Abstract
It has been suggested that climate change at the Cretaceous–Palaeogene (K–Pg) boundary, initiated by a bolide impact or volcanic eruptions, caused species with temperature-dependent sex determination (TSD), including dinosaurs, to go extinct because of a skewed sex ratio towards all males. To test this hypothesis, the sex-determining mechanisms (SDMs) of Cretaceous tetrapods of the Hell Creek Formation (Montana, USA) were inferred using parsimony optimizations of SDMs on a tree, including Hell Creek species and their extant relatives. Although the SDMs of non-avian dinosaurs could not be inferred, we were able to determine the SDMs of 62 species; 46 had genotypic sex determination (GSD) and 16 had TSD. The TSD hypothesis for extinctions performed poorly, predicting between 32 and 34 per cent of survivals and extinctions. Most surprisingly, of the 16 species with TSD, 14 of them survived into the Early Palaeocene. In contrast, 61 per cent of species with GSD went extinct. Possible explanations include minimal climate change at the K–Pg, or if climate change did occur, TSD species that survived had egg-laying behaviour that prevented the skewing of sex ratios, or had a sex ratio skewed towards female rather than male preponderance. Application of molecular clocks may allow the SDMs of non-avian dinosaurs to be inferred, which would be an important test of the pattern discovered here.
Keywords: Cretaceous, temperature-dependent sex determination, extinction
1. Introduction
Geological evidence indicates that a large bolide hit the Yucatan Peninsula at the Cretaceous–Palaeogene (K–Pg) boundary (ca 65.5 Ma) [1,2], whereas other evidence indicates that massive volcanic eruptions on the Indian plate peaked slightly before the K–Pg boundary [3]. It has been widely suggested that one or both events were responsible for the mass extinction at the K–Pg boundary and that each had profound effects on global climate. The impact vapourized large quantities of evaporite minerals, and the resulting sulphate aerosols probably seeded clouds that reflected solar radiation [4]. The volcanic eruptions, which formed the Deccan Traps of India, released large quantities of CO2 into the atmosphere and may have initiated global warming [5]. Those species that had temperature-dependent sex determination (TSD) are expected to have been negatively impacted by these climate changes [6,7].
In TSD, the sex of the embryo is determined by the incubation temperature of the eggs. Incubation at the pivotal temperature(s) yields a 1 : 1 sex ratio, small temperature deviations yield an unbalanced sex ratio and larger deviations yield single-sex clutches [8]. In genotypic sex determination (GSD), a sex-determining gene activates a downstream cascade of other genes that are responsible for testis or ovarian development. The specific chromosomes and genes in GSD have evolved independently in numerous lineages, suggesting that it has adaptive benefits [7]. Therian mammals employ an XX–XY, male heterogametic system that evolved from autosomes when the SRY (testis-determining) gene emerged on what became the Y chromosome. Exactly when this transformation occurred depends on homologies of the complicated monotreme XX–XY system [9]. In contrast, birds employ a female heterogametic (ZZ–ZW) system that according to recent experimental evidence [10] leads to testicular development with a double dosage of the Z-linked gene DMRT1.
It has been suggested that non-avian dinosaurs had TSD, that temperature change at the K–Pg boundary led to male-dominated populations of non-avian dinosaurs via TSD and that this imbalance led to their extinction [6,7]. Although elements of this hypothesis have been criticized (i.e. [11]), there has been no systematic attempt to test whether Cretaceous species with TSD were more prone to extinction than their GSD cohorts. Thus, in the present study, we are determining whether Cretaceous species of tetrapods with TSD experienced substantially more extinctions than those with GSD at the K–Pg boundary. Ideally, several regions would be examined, but unfortunately only the Cretaceous Hell Creek Formation and Early Palaeocene Tullock Formation display near-continuous non-marine sedimentation across the K–Pg boundary, have an unambiguous K–Pg boundary and have rich and intensively studied fossil faunas above and below the boundary [12].
2. Material and methods
Survivorship at the K–Pg boundary was based on table 5.1 of Archibald [12], which was compiled from the Hell Creek and Tullock formations of Garfield and McCone Counties, Montana, USA. Minor modifications were made to this table to incorporate studies published since 1996 (see the electronic supplementary material). Explanatory power of the TSD hypothesis is determined by counting the number of taxa whose extinction or survival is correctly predicted. Taxa that have TSD are predicted to have gone extinct, whereas taxa that have GSD are predicted to have survived. The statistical significance of differences in extinction frequencies between species with TSD and those with GSD was determined using Fisher's exact test of independence [13] in the computer application SPSS.
To infer the SDMs of Hell Creek tetrapods, three character states for SDM (XX/XY, ZZ/ZW and TSD) were mapped onto a phylogeny including extant taxa and Hell Creek species in MacClade v. 4.08 [14]. Most parsimonious reconstructions were considered for each internal branch, and SDMs were treated as an unordered, multistate character. In the absence of total evidence, comprehensive phylogenies that include Hell Creek and extant taxa, SDMs were reconstructed on a well-supported molecular tree of tetrapods, with fossil taxa placed next to their closest extant relatives, as determined by morphological studies (see the electronic supplementary material). For extant taxa, we used modified versions of the SDM dataset and phylogeny employed by Organ & Janes [15] (see the electronic supplementary material).
3. Results
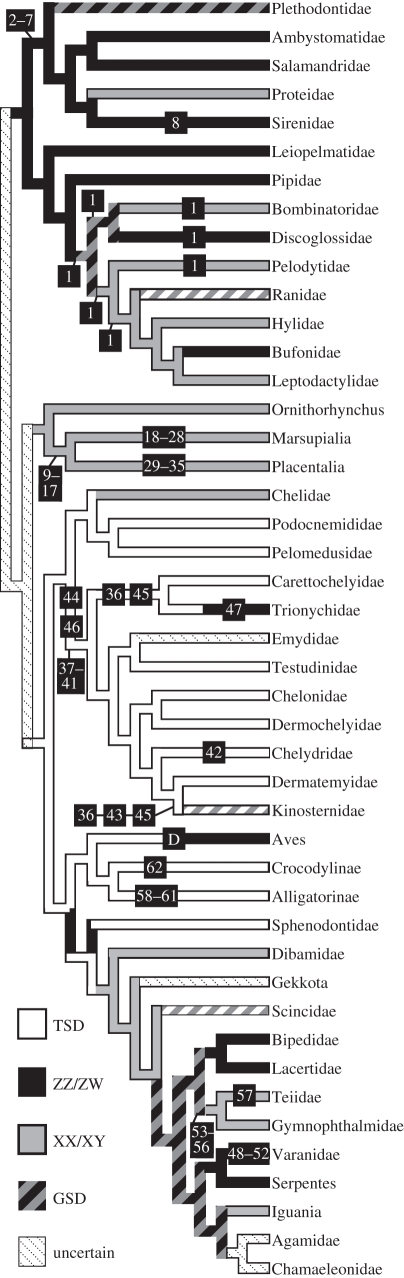
The TSD hypothesis was originally developed to explain the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs, but unfortunately the SDM of non-avian dinosaurs remains speculative because birds, their closest extant relatives [16], have GSD whereas crocodylians, their next closest relatives [17], have TSD [6]. The GSD of extant birds evolved somewhere on the branch leading from their common ancestor with crocodylians, so that it is equally parsimonious to infer that all non-avian dinosaurs and basal avialans like Anchiornis and Archaeoptetyx had TSD or that all dinosaurs, including extinct birds, had GSD (figure 1).
Figure 1.
Most parsimonious optimization of sex-determining mechanisms on a phylogeny of extant tetrapods. Numbers indicate where extinct taxa of the Hell Creek Formation attach to this tree (see the first column of table 1). D, Dinosauria. Hatched branches indicate polymorphism (terminal branches) or ambiguity (internal branches). See the electronic supplementary material for studies that support this topology, the placement of extinct taxa, and for taxa whose SDM could not be reconstructed.
For the 68 non-dinosaur tetrapods of the Hell Creek Formation, SDMs can be inferred in 62 of them (figure 1). GSD is inferred to have occurred in 46 of these species, including all mammals, amphibians and lizards; and TSD is inferred to have occurred in 16 of these species, 11 turtles and all crocodylians. The TSD hypothesis is a very poor predictor of extinction (table 1); of the 32 extinctions and 30 survivals of the K–Pg event in eastern Montana, only 32.3 per cent are explained. If rare taxa are ignored, which may mitigate pseudoextinctions, the performance of the TSD hypothesis is still dismal; only 34 per cent of 16 extinctions and 25 survivals are explained. Our results are also robust to alternate tree topologies and to the inclusion of less-reliable SDM data (see the electronic supplementary material).
Table 1.
List of species from the Hell Creek Formation of Garfield and McCone Counties Montana, USA, their survivorship across the K–Pg boundary (mainly from [12]) and whether individual species fates are predicted by the TSD hypothesis.
| species | no. in figure 1 | classification | SDM | K/Pg extinction | TSD hypothesis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scotiophryne pustulosa | 1 | Lissamphibia | XY or ZW | survived | predicted |
| Opisthotriton kayi | 2 | Lissamphibia | ZW | survived | predicted |
| Prodesmodon copei | 3 | Lissamphibia | ZW | survived | predicted |
| Albanerpeton nexuosus | 4 | Lissamphibia | ZW | survived | predicted |
| Lisserpeton bairdi | 5 | Lissamphibia | ZW | survived | predicted |
| cf. Piceoerpeton sp. | 6 | Lissamphibia | ZW | survived | predicted |
| Scapherpeton tectum | 7 | Lissamphibia | ZW | survived | predicted |
| Habrosaurus dilatus | 8 | Lissamphibia | ZW | survived | predicted |
| Cimolodon nitidus | 9 | Mammalia: Multituberculata | XY | survived | predicted |
| Cimolomys gracilus | 10 | Mammalia: Multituberculata | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Meniscoessus robustus | 11 | Mammalia: Multituberculata | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Cimexomys minor | 12 | Mammalia: Multituberculata | XY | survived | predicted |
| Essonodon browni | 13 | Mammalia: Multituberculata | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Paracimexomys priscus | 14 | Mammalia: Multituberculata | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Mesodma formosa | 15 | Mammalia: Multituberculata | XY | survived | predicted |
| Mesodma hensleighi | 16 | Mammalia: Multituberculata | XY | survived | predicted |
| Mesodma thompsoni | 17 | Mammalia: Multituberculata | XY | survived | predicted |
| Didelphodon vorax | 18 | Mammalia: Metatheria | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Glasbius twitchelli | 19 | Mammalia: Metatheria | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Pediomys cooki | 20 | Mammalia: Metatheria | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Pediomys elegans | 21 | Mammalia: Metatheria | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Pediomys florencae | 22 | Mammalia: Metatheria | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Pediomys hatchery | 23 | Mammalia: Metatheria | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Pediomys krejcii | 24 | Mammalia: Metatheria | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Alphadon marshi | 25 | Mammalia: Metatheria | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Alphadon wilsoni | 26 | Mammalia: Metatheria | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Protalphadon lulli | 27 | Mammalia: Metatheria | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Turgidodon rhaister | 28 | Mammalia: Metatheria | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Gypsonictops hypoconus | 29 | Mammalia: Eutheria | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Gypsonictops illuminatus | 30 | Mammalia: Eutheria | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Batodon tenuis | 31 | Mammalia: Eutheria | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Cimolestes cerberoides | 32 | Mammalia: Eutheria | XY | survived | predicted |
| Cimolestes incisus | 33 | Mammalia: Eutheria | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Cimolestes propalaeoryctes | 34 | Mammalia: Eutheria | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Cimolestes stirtoni | 35 | Mammalia: Eutheria | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Adocus sp. | 36 | Reptilia: Testudines | TSD | survived | unpredicted |
| Eubaena cephalica | 37 | Reptilia: Testudines | TSD | survived | unpredicted |
| Neurankylus cf. eximus | 38 | Reptilia: Testudines | TSD | survived | unpredicted |
| Peckemys brinkman | 39 | Reptilia: Testudines | TSD | survived | unpredicted |
| Stygiochelys estesi | 40 | Reptilia: Testudines | TSD | survived | unpredicted |
| Palatobaena cohen | 41 | Reptilia: Testudines | TSD | survived | unpredicted |
| Protochelydra sp. | 42 | Reptilia: Testudines | TSD | survived | unpredicted |
| Emarginochelys cretacea | 43 | Reptilia: Testudines | TSD | survived | unpredicted |
| ‘Clemmys’ backmani | 44 | Reptilia: Testudines | TSD | survived | unpredicted |
| Basilemys sinuosa | 45 | Reptilia: Testudines | TSD | extinct | predicted |
| Compsemys victa | 46 | Reptilia: Testudines | TSD | survived | unpredicted |
| Apalone sp. | 47 | Reptilia: Testudines | ZW | survived | predicted |
| Odaxosaurus piger | 48 | Reptilia: Squamata | ZW | survived | predicted |
| Paraderma bogerti | 49 | Reptilia: Squamata | ZW | extinct | unpredicted |
| Parasaniwa wyomingensis | 50 | Reptilia: Squamata | ZW | extinct | unpredicted |
| Palaeosaniwa canadensis | 51 | Reptilia: Squamata | ZW | extinct | unpredicted |
| Exostinus lancensis | 52 | Reptilia: Squamata | ZW | survived | predicted |
| Contogenys sloani | 53 | Reptilia: Squamata | XY or ZW | survived | predicted |
| Chamops segnis | 54 | Reptilia: Squamata | XY or ZW | extinct | unpredicted |
| Haptochamops placodon | 55 | Reptilia: Squamata | XY or ZW | extinct | unpredicted |
| Leptochamops denticulatus | 56 | Reptilia: Squamata | XY or ZW | extinct | unpredicted |
| Peneteius aquilonius | 57 | Reptilia: Squamata | XY | extinct | unpredicted |
| Brachychampsa montana | 58 | Reptilia: Crocodilia | TSD | extinct | predicted |
| undescribed alligatoroid A | 59 | Reptilia: Crocodilia | TSD | survived | unpredicted |
| undescribed alligatoroid B | 60 | Reptilia: Crocodilia | TSD | survived | unpredicted |
| Leidyosuchus sternbergi | 61 | Reptilia: Crocodilia | TSD | survived | unpredicted |
| Thoracosaurus neocessariensis | 62 | Reptilia: Crocodilia | TSD | survived | unpredicted |
Even more remarkable is that of the 16 taxa inferred to have had TSD (table 1), only two of them (i.e. Basilemys sinuosa and Brachychampsa montana) went extinct. In contrast, species with GSD suffered many more extinctions; 28 out of 46 species went extinct (61%). Metatherians (11 species) were entirely wiped out as were all but one undetermined species of eutherian (one species of Cimolestes is tentatively assumed to have evolved into Cimolestes simpsoni). Multituberculates did somewhat better, with five out of nine species surviving. Only three out of 10 squamates, all of which are inferred to have had GSD, survived into the Palaeocene. The differences in rates of survival of taxa with TSD as compared with those with GSD are statistically significant (p = 0.001).
4. Discussion
Although we do not have a compelling explanation for why taxa with TSD fared better than those with GSD at the K–Pg boundary, the apparent immunity of species with TSD is easier to explain. One possibility is that the abiotic event that precipitated the K–Pg mass extinction did not change global temperatures. Oxygen isotopes in foraminifera and tree leaf-margin analyses [18] do not support an abrupt change in temperatures at the K–Pg boundary. Instead, they support a cooling that began 100 ka before and then persisted through the K–Pg boundary. That said, a cold snap, such as one induced by a bolide impact, may have been too brief [1] to be recorded in the geological record. Second, it is possible that TSD species can effectively respond to temperature changes by shifting pivotal temperatures [19], altering their choice of nest sites [20] or by rapid habitat tracking [21]. If any of the above suggestions are true, we would expect that TSD and GSD species would have similar extinction rates, but then what can explain the relatively low percentage of extinctions in TSD taxa? We speculate that traits that co-occur with TSD in turtles and crocodilians, such as ectothermy, may have allowed a higher percentage of TSD taxa to survive the K–Pg extinction.
Two aspects of the apparent survivorship of TSD species during the K–Pg mass extinction warrant further investigation. If molecular clocks can be applied to the sex chromosomes of birds, then it may be possible to estimate when GSD evolved on the dinosaur branch leading to birds and which Hell Creek dinosaurs had GSD. Second, it would be important to test survivorship of TSD species at other intervals of Earth history where climate change occurred. Turtles and crocodilians, which primarily have TSD, also fared well during the Palaeocene–Eocene thermal maximum [22,23]. These same groups experienced drops in diversity during Late Eocene cooling, although the drop in crocodilians maybe a sampling artefact [23] and turtle extinctions were concentrated among aquatic taxa, suggesting that aridification, not cooling, was to blame [24]. Recently, there has been concern about the future of TSD species if global temperatures continue to rise (e.g. [25]). Our findings offer the hope that in a world facing human-induced climate change, species with TSD may still find a way to survive.
References
- 1.Alvarez L. W., Alvarez W., Asaro F., Michel H. V. 1980. Extraterrestrial cause for the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction. Science 208, 1095–1108 10.1126/science.208.4448.1095 (doi:10.1126/science.208.4448.1095) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hildebrand A. R., Penfield G. T., Kring D. A., Pilkington M., Camargo Z. A., Jacobsen S. B., Boynton W. V. 1991. Chicxulub Crater: a possible Cretaceous/Tertiary boundary impact crater on the Yucatán Peninsula, Mexico. Geology 19, 867–871 (doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1991)019<0867:CCAPCT>2.3.CO;2) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Keller G., Adatte T., Gardinc S., Bartolinic A., Bajpaid S. 2008. Main Deccan volcanism phase ends near the K–T boundary: evidence from the Krishna–Godavari Basin, SE India. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 268, 293–311 10.1016/j.epsl.2008.01.015 (doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2008.01.015) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pope K. O., Baines K. H., Ocampo A. C., Ivanov B. A. 1997. Energy, volatile production, and climatic effects of the Chicxulub Cretaceous/Tertiary impact. J. Geophys. Res. 102, 21 645–21 664 10.1029/97JE01743 (doi:10.1029/97JE01743) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.McLean D. M. 1985. Deccan Traps mantle degassing in the terminal Cretaceous marine extinctions. Cretaceous Res. 6, 235–259 10.1016/0195-6671(85)90048-5 (doi:10.1016/0195-6671(85)90048-5) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ferguson M. W. J., Joanen T. 1982. Temperature of egg incubation determines sex in Alligator mississippiensis. Nature 296, 850–853 10.1038/296850a0 (doi:10.1038/296850a0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Miller D., Summers J., Silber S. 2004. Environmental versus genetic sex determination: a possible factor in dinosaur extinction? Fertil. Steril. 81, 954–964 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2003.09.051 (doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2003.09.051) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Valenzuela N. 2004. Temperature-dependent sex determination. In Reptilian incubation: environment and behaviour (ed. Deeming D. C.), pp. 211–227 Nottingham, UK: Nottingham University Press [Google Scholar]
- 9.Veyrunes F., et al. 2009. Bird-like sex chromosomes of platypus imply recent origin of mammal sex chromosomes. Genome Res. 18, 965–973 10.1101/gr.7101908 (doi:10.1101/gr.7101908) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Smith C. A., Roeszler K. N., Ohnesorg T., Cummins D. M., Farlie P. G., Doran T. J., Sinclair A. H. 2009. The avian Z-linked gene DMRT1 is required for male sex determination in the chicken. Nature 461, 267–271 10.1038/nature08298 (doi:10.1038/nature08298) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rage C. 1998. Latest Cretaceous extinction and environmental sex determination in reptiles. Bull. Soc. géol. France 169, 479–483 [Google Scholar]
- 12.Archibald J. D. 1996. Dinosaur extinction and the end of an era: what the fossils say, p. 237 New York, NY: Columbia University Press [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sokal R. R., Rohlf F. J. 1995. Biometry. New York, NY: W. H. Freeman and Company [Google Scholar]
- 14.Maddison D. R., Maddison W. P. 2003. MacClade, v. 4.08. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates. See http://macclade.org/macclade.html [Google Scholar]
- 15.Organ C. L., Janes D. E. 2008. Evolution of sex chromosomes in Sauropsida. Integr. Comp. Biol. 48, 512–519 10.1093/icb/icn041 (doi:10.1093/icb/icn041) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Xu X., Zhou Z., Wang X., Kuang X., Zhang F., Du X. 2003. Four-winged dinosaurs from China. Nature 421, 335–340 10.1038/nature01342 (doi:10.1038/nature01342) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gauthier J., Kluge A. G., Rowe T. 1998. Amniote phylogeny and the importance of fossils. Cladistics 4, 105–225 10.1111/j.1096-0031.1988.tb00514.x (doi:10.1111/j.1096-0031.1988.tb00514.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wilf P., Johnson K. R., Huber B. T. 2003. Correlated terrestrial and marine evidence for global climate changes before mass extinction at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 100, 599–604 10.1073/pnas.023470110 (doi:10.1073/pnas.023470110) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Janzen F. J., Paukstis G. L. 1991. Environmental sex determination in reptiles: ecology, evolution, and experimental design. Q. Rev. Biol. 66, 149–179 10.1086/417143 (doi:10.1086/417143) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Doody J. S., Guarino E., Georges A., Corey B., Murray G., Ewert M. 2006. Nest site choice compensates for climate effects on sex ratios in a lizard with environmental sex determination. Evol. Ecol. 20, 307–330 10.1007/s10682-006-0003-2 (doi:10.1007/s10682-006-0003-2) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kallimanis A. S. 2010. Temperature dependent sex determination and climate change. Oikos 119, 197–200 10.1111/j.1600-0706.2009.17674.x (doi:10.1111/j.1600-0706.2009.17674.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hutchison J. H. 1998. Turtles across the Paleocene/Eocene epoch boundary in west-central North America. In Late Paleocene–Early Eocene climatic and biotic events in the marine and terrestrial records (eds Aubry M.-P., Lucas S. G., Berggren W. A.), pp. 401–408 Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press [Google Scholar]
- 23.Marwick P. J. 1998. Crocodilian diversity in space and time: the role of climate in paleoecology and its implication for understanding K/T extinctions. Paleobiology 24, 470–497 [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hutchison J. H. 1992. Western North American reptile and amphibian record across the Eocene–Oligocene boundary and its climatic implications. In Eocene–Oligocene climatic and biotic evolution (eds Prothero D. R., Berggren W. A.), pp. 451–463 Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mitchell N. J., Kearney M. R., Nelson N. J., Porter W. P. 2008. Predicting the fate of a living fossil: how will global warming affect sex determination and hatching phenology in tuatara? Proc. R. Soc. B 275, 2185–2193 10.1098/rspb.2008.0438 (doi:10.1098/rspb.2008.0438) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]