Abstract
Poly(dA).poly(dT), but not B-form DNA, is specifically recognized by experimentally induced anti-kinetoplast or anti-poly(dA).poly(dT) immunoglobulins. Antibody binding is completely competed by poly(dA).poly(dT) and poly(dA).poly(dU) but not by other single- or double-stranded DNA sequences in a right-handed B-form. Antibody interaction with poly(dA).poly(dT) depends on immunoglobulin concentration, incubation time and temperature, and is sensitive to elevated ionic strengths. Similar conformations, for example, (dA)4-6 X (dT)4-6, in the kinetoplast DNA of the parasite Leishmania tarentolae are also immunogenic and induce specific anti-poly(dA).poly(dT) antibodies. These antibody probes specifically recognize nuclear and kinetoplast DNA in fixed flagellated kinetoplastid cells as evidenced by immunofluorescence microscopy. Anti-poly(dA).poly(dT) immunofluorescence is DNase-sensitive and competed by poly(dA).poly(dT), but not other classical double-stranded B-DNAs. Thus, these unique cellular B'-DNA helices are immunogenic and structurally similar to synthetic poly(dA).poly(dT) helices in solution.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
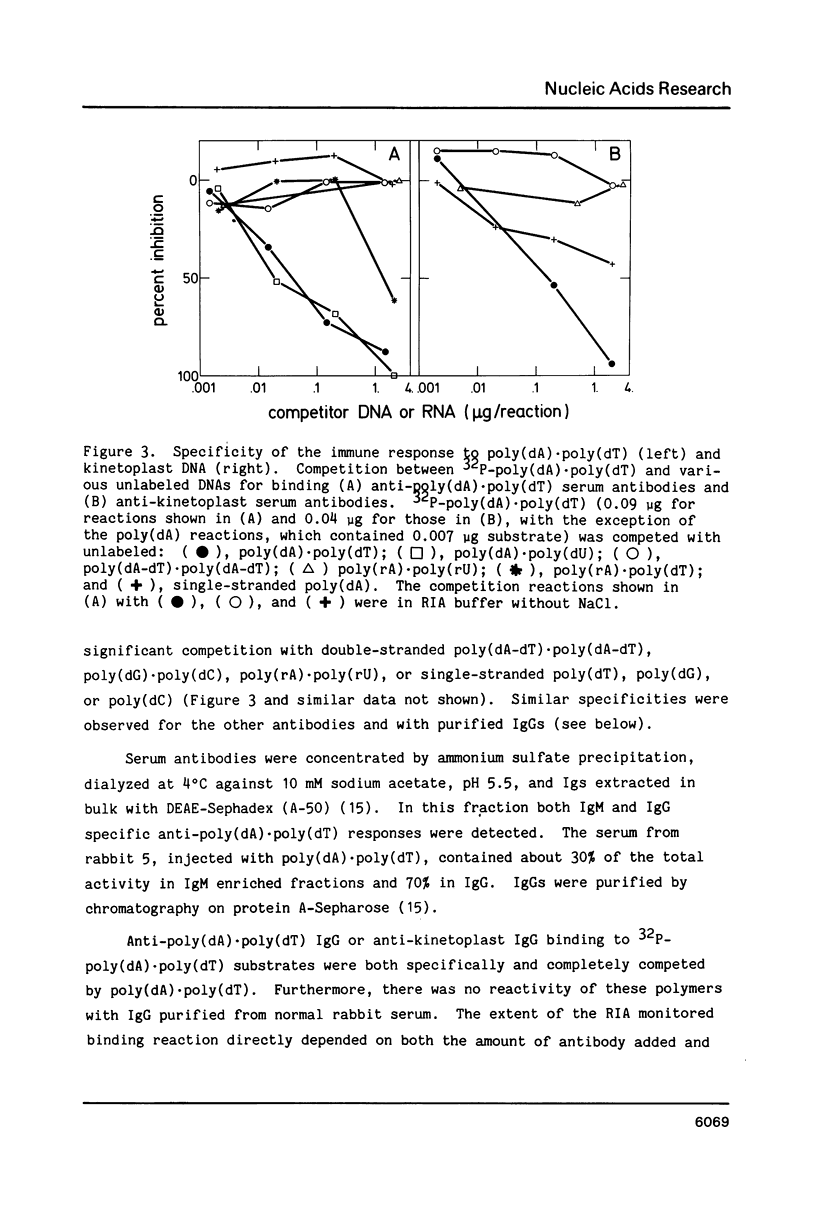
- Alexeev D. G., Lipanov A. A., Skuratovskii IYa Poly(dA).poly(dT) is a B-type double helix with a distinctively narrow minor groove. 1987 Feb 26-Mar 4Nature. 325(6107):821–823. doi: 10.1038/325821a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Arnott S. The sequence dependence of circular dichroism spectra of DNA duplexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Sep;2(9):1493–1502. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.9.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Hall I. H., Puigjaner L. C. Heteronomous DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4141–4155. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Hukins D. W. Optimised parameters for A-DNA and B-DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 28;47(6):1504–1509. doi: 10.1016/0006-291X(72)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann S., Wang J. C. On the sequence determinants and flexibility of the kinetoplast DNA fragment with abnormal gel electrophoretic mobilities. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. DNA bending at adenine . thymine tracts. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):501–506. doi: 10.1038/320501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Martinson H. G. Nucleosomes will not form on double-stranded RNa or over poly(dA).poly(dT) tracts in recombinant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6869–6888. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacour F., Nahon-Merlin E., Michelson M. Immunological recognition of polynucleotide structure. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1973;62:1–39. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65772-6_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madaio M. P., Hodder S., Schwartz R. S., Stollar B. D. Responsiveness of autoimmune and normal mice to nucleic acid antigens. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):872–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C. Sequence dependence of the helical repeat of DNA in solution. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):375–378. doi: 10.1038/292375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prevelige P. E., Jr, Fasman G. D. Studies on synthetic chromatins containing poly(dA-dT) X poly(dA-dT) and poly(dG-dC) X poly(dG-dC). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 20;739(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prunell A. Nucleosome reconstitution on plasmid-inserted poly(dA) . poly(dT). EMBO J. 1982;1(2):173–179. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01143.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. Sequence-dependent helical periodicity of DNA. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):378–380. doi: 10.1038/292378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D. Nucleosome cores reconstituted from poly (dA-dT) and the octamer of histones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979;6(5):1805–1816. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.5.1805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. Use of in vitro 32P labeling in the sequence analysis of nonradioactive tRNAs. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:58–109. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Künzler P. Cromatin and core particles formed from the inner histones and synthetic polydeoxyribonucleotides of defined sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1387–1415. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D. Doubls-helical polynucleotides: immunochemical recognition of differing conformations. Science. 1970 Aug 7;169(3945):609–611. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3945.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D. The experimental induction of antibodies to nucleic acids. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):70–85. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D. The specificity and applications of antibodies to helical nucleic acids. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1975 May;3(1):45–69. doi: 10.3109/10409237509102552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartell R. M., Harrell J. T. Characteristics and variations of B-type DNA conformations in solution: a quantitative analysis of Raman band intensities of eight DNAs. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2664–2671. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling D. A., Arndt-Jovin D. J., Robert-Nicoud M., McIntosh L. P., Thomae R., Jovin T. M. Immunoglobulin recognition of synthetic and natural left-handed Z DNA conformations and sequences. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 5;176(3):369–415. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90495-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]