sites. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 17;155(1):167–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corasanti J. G., Hobika G. H., Markus G. Interference with dimethylhydrazine induction of colon tumors in mice by epsilon-aminocaproic acid. Science. 1982 May 28;216(4549):1020–1021. doi: 10.1126/science.6805074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Cochran M. D., Dobkin C., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Three regions upstream from the cap site are required for efficient and accurate transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in mouse 3T6 cells. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):695–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finer M. H., Gerstenfeld L. C., Young D., Doty P., Boedtker H. Collagen expression in embryonic chicken chondrocytes treated with phorbol myristate acetate. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1415–1424. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Green H. Changes in keratin gene expression during terminal differentiation of the keratinocyte. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerstenfeld L. C., Finer M. H., Boedtker H. Altered beta-actin gene expression in phorbol myristate acetate-treated chondrocytes and fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1425–1433. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard J. M., Caput D., Williams S. R., Martin D. W., Jr Cloning of human purine-nucleoside phosphorylase cDNA sequences by complementation in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4281–4285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Fuchs E. The cDNA sequence of a Type II cytoskeletal keratin reveals constant and variable structural domains among keratins. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):915–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Fuchs E. The cDNA sequence of a human epidermal keratin: divergence of sequence but conservation of structure among intermediate filament proteins. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90424-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley-Nelson P., Stanley J. R., Schmidt J., Gullino M., Yuspa S. H. The tumor promoter, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate accelerates keratinocyte differentiation and stimulates growth of an unidentified cell type in cultured human epidermis. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Jan;137(1):155–167. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrlich P., Mallick U., Ponta H., Rahmsdorf H. J. Genetic changes in mammalian cells reminiscent of an SOS response. Hum Genet. 1984;67(4):360–368. doi: 10.1007/BF00291392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hönigsmann H., Wolff K., Konrad K. Epidermal lysosomes and ultraviolet light. J Invest Dermatol. 1974 Oct;63(4):337–342. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12680332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikenaga M., Ichikawa-Ryo H., Kondo S. The major cause of inactivation and mutation by 4-nitroquinoline 1-oixde in Escherichia coli: excisable 4NQO-purine adducts. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 25;92(2):341–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90233-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbra R. J., Karin M. Metallothionein gene expression is regulated by serum factors and activators of protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1358–1363. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Järvinen M. Purification and some characteristics of the human epidermal SH-protease inhibitor. J Invest Dermatol. 1978 Aug;71(2):114–118. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12546165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy A. R., Little J. B. Protease inhibitors suppress radiation-induced malignant transformation in vitro. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):825–826. doi: 10.1038/276825a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon C. J., Walker G. C. DNA-damaging agents stimulate gene expression at specific loci in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2819–2823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. C., Parsons S., Hanawalt P. C. DNA repair in cultured keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Jul;81(1 Suppl):179s–183s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12541076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machleidt W., Borchart U., Fritz H., Brzin J., Ritonja A., Turk V. Protein inhibitors of cysteine proteinases. II. Primary structure of stefin, a cytosolic protein inhibitor of cysteine proteinases from human polymorphonuclear granulocytes. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1983 Nov;364(11):1481–1486. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1983.364.2.1481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhani H. D., Bohr V. A., Hanawalt P. C. Differential DNA repair in transcriptionally active and inactive proto-oncogenes: c-abl and c-mos. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):417–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90327-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Rautmann G., Magun B. E., Breathnach R. Epidermal growth factor or serum stimulation of rat fibroblasts induces an elevation in mRNA levels for lactate dehydrogenase and other glycolytic enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):711–726. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyn M. S., Rossman T., Troll W. A protease inhibitor blocks SOS functions in Escherichia coli: antipain prevents lambda repressor inactivation, ultraviolet mutagenesis, and filamentous growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1152–1156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Volc-Platzer B., Krepler R. Different keratin polypeptides in epidermis and other epithelia of human skin: a specific cytokeratin of molecular weight 46,000 in epithelia of the pilosebaceous tract and basal cell epitheliomas. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):285–295. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Howard B. H., Berg P. Synthesis of rabbit beta-globin in cultured monkey kidney cells following infection with a SV40 beta-globin recombinant genome. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):108–114. doi: 10.1038/277108a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins D. E., Rohrlich S. T. The role of proteinases in cellular invasiveness. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 29;695(3-4):177–214. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(83)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak K., Wolny M., Banaś T. The complete amino acid sequence of human muscle glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 16;134(2):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80587-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noyes B. E., Stark G. R. Nucleic acid hybridization using DNA covalently coupled to cellulose. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):301–310. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson E. K., Pera M. F., Emmerson A., Gorman P. A. Differential effects of complete and second-stage tumour promoters in normal but not transformed human and mouse keratinocytes. Carcinogenesis. 1984 Aug;5(8):1071–1077. doi: 10.1093/carcin/5.8.1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponec M., Kempenaar J. A., De Kloet E. R. Corticoids and cultured human epidermal keratinocytes: specific intracellular binding and clinical efficacy. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Mar;76(3):211–214. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12525761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RayChaudhury A., Marchuk D., Lindhurst M., Fuchs E. Three tightly linked genes encoding human type I keratins: conservation of sequence in the 5'-untranslated leader and 5'-upstream regions of coexpressed keratin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):539–548. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinwald J. G., Green H. Serial cultivation of strains of human epidermal keratinocytes: the formation of keratinizing colonies from single cells. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):331–343. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(75)80001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Räsänen O., Järvinen M., Rinne A. Localization of the human SH-protease inhibitor in the epidermis. Immunofluorescent studies. Acta Histochem. 1978;63(2):193–196. doi: 10.1016/S0065-1281(78)80025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorpp M., Mallick U., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. UV-induced extracellular factor from human fibroblasts communicates the UV response to nonirradiated cells. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):861–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90421-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. R., Westphal K. H., Rigby P. W. Activation of mouse genes in transformed cells. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):557–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90388-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taichman L. B., Setlow R. B. Repair of ultraviolet light damage to the DNA of cultured human epidermal keratinocytes and fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol. 1979 Sep;73(3):217–219. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12514242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M., Stephenson P. Role of the conserved AAUAAA sequence: four AAUAAA point mutants prevent messenger RNA 3' end formation. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1045–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.6208611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet mutagenesis and inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):869–907. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.869-907.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]