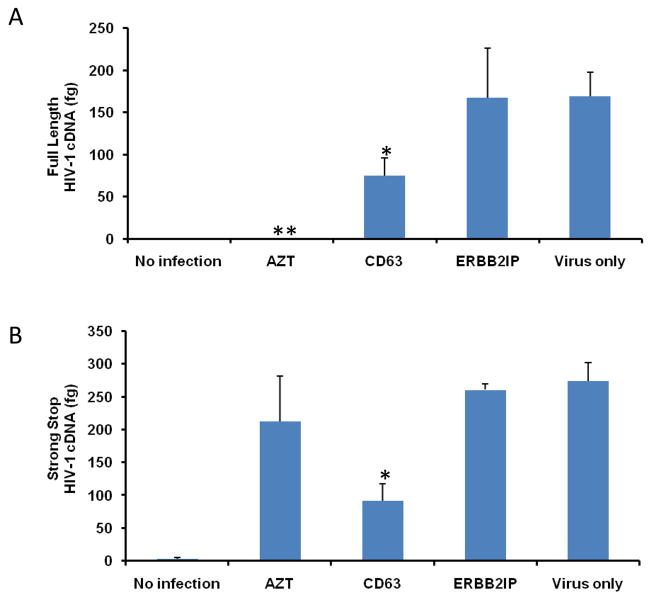
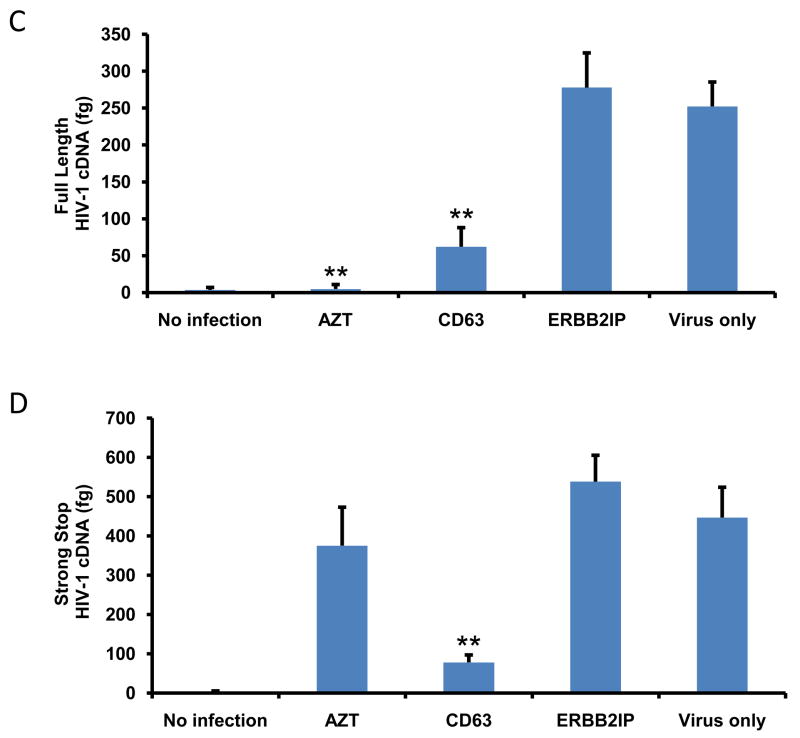
Figure 5. CD63 silencing reduces HIV-1 reverse transcription in human MDMs and U373-MAGI-CCR5 cells.
The effect of HIV-1 reverse transcription on the formation of full length cDNA (A and C) and the initiation of strong stop (B and D) were performed in MDMs (5 × 105 cells/well) and in U373-MAGI-CCR5 cells (1 × 105 cells/well) that were transfected with 50 nM siRNAs (CD63 and ERBB2IP). Forty-eight hours post-transfection, cells were infected with HIV-1 SX (m.o.i. = 0.02). For controls, cells were treated with reverse transcriptase inhibitor AZT (1 μM); cells infected with virus only; and untreated cells. Small non-genomic DNA was isolated from controls and CD63 siRNA-transfected MDMs and U373-MAGI-CCR5 cells at 24 h post infection. Primers M667/M661, along with probe MH603, was used to quantify full-length cDNA formation (A and C), and primers M667/AA55, along with probe MH603 was used to quantify strong stop cDNA formation (B and D) by real time PCR. *P<0.05, compared with ERBB2IP group.